Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differentiation Worksheet
Uploaded by
SarahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differentiation Worksheet
Uploaded by
SarahCopyright:
Available Formats
C3
MATHEMATICS
SUPPORT CENTRE
Title: Calculus: Differentiation using the chain rule.
Target: On completion of this worksheet you should be able to use the chain rule to
differentiate functions of a function.
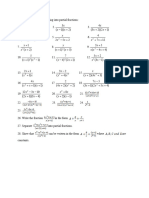
y = x3 + 2 is a function of x Exercise
y = (x3 + 2)2 is a function (the square) of Differentiate the following functions with
the function (x + 2) of x.
3 respect to x:
1. 4(x2 + 1)2
To differentiate this
2. 3(x2 + 1)-1
we write u = (x + 2) , so that y = u
3 2
3. 2(x4 + x)-1
4. 2(x3 – x)-2
dy dy du 5.
½
The chain rule is that = × (x + 1)
dx du dx 6. (x + 1)-
½
For our example ½
7. 2(x + 3)
dy du
= 2u and = 3x 2 , 8. (x2 + 1)
½
du dx ½
9. (x2 + 4x)
dy
= 2u × 3x 2 = 2( x 3 + 2) × 3 x 2 = 6 x 2 ( x 3 + 2) 10. 4(x3 + 1)
½
dx ½
11. (x2 + 3x)-
½
12. 3(x2 + 4x)-
Exercise
Answers:
Differentiate the following functions with
respect to x: 1. 16x(x2 + 1)
2. –6x(x2 + 1)-2
1. (x + 1)3 3. –2(x4 + x)-2(4x3 + 1)
2. (x + 2)4 4. -4(x3 – x)-3(3x2 – 1)
3. (x2 + 3)4 5. ½(x + 1)-
½
4. (x2 + 5x –2)2 3
1 −
5. (x2 + 4)-1 6. − ( x + 1) 2
6. (x4 + 3x)-2 2
½
7. (x3 + 2x2 + 5x + 2)3 7. (x + 3)-
½
8. (5x5 – 4x3)-3 8. x(x2 + 1)-
½
Answers: 9. (x2 + 4x)- (x + 2)
½
10. 6x2(x3 + 1)-
1. 3(x + 1)2 3
1 −
2. 4(x + 2)3 11. − ( x 2 + 3x ) 2 (2 x + 3)
3. 4(x2 + 3)3 × 2x = 8x(x2 + 3)3 2
4. 2(x2 + 4x – 2)(2x + 5) 3
3 2 −
5. -2x(x2 + 4)-2 12. − ( x + 4 x) 2 (2 x + 4)
2
6. -2(x4 + 3x)-3(4x + 3)
7. 3(x3 + 2x2 + 5x + 2)2(3x2 + 4x + 5)
8. -3(3x2 – 4x3)-4(25x4 – 12x2)
© Mathematics Support Centre, Coventry University, 2001
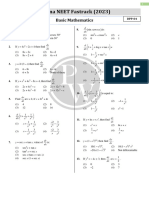
Exercise Answers.
Differentiate the following functions with 1.
9 x2 (x3 + 5)-¼
respect to x; 2. 6(x – x + 1) (4x -1)
4 -¼ 3
( Hint: for some functions simplify first, −7
then differentiate) 3. − 3( x − 7 x + 3)
2 4
(2 x − 7 )
1. 4(x3 + 5)
¾ 4. simplify: 3x 2 + 4 x to (3x2+ 4x)½
differentiate to give (3x+2)(3x + 4x)
¾ 2 -½
2. 8(x – x + 1)
4
-¾
3. 4(x – 7x + 3)
2
1
4. 3x + 4 x
2
5. simplify:
3
2 x + 6 x to ( 2 x + 6 x )
2 2 3
differentiate to give
5.
3
2 x2 + 6x −2
1
( 2 x 2 + 6 x ) 3 (4 x + 6)
1 3
6. −2
( x − 1)
4
2
= ( 2 x 2 + 6 x ) 3 ( 2 x + 3)
1 3
7.
( 2 x + 7)
3
1
3 6. simplify: to (x - 1)-1
4
8.
(5 x − 4 )
2 ( x − 1) 4
differentiate to give - 4x (x - 1)-2
3 4
1
9. 1
( x + x) 2
3
7. simplify: to (2x + 7)-1
3
( 2 x + 7)
3
7
10. differentiate to give - 6x (2x + 7)-2
2 3
( x + x) 2
2
3
8. simplify: to 3(5x - 4)-1
2
5
11. (5 x − 4 ) 2
( 2 x + 3x )
3
differentiate to give - 30x(5x - 4)-2
2
1
12.
( x + 1) 9. simplify:
1
to (x + x)-2
3
1 ( x + x) 2 3
13.
differentiate to give - 6x (x + x)-3
2 3
2x3 + 5
14. (3x - 7 x + 3 x - 5 x)
4 3 2 3
15. (x + 5 x) + 2(x - 5x)
2 2 3 3 7
10. simplify: to 7(x + x)-2
2
( x + x) 2 2
differentiate to give - 14(2x+1)(x +x)-3
2
11. -15(2x + 3x) (2x + 1)
3 -2 2
1
12. simplify: to (x + 1)
-½
( x + 1)
−3
1
differentiate to give − (x + 1) 2
2
−3
13. − 3x( 2 x + 5)
3 2
14. 3(3x -7 x +3 x -5x) (12x -21x + 6x-5)
4 3 2 2 3 2
15. 2(x + 5 x)(2x+5) + 6(x - 5x) (3x - 5)
2 3 2 2
© Mathematics Support Centre, Coventry University, 2001
You might also like
- Jozette Roberts Matrices Lesson Plan Two Inverse of Matricies 1Document5 pagesJozette Roberts Matrices Lesson Plan Two Inverse of Matricies 1api-403984108No ratings yet
- Diagonalizable MatrixDocument8 pagesDiagonalizable MatrixAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths in Focus Adv Yr 12 CH 4Document116 pagesMaths in Focus Adv Yr 12 CH 4Luo67% (3)
- 1 Vectors and TensorsDocument130 pages1 Vectors and TensorsRabindraSubediNo ratings yet
- Matheng Skript 1213Document227 pagesMatheng Skript 1213mcrajpuraNo ratings yet
- Calculo 1 Semana 4 IaccDocument6 pagesCalculo 1 Semana 4 Iaccangel navarroNo ratings yet
- (A) Theansweris2x: © Knut Sydsæter, Peter Hammond, and Arne Strøm 2012Document2 pages(A) Theansweris2x: © Knut Sydsæter, Peter Hammond, and Arne Strøm 2012Liv FernandezNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Systems of EquationsDocument1 pageLinear Algebra Systems of EquationsIsaque MaiaNo ratings yet
- Soal-Soal TurunanDocument35 pagesSoal-Soal TurunanWilbert MannNo ratings yet
- 2023 Partial FractionsDocument1 page2023 Partial FractionsjrambertpccttNo ratings yet
- F5 Tutorial 2Document1 pageF5 Tutorial 2g-05288283No ratings yet
- NewProgress - AMaths TB (Sol) - ch13Document1 pageNewProgress - AMaths TB (Sol) - ch13kkakilaiNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths InequalitiesDocument2 pagesBasic Maths InequalitiesShivam GautamNo ratings yet
- Partial Fraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesPartial Fraction WorksheetJan Leynard ParraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XDocument6 pagesExercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XSpell MasterTMNo ratings yet
- Mcs 1 1 PRBDocument3 pagesMcs 1 1 PRBDan AlexNo ratings yet
- Algebraic FractionsDocument2 pagesAlgebraic FractionsHope MaboteNo ratings yet
- INTEGRATION WRKSHTDocument16 pagesINTEGRATION WRKSHTAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Implicit Differentiation Selected Problems: Matthew Staley September 20, 2011Document8 pagesImplicit Differentiation Selected Problems: Matthew Staley September 20, 2011Stephanie DoceNo ratings yet
- Expanding bracketsDocument2 pagesExpanding bracketsstovbik.anastasiyaNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 057Document9 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 057janvincentcentinoNo ratings yet
- 5 Grado AlgebraDocument1 page5 Grado AlgebraRubenDionicioCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Grade10 TERM3 TUTORIAL MEMODocument21 pagesGrade10 TERM3 TUTORIAL MEMOFarhaan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3Document10 pagesNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3shahid100% (1)
- Basic Mathematics DPP 04 (of Lecture 05)Document3 pagesBasic Mathematics DPP 04 (of Lecture 05)munimunendra00No ratings yet
- Bab 2 Jawapan PenDocument66 pagesBab 2 Jawapan PenAnis AthirahNo ratings yet
- IntegarlesDocument5 pagesIntegarlesLuis Eduardo Vargas GutierrezNo ratings yet
- X X X X X X X X X X X Dy DX Dy DX X Dy DX X: Differentiation 1. (A) 1Document3 pagesX X X X X X X X X X X Dy DX Dy DX X Dy DX X: Differentiation 1. (A) 1Dipon AminNo ratings yet
- ECON 205 Homework Solutions: Intermediate Math for EconomicsDocument72 pagesECON 205 Homework Solutions: Intermediate Math for EconomicsExperimental BeXNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones IDocument3 pagesEcuaciones IJULIO HEBERTH RIOS GARCIANo ratings yet
- Alejandro - Final Part 1Document18 pagesAlejandro - Final Part 1Steven PaulNo ratings yet
- TurÍa de DerivadasDocument3 pagesTurÍa de DerivadasGerson DueñasNo ratings yet
- Itle Card: Uide Card Ctivity CardDocument2 pagesItle Card: Uide Card Ctivity Cardbernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Miscellaneous ProblemsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Miscellaneous ProblemsAngel HilasacaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Logarithmic, Exponential, and Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument26 pagesDerivatives of Logarithmic, Exponential, and Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsGustavo VieceliNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.7 (Solutions) : y X X X XDocument9 pagesExercise 2.7 (Solutions) : y X X X XAli Hassan PalijoNo ratings yet
- TurÍa de DerivadasDocument2 pagesTurÍa de Derivadasnathalia_06201No ratings yet
- MATH 30.13 Long Test 1 Practice Problems-3Document2 pagesMATH 30.13 Long Test 1 Practice Problems-3enzo.goNo ratings yet
- Turunan Fungsi AljabarDocument1 pageTurunan Fungsi AljabarKholid RamadanaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1esoDocument3 pagesAlgebra 1esoalberto580ANo ratings yet
- IV BIM - 1ero. Año - Guía 6 - Ecuaciones 1er Grado ConDocument2 pagesIV BIM - 1ero. Año - Guía 6 - Ecuaciones 1er Grado ConVictor Alan Vela VasquezNo ratings yet
- Factoring ReviewDocument1 pageFactoring ReviewSamir SolimanNo ratings yet
- Synthetic and LD PuzzlesDocument3 pagesSynthetic and LD PuzzlesmsbakermathNo ratings yet
- Operation On FunctionDocument5 pagesOperation On FunctionRandy MaltoNo ratings yet
- 12th ClassDocument7 pages12th ClassNeelkant DubeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 40 - By-KamalDocument8 pagesChapter 40 - By-Kamalقاسم علاوNo ratings yet
- Calculating derivatives of functionsDocument3 pagesCalculating derivatives of functionsLaura Gómez CardonaNo ratings yet
- Aporte 3 Tarea 3 DerivadasDocument3 pagesAporte 3 Tarea 3 DerivadasLaura Gómez CardonaNo ratings yet
- 1.2Document8 pages1.2Chooi Jia YueNo ratings yet
- Soal Terbimbing Limit Bagian 1Document2 pagesSoal Terbimbing Limit Bagian 1Roki HermawanNo ratings yet
- SOL Regla de La Cadena. Recta Tangente y Recta NormalDocument14 pagesSOL Regla de La Cadena. Recta Tangente y Recta NormalJavier Alejandro Manrique CatalanNo ratings yet
- Nama: Sitti Fatma Kelas: XI AP 2 Tugas 2Document2 pagesNama: Sitti Fatma Kelas: XI AP 2 Tugas 2NUR ASMA RIZKYNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument15 pagesCalculusthesonofthewarrior123No ratings yet
- Extended Power Rule, Chain Rule & Product RuleDocument11 pagesExtended Power Rule, Chain Rule & Product RuleNoor AzyraaaNo ratings yet
- Enma 101 Exam 1-6 3Document21 pagesEnma 101 Exam 1-6 3Aquino EricNo ratings yet
- Ch8 - More About Equations - EX8CDocument17 pagesCh8 - More About Equations - EX8CWayne TsoiNo ratings yet
- 4.S2 SOL Regla de La Cadena. Recta Tangente y Recta Normal 2019-2Document14 pages4.S2 SOL Regla de La Cadena. Recta Tangente y Recta Normal 2019-2taniaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Expression and EquationsDocument6 pagesQuadratic Expression and EquationsVisnuVaratanNo ratings yet
- 수상Document100 pages수상강주혜No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Full SolutionsDocument66 pagesChapter 2 Full SolutionsHOH WAN YING MoeNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 (Integral Tak Tentu)Document2 pagesMateri 1 (Integral Tak Tentu)Kharisma siti munawarohNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1Document2 pagesTarea 1Alejandro LapoNo ratings yet
- MCR3UC - Functions: Grade 11, University Preparation, 1.0 Credit Unit 1: Characteristics of Functions Key Questions - (5x) 1 + 3 (4x) + 1 (6) XDocument10 pagesMCR3UC - Functions: Grade 11, University Preparation, 1.0 Credit Unit 1: Characteristics of Functions Key Questions - (5x) 1 + 3 (4x) + 1 (6) XKhara BurrsNo ratings yet
- 01 - Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument6 pages01 - Sets, Relations and Functionsjitender8No ratings yet
- Previous Years' CBSE Board Questions: Number Less 5Document3 pagesPrevious Years' CBSE Board Questions: Number Less 5Somya ShekharNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Analytic FunctionsDocument152 pagesUnit 4 Analytic Functionsfshjmij61No ratings yet
- M.Sc. Mathematics Entrance Exam 2012Document12 pagesM.Sc. Mathematics Entrance Exam 2012sumitruNo ratings yet
- 12th DIFFERENTIATION: - Theory & ProblemsDocument11 pages12th DIFFERENTIATION: - Theory & Problemsarjun sabuNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Polynomial Functions ReviewDocument2 pages7.1 Polynomial Functions ReviewD AnandhiNo ratings yet
- 21.1 Cauchy Goursat TheoremDocument10 pages21.1 Cauchy Goursat TheoremNaga ArjunNo ratings yet
- MRlibDocument16 pagesMRlibVishnu RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Deleted Part of Class 12-MathsDocument2 pagesDeleted Part of Class 12-Mathsalt fNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra by Prof. R. Vittal Rao: Integral DomainDocument5 pagesLinear Algebra by Prof. R. Vittal Rao: Integral Domainrahul nehraNo ratings yet
- 1analytic and Harmonic FunctionsDocument9 pages1analytic and Harmonic FunctionsNelvin Rivera NoolNo ratings yet
- Multi Variable Calculus NotesDocument105 pagesMulti Variable Calculus NotesmuhammadtalNo ratings yet
- ESE Formula SheetDocument8 pagesESE Formula SheetAmir Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Quarter One Pacing GuideDocument4 pagesAlgebra 2 Quarter One Pacing Guideapi-259543534No ratings yet
- Splash NotesDocument15 pagesSplash NotesKlm FlmNo ratings yet
- 2 Analytic Solved ProblemDocument7 pages2 Analytic Solved ProblemAshutosh Singh100% (7)
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mathematics AlgebraDocument9 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mathematics AlgebraNikhilSharmaNo ratings yet
- PM 6 4 Filtered BackprojectionDocument23 pagesPM 6 4 Filtered BackprojectionMustafa Berkan BİÇERNo ratings yet
- Winter 2014 Math 112 Exam 1Document9 pagesWinter 2014 Math 112 Exam 1Tuğba AydemirNo ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument10 pagesCryptographyKarylle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ma5355 Ttpde Unit 1 Class 4Document36 pagesMa5355 Ttpde Unit 1 Class 4Karunambika ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Functions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterDocument9 pagesFunctions: The Domain and Range: Jackie Nicholas Jacquie Hargreaves Janet HunterHussein JaberNo ratings yet
- QrmethodDocument13 pagesQrmethodAshish MeenaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesDifferentiation - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024SAMRIDH SAHANo ratings yet
- Function of Complex Variables: Project SynopsisDocument8 pagesFunction of Complex Variables: Project SynopsisYASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Language Fundamentals: Entering CommandsDocument109 pagesLanguage Fundamentals: Entering CommandsNor ManNo ratings yet