Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Snell's Law - Definition and Derivation
Uploaded by
Abdul Azeem KhosoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Snell's Law - Definition and Derivation
Uploaded by
Abdul Azeem KhosoCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas (/formulas/) Math Formulas (/math-formulas/) Basic Math Formulas (/basic-math-formulas/) Physics Formulas (/physics-formulas/)
Chemistry Formulas (/chemistry-formulas/)
Snells Law Formula
Snell’s Law
Snell’s law gives the degree of refraction and relation between the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction and refractive indices
of a given pair of media. We know that light experiences the refraction or bending when it travels from one medium to another
medium. Snell’s law predicts the degree of the bend. It is also known as the law of refraction. In 1621, Willebrord Snell discovered
the law of refraction, hence called Snell’s law.
Snell’s law is defined as “The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the
light of a given colour and for the given pair of media”. Snell’s law formula is expressed as:
sin i
= constant = μ
sin r
Where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction. This constant value is called the refractive index
of the second medium with respect to the first.
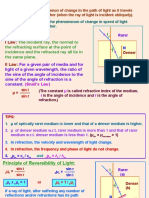
The following is a diagrammatic representation:
Snell’s law formula is derived from Fermat’s principle. Fermat’s principle states that “light travels in the shortest path that takes the
least time”.
The normal on the surface is used to gauge the angles that the refracted ray creates at the contact point. n1 and n2 are the two
different mediums that will impact the refraction.θ1 is the angle of incidence; θ2 is the angle of refraction.
Applications of Snell’s Law Formula in Real Life:
Snell’s law has a wide range of applications in physics especially in the branch of optics . It is
used in optical apparatus such as eyeglasses, contact lenses, cameras, rainbows. There is an instrument called a refractometer that
uses Snell’s law to calculate the refractive index of liquids. It is used all the time in the candy-making industry.
You might also like
- Refraction 4Document1 pageRefraction 4Ajay AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocument3 pagesCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreAñoop GāurNo ratings yet
- Assignmnent#2 OptoelectronicsDocument5 pagesAssignmnent#2 OptoelectronicsAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: LightDocument9 pagesChapter 12: LightLi HongNo ratings yet
- Understanding Optics &optical CommunicationsDocument44 pagesUnderstanding Optics &optical CommunicationsWondimu KenateNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument15 pagesRefractionIli AtallaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Snell's Law of Refraction: CheckpointDocument9 pagesExperiment 2: Snell's Law of Refraction: CheckpointAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- "Twinkle Twinkle Little Star - . ." Why Do Stars Twinkle But Not Planets?Document16 pages"Twinkle Twinkle Little Star - . ." Why Do Stars Twinkle But Not Planets?varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Determination of Refraction IndexDocument3 pagesDetermination of Refraction IndexDrakalopNo ratings yet
- Dispersion and Snells LawDocument5 pagesDispersion and Snells Lawklerni07No ratings yet
- LightDocument84 pagesLightsenjicsNo ratings yet
- FAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000319 Reference Material I 18-Oct-2022 Fundamental of OpticsDocument13 pagesFAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000319 Reference Material I 18-Oct-2022 Fundamental of OpticsPritam PatraNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 Physics For Computer ScienceDocument34 pagesLect 4 Physics For Computer ScienceTinesha Firstlady-Kruffabulous LeveneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrosDocument13 pagesIntroduction To MicrosLindsayPat8911No ratings yet
- Assignment#2 OptoelectronicsDocument4 pagesAssignment#2 OptoelectronicsAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- 3.refraction Tir, Optical FibreDocument5 pages3.refraction Tir, Optical FibreSrushti ChouguleNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument15 pagesRefractionStudent ResearchNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document5 pagesPhysics Light Reflection and Refraction 1Vj RanchesNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Refraction ExperimentDocument13 pagesIGCSE Physics Refraction ExperimentTamer A. Dakkak100% (1)
- Physics - Reflection & Refraction: Sahil KhandareDocument11 pagesPhysics - Reflection & Refraction: Sahil KhandaressskNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document22 pagesWa0004.spiritualmind61No ratings yet
- Laws of Refraction:: I LawDocument4 pagesLaws of Refraction:: I LawhareeshNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction 24898Document20 pagesReflection and Refraction 24898Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document13 pagesExperiment 7Timothy Gregoire Jr.No ratings yet
- RefractionDocument12 pagesRefractionJustin MadrisitaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11: Chapter 17: Reflection and RefractionDocument4 pagesPhysics 11: Chapter 17: Reflection and Refractionclim3953No ratings yet
- Rectilinear PropagationDocument5 pagesRectilinear PropagationAudrea MendozaNo ratings yet
- Laws of Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesLaws of Refraction of Lightpadmja4purohitNo ratings yet
- LightDocument17 pagesLightAhmad ZebNo ratings yet
- Reflection and RefracionDocument21 pagesReflection and RefracionJames Yuri ArcaNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light Plane Surfaces PDFDocument3 pagesRefraction of Light Plane Surfaces PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument17 pagesIndexcocindiazaNo ratings yet
- Normal Angle of IncidenceDocument4 pagesNormal Angle of IncidencealfiqainiNo ratings yet
- Lyceum of The Philippines University Cavite Campus Department of EngineeringDocument3 pagesLyceum of The Philippines University Cavite Campus Department of EngineeringJadeNo ratings yet
- Light: Secondary 3 PhysicsDocument20 pagesLight: Secondary 3 PhysicsFarogh Hamid100% (1)
- Final Report Exer 9Document7 pagesFinal Report Exer 9Jorel Matthew TorioNo ratings yet
- Physics Refraction of Light Part A.: - Nameet MehtaDocument15 pagesPhysics Refraction of Light Part A.: - Nameet MehtaAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Reflection and RefractionDocument5 pagesPhysics Light Reflection and RefractionVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- L11 Snell 2019Document3 pagesL11 Snell 2019music.acoustic.nowNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument5 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectNisaar Jogi50% (2)
- Sympgeom 1Document57 pagesSympgeom 1we_spidus_2006No ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175) : Ray TheoryDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175) : Ray TheorySaikat MahmudNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8b - Wave Behaviour: Will Focus On Light, MostlyDocument69 pagesLesson 8b - Wave Behaviour: Will Focus On Light, MostlyzNo ratings yet
- Refraction at Plane Surfaces Report To FinalDocument13 pagesRefraction at Plane Surfaces Report To FinalProy DC100% (1)
- Laws of ReflectionDocument21 pagesLaws of ReflectionKashaf AbbasiNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument4 pagesRefractionJadie BabyyyNo ratings yet
- Law of Reflection and RefractionDocument21 pagesLaw of Reflection and RefractionDarious PenillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Report Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"Document10 pagesExperiment Report Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"dita wulanNo ratings yet
- Phychem Lab ReportDocument3 pagesPhychem Lab Report전YsabelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Light and Electromagnetic Waves LecturerDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Light and Electromagnetic Waves LecturerSalama RagabNo ratings yet
- Refraction Lesson 3 and 4Document17 pagesRefraction Lesson 3 and 4Yohanes FevianNo ratings yet
- Snellius's LawDocument20 pagesSnellius's LawAgung MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Snells LawDocument2 pagesSnells LawlailaiketongNo ratings yet
- SnellDocument3 pagesSnellHisham AlfadilNo ratings yet
- Refractio N OF LightDocument8 pagesRefractio N OF LightYoNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument11 pagesRefraction of Lightshamitmajor100% (1)
- AnalysisDocument3 pagesAnalysisJedd AralesNo ratings yet
- Physics Light Waves SanowarDocument11 pagesPhysics Light Waves SanowarMin HanbyeolNo ratings yet
- Light EditedDocument41 pagesLight Editedmarc daniel ortizNo ratings yet
- Raoult's Law: Solution Solvent o SolventDocument8 pagesRaoult's Law: Solution Solvent o SolventAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 WebDocument26 pagesLecture10 WebAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- List of Societies Sukkur NewDocument31 pagesList of Societies Sukkur NewAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 4.3 Sine WavesDocument7 pagesLecture Notes 4.3 Sine WavesAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- University of Sindh Information Technology Services Centre - ITSCDocument5 pagesUniversity of Sindh Information Technology Services Centre - ITSCAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Chemistry Senior Secondary 2 Teachers GuideDocument108 pagesExcellence in Chemistry Senior Secondary 2 Teachers GuideAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Analytical Assignment Abdul Azeem 2K20-CHEE-1Document29 pagesAnalytical Assignment Abdul Azeem 2K20-CHEE-1Abdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Islamiat Chapter 1 Fundamental BeliefsDocument39 pagesIslamiat Chapter 1 Fundamental BeliefsAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Henry's Law - Pharm Eng I - 2nd YrDocument7 pagesHenry's Law - Pharm Eng I - 2nd YrAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Cmd. 00427991823503 Cmd. 00427991823503 Cmd. 00427991823503 Cmd. 00427991823503Document2 pagesCmd. 00427991823503 Cmd. 00427991823503 Cmd. 00427991823503 Cmd. 00427991823503Abdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Shaheed Benazirabad NA Wise (213-214)Document85 pagesConsolidated Shaheed Benazirabad NA Wise (213-214)Abdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet