Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Tissues - Practice Questions
Uploaded by
Aruna Patil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Anskey Plant Tissues
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesPlant Tissues - Practice Questions
Uploaded by
Aruna PatilCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
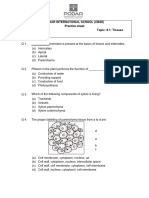
PLANT TISSUES - PRACTICE QUESTIONS
1. A tissue whose cells are capable of dividing and re-dividing is called
(a) complex tissue
(b) connective tissue
(c) permanent tissue
(d) meristematic tissue
D
2. The size of the stem increases in the width due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) intercalary meristem
(c) primary meristem
(d) lateral meristem
D
3. Sieve tubes and companion cells are present in
(a) xylem
(b) phloem
(c) cork
(d) cambium
B
4. The cells of cork are dead and have a chemical in their walls that makes them impervious to
gases and water. The chemical is
(a) lignin
(b) suberin
(c) cutin
(d) wax
B
5. Permanent tissue takes a fixed shape, size and function after its formation. So we call them
a. Totipotent b. Differentiated c. lenticel d. cloned
B
6. Food storing simple permanent tissue is:
a. Parenchyma b. Collenchyma c. Scleroid d. None
A
7. Chlorenchyma and aerenchyma both are a type of:
a. Parenchyma b. Vascular bundle c. Xylem d. Phloem.
A
8. Tissues in tendrils of a climber plant and leaf stalk of a plant are examples of which tissue?
a. Parenchyma b. Collenchyma c. Vascular d. Bark
A
9. Lignified thick cell wall with no cytoplasmic space in a cell is characteristic of:
a. Parenchyma b. Collenchyma c. Sclerenchyma d. Epidermis
C
10. The pore through which transpiration in plant occurs is:
a. Stoma b. Vacuole c. Plastid d. None
A
11. Guard cells and stoma are found in which part of the plant?
a. Parenchyma b. Collenchyma c. Sclerenchyma d. Epidermis
D
12. One of the tissues in the given options is dead tissue. Identify it.
a. Parenchyma b. Collenchyma c. Sclerenchyma d. Xylem
C
13. Phloems and xylems are:
a Simple permanent tissue b. Complex permanent tissue c. Vascular tissue d. b & c
D
14. Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
B
15. Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
(d) Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
C
16. Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
B
17. Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
B
18. Meristematic tissues in plants are
(a) localised and permanent
(b) not limited to certain regions
(c) localised and dividing cells
(d) growing in volume
C
19. Which is not a function of epidermis?
(a) Protection from adverse condition
(b) Gaseous exchange
(c) Conduction of water
(d) Transpiration
C
20. The dead element present in the phloem is
(a) companion cells
(b) phloem fibres
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) sieve tubes
B
21. Which of the following does not lose their nucleus at maturity?
(a) Companion cells
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Vessel
(d) Sieve tube cells
A
22. In desert plants, rate of water loss gets reduced due to the presence of
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(c) lignin
(d) suberin
A
23. A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the side ways conduction of water in
the branches is
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
B
24. A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the ground level. After 3
years the nail will
(a) move downwards
(b) move upwards
(c) remain at the same position
(d) move sideways
C
25. Parenchyma cells are
(a) relatively unspecified and thin walled
(b) thick walled and specialised
(c) lignified
(d) none of these
A
26. Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of
(a) cellulose
(b) lipids
(c) suberin
(d) lignin
C
27. The water conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperm is
(a) vessels
(b) sieve tube
(c) tracheids
(d) xylem fibres
C
Fill in the blanks
(a) ________ are forms of complex tissue. XYLEM AND PHLOEM
(b) ________ have guard cells. STOMATA
(c) Cells of cork contain a chemical called ________ . SUBERIN
(d) Husk of coconut is made of ________ tissue. SCLERENCHYMA
(e) ________ gives flexibility in plants. COLLENCHYMA
(f) ________ and ________ are both conducting tissues. XYLEM AND PHLOEM
(g) Xylem transports ________ and ________ from soil. WATER AND MINERALS
(h) Phloem transport ________ from ________ to other parts of the plant. FOOD, LEAVES
(i) Cork cells possesses ________ on their walls that makes it impervious to gases and water.
SUBERIN
(j) ________ have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature. SIEVE TUBES
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You might also like
- Classification and Impression Techniques of ImplantsDocument72 pagesClassification and Impression Techniques of ImplantsvanillalavenderNo ratings yet
- 2-Epithelium MCQ Asnan Ainshams DR - Zahra 2020Document9 pages2-Epithelium MCQ Asnan Ainshams DR - Zahra 2020Shay Os100% (1)
- Simplified Notes For Biology StudiesDocument56 pagesSimplified Notes For Biology Studiesabi_5dec94100% (5)
- Histology Mock ExamDocument73 pagesHistology Mock ExamRozen GaiserNo ratings yet
- The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of IndiaDocument202 pagesThe Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of Indiaalexpharm100% (3)
- Plant AnatomyDocument806 pagesPlant AnatomydianNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Multiple ChoiceDocument47 pagesCell Biology Multiple Choicezuft82% (11)
- Human Body Systems Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesHuman Body Systems Lesson Plan 1api-338430889100% (2)
- MCQS Zoology PDFDocument102 pagesMCQS Zoology PDFBilal Ahmad KhechiNo ratings yet
- Tissues MCQDocument3 pagesTissues MCQananthi rajasekarNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument8 pagesTissuesJanak Priya pandNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants-1Document80 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants-1aditya kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tissues Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesTissues Multiple Choice QuestionsUday HaldarNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Exemplar Chapter 6Document8 pages9 Science Exemplar Chapter 6AKHILA.SURESHNo ratings yet
- Qs - Plant AnatomyDocument16 pagesQs - Plant AnatomyPushpa DhruvNo ratings yet
- DIPASREE - ROYCHOWDHURYAnatomy Short Questions2020-08-22Anatomy Short Questions 22-8-2020Document11 pagesDIPASREE - ROYCHOWDHURYAnatomy Short Questions2020-08-22Anatomy Short Questions 22-8-2020Nigar MoinNo ratings yet
- BIO (MID-TestBank) MEODocument98 pagesBIO (MID-TestBank) MEOromaehab201912No ratings yet
- SCIENCE CH 6 MCQSDocument9 pagesSCIENCE CH 6 MCQSRaghavNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12Document12 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12NaliniKumaresanNo ratings yet
- Tissues MCQDocument9 pagesTissues MCQtraptisharma3342No ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersDocument13 pagesTissues Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersSCIENCE WORK [AMP] ActivitiesNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS-question 40Document10 pagesANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS-question 40Max TenisonNo ratings yet
- Output 231016 141817-52-63Document12 pagesOutput 231016 141817-52-63123No ratings yet
- MCQ 1Document4 pagesMCQ 1Maxine foyeNo ratings yet
- G10 Mid-Term RevisionDocument239 pagesG10 Mid-Term RevisionMartria EhabNo ratings yet
- PS CB IX Bio 6.1 TissuesDocument3 pagesPS CB IX Bio 6.1 TissuesAditi JaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsahvaabdulNo ratings yet
- Class 9 BiologyDocument32 pagesClass 9 BiologyAbinaya ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- WS CH 6 - 2Document2 pagesWS CH 6 - 2ayan.aggarwallNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Biology Plant Anatomy Plant TissuesDocument13 pagesNEET UG Biology Plant Anatomy Plant TissuesNigar MoinNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument12 pagesAnatomysriNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 16 Best (49 S.Q'S)Document16 pagesBiology Chapter 16 Best (49 S.Q'S)ranajawad579No ratings yet
- Udaan 40 +1 Bio 13.08.2023Document6 pagesUdaan 40 +1 Bio 13.08.2023mohdhashim8789No ratings yet
- MCQ S ZoologyDocument102 pagesMCQ S ZoologySapath GuptaNo ratings yet
- Zoology QP 04-08-2023Document17 pagesZoology QP 04-08-2023sujathadevarakonda81No ratings yet
- Neet Biology Chapter Wise SampleDocument21 pagesNeet Biology Chapter Wise SampleRamanna ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- MCEE BL Model Entrance Exam 2079Document16 pagesMCEE BL Model Entrance Exam 2079Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants ChapterDocument15 pagesFlowering Plants ChapterSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper BiologyDocument3 pagesSample Paper BiologyMini PGNo ratings yet
- 7structural Organization in Animals PDFDocument8 pages7structural Organization in Animals PDFDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Test 12 ExamDocument8 pagesTest 12 ExamTamal NayakNo ratings yet
- Neet Structural Organisation in Animals Important QuestionsDocument18 pagesNeet Structural Organisation in Animals Important QuestionsARKA NEET BIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Biology: Class - Ix (Cbse)Document6 pagesBiology: Class - Ix (Cbse)naman mahawerNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation NewDocument10 pagesStructural Organisation NewRuthraNo ratings yet
- Tissue Classification TestDocument5 pagesTissue Classification TestAnwesh NayakNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Part 2Document14 pagesBiology Notes Part 2ranajawad579No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument19 pagesBiologyBhavyaraj GohilNo ratings yet
- NEET BIOLOGY Structural Organization of AnimalsDocument93 pagesNEET BIOLOGY Structural Organization of AnimalsMonish KumarNo ratings yet
- 11th Bio Zoology Pure Zoology One Marks emDocument8 pages11th Bio Zoology Pure Zoology One Marks emmrclutchgod001No ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in Animalssrinu.lichflNo ratings yet
- Zoology Mcqs SolvedDocument102 pagesZoology Mcqs SolvedMhammad AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sistem OtotDocument14 pagesSistem OtotLeni MileniNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 14Document7 pagesBio Chapter 14junaid mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For Class IXDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For Class IXMaqsood 9682619146No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For Class IXDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For Class IXsujit patraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Structure and Functiongobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- YCT Anatomy of Flowering Plants NEET Questions PracticeDocument36 pagesYCT Anatomy of Flowering Plants NEET Questions PracticepreitaphilenaNo ratings yet
- NCS - Revision - SCIENCE ONLINE MCQ TEST (28082020) - Que-30-08-2020Document3 pagesNCS - Revision - SCIENCE ONLINE MCQ TEST (28082020) - Que-30-08-2020Diksha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Master Stroke Booklet Volume - 2Document122 pagesNcert Master Stroke Booklet Volume - 2Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For Class IXDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For Class IXsujit patraNo ratings yet
- 06. ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTSDocument13 pages06. ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTSPRERANA MNo ratings yet
- 2019 BMS1021 Practice QuestionsDocument12 pages2019 BMS1021 Practice QuestionsPooja GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class IX-Mid Term QB - Biology (2023-24)Document2 pagesClass IX-Mid Term QB - Biology (2023-24)NEHARIKA SAINANINo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument19 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsLol Boi100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 13 Concepts 01 35 Human Biology Answers PDFDocument145 pagesBiology Chapter 13 Concepts 01 35 Human Biology Answers PDFKamryn MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learner'S Activity Sheet For Quarter 2, Week - 4Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: Learner'S Activity Sheet For Quarter 2, Week - 4RubenNo ratings yet
- Roots, Stems and Leaves: Structure and FunctionsDocument64 pagesRoots, Stems and Leaves: Structure and FunctionsJeli Mae Ysabel PerezNo ratings yet
- STD Ix Lesson Plan Sci-IIDocument2 pagesSTD Ix Lesson Plan Sci-IIshaheen ansariNo ratings yet
- Solution Brahmastra SMT-1 22-01-2023Document40 pagesSolution Brahmastra SMT-1 22-01-2023Vaibhav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes BiologyDocument144 pages1st Year Notes BiologyAkbar Dad BabarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 BiologyDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1 Biologyparvenassri prabakharanNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Sugar CaneDocument706 pagesSugar CaneIvan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Erata Textbook Science f1Document9 pagesErata Textbook Science f1JocleynNo ratings yet
- Study Guide # 1: Human AnatomyDocument1 pageStudy Guide # 1: Human Anatomydr amjadNo ratings yet
- 9th Bio Chapter 1 (1-32)Document32 pages9th Bio Chapter 1 (1-32)gmian9012No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The AmnioChorionic MembraneDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The AmnioChorionic MembraneArfi FachrulNo ratings yet
- Divergent metabolomes and proteomes in dual cucurbit phloem systemsDocument6 pagesDivergent metabolomes and proteomes in dual cucurbit phloem systemsAizat HawariNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Human Body SystemDocument19 pagesScience 4 Human Body SystemSisouphan PakseNo ratings yet
- NTSE Question Paper 2014 (Stage-I) MAT, SAT and English with Answer Key (Andra PradeshDocument44 pagesNTSE Question Paper 2014 (Stage-I) MAT, SAT and English with Answer Key (Andra Pradeshgeethu ajayNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Answers Key - DATDocument12 pagesScience 7 - Answers Key - DATryan anthony manubayNo ratings yet
- Biology 5 - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesBiology 5 - Anatomy and PhysiologyCristal Jean BalucanNo ratings yet
- Living organisms and their classificationDocument4 pagesLiving organisms and their classificationBRIJESH SAVANTNo ratings yet
- World of PlantsDocument3 pagesWorld of PlantsWinter Summer SmithNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science 1st Semester ReviewDocument60 pages7th Grade Science 1st Semester ReviewtssandovalNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cardiovascular System (Histologi)Document57 pagesHistology of Cardiovascular System (Histologi)missirena100% (1)
- University of Perpetual Help System Laguna-Isabela Campus Quiz on Cells and TissuesDocument4 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help System Laguna-Isabela Campus Quiz on Cells and TissuesMountain DewNo ratings yet