Professional Documents
Culture Documents
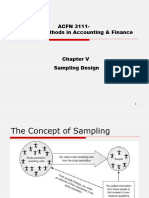
Slide 16 Multi-Stage Sampling (Multi-Stage Cluster Sampling
Uploaded by
Afaq BhuttaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Slide 16 Multi-Stage Sampling (Multi-Stage Cluster Sampling
Uploaded by
Afaq BhuttaCopyright:
Available Formats
Slide 16
Multi-stage sampling (multi-stage cluster sampling
* This is the creation of a cluster sampling, generally used to solve a geographical population's
challenges, when face-to-face relations are required or when a sample framework for a big
geographical region is costly, and time-consuming. However, you may use it for any distinct
groupings, like cluster samples, including ones which are not geographically based. The
technology includes the collection of certain random samples of a series of cluster
Slide 19
Quota sampling
It is not completely random and is usually used for surveys. It is premised that the population of your
sample is the same as the variable in your sample for various quota variables. Quota sampling is
therefore a form of layered sample with a non-random case selection within stratum
Slide 20
Distribute the people into particular groups.
Based on the relevant and accessible facts, calculate the quota for each category.
Give each interviewer a 'assigned' indicating the number of instances to gather data in each quota.
To produce the whole sample, combine the data acquired by the interviewers.
Slide 21
Purposive sampling
* Purposeful or judgemental sampling will allow you to choose situations which will allow you to
answer your question(s) and achieve your goals.
* This sample is frequently used to deal with smaller samples, such as case studies and to pick
particularly informative examples.
* Slide 22
Snowball sampling
1. Is utilised often when individuals of the intended demographic are difficult to identify. For
example, you consequently need individuals who work while receiving unemployment benefit:
2. Contact the population for one or two cases.
3. Please ask for other cases.
4. Ask new cases for further new cases (and so on)
5. Stop when there are no additional cases or the sample is as large as possible.
Slide 23
Self selecting sampling
1. It happens when you normally let folks to determine their willingness to participate in study.
2. Publish your case need either by advertising or by requesting people to participate in it.
3. Gather data from respondents
Slide 24
Convenience sampling
* Comfort sampling involves selecting cases that may be easily obtained in a random fashion for
your sample.
* The sample selection method is kept till the desired sample size has been obtained.
* While the sample approach is often used, it is because the samples are easy to get that
instances might induce biases and affects beyond your control.
You might also like
- Sampling Design: Chapter FourDocument31 pagesSampling Design: Chapter FourSamson HaileyesusNo ratings yet
- Research Chapter 4Document50 pagesResearch Chapter 4Yoseph KassaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Lecture 4Document43 pagesResearch Methodology: Lecture 4TrupalNo ratings yet
- Week05 Confidence IntervalsDocument122 pagesWeek05 Confidence Intervalsa.bocus2510No ratings yet
- Unit Sampling: StructureDocument13 pagesUnit Sampling: Structureromesh10008No ratings yet
- SamplingDocument65 pagesSamplingIshrat Hussain TuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - SamplingDocument56 pagesChapter 5 - SamplingElenear De OcampoNo ratings yet
- INSTITUTE - University School of Business DEPARTMENT - ManagementDocument42 pagesINSTITUTE - University School of Business DEPARTMENT - ManagementAditi MittalNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument52 pagesSamplingAkshay WankhedeNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit-2Document17 pagesBRM Unit-2PunithNo ratings yet
- Lesson 09Document16 pagesLesson 09Hari Priya ENo ratings yet
- Sampling by KapilDocument35 pagesSampling by KapilPrakrit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument18 pagesResearch MethodologySaidu TanimuNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Presented To Dr. Dibyojyoti Bhattacharjee Reader Dba-Sms Assam UniversityDocument31 pagesSampling: Presented To Dr. Dibyojyoti Bhattacharjee Reader Dba-Sms Assam UniversitySujoy PaulNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 SamplingDocument84 pagesUnit 4 SamplingManish KumawatNo ratings yet
- PR 1 - Week 2 - 4th Qtr.Document33 pagesPR 1 - Week 2 - 4th Qtr.LUNINGNING ADARNANo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic: Lahore School of Aviation The University of LahoreDocument6 pagesAssignment Topic: Lahore School of Aviation The University of LahoreSaad ali SaifNo ratings yet
- Defining The Target PopulationDocument25 pagesDefining The Target PopulationHiwot TerefeNo ratings yet
- Report On Sampling TechniquesDocument44 pagesReport On Sampling TechniquesTimoy Cajes0% (1)
- L8 Sampling & Sample SizeDocument38 pagesL8 Sampling & Sample SizeNuhamin TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Populationa and SamplingDocument85 pagesPopulationa and Samplinghenok birukNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document29 pagesUnit 12preciousudoh64No ratings yet
- Block 4Document93 pagesBlock 4dalkota motaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2-Sampling & Sampling DesignDocument34 pagesChapter 3.2-Sampling & Sampling DesignStivanos HabtamuNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorDocument23 pagesAmity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorMayank TayalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Sampling DesignDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Sampling DesignYasinNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument36 pagesSamplingMark John Meneses PanganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sampling and Data CollectionDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Sampling and Data CollectionPhương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Research Methods - Chapter 4Document69 pagesResearch Methods - Chapter 4Lakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4c Sampling TechniquesDocument36 pagesChapter 4c Sampling TechniqueswossenNo ratings yet
- Sampling, Sampling DistributionDocument11 pagesSampling, Sampling DistributionjackblackNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH METHODS Notes 3 (METHODOLOGY) - ELLENDocument67 pagesRESEARCH METHODS Notes 3 (METHODOLOGY) - ELLENdarre32nNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniqesDocument48 pagesSampling TechniqessulemanNo ratings yet
- MRM-Unit 3Document14 pagesMRM-Unit 3Rakshith gowda H DNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Sampling in Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocument8 pagesThe Difference Between Sampling in Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchVilayat AliNo ratings yet
- Week02B Collecting Sample DataDocument30 pagesWeek02B Collecting Sample Dataa.bocus2510No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document5 pagesChapter 7bilawalNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument38 pagesSamplingPaUl CyRuS rOmAgOsNo ratings yet
- Q. 5 (A) Being Manager Planning & Development Under What Conditions Would You Recommend: 2. Simple Random Sample and Cluster SampleDocument5 pagesQ. 5 (A) Being Manager Planning & Development Under What Conditions Would You Recommend: 2. Simple Random Sample and Cluster SamplehumairamanzoorNo ratings yet
- Research-Ch-4 - Sampling DesignDocument42 pagesResearch-Ch-4 - Sampling Designaddisyawkal18No ratings yet
- Sampling Design - Group ThreeDocument38 pagesSampling Design - Group ThreeWasihunNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 Sampling DesignDocument74 pagesChapter-7 Sampling DesignShikha SinghNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design and Introduction To StatisticsDocument39 pagesSampling Design and Introduction To StatisticsLoojee BaylesNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.1 Statisitcs and ProbabilityDocument27 pagesLESSON 3.1 Statisitcs and ProbabilityMaricris OcampoNo ratings yet
- LM07 Estimation and Inference IFT NotesDocument10 pagesLM07 Estimation and Inference IFT NotesYuri BNo ratings yet
- CH - 6 Sampling Design and ProcedureDocument7 pagesCH - 6 Sampling Design and ProcedureAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Q - Q Research Methods - LT - 13Document36 pagesQ - Q Research Methods - LT - 13M.RaziNo ratings yet
- Pangilinan - Rodel - Med001 - Final RequiremnetsDocument3 pagesPangilinan - Rodel - Med001 - Final Requiremnetspangilinanrodel0No ratings yet
- Research Methods - SamplingDocument34 pagesResearch Methods - SamplingMohsin RazaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Sample Design and ProcedureDocument5 pagesCH 4 Sample Design and ProcedureTasfa ZarihunNo ratings yet
- Q3. Define Sampling and Types of Sampling Methods? A3. SamplingDocument3 pagesQ3. Define Sampling and Types of Sampling Methods? A3. SamplinglovemethewayiamNo ratings yet
- Topic-8: Out Line of The SessionDocument33 pagesTopic-8: Out Line of The Sessionsadmansarker8No ratings yet
- Business Analytics Anna University 2 Mark QuestionsDocument13 pagesBusiness Analytics Anna University 2 Mark QuestionsAkhil TacoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5&6Document104 pagesChapter 5&6Dawit MihiretNo ratings yet
- Sampling, Sampling Techniques and Sampling DistributionsDocument70 pagesSampling, Sampling Techniques and Sampling Distributionssinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Suprihatin Departemen Teknologi Industri Pertanian Ipb 2004Document30 pagesSampling: Suprihatin Departemen Teknologi Industri Pertanian Ipb 2004Khoirul UmamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sampling TechniquesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Sampling TechniquesMingma TamangNo ratings yet
- Sample Designing: Prof. Ranjeet Kumar ChoudharyDocument26 pagesSample Designing: Prof. Ranjeet Kumar Choudharypayal khatriNo ratings yet
- 05 SamplingDocument49 pages05 Samplinganon_602869128No ratings yet
- Survey Sampling Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandSurvey Sampling Theory and ApplicationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- ITC - Chapter # 7Document29 pagesITC - Chapter # 7Afaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- ITC - Chapter # 14Document20 pagesITC - Chapter # 14Afaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- ITC - Chapter # 11Document43 pagesITC - Chapter # 11Afaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Final Itc Project Farah Aslam 018Document12 pagesFinal Itc Project Farah Aslam 018Afaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Final AssignmentDocument25 pagesBusiness Studies Final AssignmentAfaq Bhutta75% (4)
- FBF Final Project Report (Financial Plan)Document6 pagesFBF Final Project Report (Financial Plan)Afaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Event Business Plan (Template Task 1) : Content Example DescriptionDocument2 pagesEvent Business Plan (Template Task 1) : Content Example DescriptionAfaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Project Report TemplateDocument13 pagesProject Report TemplateAfaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Activity (Strength and WeaknessDocument4 pagesActivity (Strength and WeaknessAfaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Afaq218) Identify 5 Business Ideas)Document2 pagesAfaq218) Identify 5 Business Ideas)Afaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument4 pagesEmotional IntelligenceAfaq BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Interim Report, Presentation, Final Report, Video Montage - 29mar2021Document21 pagesRubrics For Interim Report, Presentation, Final Report, Video Montage - 29mar2021farhanaNo ratings yet
- Readings Philippine History: Dr. Imelda C. Nery Virgilio V. Dolina Paul John G. SionDocument151 pagesReadings Philippine History: Dr. Imelda C. Nery Virgilio V. Dolina Paul John G. SionSvan Codm100% (9)
- Project Title:-Impact of Celebrity Endorsement On Buying Behavior of Consumers and Source of Brand Building AbstractDocument9 pagesProject Title:-Impact of Celebrity Endorsement On Buying Behavior of Consumers and Source of Brand Building AbstractRajesh InsbNo ratings yet
- Implications of Research Fraud ProjectDocument8 pagesImplications of Research Fraud ProjectRoxana MaleaNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter For Aml AnalystDocument4 pagesCover Letter For Aml Analystbcr9srp467% (3)
- Effectivenessofusinggame PDFDocument9 pagesEffectivenessofusinggame PDFGlenda Manalo CochingNo ratings yet
- 1st Activity For ICTDocument2 pages1st Activity For ICTRou Ann NavarrozaNo ratings yet
- DAVID LOHER, SABINE STRASSER AND GEORGETA STOICA Politics of Precarity: Neoliberal Academia Under Austerity Measures and Authoritarian ThreatDocument11 pagesDAVID LOHER, SABINE STRASSER AND GEORGETA STOICA Politics of Precarity: Neoliberal Academia Under Austerity Measures and Authoritarian Threatdal38No ratings yet
- Critique Paper BSUDocument4 pagesCritique Paper BSUAndrei Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dinio Padua Balitt Final ManuscriptDocument107 pagesDinio Padua Balitt Final ManuscriptYelena AvionnaNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Inventory of Motives For Becoming An Orchestra ConductorDocument17 pagesA Systematic Inventory of Motives For Becoming An Orchestra ConductorMirelaAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Leander Marquardt DissertationDocument4 pagesLeander Marquardt DissertationBuyWritingPaperCanada100% (1)
- World Psychiatry - October 2013Document100 pagesWorld Psychiatry - October 2013zokica5No ratings yet
- MMW Gec 3 Midterm m1Document76 pagesMMW Gec 3 Midterm m1Dexter BoscainoNo ratings yet
- Oklahoma State University Findings On MorgellonsDocument4 pagesOklahoma State University Findings On MorgellonsSpace_Hulker100% (5)
- Chapter 9 One Sample Hypothesis TestingDocument25 pagesChapter 9 One Sample Hypothesis TestingLakhan Subhash TrivediNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument10 pagesEnergyNikhil BabuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Consumer Behaviour OnlineDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Consumer Behaviour OnlineKelly NguyenNo ratings yet
- ERG Review Paper - 10 PagesDocument11 pagesERG Review Paper - 10 PagespriyaNo ratings yet
- The Environmental Audit Report (External Audit)Document3 pagesThe Environmental Audit Report (External Audit)Sheyyan TanNo ratings yet
- Geography Paper 4 Flashcards-2Document16 pagesGeography Paper 4 Flashcards-2faryal khanNo ratings yet
- Absera EliasDocument112 pagesAbsera EliasNejash Abdo IssaNo ratings yet
- ACYASR1 Syllabus T1-AY2023-2024Document13 pagesACYASR1 Syllabus T1-AY2023-2024Janea Lorraine TanNo ratings yet
- Seven Elements For Capacity Development For Disaster Risk ReductionDocument4 pagesSeven Elements For Capacity Development For Disaster Risk ReductionPer BeckerNo ratings yet
- Writing - Free Writing Short NarrativeDocument11 pagesWriting - Free Writing Short NarrativeSaravana SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technology MS ExcelDocument28 pagesEmpowerment Technology MS ExcelDiana Leonidas100% (3)
- Internship ReportDocument45 pagesInternship ReportAsif Rajian Khan Apon100% (2)
- Syllabus 3rd Year B.ArchDocument40 pagesSyllabus 3rd Year B.ArchHarshita MittalNo ratings yet
- SAS 1201 Probability and Statistics IDocument5 pagesSAS 1201 Probability and Statistics ISaizzoh mozzarellaNo ratings yet
- Strut and Tie Modelling of Reinforced Concrete DeepDocument18 pagesStrut and Tie Modelling of Reinforced Concrete DeepHunny VermaNo ratings yet