Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Steps For Assembly
Common Steps For Assembly
Uploaded by
NIkhil Raj B0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThe document provides guidelines for assembly and assembly drawings. It recommends dividing large assemblies into subassemblies of 6 or fewer parts. Components should be assembled starting from the base and working upwards, with at least 3 mates constraining each axis to fully define the assembly. Patterns and mirrors should be used for repetitive parts. Assembly drawings should include an isometric and exploded view on sheet 1, front and top views with dimensions on sheet 2, and assembly notes on sheet 3.
Original Description:
Original Title
assembly Document
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides guidelines for assembly and assembly drawings. It recommends dividing large assemblies into subassemblies of 6 or fewer parts. Components should be assembled starting from the base and working upwards, with at least 3 mates constraining each axis to fully define the assembly. Patterns and mirrors should be used for repetitive parts. Assembly drawings should include an isometric and exploded view on sheet 1, front and top views with dimensions on sheet 2, and assembly notes on sheet 3.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCommon Steps For Assembly
Common Steps For Assembly
Uploaded by
NIkhil Raj BThe document provides guidelines for assembly and assembly drawings. It recommends dividing large assemblies into subassemblies of 6 or fewer parts. Components should be assembled starting from the base and working upwards, with at least 3 mates constraining each axis to fully define the assembly. Patterns and mirrors should be used for repetitive parts. Assembly drawings should include an isometric and exploded view on sheet 1, front and top views with dimensions on sheet 2, and assembly notes on sheet 3.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
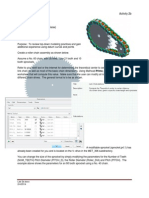
Common steps for assembly
When there are more number of components in a single
assembly, divide it into sub assemblies with less than 10 parts or
such.(optimal number is 6)
Always start the assembly from the base, And then start
assembling from bottom portion to the top as it should be done
during practical assembly.
Make sure to fix the bottom/base component to constrain the
motion.
As suggested a minimum of 3 mates that is on each axis should
be done and rotations should be locked to be fully defined and
constrained.
Always make sure that orientation is properly as required before
starting the assembly.
Whenever there are repetitive parts ,use patterns and mirrors
with proper references to save time and work.
Components with two or more holes can be assembled using
concentric mate to avoid more number of mates.
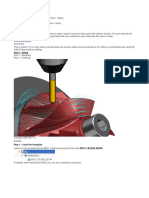
To make assembly drawings:
Sheet 1:- Always choose the better orientation to project the
most of the information, select isometric and exploded view to
be projected(exploded view should done in assembly before
drawing and then should be rebuilt and saved)
Exploded view is required to explain the people how the actual
assembly is to be done.
Generate bill of materials from the tool bar in annotations for all
the considered and place it on sheet 1.
All the individual components should be numbered using add
balloon command by selecting each part, this is done so that
each part can be identified in bill of materials.
Sheet 2:- select front and top views to be projected, and add
respective dimensions to each aspect of the assembly using
ordinate dimensions (like total length, breadth and width of the
overall assembly and distance of intermediate parts).
Sheet 3:-a brief procedure of some important notes during
assembly should be typed, so the assembler can understand
some of the complex joints.
You might also like
- Designing A StaplerDocument41 pagesDesigning A StaplerEmmanuel Morales ChilacaNo ratings yet
- Top Down ModelingDocument29 pagesTop Down ModelingDhoom MachaleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - A Simple AssemblyDocument12 pagesTutorial 4 - A Simple AssemblyKish NvsNo ratings yet
- Mouse Mould DesignDocument7 pagesMouse Mould Designthuc2014No ratings yet
- Information Sheet No. 3 LO3. Construct Assembly Drawing Assembly DrawingDocument6 pagesInformation Sheet No. 3 LO3. Construct Assembly Drawing Assembly DrawingJohnArgielLaurenteVictorNo ratings yet
- Assemblies - Worked Examples: Assembly ConstraintsDocument9 pagesAssemblies - Worked Examples: Assembly ConstraintsJunaid YNo ratings yet
- 4-1-Lesson PlanDocument43 pages4-1-Lesson PlanZero TwoNo ratings yet
- Create Assembly Model Top DownDocument8 pagesCreate Assembly Model Top Downsorry can'thelpitNo ratings yet
- Assembly and Detail Drawings ReadingDocument5 pagesAssembly and Detail Drawings ReadingJeyEnDee 20No ratings yet
- Creating Detail Drawings: BackgroundDocument3 pagesCreating Detail Drawings: BackgroundMahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2: Pro/E Wildfire 5.0 Assembly and Motion Analysis: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesTutorial 2: Pro/E Wildfire 5.0 Assembly and Motion Analysis: ObjectivesC.E. Ishmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Session 12Document50 pagesSession 12etaNo ratings yet
- Working Drawings and AssembliesDocument16 pagesWorking Drawings and AssembliesZojj UliNo ratings yet
- Assembly-Modeling ClassDocument63 pagesAssembly-Modeling Classkumar km100% (4)
- Assembly DrawingDocument19 pagesAssembly DrawingJohn EgbongNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Northeastern UniversityDocument26 pagesDepartment of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Northeastern UniversityIvanZavaletaNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCT Assembly Drawing 8Document24 pagesCONSTRUCT Assembly Drawing 8JOSEPH ONGNo ratings yet
- Cad Ex12 PDFDocument3 pagesCad Ex12 PDFAmir AmiriNo ratings yet
- Pro e WorkoutDocument18 pagesPro e WorkoutRahulNo ratings yet
- ME5013 Assignment Section A-2014 PDFDocument5 pagesME5013 Assignment Section A-2014 PDFJanLuiz2015No ratings yet
- KWeld Assembly Manual r5.Document9 pagesKWeld Assembly Manual r5.fvozzella3No ratings yet
- Solidworks Drawing TutorialDocument4 pagesSolidworks Drawing TutorialMarco Alonzo Rodriguez MallquiNo ratings yet
- Chain Drive Patterned Datum Points Top-Down Modeling (Review) Release Creo 2.0 Level 7 ContinuedDocument9 pagesChain Drive Patterned Datum Points Top-Down Modeling (Review) Release Creo 2.0 Level 7 ContinuedJosephi_abbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Working DrawingDocument63 pagesChapter 12 Working DrawingLhen Mediante AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Abaqus GuideDocument22 pagesAbaqus GuideDavid SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Proe 06Document18 pagesProe 06Harpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- DUKW APC - Print and Build Instructions - by AiRDocument9 pagesDUKW APC - Print and Build Instructions - by AiRjuan sebastian cuadrado ayolaNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Shear StrengthDocument3 pagesExperiment On Shear Strengthalvineugene45No ratings yet
- Turbomachinery Milling With NX CAMDocument23 pagesTurbomachinery Milling With NX CAMRabos ElNo ratings yet
- Inventor Assembly ModelingDocument0 pagesInventor Assembly ModelingAnilkumar KrNo ratings yet
- Top Down Design: PrerequisitesDocument18 pagesTop Down Design: Prerequisitesmaria10018012No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2: Assembly and Solidworks MotionDocument10 pagesTutorial 2: Assembly and Solidworks Motionkiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- 8 - Working Drawings in AutocadDocument12 pages8 - Working Drawings in AutocadBijay Krishna DasNo ratings yet
- Exam 2Document4 pagesExam 2api-253978194No ratings yet
- AS019 Technical Drawing 2 TH InstDocument50 pagesAS019 Technical Drawing 2 TH InstSameera KodikaraNo ratings yet
- Assembly ModelingDocument43 pagesAssembly Modelingwadlan0% (1)
- Exercise 3 PDFDocument20 pagesExercise 3 PDFMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Drawing StandardsDocument12 pagesDrawing StandardsAgung Bayu100% (1)
- Assembly Projects: Locating The PartsDocument18 pagesAssembly Projects: Locating The PartsseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- Sizing Guide: Front View Side View Top ViewDocument5 pagesSizing Guide: Front View Side View Top ViewGreenedNo ratings yet
- 07) Design Process Final For Elliptical TrammelDocument4 pages07) Design Process Final For Elliptical TrammelMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- 6.working Drawing PDFDocument3 pages6.working Drawing PDFUNKNOWNNo ratings yet
- Beddows WP3 Tech Draw Workbook Section Views 14 PagesDocument14 pagesBeddows WP3 Tech Draw Workbook Section Views 14 PagesAjhay BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Top Down Assembly ModelingDocument12 pagesTop Down Assembly ModelingSangeet Kr SinghNo ratings yet
- Blueprint Parts Assignment - Spring 2021Document1 pageBlueprint Parts Assignment - Spring 2021Conrad WillettNo ratings yet
- General Design Guidelines For Manual AssemblyDocument74 pagesGeneral Design Guidelines For Manual AssemblySube Singh Insan100% (2)
- Autodesk Inventor - Design AcceleratorDocument23 pagesAutodesk Inventor - Design AcceleratorNickie CaabayNo ratings yet
- Working DrawingsDocument45 pagesWorking Drawingssandeep_gaikwad275% (4)
- CNC-03-Flat Pack Design PreparationDocument16 pagesCNC-03-Flat Pack Design Preparationmarius_danila8736No ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Types of Machine DrawingDocument19 pagesLecture 2. Types of Machine DrawingaddisudagneNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling System Best Practices: Model ScaleDocument4 pages3D Modeling System Best Practices: Model ScaleSwati Gadave-ChouguleNo ratings yet
- DRAW10W - Assembly DrawingDocument8 pagesDRAW10W - Assembly DrawingPaolo GochingcoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 PDFDocument20 pagesExercise 3 PDFSameer AmjadNo ratings yet
- Working Drawings and Assemblies: Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesWorking Drawings and Assemblies: Basic ConceptsSwasthikNo ratings yet
- ASSEMBLY, Layers, Parameters PPSXDocument27 pagesASSEMBLY, Layers, Parameters PPSXPrateek ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- A Classification System to Describe Workpieces: DefinitionsFrom EverandA Classification System to Describe Workpieces: DefinitionsW. R. MacconnellNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)No ratings yet
- Micro-Fulfillment Top PlayersDocument5 pagesMicro-Fulfillment Top PlayersNIkhil Raj BNo ratings yet
- Linear Induction Motors: Y. LalithaDocument19 pagesLinear Induction Motors: Y. LalithaNIkhil Raj BNo ratings yet
- Digital Twin TechnologyDocument10 pagesDigital Twin TechnologyNIkhil Raj BNo ratings yet
- Six SigmaDocument11 pagesSix SigmaNIkhil Raj BNo ratings yet
- Methodology: PlanningDocument5 pagesMethodology: PlanningNIkhil Raj BNo ratings yet
- Chain ConveyorDocument9 pagesChain ConveyorNIkhil Raj BNo ratings yet