Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solve The Following Spectral Problems As Far As Possible Give Possible Justifications. Also Predict The Fragmentation Pattern
Uploaded by
ramesh pokhrelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solve The Following Spectral Problems As Far As Possible Give Possible Justifications. Also Predict The Fragmentation Pattern
Uploaded by
ramesh pokhrelCopyright:
Available Formats
Solve the following spectral problems as far as possible give possible
justifications. Also predict the fragmentation pattern.
1. An organic compound C6H10O4 shows the following spectral data.
UV: No significance absorbance above 210nm
IR: Significant absorption band at 1760, and 2950 cm -1.
PMR: 1.5 (3H, d, J = 7cps), 2.2 (6H, s)and 6.8 (1H, q,J = 7cps).
CMR (Proton decoupled): Four signals at = 18, 20, 88, 168.
CMR (Off resonance decoupled): two overlapping quartets at 19, One doublet at 88, One singlet 168.
Mass: Prominent peaks at m/e 146, 87 and 43.
Deduce the structure of the compound.
2. An organic compound C3H5O2Br shows the following spectral data.
UV: max 223 nm, max100
IR: Significant absorption band at 2900-3125, 2690, 2600, 1715, and 1440 cm -1.
PMR: 1.83 (3H, d, J = 7cps), 4.52 (1H, q, J = 7cps) and4.93 (1H, s,exchange with D2O).
Mass: Prominent peaks at m/e 151/154, in the ratio 1:1.
Deduce the structure of the compound.
3. An organic compound C6H10O2 shows the following spectral data.
UV: max 250 nm
IR: Significant absorption band at 3000-2900, 1705, and 1180 cm -1.
PMR: 2.2 (6H, s), 2.7 (4H, s) and 4.93 (1H, s, exchange with D2O).
CMR (Proton decoupled): Three signals at = 28, 36, 208.
CMR (Off resonance decoupled): One quartet at 28, One Triplet at 36, One singlet 208.
Mass: Prominent peaks at m/e 214, 99 and 43.
Deduce the structure of the compound.
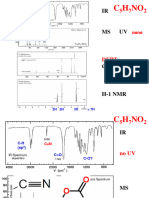
4. An organic compound containing C, H, and Oxygen shows the following spectral data.
UV: max 274 nm, max17
IR: Significant absorption band at 2900, 1705, and 1460 cm -1.
PMR: 2.48( q, J = 7.2cps), 2.12(s) and 1.07 (t, J = 7.2cps)In the intensity ratio 2:3:3
CMR (Proton noise decoupled): Four signals.
CMR (Off resonance decoupled): One quartet at 8.00, One quartet at 38, One singlet 209.
Mass: Prominent peaks at m/e 72, 57, 43and 29.
Deduce the structure of the compound.
5. An organic compound containing C 9H10 O2 shows the following spectral data.
UV: max 257 nm, max 194
IR: Significant absorption band at 3040, 2950, 1740, 1480, 1440, 1220, 750 and 700 cm -1.
PMR: 1.96( 3H, s), 5.00(2H, s) and 7.22 (5H, s)
CMR (Off resonance decoupled): Two singlets, One triplet, One quartet and three doublets. One of
singlet is at 171 and other is at 136.
Mass: Prominent peaks at m/e 150, 108, 91, 79, 78 and 77.
Deduce the structure of the compound.
6. An organic compound containing C 5H11Cl shows the following spectral data.
IR: Significant absorption band at 2950, and 800 cm -1.
PMR: 1.00( 3H, t, J = 7cps), 1.6(6H, s) and 1.8 (2H, q, J = 7cps)
CMR (Off resonance decoupled): Two quartets, tripletand Onesinglet, singlet is at 70.
CMR (Proton decoupled): four singlets
Mass: Prominent peaks at m/e 106/108(3:1 ratio), 70 and 55.
Deduce the structure of the compound.
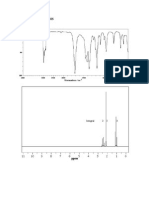
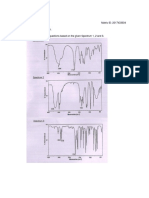
7. Explain the spectral data and deduce the structure of the compound from the given spectra
8. Explain the spectral data and deduce the structure of the compound from the given spectra
9. Explain the spectral data and deduce the structure of the compound from the given spectra
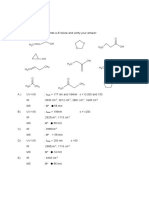
Answers:
O 5.
O C O
CH3
H3C HC CH2 O C CH3
O C CH3 Cl
1. O
H3C C CH2 CH3
6. CH3
H3C CH COOH
2. Br
O
CH2 C CH3
7.
O O
3. H3C C CH2 CH2 C CH3
O
C CH2 CH3
8.
4. H3C C CH2 CH3 (solved problem) OH
9. H3C CH CH2 CH3
Solved Problem 4 :
UV: max 274nm, max 17
IR: band 2900, 1705, and 1460Cm-1
PMR: 2.48 (q, J= 7.2 cps), 2.12 (s) and 1.07 (t, J=7.2 cps) in the intensity ratio of 2:3:3.
13C NMR: (proton noise decoupled): Shows four signals.
13CNMR (Off resonance decoupled): = 8.00 (q), 29 (q), 38(t) and 209 (s)
Mass: Prominent peak 72(M+), 57, 43, and 29.
Solution:
Analyzing the UV spectra:
- Absorbance at UV region with low molar absorptivity shows the
presence of C=O chromophore and n to * transition. n n transtion
Analyzing the IR spectra:
- Presence of band at 2900cm-1 indicates the presence of C-H stretch.(Most of hydrocarbon gives
this absorption).
- Presence of band at 1705cm-1 indicates the presence of C=O stretch.
- Presence of band at 1460cm-1 indicates the presence of C-H bending.
Analyzing the PNMR,C13 spectraand C13 off resonance decoupled spectra:
- Three peaks at ,…… , …, represents three types of non equivalent protons.
- Quartet, Triplet, and singlet peaks shows the presence of 3, 2, and no neighboring protons.
- The intensity ratio of 2:3:3
- Presence of 4 kinds of non equivalent carbons.
- It also shows that two of the carbon is linked with 3hree protons, one carbon is linked with two
proton and one of the carbon with singlet has no proton in it.
- The positions are also indicated by chemical shift values. (presence of electronegative species
and anisotropic nature affects the chemical shift values)
Tentative NMR spectras:
Analyzing the Mass spectra.
- Mass of the molecular ion peak 72, 57,
- Peak at 29, may predict the presence of CH 3CH2
- Peak at 57, shows the loss of 72 – 57 = 15 mass, which suggest the presence of CH 3 loss.
- Peak at 43, shows the loss of 72 – 43 = 27 mass, which suggest or confirms the presence of
CH3CH2.
Fragmentation patterns
O + O
+ +
H3C C CH2 CH3 H3C C O H3C C H2C CH3
m/z = 43
stable ions/radicals
m/z = 72
O O
+ +
H 3C C CH2 CH3 O C CH2 CH3 H3C C
m = 72 H2C
+
CH3
m/z = 57
m/z = 29
O + O
+ +
H3C C CH2 CH3 H3C C O H3C C H2C CH3
m/z = 43
stable ions/radicals
m/z = 72
O O
+ +
H 3C C CH2 CH3 O C CH2 CH3 H3C C
m = 72 H2C
+
CH3
m/z = 57
m/z = 29
The compound is: Butanone
O
H3C C CH2 CH3
You might also like
- SPEKTROSKOPI MASSADocument25 pagesSPEKTROSKOPI MASSAVita Maryam H.No ratings yet
- NMR SpectrosDocument32 pagesNMR SpectrosIndhuja Preethi BNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Solutions of StructureDocument21 pagesSpectroscopic Solutions of StructureKassimNo ratings yet
- Hướng Dẫn Lẫm Bẫi Tẫp Kết Hớp Phổ Hổng Ngổẫi Vẫ Khổi PhổDocument19 pagesHướng Dẫn Lẫm Bẫi Tẫp Kết Hớp Phổ Hổng Ngổẫi Vẫ Khổi PhổAn Lê TrườngNo ratings yet
- Key IR Spectroscopy Signals Identify Organic ReactionsDocument3 pagesKey IR Spectroscopy Signals Identify Organic ReactionsZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- 215-216 HH W13-Nmr-Iii PDFDocument2 pages215-216 HH W13-Nmr-Iii PDFRodrigo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Spectra ProblemsDocument111 pagesSpectra ProblemsChandra Reddy100% (1)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrosDocument24 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroshatna sayNo ratings yet
- Problem: C = 62.68%, H = 4.51%, N = 20.88Document15 pagesProblem: C = 62.68%, H = 4.51%, N = 20.88Chandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument54 pagesSpectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDamar Nurwahyu BimaNo ratings yet
- NMR spectroscopy identifies organic structuresDocument34 pagesNMR spectroscopy identifies organic structuresQuratul AinNo ratings yet
- ws4 PDFDocument5 pagesws4 PDFmohammedabubakrNo ratings yet
- Molecular Formulas and SpectroscopyDocument21 pagesMolecular Formulas and SpectroscopyNurdianAsriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Amides_sparkman2011Document6 pagesChapter 10 - Amides_sparkman2011elenitabastosNo ratings yet
- 3- Carbon-13-NMR (1)Document21 pages3- Carbon-13-NMR (1)ahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- C-13 NMRDocument27 pagesC-13 NMRDeby Aulia Tri NNo ratings yet
- CHE320 OS Test 1 Key QN 4Document2 pagesCHE320 OS Test 1 Key QN 4PdomNo ratings yet
- CHM260 FTIR tutorial questionsDocument4 pagesCHM260 FTIR tutorial questionsadlina asnawiNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument49 pagesMass SpectrometryUbaid ShabirNo ratings yet
- 11.3 Spectroscopic Identification of Organic CompoundsDocument57 pages11.3 Spectroscopic Identification of Organic CompoundslunaisdrowsyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Gurumeet C Wadhawa Department of Chemistry Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil, College Vashi, Navi MumbaiDocument44 pagesDr. Gurumeet C Wadhawa Department of Chemistry Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil, College Vashi, Navi MumbaiGurumeet WadhavaNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy GuideDocument5 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy GuideTux BsdNo ratings yet
- HPLCDocument20 pagesHPLCNugroho HartonoNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples: CH CH + CL CH CH CLDocument10 pagesSolved Examples: CH CH + CL CH CH CLHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Elimination ReactionDocument6 pagesElimination ReactionDxng 1No ratings yet
- CLS - ENG 22 23 XI - Che - Target 5 - Level 1 - Chapter 10 PDFDocument38 pagesCLS - ENG 22 23 XI - Che - Target 5 - Level 1 - Chapter 10 PDFSaksham Chamoli 10 G , 27No ratings yet
- Problems: Syn To The Methyl GroupDocument1 pageProblems: Syn To The Methyl Grouppanda biruNo ratings yet
- PracticeDocument1 pagePracticeMark KaiserNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercise C17Document5 pagesPractice Exercise C17utpNo ratings yet
- DR Rafiq Zakaria Campus, Maulana Azad College, DR Ahmad Zaheer Lecture SeriesDocument97 pagesDR Rafiq Zakaria Campus, Maulana Azad College, DR Ahmad Zaheer Lecture Seriesmohsin abdul azizNo ratings yet
- How To Find No of Structural Isomers by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument2 pagesHow To Find No of Structural Isomers by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry81% (16)
- Carbenes and NitrenesDocument13 pagesCarbenes and NitrenesdevendraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Education Study Program: Ira Lestari, S.Si. M.Si Universit of TanjungpuraDocument23 pagesChemistry Education Study Program: Ira Lestari, S.Si. M.Si Universit of TanjungpuraTri indri yaniNo ratings yet
- Ef0c00890 Si 001Document6 pagesEf0c00890 Si 001Austin SmithNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid & Derivatives-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acid & Derivatives-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Alkyne-Anna IN CLASS 1Document26 pagesAlkyne-Anna IN CLASS 1Siti Farhanah Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Hydrocarbonmeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry: Concepts For Chiral CompoundsDocument6 pagesStereochemistry: Concepts For Chiral CompoundsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- SCHB032 - Memo - Test 1 2022Document5 pagesSCHB032 - Memo - Test 1 2022emjayNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry of SN Reactions PPT - Copy - Copy-1Document28 pagesStereochemistry of SN Reactions PPT - Copy - Copy-1Vidya Rani100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Kristia Stephanie BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios QO1-1Document3 pagesEjercicios QO1-1hector juarezNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Carbon Hybridization and ElectronegativityDocument72 pages13C NMR Carbon Hybridization and ElectronegativityShweta BishtNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 1Document33 pagesAlkenes 1Abdullah AmjadNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrosDocument36 pagesMass SpectrosErsya NurriaNo ratings yet
- Use Your Notes From The Functional Group Tests We Looked at Last Lesson To Answer The 6 Mark Exam Question BelowDocument11 pagesUse Your Notes From The Functional Group Tests We Looked at Last Lesson To Answer The 6 Mark Exam Question BelowMaliha RiazNo ratings yet
- Topic 20 Answers To ExercisesDocument4 pagesTopic 20 Answers To ExercisesSiti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- S DQPK SNyf 9 WNJHups Y4 UDocument38 pagesS DQPK SNyf 9 WNJHups Y4 UKushal DubeyNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionDocument17 pagesNucleophilic Substitution ReactionRojo JohnNo ratings yet
- Cls Jeead-17-18 Xi Che Target-4 Set-2 Chapter-12Document42 pagesCls Jeead-17-18 Xi Che Target-4 Set-2 Chapter-12Samarjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Carbenes and Nitrenes by IIT CampusDocument13 pagesCarbenes and Nitrenes by IIT CampusHemant soni100% (1)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrosDocument39 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrosknkoradiyaNo ratings yet
- SPEC6A problems 3-5 answersDocument19 pagesSPEC6A problems 3-5 answersnonkululekomoya26No ratings yet
- Basics of Photochemistry and Norrish Type I ReactionDocument12 pagesBasics of Photochemistry and Norrish Type I Reactionnidhi vashisthaNo ratings yet
- Réarrangement RadicalaireDocument5 pagesRéarrangement RadicalaireRaf Belo100% (1)
- Stereochirality R or SDocument52 pagesStereochirality R or SnifafaniNo ratings yet
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringFrom EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Chemical Process Technology - IDocument15 pagesChemical Process Technology - Iramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Assignment II-2018 (MCSC-202)Document2 pagesAssignment II-2018 (MCSC-202)ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Math 208 Assignment - Problems on Discrete and Continuous Random VariablesDocument9 pagesMath 208 Assignment - Problems on Discrete and Continuous Random Variablesramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document7 pagesLecture 2SATHISHNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2018-05-23Document16 pagesNew Doc 2018-05-23ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Problem 1) : CHEG 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution To Homework #3Document17 pagesProblem 1) : CHEG 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution To Homework #3ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Created by Unlicensed Version: Proess Flow Diagram For Hydrogen Production From Steam Reforming of Natural GasDocument1 pageCreated by Unlicensed Version: Proess Flow Diagram For Hydrogen Production From Steam Reforming of Natural Gasramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Summary Report of Every Chapter of PLANT DESIGN FOR THE PRODUCTION OF 1800 TONNES OF TOMATO PASTE PER DAY FROM FRESH TOMATOESDocument15 pagesSummary Report of Every Chapter of PLANT DESIGN FOR THE PRODUCTION OF 1800 TONNES OF TOMATO PASTE PER DAY FROM FRESH TOMATOESramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- CHEG 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution To Homework #2Document7 pagesCHEG 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution To Homework #2ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Paint IndustriesDocument43 pagesPaint Industriesramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Cheg 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Homework #4: H H Cacl Cacl H Cacl HDocument10 pagesCheg 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Homework #4: H H Cacl Cacl H Cacl Hramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Solution To Homework 4 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesSolution To Homework 4 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- CHEG 211 Thermodynamics Homework #1 ProblemsDocument6 pagesCHEG 211 Thermodynamics Homework #1 Problemsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Technology - IDocument15 pagesChemical Process Technology - Iramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Teaching Note #3 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesTeaching Note #3 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Teaching Materials 1 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesTeaching Materials 1 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Problem 1) : CHEG 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution To Homework #3Document17 pagesProblem 1) : CHEG 211 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution To Homework #3ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Teaching Materials 1 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesTeaching Materials 1 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Reactor Design and EquilibriumDocument6 pagesChemical-Reactor Design and Equilibriumramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Teaching Note #3 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesTeaching Note #3 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Solution To Exam #1 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (2018)Document2 pagesSolution To Exam #1 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (2018)ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Solution To Homework #2 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesSolution To Homework #2 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrel100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesThermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- CHEG 211 Chemical Process Calculation Homework #1Document2 pagesCHEG 211 Chemical Process Calculation Homework #1ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Solution To Homework #3 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesSolution To Homework #3 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Solution To Exam #2 For Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSolution To Exam #2 For Chemical Engineering Thermodynamicsramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Laxmi Prasad Devkota's poem "The LunaticDocument2 pagesLaxmi Prasad Devkota's poem "The Lunaticramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Scientific InquiryDocument1 pageScientific Inquiryramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Solution To Homework #1 For Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument7 pagesSolution To Homework #1 For Chemical Reaction Engineeringramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Keeping Errors at BayDocument1 pageKeeping Errors at Bayramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- The DB2 Engine - The Life Cycle of A SQL StatementDocument70 pagesThe DB2 Engine - The Life Cycle of A SQL StatementPrashant LenkaNo ratings yet
- Bagi Latihan Soal 3Document3 pagesBagi Latihan Soal 3MUH LULU BNo ratings yet
- Background Surya NepalDocument11 pagesBackground Surya NepalUjibpradhan67% (3)
- Notes BST - CH 1Document5 pagesNotes BST - CH 1Khushi KashyapNo ratings yet
- Sacha Doucet-Kim Cancer AssignmentDocument3 pagesSacha Doucet-Kim Cancer AssignmentSacha Doucet-KimNo ratings yet
- 562ue 2014-06Document55 pages562ue 2014-06vijayramaswamyNo ratings yet
- Music For ChildrenDocument6 pagesMusic For Childrenscribblers1813% (8)
- Measure Dark Triad Personality TraitsDocument5 pagesMeasure Dark Triad Personality TraitsLidia BorleanNo ratings yet
- 2006 Arawak Languages Encyclopedia of Language and LinguisticsDocument4 pages2006 Arawak Languages Encyclopedia of Language and LinguisticsSheldon JungleNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineDocument4 pagesKinematics of MachineSumit KambleNo ratings yet
- Research PhilosophyDocument4 pagesResearch Philosophygdayanand4uNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Kaldor On Adam Smith and Allyn Young: Review of Political EconomyDocument20 pagesNicholas Kaldor On Adam Smith and Allyn Young: Review of Political EconomyAdolfo MedranoNo ratings yet
- 1 Calimutan v. People - G.R. No. 152133Document1 page1 Calimutan v. People - G.R. No. 152133eiram23100% (1)
- UP Law Bar Exam Suggested AnswersDocument16 pagesUP Law Bar Exam Suggested AnswersprincessmagpatocNo ratings yet
- Lighthouse December 18, 2014Document28 pagesLighthouse December 18, 2014andreahowryNo ratings yet
- Soal B Inggris Uas KLS X OllaDocument25 pagesSoal B Inggris Uas KLS X OllaRidwan, S.Pd.,M.SiNo ratings yet
- Indian Blood: HIV and Colonial Trauma in San Francisco's Two-Spirit CommunityDocument17 pagesIndian Blood: HIV and Colonial Trauma in San Francisco's Two-Spirit CommunityUniversity of Washington PressNo ratings yet
- Historical CriticismDocument1 pageHistorical CriticismPatricia Ann Dulce Ambata67% (3)
- Indikasi, Teknik Pembuatan Stoma, ReanastomosispptDocument43 pagesIndikasi, Teknik Pembuatan Stoma, ReanastomosispptErwin Aritama Ismail100% (1)
- Sivaganga Dist-List of Polling Stations For 185-Tiruppattur Assembly ConstituencyDocument85 pagesSivaganga Dist-List of Polling Stations For 185-Tiruppattur Assembly ConstituencyGanesanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of An Effective CounselorDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of An Effective CounselorAbbas KhanNo ratings yet
- Organic ReactionsDocument73 pagesOrganic ReactionsKrishnaah Doraj100% (1)
- Hieu Doan: The Path of PowerDocument206 pagesHieu Doan: The Path of Powerhulu12100% (1)
- Labman PDFDocument76 pagesLabman PDFJames OnsachiNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in 3is (Inquiries, Investigation, Immersion)Document5 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in 3is (Inquiries, Investigation, Immersion)Roselyn Relacion LucidoNo ratings yet
- Public Service Commission, West Bengal: Notice Inviting Expression of Interest For Enlistment As LawyersDocument3 pagesPublic Service Commission, West Bengal: Notice Inviting Expression of Interest For Enlistment As LawyersITI JobNo ratings yet
- Agoraphobia - Simmel and Kracauer - Anthony VidlerDocument16 pagesAgoraphobia - Simmel and Kracauer - Anthony VidlerArthur BuenoNo ratings yet
- ED 206 Course OutlineDocument1 pageED 206 Course OutlineChe Insik RecabarNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram of Three-Component Liquid SystemDocument11 pagesPhase Diagram of Three-Component Liquid SystemVanessa Denise Aguilar100% (2)
- Sample OMR Sheet Marking PDFDocument1 pageSample OMR Sheet Marking PDFMuraliNo ratings yet