Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mbridge IGCSE Core and Extended Mathematics 3rd Edition
Uploaded by
christine lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageOriginal Title
Core and Extended Mathematics Glossary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageMbridge IGCSE Core and Extended Mathematics 3rd Edition
Uploaded by
christine leeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Cambridge IGCSE®
Core and Extended
Mathematics Glossary
Term Translation Definition
= = means is equal to. For example, 3 1 4 5 7
≠ ≠ means is not equal to. For example, 3 1 4 ≠ 8
> > means is greater than. For example, 8 > 3 1 4
< < means is less than. For example, 3 1 4 < 8
≥ ≥ means is greater than or equal to. For example, x ≥ 5 means x is any
number greater than or equal to 5
≤ ≤ means is less than or equal to. For example, x ≤ 5 means x is any
number less than or equal to 5
∈ ∈means belongs to.
e ∈S means the element e belongs to the set S
∉ ∉means does NOT belong to.
e ∉S means the element e does not belong to the set S
⊆ ⊆ means is a subset of.
So X ⊆ Y means X is a subset of Y
⊆⁄ ⊆⁄ means is NOT a subset of.
So X ⊆⁄ Y means X is not a subset of Y
⊂ ⊂ means is a proper subset of.
So X ⊂ Y means X is a proper subset of Y
⊄ ⊄ means is NOT a proper subset of.
So X ⊄ Y means X is not a proper subset of Y
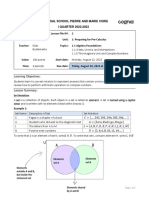
A∩B A ∩ B means all the elements that belong to BOTH set A and set B
A ∩ B denotes the elements that are in the intersection of A and B
on a Venn diagram
A∪B The union of sets A and B, A ∪ B, is all the elements that belong to
EITHER set A OR set B OR both.
ξ The universal set, ξ, for any particular problem is the set which
contains all the possible elements for that problem.
∅ ∅ is the symbol for the empty set. The empty set has no elements
in it.
acute angle An acute angle lies between 0° and 90°.
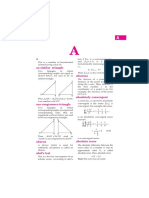
acute angled triangle In an acute angled triangle, all three angles are less than 90°.
adjacent In a right-angled triangle the adjacent is the side which is next to the
angle.
A
θ
B adjacent C
Cambridge IGCSE Core and Extended Mathematics 3rd edition Teacher’s Resource © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2013 1
You might also like
- Logic, Sets, and Proofs: David A. Cox and Catherine C. Mcgeoch Amherst CollegeDocument7 pagesLogic, Sets, and Proofs: David A. Cox and Catherine C. Mcgeoch Amherst CollegePritam GainNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Symbols: Symbol ExplanationDocument26 pagesMathematical Symbols: Symbol ExplanationChris AurelioNo ratings yet
- The Phrase Book: Basic Words and Symbols of Higher MathematicsDocument8 pagesThe Phrase Book: Basic Words and Symbols of Higher MathematicsjernejamNo ratings yet
- Midterm Concept NotesDocument27 pagesMidterm Concept NotesDaryl MardNo ratings yet
- List of Mathematical SymbolsDocument23 pagesList of Mathematical SymbolsCesar RNo ratings yet
- Language, Symbols and ConventionsDocument32 pagesLanguage, Symbols and ConventionsFamily SonzaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbol: Learning OutcomesDocument16 pagesMathematical Language and Symbol: Learning OutcomesAivie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Mathematical Language and Symbolshiro100% (1)
- NotationDocument1 pageNotationFredNo ratings yet
- Section 3.3 Equivalence RelationsDocument13 pagesSection 3.3 Equivalence RelationsThadsanamoorthyKishokumarKumarNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE AND SYMBOLS. (Part 1)Document4 pagesMATHEMATICAL LANGUAGE AND SYMBOLS. (Part 1)Ronaldo RamosNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions and OperationsDocument28 pagesAlgebraic Expressions and OperationsDiana Patricia NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Learning Mathematic With EnglishDocument5 pagesLearning Mathematic With EnglishPratiwyNo ratings yet
- Math SymbolsDocument22 pagesMath SymbolsHoang GiangNo ratings yet
- Math1 Module1Document33 pagesMath1 Module1Karla Charmagne SalivaNo ratings yet
- The Language of MathematicsDocument109 pagesThe Language of MathematicsAl-Vi John CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Logical Statements SolutionsDocument4 pagesWorksheet: Logical Statements SolutionsShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Limits and Sets: Topic 1Document16 pagesLimits and Sets: Topic 1fleminm1No ratings yet
- Direct Proof: Rational NumbersDocument4 pagesDirect Proof: Rational NumbersAbdullah ShahidNo ratings yet
- Compendium: AlgebraDocument16 pagesCompendium: AlgebraAbhijeet GauravNo ratings yet
- Relations: ENSIA 2022Document64 pagesRelations: ENSIA 2022القناة الرسمية للقرآن الكريمNo ratings yet
- M1-4-Mesleki IngilizceDocument22 pagesM1-4-Mesleki IngilizceÖznur CifciNo ratings yet
- Analysis Set TheoryDocument1 pageAnalysis Set Theorymergun919No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet of Mathemtical Notation and TerminologyDocument1 pageCheat Sheet of Mathemtical Notation and TerminologySaharsha BhandariNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols Version2Document4 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols Version2LevysorianoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Notation: Gabriel RobinsDocument11 pagesBasic Concepts and Notation: Gabriel RobinselkamelNo ratings yet
- Mitmw 2Document38 pagesMitmw 2Kien Eisaiah CruzNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 ReviewDocument4 pagesMidterm 1 ReviewJovan WhiteNo ratings yet
- Logic Set TheoryDocument3 pagesLogic Set TheorykateaubreydemavivasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 (Sec A)Document18 pagesLecture 34 (Sec A)Pro SoftwareNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument5 pagesMathematics in Modern WorldvkleintoyNo ratings yet
- Translation:: English Phrases Into Algebraic ExpressionsDocument19 pagesTranslation:: English Phrases Into Algebraic ExpressionsRosen AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols PDFDocument46 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols PDFNove TrapsiNo ratings yet
- M1W1T4 Pas 1.3Document11 pagesM1W1T4 Pas 1.3dexiham591No ratings yet
- Lect 35Document5 pagesLect 35Nguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Basic AlgebraDocument36 pagesBasic AlgebraDrey MaguddayaoNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1 in MMW Ch2 Updated 08272022Document10 pagesLearning Material 1 in MMW Ch2 Updated 08272022John TacordaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Logic: Uha IsnainiDocument43 pagesMathematical Logic: Uha IsnainiAntonNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument48 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsPL05CANO, DRAE P.No ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Set Theory Set: A Set Is Collection of Well Defined ObjectsDocument28 pagesUNIT-2 Set Theory Set: A Set Is Collection of Well Defined ObjectsScar GamingNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language & SymbolsDocument18 pagesMathematical Language & SymbolsClaire Angelie RuayaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument30 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsAl Cris Barro100% (3)
- 1.1 Set and Set OperationsDocument82 pages1.1 Set and Set OperationsRaymart LeysonNo ratings yet
- Logical Symbolism and Sets: Tiko JavakhadzeDocument11 pagesLogical Symbolism and Sets: Tiko JavakhadzeSalo KapanadzeNo ratings yet
- 2nd Chapitre - CompressedDocument13 pages2nd Chapitre - Compressedsoul.elkolliNo ratings yet
- List of Mathematical SymbolsDocument24 pagesList of Mathematical Symbolswork forceNo ratings yet
- Supplement (Set Theory)Document5 pagesSupplement (Set Theory)mac as macNo ratings yet
- 2 - Mathematical Induction & Equivalence RelationsDocument5 pages2 - Mathematical Induction & Equivalence Relationsrahimacamen21No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 11 Algebra NotesDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 11 Algebra NotesEtrans 9No ratings yet
- Algebraic Expression and TermsDocument17 pagesAlgebraic Expression and TermsJommarVocalTagalogNo ratings yet
- Maths DictionaryDocument25 pagesMaths DictionaryManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Eigenvalues and Fuzzy Eigen Vectors For Fuzzy MatrixDocument6 pagesFuzzy Eigenvalues and Fuzzy Eigen Vectors For Fuzzy MatrixarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Math Lesso File 2 (With Exercizes)Document5 pages10th Grade Math Lesso File 2 (With Exercizes)Andrés CuadraNo ratings yet
- Reflexive PropertyDocument3 pagesReflexive PropertyNadine EllingtonNo ratings yet
- Sets and FunctionsDocument12 pagesSets and FunctionsShkidt IsaacNo ratings yet
- Equivalence RelationDocument5 pagesEquivalence RelationElgie LiwagonNo ratings yet
- X X X Y, X / Y ,: Set Theory GrinshpanDocument1 pageX X X Y, X / Y ,: Set Theory GrinshpanBenjamin PhuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.b - Solutions of Higher Order ODE - Part 2-2ADocument37 pagesLecture 1.b - Solutions of Higher Order ODE - Part 2-2AJohn Carlo CortezNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map 9Document14 pagesCurriculum Map 9glemae ramosNo ratings yet
- Algebra TilesDocument56 pagesAlgebra Tilesboostoberoi100% (1)
- Set Cse Ca 1Document13 pagesSet Cse Ca 1Bhumika BiyaniNo ratings yet
- Set-1 Sec-BDocument5 pagesSet-1 Sec-Bapi-19808758No ratings yet
- Module in Number Theory: Table of ContentDocument11 pagesModule in Number Theory: Table of ContentAdriane TingzonNo ratings yet
- 10 Math Imp Ch6 Introduction TrigonometryDocument5 pages10 Math Imp Ch6 Introduction TrigonometryZakiQureshiNo ratings yet
- FA15 CS188 Lecture 08 PL Semantics and Inference - pptx-2Document25 pagesFA15 CS188 Lecture 08 PL Semantics and Inference - pptx-2ateiskaNo ratings yet
- Formulae: Higher Tier: Section CrossDocument15 pagesFormulae: Higher Tier: Section CrosshardsinghNo ratings yet
- A Chebyshev Spectral Collocation Method For SolvingDocument18 pagesA Chebyshev Spectral Collocation Method For SolvingGiovanniCuocoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material - Linear and Quadratic FunctionsDocument3 pagesStrategic Intervention Material - Linear and Quadratic FunctionsApril Gonzales80% (10)
- IGNOU MCA MCS-21 Solved Assignments 2011Document17 pagesIGNOU MCA MCS-21 Solved Assignments 2011Syedkareem_hkgNo ratings yet
- Euclid Biography: Quick FactsDocument2 pagesEuclid Biography: Quick FactsAbhinav Pathak100% (2)
- 0606 MW Otg MS P11Document8 pages0606 MW Otg MS P11Yu Yan ChanNo ratings yet
- Integral of SQRT (Tanx)Document1 pageIntegral of SQRT (Tanx)wyrmczarNo ratings yet
- MFEMD Ch09Document10 pagesMFEMD Ch09Abdel DaaNo ratings yet
- 07a80809 OperationsresearchDocument11 pages07a80809 OperationsresearchSharanya ThirichinapalliNo ratings yet
- Cherry Rose T. Malgapo: Probability and StatisticsDocument26 pagesCherry Rose T. Malgapo: Probability and StatisticscherryNo ratings yet
- Binary:: Base 2 and Base 10 LearnDocument12 pagesBinary:: Base 2 and Base 10 LearnFitzuan FitriNo ratings yet
- Scilab/C2/Getting-Started/English: From Script - Spoken-TutorialDocument6 pagesScilab/C2/Getting-Started/English: From Script - Spoken-Tutorialds vidhyaNo ratings yet
- DSPA Solution Manual Chap 5 - KK ParhiDocument7 pagesDSPA Solution Manual Chap 5 - KK ParhiNESEGANo ratings yet
- Grigori PerelmanDocument9 pagesGrigori PerelmanMarios DarvirasNo ratings yet
- Systematic Circuit Analysis: Nodal Analysis Chapter 4 Section 1Document55 pagesSystematic Circuit Analysis: Nodal Analysis Chapter 4 Section 1Marvin - Soriente VILLALUNANo ratings yet
- Computer Center CaseDocument13 pagesComputer Center CaseNguyễn LâmNo ratings yet
- PWNSAT 2023 SyllabusDocument5 pagesPWNSAT 2023 SyllabusBaby SinghNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Fourth Form Unit PlanDocument5 pagesMathematics Fourth Form Unit PlanChet AckNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam - Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesPrelim Exam - Data Analysisgellert grindelwaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 Introduction: STAT3907 Linear Models and ForecastingDocument14 pagesChapter 0 Introduction: STAT3907 Linear Models and ForecastingKenneth WongNo ratings yet
- Math and Music Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMath and Music Lesson Planapi-258333563No ratings yet