Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Derivations .: Description Method
Uploaded by
josOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Derivations .: Description Method
Uploaded by
josCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 2
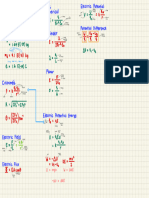
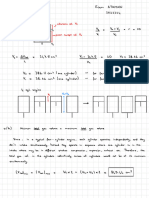
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF METHOD & DERIVATIONS .
Amember , being loaded with any system of looding , is first
considered fixed
of both ends . For this assumed and condition there will be a
at each moment
end of the member , and these moments will be defined as the Fixing Moments
Let Fn be the fixing moment at the right hand end of the member . and Ff
the fixing moment at the left hand end of the member . The values of these
fixing moments may be found for different types of looding on Pages 67 & 68 .
This loaded member is then assumed to be restrained at both ends by any
number of restraining members , and the for ends of these restraining members
are assumed to be fixed . For this condition , which is shown on diagram No . / ,
the moments at the ends of the looded member will no longer be the fixing
moments , but may bo found from Equation No . / which is derived below .
къ
LO KD
Kg
+ +
:
Kc
+
Ko +
Ko
=e
K
ño
SKf
www sko
DIAGRAM NO /
.
No the
loading restraint for the derivation
of
This shows conditions and
of
Looded Member
at
Equation Moments Ends
of
.
)
.
(
/
DERIVATION OF EQUATION NO
OF
AT
MOMENT END LOADEDMEMBER
(
. )
I
.
the
18
Equations given
on
Standard Slope Deflection Page
of
From the bottom
Assuming roo and unity
1
E
Ff Fn )
(
:
20n
Of
2K1
M
+
O
+ -
(
) )
en
Mf
2K1 20f
>
+
(
at
All the restraining members are considered fixed their far ends a .
the loaded member may replaced
by
be
at
These members each end
of
of
single member equal stiffness the sum their stiffnesses
to
in
.
Of on
2EKn 2en Rnki
M
= =
=
3
4
- -
- -
( (
) )
Rf
Ki
KF
Mf
20f
28
4
Of on
KIRO
☺
from
M
=
3
4
- -
/ /
Rf
from Mf 4Ki
=
*
Substituting we get
On
the values
Of
of
and from and Dond and
in
5
6
Ff FR
- - - -
M
0
Mf
Phn
8
You might also like
- IL" IL": "Vanities" David KirshenbaumDocument10 pagesIL" IL": "Vanities" David KirshenbaumNicholas Steven KingNo ratings yet
- Fakm - Vor-Dme Rwy 02 - Vor-01 12dec2013Document1 pageFakm - Vor-Dme Rwy 02 - Vor-01 12dec2013DeanNo ratings yet
- Graded Assignment: Unit Test, Part 2: Radicals and Complex NumbersDocument3 pagesGraded Assignment: Unit Test, Part 2: Radicals and Complex NumbersManuk SogomonyanNo ratings yet
- Do Global Economic and Political Integrations Bring More Harm To The Philippines and The Filipinos or Not? Articulate Your StanceDocument3 pagesDo Global Economic and Political Integrations Bring More Harm To The Philippines and The Filipinos or Not? Articulate Your StancenonononowayNo ratings yet
- Response 13 EPC 2Document4 pagesResponse 13 EPC 2Steven HimawanNo ratings yet
- DCM MatrixDocument2 pagesDCM Matrixsonyvioi5No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDocument24 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwansuyash KumarNo ratings yet
- Ackerman Design PDFDocument4 pagesAckerman Design PDFJomin JosephNo ratings yet
- Brill Greek Epichoric Option v1Document1 pageBrill Greek Epichoric Option v1oarion_hunterNo ratings yet
- Formula CheatsheetDocument1 pageFormula CheatsheetGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- R&des QPDocument3 pagesR&des QPManish BisoiNo ratings yet
- Tugas 7Document1 pageTugas 7septya hanantaNo ratings yet
- Modified 2 Page Notes - ElectrostaticsDocument7 pagesModified 2 Page Notes - ElectrostaticsZarnaab ZahirNo ratings yet
- PGCPS Milestone School Cell Tower Weekly Reports Show Cell Tower ProcessDocument8 pagesPGCPS Milestone School Cell Tower Weekly Reports Show Cell Tower ProcessSafe Tech For SchoolsNo ratings yet
- Before Exam SeeDocument4 pagesBefore Exam SeearpanpurkaitpersonalNo ratings yet
- Rana TE-1Document105 pagesRana TE-1Maulik PatelNo ratings yet
- EX9 Una BombaDocument2 pagesEX9 Una BombaRoger UnoxxNo ratings yet
- J519 BCM PinoutsDocument6 pagesJ519 BCM PinoutssaniNo ratings yet
- Kelmo Electric Actuator Driven Compact Ball Valves: MAS Sakti EmailDocument2 pagesKelmo Electric Actuator Driven Compact Ball Valves: MAS Sakti EmailJohnIbanesNo ratings yet
- Ofgasolineused - .IM?yrg (Ggs - kg1m3: Furs 13.89ms 12.79NDocument1 pageOfgasolineused - .IM?yrg (Ggs - kg1m3: Furs 13.89ms 12.79Nchee xiongyewNo ratings yet
- EMRA Mineral Ore Concession MapDocument1 pageEMRA Mineral Ore Concession Mapkareem AminNo ratings yet
- Rayocs: DiscussedDocument4 pagesRayocs: DiscussedMatthew ListroNo ratings yet
- Ôn Thi Lịch Sử Kiến Trúc (Học)Document14 pagesÔn Thi Lịch Sử Kiến Trúc (Học)Trần Hải LinhNo ratings yet
- Upd C11 CHM EngDocument18 pagesUpd C11 CHM EngArinjoy Mervyn GomesNo ratings yet
- EMA3050 Oct 17Document5 pagesEMA3050 Oct 17Alicina DaleNo ratings yet
- The Corvette: A Nathaniel Drinkwater NovelFrom EverandThe Corvette: A Nathaniel Drinkwater NovelRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- 2 4Document1 page2 4josNo ratings yet
- Statements Are: Half Yearly Am - (2022-2023)Document8 pagesStatements Are: Half Yearly Am - (2022-2023)RomitNo ratings yet
- CBR Curve PDFDocument1 pageCBR Curve PDFMathias OnosemuodeNo ratings yet
- Further Mech Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesFurther Mech Cheat SheetmaneetbhattNo ratings yet
- Hall 1996Document11 pagesHall 1996Enrique G Mancheno MendezNo ratings yet
- Bridging Course (P1L1)Document6 pagesBridging Course (P1L1)Jayson BayogoNo ratings yet
- Divide y ConquistaDocument16 pagesDivide y Conquistasanti10sepNo ratings yet
- Making Your Own Motor Fuel 1943 - StetsonDocument100 pagesMaking Your Own Motor Fuel 1943 - StetsonDarwinNo ratings yet
- Стоянка, консервация АнглDocument5 pagesСтоянка, консервация Англc6txds2zpnNo ratings yet
- Cardio 2 - X-RayDocument45 pagesCardio 2 - X-RaySaja SaqerNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics and The AtomDocument1 pageQuantum Mechanics and The AtomMarciaNo ratings yet
- 00437V30LDocument1 page00437V30Lmohdpilot1No ratings yet
- New UtilityDocument1 pageNew UtilityShadrack kiprotichNo ratings yet
- Shipping World & Shipbuilder, July-Aug.2013 CO2 Fire-FightingDocument45 pagesShipping World & Shipbuilder, July-Aug.2013 CO2 Fire-Fightinggnd100100% (1)
- L1 FrequencyResponseDocument8 pagesL1 FrequencyResponseCHAYANIN AKETANANUNNo ratings yet
- L1 FrequencyResponseDocument8 pagesL1 FrequencyResponseCHAYANIN AKETANANUNNo ratings yet
- Malappuram: Census of India 2001Document554 pagesMalappuram: Census of India 2001FathimaNo ratings yet
- Z-R550 - Z-R560 (CX-ZR550 - ZR560) Diagrama-9838Document8 pagesZ-R550 - Z-R560 (CX-ZR550 - ZR560) Diagrama-9838LucioLopezNo ratings yet
- Pages From Dorman Longs - Handbook For Constructional Engineers - 1895-73Document1 pagePages From Dorman Longs - Handbook For Constructional Engineers - 1895-73Fornvald TamasNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument1 page2 PDFSim Pei YingNo ratings yet
- EECE 334 - Final Exam NotesDocument1 pageEECE 334 - Final Exam Notes. .No ratings yet
- Dashboard: Scarl Ett Whi Teni NG of F I Ci Al Shop Bel I A Cosmeti CDocument1 pageDashboard: Scarl Ett Whi Teni NG of F I Ci Al Shop Bel I A Cosmeti Cmuhammad syidiqNo ratings yet
- Quiz2 Shaikh MuhammadDocument4 pagesQuiz2 Shaikh MuhammadMuhammad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MS20026DDocument2 pagesMS20026DthomasNo ratings yet
- Biologi X 2Document1 pageBiologi X 2jakyNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection - Theory PDFDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection - Theory PDFHaikal HakimNo ratings yet
- 진동공학 0904Document7 pages진동공학 0904SangMin ShinNo ratings yet
- Cyl#nder)Document4 pagesCyl#nder)Ecem AtamanNo ratings yet
- HW5 SolDocument15 pagesHW5 Sol蒲念文No ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument293 pagesCardiologyMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ya Vas LyublyuDocument6 pagesYa Vas Lyublyusantiagogt8No ratings yet
- Handout-And-HomeworkDocument14 pagesHandout-And-Homeworkvedprakash sumanNo ratings yet
- Notas 4 - 2 Sep - Mapeos Entre Variedades 1Document3 pagesNotas 4 - 2 Sep - Mapeos Entre Variedades 1Daniel MedelNo ratings yet
- ES 230 Lecture 14 PDFDocument4 pagesES 230 Lecture 14 PDFJessie F. SermanNo ratings yet
- Manual Tecnico Actuador Neumatico Bray S92 93 PDFDocument1 pageManual Tecnico Actuador Neumatico Bray S92 93 PDFlcs2006mvNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics - One ShotDocument74 pages12th Physics - One ShotKaranNo ratings yet
- MDP 39015079943414 21 1657038395Document1 pageMDP 39015079943414 21 1657038395josNo ratings yet
- MDP 39015079943414 19 1657038287Document1 pageMDP 39015079943414 19 1657038287josNo ratings yet
- Of Journal Welding: 171 Cast SteelDocument1 pageOf Journal Welding: 171 Cast SteeljosNo ratings yet
- MDP 39015079943414 18 1657038282Document1 pageMDP 39015079943414 18 1657038282josNo ratings yet
- ., - of of Engi, - , .Document1 page., - of of Engi, - , .josNo ratings yet
- Guillet,, - . - , - ,, - Alloys Iron - Mineral: Steel P 194 and P 1895 The Uses Manganese 424 426Document1 pageGuillet,, - . - , - ,, - Alloys Iron - Mineral: Steel P 194 and P 1895 The Uses Manganese 424 426josNo ratings yet
- MDP 39015079943414 25 1657038408Document1 pageMDP 39015079943414 25 1657038408josNo ratings yet
- Arthur - MakingDocument1 pageArthur - MakingjosNo ratings yet
- MDP 39015079943414 16 1657038275Document1 pageMDP 39015079943414 16 1657038275josNo ratings yet
- Of Of, .:, - . of Civil, - , - , - . Larry Made - . Age, - , - , - ,, Larry - . - in Foundry - Was - . TreatDocument1 pageOf Of, .:, - . of Civil, - , - , - . Larry Made - . Age, - , - , - ,, Larry - . - in Foundry - Was - . TreatjosNo ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageAjosNo ratings yet
- It But Trivial - That: Its Encouragement To The of ThisDocument1 pageIt But Trivial - That: Its Encouragement To The of ThisjosNo ratings yet
- Harry .:, - ., - , - . Of,, - Prop Mild EdDocument1 pageHarry .:, - ., - , - . Of,, - Prop Mild EdjosNo ratings yet
- Jay - Manufacturing - , ,, - High Of, - Rolls JournalDocument1 pageJay - Manufacturing - , ,, - High Of, - Rolls JournaljosNo ratings yet
- I, I - I Of, Not, - IDocument1 pageI, I - I Of, Not, - IjosNo ratings yet
- Manganese Steel: Ulu G6Document1 pageManganese Steel: Ulu G6josNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Manganese Steel, - of of Of, .Document1 pageBibliography: Manganese Steel, - of of Of, .josNo ratings yet
- Design Multistory Buildings Maxi - of It of - , ConDocument1 pageDesign Multistory Buildings Maxi - of It of - , ConjosNo ratings yet
- Multistory Buildings Will: For That PartitionDocument1 pageMultistory Buildings Will: For That PartitionjosNo ratings yet
- Without Engineer) Without (In - , .Document1 pageWithout Engineer) Without (In - , .josNo ratings yet
- Preface: Carnegie Library 1927Document1 pagePreface: Carnegie Library 1927josNo ratings yet
- Example Applications: of The Nehrp Guidelines For The Seismic Rehabilitation of BuildingsDocument1 pageExample Applications: of The Nehrp Guidelines For The Seismic Rehabilitation of BuildingsjosNo ratings yet
- Welding, - , .) of - Armor Matter (Age 61 - , - ., - . Journal of Iron, - , .Document1 pageWelding, - , .) of - Armor Matter (Age 61 - , - ., - . Journal of Iron, - , .josNo ratings yet
- Multistory BuildingsDocument1 pageMultistory BuildingsjosNo ratings yet
- Design Multistory Buildings: Is InvolvedDocument1 pageDesign Multistory Buildings: Is InvolvedjosNo ratings yet
- Gravity Loads Multistory BuildingsDocument1 pageGravity Loads Multistory BuildingsjosNo ratings yet
- Design Multistory Buildings: Be Applied or More May at The Rate No Reduction As DeterminedDocument1 pageDesign Multistory Buildings: Be Applied or More May at The Rate No Reduction As DeterminedjosNo ratings yet
- AND Multistory Buildings: Floor Stair DesignDocument1 pageAND Multistory Buildings: Floor Stair DesignjosNo ratings yet
- Design Multistory Buildings: (ExceptDocument1 pageDesign Multistory Buildings: (ExceptjosNo ratings yet
- Sesse: Multistory Buildings Concrete Joist ofDocument1 pageSesse: Multistory Buildings Concrete Joist ofjosNo ratings yet
- G11 - ENGPROF - Week 9Document11 pagesG11 - ENGPROF - Week 9Shendy Acosta100% (1)
- Operation and Control Philosophy: PROJ Kurdistan Pumping Station (KPS2)Document21 pagesOperation and Control Philosophy: PROJ Kurdistan Pumping Station (KPS2)Nobar GulajanNo ratings yet
- University of TripoliDocument10 pagesUniversity of TripoliRahaf NasrNo ratings yet
- New - PDS Innova IGS 530 - 2017Document20 pagesNew - PDS Innova IGS 530 - 2017TRUONG HOANG DUCNo ratings yet
- Logistic Regression Assignment - TrainDocument1,145 pagesLogistic Regression Assignment - TrainAnkit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Pathways 4 Listening & Speaking Unit 4 TestDocument8 pagesPathways 4 Listening & Speaking Unit 4 TestaLeKs GaRcíA100% (1)
- CHM556 - Experiment 1 - Isolation of Caffeine From A Tea BagDocument8 pagesCHM556 - Experiment 1 - Isolation of Caffeine From A Tea Bagnabilahdaud93% (45)
- Past Simple WH Questions Word Order Exercise 2Document3 pagesPast Simple WH Questions Word Order Exercise 2karen oteroNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: WarningDocument3 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: Warningمحمد کاشفNo ratings yet
- Sw. Pt. Nawal Kishore Sharma Government P.G. College, Dausa: Applica On IDDocument6 pagesSw. Pt. Nawal Kishore Sharma Government P.G. College, Dausa: Applica On IDSumer SainiNo ratings yet
- 5 Fit Tolerances-Problem SolvingDocument10 pages5 Fit Tolerances-Problem SolvingSHIVANANDA DALEINo ratings yet
- Critical Study of Richard Dawkins, The God DelusionDocument10 pagesCritical Study of Richard Dawkins, The God DelusionJuan Pablo Pardo BarreraNo ratings yet
- ASTM - E1137 - مشخصات دماسنجهای مقاومتی صنعتیDocument7 pagesASTM - E1137 - مشخصات دماسنجهای مقاومتی صنعتیhosein bagheriNo ratings yet
- Awra Amba RJ 300612 EN BDDocument86 pagesAwra Amba RJ 300612 EN BDTop ListorsNo ratings yet
- Appraisal Goals and AttributesDocument3 pagesAppraisal Goals and AttributesRasheed Ahamad0% (1)
- Sony DVR-VX2000 ManualDocument92 pagesSony DVR-VX2000 ManualHenryNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping Services NCII Quarter 3 PDF HousekeepingDocument1 pageHousekeeping Services NCII Quarter 3 PDF HousekeepingSalve RegineNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques NcatDocument191 pagesQuantitative Techniques NcatJeremiah AkonyeNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument6 pagesGlobalizationSanskruti PathakNo ratings yet
- Chemical EtchDocument18 pagesChemical EtchznpfgNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Holiday HomeworkCOMPETENCY BASED 20230519124608767Document56 pagesClass 10 Maths Holiday HomeworkCOMPETENCY BASED 20230519124608767Itz me KARTIKKKNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Heat Transfer in Steelwork Protected and Unprotected SteelworkDocument23 pages2.2 Heat Transfer in Steelwork Protected and Unprotected SteelworkMahbub AlamNo ratings yet
- Esia Report: Sustainable Akkar Wind Farm, LebanonDocument738 pagesEsia Report: Sustainable Akkar Wind Farm, LebanonAnderson Martins Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- ADMN-2-002, Issue 01, Procedure For Personal Hygiene, Employee Facility and HousekeepingDocument4 pagesADMN-2-002, Issue 01, Procedure For Personal Hygiene, Employee Facility and HousekeepingSmsajid WaqasNo ratings yet
- 3.2.5.applying The Normal Curve Concepts in Problem Solving PDFDocument3 pages3.2.5.applying The Normal Curve Concepts in Problem Solving PDFJhasmin Jane LagamayoNo ratings yet
- ICT Basic Types of ComputerDocument7 pagesICT Basic Types of ComputerMomina B KhanNo ratings yet
- PSE PG Structure ModifedDocument61 pagesPSE PG Structure ModifedAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- PAPER (14) - Puucho PDFDocument21 pagesPAPER (14) - Puucho PDFethan tylerNo ratings yet