Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomi 643
Uploaded by
winOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomi 643
Uploaded by
winCopyright:
Available Formats
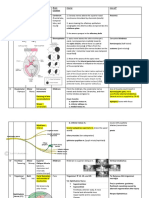
Table 40.
1 Development of the brain
Primary vesicle Region Structure
40 Brain
Prosencephalon Telencephalon (cerebrum) Cerebral cortex, white matter, and basal ganglia
(forebrain) Diencephalon Epithalamus (pineal), dorsal thalamus, subthalamus, and hypothalamus
Neural Mesencephalon (midbrain)* Tectum, tegmentum, and cerebral peduncles
tube Cerebellum Cerebellar cortex, nuclei, and peduncles
Rhombencephalon Metencephalon
Pons*
(hindbrain) Nuclei and fiber tracts
Myelencephalon Medulla oblongata*
* The mesencephalon, pons, and medulla oblongata are collectively known as the brainstem.
Fig. 40.5 Embry onic development of the brain
Left lateral view.
Cervical flexure
Medulla Insula
Cranial oblongata
flexure Pons Pons
Optic Medulla
cup oblongata
Telodien-
A Start of 2nd month. cephalic C 3rd mont h of development.
sulcus
Insula
Pituitary Eye
primordium
Mammillary Pons Medulla
Olfactory bulb
tubercle oblongata
B End of 2nd month. D 7th mont h.
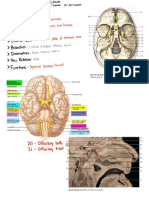
Fig. 40.6 Adult brain
See Fig. 40.12 for lobes of the cerebrum. CN, cranial nerve.
Central sulcus Frontal Longitudinal cerebral
Precentral Postcentral lobe fissure
gyrus gyrus
Frontal Olfactory n.
lobe (CN I)
Optic n. (CN II)
Occipital Hypophysis
Lateral sulcus lobe
Temporal
Temporal lobe Pons
Pons
lobe
Medulla Cerebellum
oblongata Medulla
oblongata
Cingulate gyrus
A Left lateral view.
Cerebellum
Cervical cord
Pineal B Basal view.
Corpus
callosum
Hypothalamus Occipital
lobe
Hypophysis
Pons
C Midsagit tal section showing the right
hemisphere. Medulla oblongata Cerebellum 625
040_Fin.indd 625 27.02.12 14:32
You might also like
- Cranial NervesDocument0 pagesCranial Nervesjeenath justin dossNo ratings yet
- Color Atlas of the BrainDocument8 pagesColor Atlas of the BrainMWNo ratings yet
- Corpus Callosum: Limbic LobeDocument7 pagesCorpus Callosum: Limbic LobePragya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diencephalon, Brainstem & CerebellumDocument1 pageDiencephalon, Brainstem & CerebellumwinNo ratings yet
- Brain Encephalon: - Brain: Embrionally Comes From Ectoderm PartDocument72 pagesBrain Encephalon: - Brain: Embrionally Comes From Ectoderm PartHana AdivaNo ratings yet
- netterDocument2 pagesnetternclov.00No ratings yet
- Virtual Laboratory Activity Worksheet On Central Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesVirtual Laboratory Activity Worksheet On Central Nervous SystemAngela ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Materials Needed:: Nervous System Laboratory ProcedureDocument7 pagesMaterials Needed:: Nervous System Laboratory ProcedureRegina GambayanNo ratings yet
- Nerve Supply of FaceDocument1 pageNerve Supply of FaceYusri Arif100% (2)
- 7Mm Frog: Structure GL Derivative Fate Function Cavity Misc. Info StructureDocument3 pages7Mm Frog: Structure GL Derivative Fate Function Cavity Misc. Info StructureJannah DangananNo ratings yet
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve: © L. Wilson-PauwelsDocument18 pagesGlossopharyngeal Nerve: © L. Wilson-PauwelsNorawaylandNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)Document14 pagesHead and Neck: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)Galo Pillajo100% (1)
- Orign and Passage of The Cranial NerveDocument20 pagesOrign and Passage of The Cranial Nerveapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Neuroscience Pathways Fall 2012Document46 pagesNeuroscience Pathways Fall 2012Yezin ShamoonNo ratings yet
- NeocortexDocument1 pageNeocortexZeromalisNilNo ratings yet
- (Dale Nibbe) Brain Reference Guide PDFDocument2 pages(Dale Nibbe) Brain Reference Guide PDFSuryakantaRoulTuntun100% (4)
- WS - Labeling The BrainDocument1 pageWS - Labeling The BrainMarques AlsoppNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve & Parotid GlandDocument30 pagesFacial Nerve & Parotid GlandChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet for Head and Neck Muscle ChartsDocument14 pagesCheat Sheet for Head and Neck Muscle Chartskaji clappNo ratings yet
- Neuro Practical I TablesDocument9 pagesNeuro Practical I TablesSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- Lab 3Document31 pagesLab 3melmotta1005No ratings yet
- List of cranial nerves and their functionsDocument2 pagesList of cranial nerves and their functionsKay Lumpas Cruda100% (1)
- Vestibulocochlear Nerve: © L. Wilson-PauwelsDocument21 pagesVestibulocochlear Nerve: © L. Wilson-PauwelsNorawaylandNo ratings yet
- STUDENT IndividualWorksheet Week4CNBSDocument30 pagesSTUDENT IndividualWorksheet Week4CNBSZoe FormosoNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves GuideDocument18 pagesCranial Nerves GuideAndrew EldeiryNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Neuro PDFDocument106 pagesAnatomi Neuro PDFsciencewarriorNo ratings yet
- Chap2 MageeDocument66 pagesChap2 MageeSerenelaNo ratings yet
- Deiuliis2019 VERTEBRADOS LA PERCA 4Document10 pagesDeiuliis2019 VERTEBRADOS LA PERCA 4Fernando Melo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nervioso First AidDocument62 pagesNervioso First Aidadrenalina1238No ratings yet
- NeuroDocument71 pagesNeuroSaily JaquezNo ratings yet
- Stu - Spinal Cord - Cranial NervesDocument8 pagesStu - Spinal Cord - Cranial NervestansihuishNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Functional ComponentsDocument7 pagesCranial Nerves Functional ComponentsCoy EnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Neuroanatomy: - Structure-Function Relationships - Non-Invasive Brain ImagingDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Neuroanatomy: - Structure-Function Relationships - Non-Invasive Brain ImagingriskadesmaraniNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Overview (Inglés) (Presentación) Autor Lennart BrodinDocument60 pagesNeuroanatomy Overview (Inglés) (Presentación) Autor Lennart BrodinJulia AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomi: Ratih VierdaDocument78 pagesNeuro Anatomi: Ratih VierdaAmeltia Utomo K. EfendiNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusDocument5 pagesParasympathetic Originates From Edinger Westphal NucleusChristine NathaliaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves TableDocument2 pagesCranial Nerves TableKim Ocampo RojasNo ratings yet
- Taste and SensationDocument10 pagesTaste and SensationWhitney KrabbenhoftNo ratings yet
- Poster01 Skeletal-System-Anterior Ledger11x17Document1 pagePoster01 Skeletal-System-Anterior Ledger11x17jeffrin alexanderNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Table - Names, FunctionsDocument1 pageCranial Nerves Table - Names, FunctionsCorina FreitasNo ratings yet
- High-Yield Neurology and Senses ReviewDocument72 pagesHigh-Yield Neurology and Senses ReviewMahmoud Abu MayalehNo ratings yet
- Otic Ganglion: Schema: Plate 145Document8 pagesOtic Ganglion: Schema: Plate 145Andreea LăzăroiuNo ratings yet
- Stroke SyndromesDocument18 pagesStroke SyndromesBETINA NICOLE SYNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves (II)Document22 pagesCranial Nerves (II)ALONDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- The Special Senses: Vision and HearingDocument34 pagesThe Special Senses: Vision and HearingpuchioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lab Assignment - Appendicular Skeleton LabelingDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Lab Assignment - Appendicular Skeleton Labelingadriana blanco galianoNo ratings yet
- Wk5 - Central Nervous System - Student Version 2023Document45 pagesWk5 - Central Nervous System - Student Version 2023Alexandra GutrovaNo ratings yet
- File 0147Document6 pagesFile 0147Tassnime SebaeiNo ratings yet
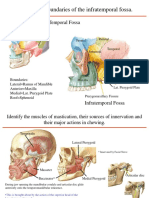
- Infra Temporal FossaDocument7 pagesInfra Temporal FossaНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Infratemporalfossa PpsDocument7 pagesInfratemporalfossa PpsНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Identify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaDocument7 pagesIdentify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaHARSHDESAI56929640No ratings yet
- Bones - ChecklistDocument3 pagesBones - ChecklistHarvey DomingoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionMarian AlecsNo ratings yet
- Michelle Renee Perez Aquino - CREATE SHEET 1 HES 036 LABDocument13 pagesMichelle Renee Perez Aquino - CREATE SHEET 1 HES 036 LABMichelle Renee AquinoNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Readings On The History and System of The Common Law - Roscoe PoundDocument646 pagesReadings On The History and System of The Common Law - Roscoe PoundpajorocNo ratings yet
- Cowell - The Wizards of Once PDFDocument315 pagesCowell - The Wizards of Once PDFtatoes n lases100% (1)
- Microsoft Security Product Roadmap Brief All Invitations-2023 AprilDocument5 pagesMicrosoft Security Product Roadmap Brief All Invitations-2023 Apriltsai wen yenNo ratings yet
- Project On Honda Two WheelersDocument46 pagesProject On Honda Two WheelersC SHIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- M HNDTL SCKT Imp BP RocDocument2 pagesM HNDTL SCKT Imp BP RocAhmed Abd El RahmanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour of Titan WatchesDocument57 pagesConsumer Behaviour of Titan Watchesmanu100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in ESPDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in ESPkaren daculaNo ratings yet
- CFPA E Guideline No 2 2013 FDocument39 pagesCFPA E Guideline No 2 2013 Fmexo62No ratings yet
- Contract of Lease 2Document4 pagesContract of Lease 2Allen Solomon TamNo ratings yet
- Difference between Especially and SpeciallyDocument2 pagesDifference between Especially and SpeciallyCarlos ValenteNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsDocument2 pagesQuick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsNaiana PaulaNo ratings yet
- Pro Ducorit UkDocument2 pagesPro Ducorit Uksreeraj1986No ratings yet
- PRM Vol1 SystemsDocument1,050 pagesPRM Vol1 SystemsPepe BondiaNo ratings yet
- CENELEC RA STANDARDS CATALOGUEDocument17 pagesCENELEC RA STANDARDS CATALOGUEHamed AhmadnejadNo ratings yet
- Robotics: Let's Talk About Robots!Document5 pagesRobotics: Let's Talk About Robots!Elizaveta KononovaNo ratings yet
- 2746 PakMaster 75XL Plus (O)Document48 pages2746 PakMaster 75XL Plus (O)Samuel ManducaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Incepta PharmaceutiDocument31 pagesInternship Report On Incepta PharmaceutihhaiderNo ratings yet
- Water Booster Pump Calculations - Plumbing Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument3 pagesWater Booster Pump Calculations - Plumbing Engineering - Eng-TipsNeal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes-February2017 - by Aslinda RahmanDocument41 pagesGrammar Notes-February2017 - by Aslinda RahmanNadia Anuar100% (1)
- BRTU-2000 Remote Terminal Unit for High Voltage NetworksDocument2 pagesBRTU-2000 Remote Terminal Unit for High Voltage NetworksLaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in TechnologyDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in TechnologyReshiela OrtizNo ratings yet
- Drainage Manual: State of Florida Department of TransportationDocument78 pagesDrainage Manual: State of Florida Department of TransportationghoyarbideNo ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement Strategies in TQMDocument28 pagesContinuous Improvement Strategies in TQMSimantoPreeomNo ratings yet
- Q3 SolutionDocument5 pagesQ3 SolutionShaina0% (1)
- Giáo Trình LPTD 2Document40 pagesGiáo Trình LPTD 2Hưng Trịnh TrọngNo ratings yet
- CS6002 1 MS Coursework Year 2012/13Document4 pagesCS6002 1 MS Coursework Year 2012/13duck19000No ratings yet
- DMG48480F021 01WN DataSheetDocument16 pagesDMG48480F021 01WN DataSheeteminkiranNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Storage PDFDocument367 pagesVsphere Storage PDFNgo Van TruongNo ratings yet
- RCD-GillesaniaDocument468 pagesRCD-GillesaniaJomarie Alcano100% (2)
- TC-21FJ30LA: Service ManualDocument33 pagesTC-21FJ30LA: Service ManualRajo Peto alamNo ratings yet