Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Rehabilitation Medicine Myopathies
Uploaded by
James P. RoncalesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Principles of Rehabilitation Medicine Myopathies
Uploaded by
James P. RoncalesCopyright:
Available Formats
Principles of Rehabilitation Medicine >Myopathies
Raj Mitra+
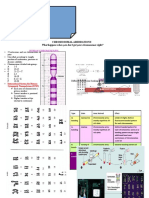
Table 75–1Muscular Dystrophies
Average age of onset for
Type of Dystrophy Inheritance pattern Protein Affected Age of Onset Rate of Progression Life Expectancy (years)
daily wheelchair use
Duchenne (DMD) X-linked Dystrophin 2–6 years old Moderate-fast 10–12 years old 20–30
Variable, typically a few Variable, after 15 years
Becker (BMD) X-linked Dystrophin Slow to moderate 40–50
years later than DMD old
Emerin (X-linked); other
30s in the X-linked form,
Emery-Dreifuss (EDMD) X-linkedAD/AR proteins in AD and AR Teens Moderate Variable
variable in the other forms
forms
Variable. Note: 20%–30%
Facioscapulohumeral
AD DUX4 Infancy–40s Slow of people with FSHD Generally unaffected
(FSHD)
ultimately use wheelchairs
LimbGirdle (LGMD) AD/AR Variable Variable Moderate Variable Variable
Typically, no wheelchair
Oculopharyngeal (OPMD) AD PABP2 30s–40s Moderate Unaffected
needed
AD, Autosomal Dominant; AR, Autosomal Recessive; BMD, Becker Muscular Dystrophy; DMD, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy; EDMD, Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy; FSHD, Facioscapulohumeral Muscular
Dystrophy; LGMD, Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy; MD, Muscular Dystrophy; OPMD, Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy.
Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (DMD and BMD; dystrophinopathies)
Date of download: 05/02/21 from AccessPhysiotherapy: accessphysiotherapy.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Table 1: Infective Endocarditis Non Infective Myocarditis Myocardidits PericarditisDocument3 pagesTable 1: Infective Endocarditis Non Infective Myocarditis Myocardidits PericarditisLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- A Genetic Cause of Alzheimer Disease Source Nat Rev Neurosci So 2015 Sep 16 9 564 74 (PMIDT26243569)Document11 pagesA Genetic Cause of Alzheimer Disease Source Nat Rev Neurosci So 2015 Sep 16 9 564 74 (PMIDT26243569)dai shujuanNo ratings yet
- Her Personal Slides EDS - Comprehensive Approach To Diagnosis and Management 6-24-19Document44 pagesHer Personal Slides EDS - Comprehensive Approach To Diagnosis and Management 6-24-19Ellen O'FarrellNo ratings yet
- Cognition and Behaviour in Frontotemporal Dementia With and Without Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument8 pagesCognition and Behaviour in Frontotemporal Dementia With and Without Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisEmmanuel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Crowell - Medical Screening and Evacuation Cauda Equina in Combat ZoneDocument9 pagesCrowell - Medical Screening and Evacuation Cauda Equina in Combat ZoneDonna TsuiNo ratings yet
- Hemato 01 00008Document13 pagesHemato 01 00008Supu VeeturiNo ratings yet
- Bookshelf NBK1119Document37 pagesBookshelf NBK1119VALENTINA ENRIQUEZ DIAZNo ratings yet
- Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy in Adolescents: Current PerspectivesDocument11 pagesDuchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy in Adolescents: Current PerspectivesBudi PutraNo ratings yet
- Muscular Dystrophy and Its Ayurvedic PerspectivesDocument149 pagesMuscular Dystrophy and Its Ayurvedic PerspectivesMuktha ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 0201B Blurring3Document11 pagesOphthalmology 0201B Blurring3Rea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Bone Dysplasia Classification: Role of GeneticsDocument3 pagesEvolution of Bone Dysplasia Classification: Role of GeneticsmgNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Genetic Defect in BMD: AON-Mediated Exon Skipping For Duchenne Muscular DystrophyDocument2 pages2.2 Genetic Defect in BMD: AON-Mediated Exon Skipping For Duchenne Muscular DystrophyFelipe RomãoNo ratings yet
- Jonathan M. Lacombe, Randall J. Roper T: Review ArticleDocument9 pagesJonathan M. Lacombe, Randall J. Roper T: Review ArticleMaría Paula Caballero BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Inheritance and PedigreeDocument58 pagesPatterns of Inheritance and Pedigreemus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Macular Disease: Fitriani Umi Hasanah 201820401011121 Pembimbing: Dr. Fatin Hamamah, SP.MDocument28 pagesAge-Related Macular Disease: Fitriani Umi Hasanah 201820401011121 Pembimbing: Dr. Fatin Hamamah, SP.MKim NayoungNo ratings yet
- The DMD Gene and Therapeutic Approaches To Restore - 2021 - Neuromuscular DisorDocument8 pagesThe DMD Gene and Therapeutic Approaches To Restore - 2021 - Neuromuscular DisorSuzie Simone Mardones SilvaNo ratings yet
- Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy GeneticsDocument86 pagesDuchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy GeneticsYoga LestariNo ratings yet
- Hansen: Sơ ĐDocument5 pagesHansen: Sơ ĐDao TruongNo ratings yet
- 195 Full PDFDocument19 pages195 Full PDFケビン土井組No ratings yet
- Long-Term Mortality in Patients With Atrial Septal Defect: A Nationwide Cohort-StudyDocument6 pagesLong-Term Mortality in Patients With Atrial Septal Defect: A Nationwide Cohort-StudyDárcio CasteloNo ratings yet
- Autosomal Recessive Inheritance (AR)Document44 pagesAutosomal Recessive Inheritance (AR)inakiNo ratings yet
- Mehu525 - U2 - T9 - Developmental Dysplasia of The HipDocument5 pagesMehu525 - U2 - T9 - Developmental Dysplasia of The HipJorge OtoyaNo ratings yet
- JCM 13 01500Document21 pagesJCM 13 01500Flavia ChNo ratings yet
- Optimizing DrugDocument10 pagesOptimizing DrugKAVIYA.R UG ZOOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Chandra Et Al-2014-Acta OphthalmologicaDocument2 pagesChandra Et Al-2014-Acta OphthalmologicaShafa KhansaNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular: Joint Displacement Without ReductionDocument5 pagesTemporomandibular: Joint Displacement Without ReductionleandrariosllNo ratings yet
- Functional Dissociative Seizures and Borderline Personality Disorder Review of Their Psychological and Neurobiological RelationshipsDocument9 pagesFunctional Dissociative Seizures and Borderline Personality Disorder Review of Their Psychological and Neurobiological RelationshipsMagali DominguezNo ratings yet
- Garry Kamdar 2016 Dystrophin Deficient CardiomyopathyDocument14 pagesGarry Kamdar 2016 Dystrophin Deficient CardiomyopathyDnisaNo ratings yet
- Blue and White Illustration Treatment and Advances in Diabetes BrocureDocument2 pagesBlue and White Illustration Treatment and Advances in Diabetes Brocureivieowie11No ratings yet
- Skeletal Dysplasias Review: Radiological FeaturesDocument7 pagesSkeletal Dysplasias Review: Radiological FeaturesaniendyawijayaNo ratings yet
- Letter and Category Fluency in Community - Dwelling Canadian SeniorsDocument12 pagesLetter and Category Fluency in Community - Dwelling Canadian Seniorsrichard LemieuxNo ratings yet
- Elusive Drusen and Changing Terminology of AMDDocument11 pagesElusive Drusen and Changing Terminology of AMDGustavo Rivera100% (1)
- Clinical Relevance of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter, Stroke, Pacemaker Implant, and Heart Failure in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular DystrophyDocument8 pagesClinical Relevance of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter, Stroke, Pacemaker Implant, and Heart Failure in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular DystrophyAndreea NistorNo ratings yet
- Duchenne Treatment 2Document25 pagesDuchenne Treatment 2Javiera Vildoso SalinasNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathological Features of The Tauopathies - MUrray - MolMechNeurodeg - 2005Document5 pagesClinicopathological Features of The Tauopathies - MUrray - MolMechNeurodeg - 2005MARIA MONTSERRAT SOMOZA MONCADANo ratings yet
- 647-Article Text-964-1-10-20200103Document4 pages647-Article Text-964-1-10-20200103MCuk2606No ratings yet
- GS6882A-RT Slides 2020Document19 pagesGS6882A-RT Slides 2020Yinebeb MezgebuNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Capitellar Osteochondritis Dissecans in Children With Chronic Radial Head Subluxation and DislocationDocument7 pagesPrevalence of Capitellar Osteochondritis Dissecans in Children With Chronic Radial Head Subluxation and DislocationAb Hakim MuslimNo ratings yet
- Adult Brainstem Gliomas ReviewDocument11 pagesAdult Brainstem Gliomas ReviewJuan Diego Martinez LemusNo ratings yet
- MS Clinicalkey 1Document4 pagesMS Clinicalkey 1aulia pratiwiNo ratings yet
- 2019 01 08 Hypermobility and Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes NZ Guideline 2019 - v1Document24 pages2019 01 08 Hypermobility and Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes NZ Guideline 2019 - v1ojwyldeNo ratings yet
- Imail: Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Danon Disease CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesImail: Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Danon Disease CardiomyopathyMathew McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Read-Through Approach For Stop Mutations in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. An UpdateDocument8 pagesRead-Through Approach For Stop Mutations in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. An UpdateL ANo ratings yet
- Final MD HGD ReportDocument100 pagesFinal MD HGD ReportJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Aberrations What Happens When You Don't Get Your Chromosomes Right?Document12 pagesChromosomal Aberrations What Happens When You Don't Get Your Chromosomes Right?Des CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- DMD Lecture 7.9.2020 (Lai PS)Document72 pagesDMD Lecture 7.9.2020 (Lai PS)Yinebeb MezgebuNo ratings yet
- Strechmark ReviewDocument13 pagesStrechmark Review郭先薈No ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations ExplainedDocument6 pagesGenetic Mutations ExplainedGeo NalobNo ratings yet
- The Clinical Diagnosis of Temporomandibula. Disorders in The Orthodontic PatmntDocument10 pagesThe Clinical Diagnosis of Temporomandibula. Disorders in The Orthodontic PatmntnomanNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument61 pagesChromosomal AbnormalitiesManisanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Clinical and Genetic Overview of Paroxysmal Moveme PDFDocument55 pagesClinical and Genetic Overview of Paroxysmal Moveme PDFRomy ZgheibNo ratings yet
- Borderline Personality Disorder 2018Document1 pageBorderline Personality Disorder 2018Nata Papanatas100% (1)
- Usefulness of Fetopathological Examination in The Diagnosis of Skeletal DysplasiasDocument1 pageUsefulness of Fetopathological Examination in The Diagnosis of Skeletal DysplasiasEmilia 5No ratings yet
- gao2015 (1)Document17 pagesgao2015 (1)saherrodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bone Tumor - Well-Defined Osteolytic Tumors and Tumor-Like LesionsDocument20 pagesBone Tumor - Well-Defined Osteolytic Tumors and Tumor-Like LesionsROSSANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledDr. Pedro Javier Cadena GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Prefixes, Suffixes, and Abbreviations: Chapter OutlineDocument20 pagesPrefixes, Suffixes, and Abbreviations: Chapter OutlineJoanne Cristie TolopiaNo ratings yet
- Madelung Deformity - BackgroundDocument5 pagesMadelung Deformity - BackgroundAnonymous bUBXIFfNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ConditionsDocument1 pageShoulder ConditionsJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Group Activity: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGroup Activity: InstructionsJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- NJBKDocument1 pageNJBKJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Sample Peer Evaluation ToolDocument2 pagesSample Peer Evaluation ToolJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Pid Application FormDocument2 pagesPid Application FormMark PesiganNo ratings yet
- ACL Reconstruction ProtocolDocument23 pagesACL Reconstruction ProtocolRoberto Tommasini100% (2)
- Japan Tour 2020Document11 pagesJapan Tour 2020James P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- NORMALGAITDocument3 pagesNORMALGAITJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Case 4Document2 pagesCase 4James P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Manual Muscle TestingDocument11 pagesManual Muscle TestingJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- ACL Reconstruction ProtocolDocument23 pagesACL Reconstruction ProtocolRoberto Tommasini100% (2)
- AlicdanRoncales RecordKeepingDocument2 pagesAlicdanRoncales RecordKeepingJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Developing and Implementing A ProgramDocument8 pagesDeveloping and Implementing A ProgramJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Page 183-184Document3 pagesPage 183-184James P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Anthro-LEC - Compatibility Mode PDFDocument20 pagesAnthro-LEC - Compatibility Mode PDFJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- DMDocument3 pagesDMJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Eval Pre-RetdemStudents MmTesting PDFDocument1 pageEval Pre-RetdemStudents MmTesting PDFJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- OFF - Campus Activity Proposal Activity Information Constancio E. Aure Sr. National High School - A CalabarzonDocument5 pagesOFF - Campus Activity Proposal Activity Information Constancio E. Aure Sr. National High School - A CalabarzonJames P. Roncales100% (1)
- Muscle Grading and Testing Procedures 508 PDFDocument5 pagesMuscle Grading and Testing Procedures 508 PDFNanda Gusmaw BarcellioNo ratings yet
- Pharma AssignmentDocument1 pagePharma AssignmentJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Moina Lower ExDocument3 pagesMoina Lower ExJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- SCHEDDocument3 pagesSCHEDJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Training Program ReportsDocument5 pagesTraining Program ReportsJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Pharma AssignmentDocument1 pagePharma AssignmentJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Week 3 ReflectionDocument1 pageWeek 3 ReflectionJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Clinical Anatomy: Abbas A. A. ShawkaDocument102 pagesLower Limb Clinical Anatomy: Abbas A. A. ShawkaJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Roncales Travellers Inn House Rules and RegulationsDocument1 pageRoncales Travellers Inn House Rules and RegulationsJames P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Physics 3 2Document5 pagesPhysics 3 2James P. RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Creative Cover LetterDocument1 pageCreative Cover LetterPaolo PerandosNo ratings yet
- De Novo Assembly of Agave Sisalana Transcriptome in Response To Drought StressDocument14 pagesDe Novo Assembly of Agave Sisalana Transcriptome in Response To Drought StressGregorio SamsaNo ratings yet
- Tet PGTRB Zoology Model Question Paper 2Document14 pagesTet PGTRB Zoology Model Question Paper 2Subbarayudu mamillaNo ratings yet
- Most Important Topics of BiologyDocument5 pagesMost Important Topics of BiologyAshraf AliNo ratings yet
- Economic Traits of PoultryDocument17 pagesEconomic Traits of PoultrySantosh Dhakal100% (2)
- Full Download Biochemistry A Short Course 2nd Edition Tymoczko Test BankDocument6 pagesFull Download Biochemistry A Short Course 2nd Edition Tymoczko Test Bankgelnernita23741372100% (33)
- Practice Cambridge IELTS 16 Reading Test 03 With ADocument8 pagesPractice Cambridge IELTS 16 Reading Test 03 With A14 Trần Huyền 10a1No ratings yet
- Practice Exam Questions For MusclesDocument2 pagesPractice Exam Questions For MusclesTracy SelkNo ratings yet
- Sumayya Arif Roll# 19-11120 Organization:UVA S: BIOT 498 Internship Course Final PresentationDocument7 pagesSumayya Arif Roll# 19-11120 Organization:UVA S: BIOT 498 Internship Course Final PresentationSumayya ArifNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity AssignmentDocument8 pagesBiodiversity AssignmentAngelica Irish Tolentino100% (1)
- Zuhad by Rida Saleem CompleteDocument38 pagesZuhad by Rida Saleem CompleteAfrah NajeebNo ratings yet
- Mathlearnermodule 130708064103 Phpapp02 PDFDocument112 pagesMathlearnermodule 130708064103 Phpapp02 PDFnel baradiNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text About The Six Kingdoms of LifeDocument6 pagesRead The Following Text About The Six Kingdoms of LifeNathalie RojasNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells - eDocument3 pagesBlood Cells - eTai Yin LAMNo ratings yet
- User Contraints FileDocument4 pagesUser Contraints FilekarlaNo ratings yet
- Effects of High Temperature On Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation byDocument8 pagesEffects of High Temperature On Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation byFábio Luís MostassoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument25 pagesCell CyclearzooshabbirNo ratings yet
- Biotechnologies Applied To Animal Reproduction, Current Trends and Practical Applications For Reproductive Management (VetBooks - Ir)Document354 pagesBiotechnologies Applied To Animal Reproduction, Current Trends and Practical Applications For Reproductive Management (VetBooks - Ir)CutlerBeckett90No ratings yet
- DVD Worksheet Unit 5Document4 pagesDVD Worksheet Unit 5Victor RoblesNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Science Prelim ExamNanetteNo ratings yet
- BT Crops - Review PaperDocument12 pagesBT Crops - Review Paperrajiv pathakNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis - WorksheetDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis - WorksheetMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fungi by Ainsworth G by AkankshaDocument33 pagesClassification of Fungi by Ainsworth G by AkankshaAkanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- ESL Brains What Can Genetic Genealogy Tell Us About Our Ancestors TV 9287Document2 pagesESL Brains What Can Genetic Genealogy Tell Us About Our Ancestors TV 9287antonina.1989No ratings yet
- Hatching Characteristics of Japanese Quail Eggs in A Tropical EnvironmentDocument3 pagesHatching Characteristics of Japanese Quail Eggs in A Tropical EnvironmentshofiNo ratings yet
- Diploma Pharmacy First Year - Hap - MCQSDocument13 pagesDiploma Pharmacy First Year - Hap - MCQSAnitha Mary Dambale91% (33)
- Rajasthan Board Class 12 Biology Ss 42 2018Document12 pagesRajasthan Board Class 12 Biology Ss 42 2018Nitin ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Regeneration OcularDocument40 pagesRegeneration OcularEDUARDO HUARTENo ratings yet
- Lect. 10 PL Path 502 PhytoplasmaDocument26 pagesLect. 10 PL Path 502 Phytoplasmadawit gNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetLuuk Van MeursNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - Bio LibretextDocument782 pagesMicrobiology - Bio LibretextJomsEve IsonNo ratings yet