Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Backgrounder: Nature-Based Solutions or The Ecosystem Approach?
Uploaded by
Aliya RahmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Backgrounder: Nature-Based Solutions or The Ecosystem Approach?
Uploaded by
Aliya RahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Backgrounder
Biodiversity
Keywords:
Nature-based solutions, ecosystems,
biodiversity and conservation, UN
Convention on Biological Diversity
(CBD)
Issue date
May 2021
KEY TERMS
Ecosystem approach: The
Convention on Biological Diversity
Potato Park, Peru. Credit: Khanh Tran-Thanh, IIED
describes the this as ‘a strategy for
the integrated management of land,
water and living resources that
promotes conservation and
sustainable use in an equitable way
… It recognizes that humans, with
their cultural diversity, are an integral
component of many ecosystems.’3
Nature-based solutions (NbS):
defined by the International Union for
Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as
‘actions to protect, sustainably
manage, and restore natural or
modified ecosystems, that address
Nature-based solutions or
societal challenges effectively and
adaptively, simultaneously providing
human well-being and biodiversity
the ecosystem approach?
benefits.’4
KEY SPACES
• Convention on Biological Diversity
A debate over terminology risks distracting (CBD) negotiations on the
attention from the key issues under discussion in post-2020 Global Biodiversity
Framework (GBF)
the post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework. • These will take place in the run up to
Here, we gauge how far the two concepts differ the 15th meeting of the Conference
of the Parties to the Convention on
Biological Diversity (CBD COP15),
The targets of the emerging post-2020 Framework and threatens to keep doing so. in October 2021.
Global Biodiversity Framework include But how different are they, and how can we
multiple references to the application of move on? WHY IS THIS
‘nature-based solutions’ (NbS). But some IMPORTANT?
Indigenous Peoples and local communities Common ground and
In February 2020, the second
have expressed concern at the use of this incompatibilities meeting of the Open-ended Working
term (see ‘Southern perspectives’, overleaf), The ecosystem approach’s core aim is
as have a number of negotiators. Negotiators Group on the post-2020 Global
the conservation of ecosystem structure Biodiversity Framework spent
point out that the Convention on Biological and functioning, in order to maintain
Diversity has already endorsed the significant time discussing whether
ecosystem services. To support this, the the term ‘nature-based solutions’
‘ecosystem approach’, including a full set of 12 interlinked principles1 underpinning the
principles and even guidance for application. works for everyone. As negotiations
ecosystem approach emphasise ‘systems intensify ahead of CBD COP15 in
Given this, the term NbS is seen as either thinking’; for example, understanding that
competing with, or potentially replacing, an October 2021, it is critical that
ecosystem management must consider the debates over terminology do not
agreed concept. Contention over these two multiple, complex interactions that occur
ideas has already taken up vital negotiation derail the number one priority:
within an area as well as between it and agreeing an ambitious framework
time in the discussions on the post-2020 adjacent ecosystems.
Contact and feedback: Dilys Roe dilys.roe@iied.org @iied www.facebook.com/theIIED
IIED Backgrounder Nature-based solutions or the ecosystem approach?
The principles also highlight the need to draw ensuring resilience and minimising any that can both halt biodiversity loss
on all forms of science and knowledge — negative impacts on biodiversity. and deliver for human wellbeing.
including Indigenous and local knowledge
Target 10. By 2030, ensure that nature-
— and for all sectors of society to participate.
Significantly, the principles advocate based solutions and the ecosystem approach SOUTHERN
decentralisation of management to the contribute to the regulation of air quality, PERSPECTIVES
hazards and extreme events, and the quality
lowest appropriate level. Representatives of Indigenous
and quantity of water for at least [XXX
Recent research2 suggests that the million] people. Peoples (IPs) have expressed
conceptual framework for NbS actually concern that ‘nature-based solutions’
As both targets go beyond biodiversity and (NbS) is another western term that
emerged from the ecosystem approach.
ecosystem conservation — aiming to separates people and nature. The
Many of the eight criteria in IUCN’s recently
contribute to other social challenges — it idea that nature delivers solutions to
published Global Standard for Nature-Based
seems appropriate that they emphasise NbS. people implies a one-way
Solutions cover similar ground to the
It is noteworthy, however, that they also refer relationship. This contradicts
principles of the ecosystem approach. But
to the agreed ecosystem approach. Indigenous worldviews, in which
there are differences. For example, NbS is
perhaps more ambitious in its focus on However, it will be important to ensure that people and nature — or biodiversity
mainstreaming and policy coherence as well some of the key principles of the ecosystem and culture — are inextricably linked
as on practical implementation, whereas the approach, which are weaker in the NbS and inter-dependent. The relationship
ecosystem approach emphasises framework, are adequately reflected in the is reciprocal, not linear. IPs worry that
decentralisation, local involvement and GBF — particularly those associated with as the concept of NbS does not
traditional knowledge. respecting and applying the rights and reflect their worldviews, neither will
knowledge of Indigenous Peoples and local NbS interventions.
The biggest difference, however, is that NbS
communities, reflecting their deep respect for In the Peruvian Andes, for example,
looks beyond biodiversity conservation to
nature. To achieve this, additional text to the concept of ‘ayllu’ (which requires
address other societal challenges, including
include and highlight the application of balance between nature and people)
climate change and food security. In fact, the
traditional concepts and knowledge could be is very much alive. But ayllu is
Global Standard stipulates that ‘NbS must
inserted into the NbS targets, and should also undermined by national policies and
deliver tangible and substantive benefits to
appear in the enabling conditions and projects, including ecosystem-based
human wellbeing.’
implementation support mechanisms. adaptation and others originating
Effect on global biodiversity from the environment sector, because
Looking ahead their focus on western science
ambition
The successful negotiation of a strong and provides little space for traditional
The term ‘nature-based solutions’ appears in ambitious post-2020 Global Biodiversity knowledge.5 Forest Peoples
two targets in the draft post-2020 Global Programme points to further
Framework is a critical first step to improving
Biodiversity Framework (GBF): concerns including the need for
progress on tackling biodiversity loss over the
Target 7. By 2030, increase contributions to next decade and beyond. Arguments over rights-based approaches to NbS.6
climate change mitigation adaption and exact terms risk distracting attention from the
disaster risk reduction from nature-based real purpose — ensuring a socially just,
solutions and ecosystems-based approaches, climate-neutral, nature-positive world. If the
ethos of the ecosystem approach — including
1
www.cbd.int/ecosystem/principles.shtml its attention to Indigenous and local knowledge
2
Cohen-Shacham, E, Andrade, A, Dalton, J, Dudley, N, and practice — is reflected in the Framework
Jones, M, Kumar, C, Maginnis, S, Maynard, S, goals, targets and enabling conditions, then
Nelson, CR, Renaud, FG, Welling, R and Walters, G debate over particular terminology used should
(2019) Core principles for successfully
implementing and upscaling Nature-based not be a reason for us to fail.
Solutions. Environ Sci Policy 98, 20–29.
3
www.cbd.int/ecosystem/description.shtml
4
Cohen-Shacham, E, Walters, G, Janzen, C and
Maginnis, S (2016) Nature-based Solutions to
address global societal challenges. IUCN, Gland,
Switzerland. Knowledge
5
Swiderska, K, Argumedo, A and Pimbert, M (2020) Products
Biocultural heritage territories: key to halting
biodiversity loss. IIED, London. pubs.iied.
org/17760iied The International Institute for Environment
and Development (IIED) promotes
6
Tugendhat, H (2021) Re-thinking nature-based
sustainable development, linking local
solutions: seeking transformative change through
culture and rights: A briefing for the post-2020 priorities to global challenges. We support
Global Biodiversity Framework. Forest Peoples some of the world’s most vulnerable people
Programme. to strengthen their voice in decision making.
FIND OUT MORE
Our work on the post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework is being undertaken as part of IIED’s ‘super year’ advocacy strategy. Find out more
about our work on the CBD and the post-2020 Framework at www.iied.org/supporting-nature-positive-equitable-global-biodiversity-framework
IIED Third Floor, 235 High Holborn, London WC1V 7DN, UK IIED publications may be shared and republished in accordance with the Creative
T: +44 (0)20 3463 7399 | www.iied.org Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License
(CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). Get more information via www.iied.org/Creative-Commons
You might also like
- Land Use and Spatial Planning: Enabling Sustainable Management of Land ResourcesFrom EverandLand Use and Spatial Planning: Enabling Sustainable Management of Land ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Why Mangroves Matter: Ecological and Socio-Economic AspectsDocument23 pagesWhy Mangroves Matter: Ecological and Socio-Economic AspectsNguwruw Chungpha MoyonNo ratings yet
- 2013.locatelli al2013.SynergTradeOffEcosystemServCostaRicaDocument10 pages2013.locatelli al2013.SynergTradeOffEcosystemServCostaRicaRM MiauNo ratings yet
- 197 569 1 SMDocument9 pages197 569 1 SMNuyul FaizahNo ratings yet
- Economic Value Estimation of Mangrove Ecosystems in IndonesiaDocument4 pagesEconomic Value Estimation of Mangrove Ecosystems in IndonesiaAbdulGaffarAgusNo ratings yet
- E1 EthicsDocument1 pageE1 Ethicswindarta.rezkiNo ratings yet
- Commodification of Natural Resources and PDFDocument10 pagesCommodification of Natural Resources and PDFKannyMucitaNo ratings yet
- Participatory Wildlife Conservation Initiatives in Nepal: January 2005Document8 pagesParticipatory Wildlife Conservation Initiatives in Nepal: January 2005Sapkota DiwakarNo ratings yet
- DeFries Nagendra2017 EcosystemManagement WickednessDocument7 pagesDeFries Nagendra2017 EcosystemManagement WickednessJefferson SalasNo ratings yet
- All Environment Organisations & ConventionsDocument11 pagesAll Environment Organisations & ConventionsappuNo ratings yet
- Environmental EventsDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Eventschiny camposanoNo ratings yet
- Forest Wellness Tourism Destination Branding For Supporting Disaster Mitigation - A Case of Batur UNESCO Global Geopark, BaliDocument13 pagesForest Wellness Tourism Destination Branding For Supporting Disaster Mitigation - A Case of Batur UNESCO Global Geopark, BalisibuyungunyuNo ratings yet
- 003 Prosiding Internasional - MangroveDocument7 pages003 Prosiding Internasional - MangroveDAUDNo ratings yet
- The NIPAS Act of 1992: Date PublishedDocument3 pagesThe NIPAS Act of 1992: Date PublishednikoNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Mangrove Pengelolaan Berkelanjutan: Kawasan Ekowisata Sumberdaya PesisirDocument7 pagesPengembangan Mangrove Pengelolaan Berkelanjutan: Kawasan Ekowisata Sumberdaya PesisirRandy NovirsaNo ratings yet
- Answers For 3.4 THE CHARTS NEED WORKDocument33 pagesAnswers For 3.4 THE CHARTS NEED WORKProsper NimleyNo ratings yet
- Analisis Vegetasi Tumbuhan Pantai Pada Kawasan Wisata Pasir Jambak, Kota PadangDocument11 pagesAnalisis Vegetasi Tumbuhan Pantai Pada Kawasan Wisata Pasir Jambak, Kota PadangMuhammad FadliNo ratings yet
- ResMngmt Week#4 1Document19 pagesResMngmt Week#4 1Iman JuniantoNo ratings yet
- 3594 EbDocument15 pages3594 EbManuel André RashtaNo ratings yet
- 17725IIEDDocument4 pages17725IIEDDea DharaNo ratings yet
- Biosphere - GuidelinesDocument35 pagesBiosphere - GuidelinesHarsh pooniaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2212041621000164 Main 1Document24 pages1 s2.0 S2212041621000164 Main 1DidiherChacon ChaverriNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Service Values For Mangroves in Southeast Asia A - 2012 - EcosystemDocument8 pagesEcosystem Service Values For Mangroves in Southeast Asia A - 2012 - Ecosystempisod77No ratings yet
- 2764 FullDocument6 pages2764 FullEra MeizaNo ratings yet
- None 133039b2Document14 pagesNone 133039b2Jims GurkhaNo ratings yet
- Nunes Triniddad Talk FINALDocument46 pagesNunes Triniddad Talk FINALdkumarlabh612No ratings yet
- Nopper Et Al 2017 One Forest Is Not Like Another The Contribution of Community Based Natural Resource Management ToDocument9 pagesNopper Et Al 2017 One Forest Is Not Like Another The Contribution of Community Based Natural Resource Management Toali hidayatNo ratings yet
- 781 3703 1 PBDocument12 pages781 3703 1 PBAgus NurrofikNo ratings yet
- Mangrovekarangsewu JMRT PDFDocument9 pagesMangrovekarangsewu JMRT PDFboruto uzumakiNo ratings yet
- 656-Article Text-2021-1-10-20231231 - 2Document18 pages656-Article Text-2021-1-10-20231231 - 2Ahmad MasykurNo ratings yet
- East Kalimantan 4Document15 pagesEast Kalimantan 4RicoNo ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Hutan Dan Lingkungan Oleh Masyarakat Baduy Di BantenDocument7 pagesPemanfaatan Hutan Dan Lingkungan Oleh Masyarakat Baduy Di BantenAzi Gunawan Arafiana PutraNo ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Hutan Dan Lingkungan Oleh Masyarakat Baduy Di BantenDocument7 pagesPemanfaatan Hutan Dan Lingkungan Oleh Masyarakat Baduy Di BantenDella AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Mangrove Rehabilitation Program in Sitio Panguig and Sitio Panguig, Brgy. Tamisan, City of Mati, Davao OrientalDocument67 pagesAssessment of Mangrove Rehabilitation Program in Sitio Panguig and Sitio Panguig, Brgy. Tamisan, City of Mati, Davao OrientalSafiyah Francisco AntingNo ratings yet
- Development of Mangrove Eco-Literacy Storytelling As Environmental Education Learning Media For Coastal Children in BantenDocument15 pagesDevelopment of Mangrove Eco-Literacy Storytelling As Environmental Education Learning Media For Coastal Children in BantenNoviUtamiRosyidNo ratings yet
- Integrating Ecosystem Services in Nature Conservation For ColombiaDocument13 pagesIntegrating Ecosystem Services in Nature Conservation For ColombiaALEXANDRA GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Valuasi Ekonomi Ekosistem Hutan MangroveDocument16 pagesValuasi Ekonomi Ekosistem Hutan MangroveYonarizaGuchianoNo ratings yet
- Minat Konsumen Dan Strategi Pengembangan EkowisataDocument7 pagesMinat Konsumen Dan Strategi Pengembangan Ekowisatarochadi kristiningrumNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2213078020300037 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2213078020300037 MainGeraldin GarayNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Faktor Biotik Dan Abiotik Terhadap Keanekaragaman Makrobentos Di Hutan Mangrove Kabupaten Lombok BaratDocument10 pagesHubungan Faktor Biotik Dan Abiotik Terhadap Keanekaragaman Makrobentos Di Hutan Mangrove Kabupaten Lombok BaratHadijahNo ratings yet
- Forest Ecology and Management: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesForest Ecology and Management: SciencedirectLeandro RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Tonin 2018Document12 pagesTonin 2018Panda PindiNo ratings yet
- DLI Sinta 3Document8 pagesDLI Sinta 3Dita AgustianNo ratings yet
- MSJTFS2019 433-442Document11 pagesMSJTFS2019 433-442Vivencia PabilonaNo ratings yet
- 21597-Article Text-84120-1-10-20190813Document15 pages21597-Article Text-84120-1-10-20190813Rony AkbarNo ratings yet
- Plant ArchivesDocument8 pagesPlant ArchivesFauzulimronNo ratings yet
- BIOSPHEREDocument7 pagesBIOSPHERESyed SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem-Based Adaptation and Climate Risk InsuranceDocument55 pagesEcosystem-Based Adaptation and Climate Risk InsuranceJobert AlegreNo ratings yet
- Div Class Title From Hope To Crisis and Back Again A Critical History of The Global CBNRM Narrative DivDocument11 pagesDiv Class Title From Hope To Crisis and Back Again A Critical History of The Global CBNRM Narrative DivPavithranNo ratings yet
- Landscape and Urban Planning: Jie Su, Alexandros GasparatosDocument15 pagesLandscape and Urban Planning: Jie Su, Alexandros GasparatosMaria Claudia VergaraNo ratings yet
- Learning With Nature (LWN) Education Project - Ap20 FDocument2 pagesLearning With Nature (LWN) Education Project - Ap20 FMariam BakerallyNo ratings yet
- Rahman Et Al-2018-Wetlands Ecology and ManagementDocument18 pagesRahman Et Al-2018-Wetlands Ecology and ManagementimtiazshahedNo ratings yet
- Genetic Frontier For Conservation - Synth Biology and Biodi ConservDocument184 pagesGenetic Frontier For Conservation - Synth Biology and Biodi ConservBarnaudNo ratings yet
- RecreationDocument11 pagesRecreationrkmontreal448No ratings yet
- Rosa & Marques 2022Document9 pagesRosa & Marques 2022stella.mdlrNo ratings yet
- Le Etal 2017 Incorporating Ecosystem Services Into Environmental ManagementDocument18 pagesLe Etal 2017 Incorporating Ecosystem Services Into Environmental ManagementNaomy ChristianiNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Terhadap Adopsi Inovasi Agroforestri Oleh Petani Program Perhutanan SosialDocument10 pagesTinjauan Terhadap Adopsi Inovasi Agroforestri Oleh Petani Program Perhutanan Sosialmuhammad fikriyaNo ratings yet
- What-Counts Final Web 0Document10 pagesWhat-Counts Final Web 0Alicia GordonNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Mangrove Menggunakan Model Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (Ndvi) : Studi Kasus Di Halmahera Utara, IndonesiaDocument22 pagesMonitoring Mangrove Menggunakan Model Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (Ndvi) : Studi Kasus Di Halmahera Utara, IndonesiaPriyadi Dwi SantosoNo ratings yet
- Portner O. Et Al 2023 Overcoming The Coupled Climate and BiodiversityDocument13 pagesPortner O. Et Al 2023 Overcoming The Coupled Climate and BiodiversityPascal Girot PignotNo ratings yet
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Document35 pagesGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)
- UniversityPhysicsVolume2 WEB 5eNhMSaDocument805 pagesUniversityPhysicsVolume2 WEB 5eNhMSaTrong Nhan Do100% (1)
- Physics WEB PDFDocument850 pagesPhysics WEB PDFKiron Sheiq100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions Unit 4 PhysicsDocument175 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Unit 4 PhysicsAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision PDFDocument129 pagesChemistry Revision PDFKamal MG KhalidNo ratings yet
- UniversityPhysicsVolume3 WEBDocument607 pagesUniversityPhysicsVolume3 WEBqwe1 ds2100% (2)
- Whose Debt Is ItDocument32 pagesWhose Debt Is ItSimranNo ratings yet
- Gender and Intersectionality in Action Research: Taking Stock, Learning Lessons and Acting On OpportunitiesDocument2 pagesGender and Intersectionality in Action Research: Taking Stock, Learning Lessons and Acting On OpportunitiesAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- BR Fing: Planning A Green and Resilient COVID-19 Recovery in The GambiaDocument4 pagesBR Fing: Planning A Green and Resilient COVID-19 Recovery in The GambiaAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- BR Fing: Sustainable Financing of The Gambia's Development in A COVID-19 EraDocument4 pagesBR Fing: Sustainable Financing of The Gambia's Development in A COVID-19 EraAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Backgrounder: Transformative Urban Recovery From COVID-19Document2 pagesBackgrounder: Transformative Urban Recovery From COVID-19Aliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2.24 Shapes of Molecules: Be CL CLDocument9 pages2.24 Shapes of Molecules: Be CL CLPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- BR Fing: New Biodiversity Framework Can Learn From Climate Change ExperienceDocument4 pagesBR Fing: New Biodiversity Framework Can Learn From Climate Change ExperienceAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Better Cities After COVID-19: Transformative Urban Recovery in The Global SouthDocument28 pagesBetter Cities After COVID-19: Transformative Urban Recovery in The Global SouthAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
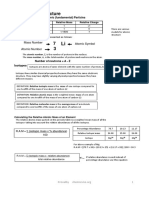
- 2.1.1 Atomic Structure: Atomic Symbol Mass NumberDocument4 pages2.1.1 Atomic Structure: Atomic Symbol Mass NumberAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Implementing The Paris Agreement: LDC Gaps and Needs in Greenhouse Gas Inventory ReportingDocument30 pagesImplementing The Paris Agreement: LDC Gaps and Needs in Greenhouse Gas Inventory ReportingAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Strengthening The Foundational Elements of The Post-2020 Global Biodiversity FrameworkDocument19 pagesStrengthening The Foundational Elements of The Post-2020 Global Biodiversity FrameworkAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 1 5 RedoxDocument2 pages2 1 5 RedoxAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pages2 2 2 Bonding and StructureAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 Halogens: Trend in Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument2 pages3.1.3 Halogens: Trend in Melting Point and Boiling PointAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2.1.4 Acids: Bases and AlkalisDocument4 pages2.1.4 Acids: Bases and AlkalisAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
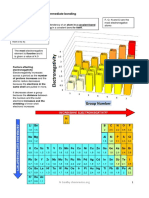
- 2 25 Intermediate BondingDocument6 pages2 25 Intermediate BondingAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Amount of Substance: Molar Gas Volume (Gas Volume Per Mole, Units DMDocument12 pages2.1.3 Amount of Substance: Molar Gas Volume (Gas Volume Per Mole, Units DMAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 Halogens: Trend in Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument2 pages3.1.3 Halogens: Trend in Melting Point and Boiling PointAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 27 Structure of Solid Crystals1Document9 pages2 27 Structure of Solid Crystals1Aliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 26 Intermolecular BondingDocument10 pages2 26 Intermolecular BondingAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding: Positive Metal Ions and The Delocalised ElectronsDocument4 pagesMetallic Bonding: Positive Metal Ions and The Delocalised ElectronsSunnyNo ratings yet
- 20 Cie Nitrogen CompoundsDocument7 pages20 Cie Nitrogen CompoundstrinhcloverNo ratings yet
- 22 Cie Analytical TechniquesDocument11 pages22 Cie Analytical TechniquesAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Name: Anjorin Adewale Olusegun MATRIC NUMBER: 190312005 Department: Geography Education Course Code: Gry122 Purpose: AssignmentDocument9 pagesName: Anjorin Adewale Olusegun MATRIC NUMBER: 190312005 Department: Geography Education Course Code: Gry122 Purpose: AssignmentAnjorin AdewaleNo ratings yet
- Soil MCQ Wihtout AnswerDocument21 pagesSoil MCQ Wihtout AnswerGopi SelvarajNo ratings yet
- LandscapeDocument13 pagesLandscapetaapsiiiNo ratings yet
- Examen Anglais Science Humaines 2022 Session Normale SujetDocument6 pagesExamen Anglais Science Humaines 2022 Session Normale Sujetitsmeselenophile xNo ratings yet
- IWRM Training ManualDocument245 pagesIWRM Training ManualsoendjajaNo ratings yet
- STP Report PDFDocument128 pagesSTP Report PDFRaviIdhayachanderNo ratings yet
- Taiga by John ReyDocument20 pagesTaiga by John ReyNiña AmatoNo ratings yet
- Practice Passage For Class PDFDocument11 pagesPractice Passage For Class PDFKumer ShinfaNo ratings yet
- Roadside LandscapeDocument10 pagesRoadside Landscapemedha mhalaskar100% (2)
- GHG Emission by Agricultural Sector.Document14 pagesGHG Emission by Agricultural Sector.Venkatagiri K SNo ratings yet
- RC 001Document207 pagesRC 001axlmartinoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document22 pagesModule 3Kurt Neo SambileNo ratings yet
- NEHADocument24 pagesNEHAAbhishek VenomNo ratings yet
- ESTPL Profile 2017 V5Document20 pagesESTPL Profile 2017 V5ENVICARENo ratings yet
- Rana Etal 2022 GlobalMagnitudeFrequencyStatisticsFailuresDocument26 pagesRana Etal 2022 GlobalMagnitudeFrequencyStatisticsFailuresHelvecioNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument2 pagesWater PollutionT NguyênNo ratings yet
- Discussion: Know ItDocument5 pagesDiscussion: Know ItDivine Nicole QuibrantosNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Final Project Report (Md. Nazmul Haque, Roll-1295)Document96 pagesB.Sc. Final Project Report (Md. Nazmul Haque, Roll-1295)nazmul_juNo ratings yet
- W-20 Hydrogeological Survey and Assessment of Selected Areas in Somaliland and Puntland PDFDocument288 pagesW-20 Hydrogeological Survey and Assessment of Selected Areas in Somaliland and Puntland PDFHamse HusseinNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument11 pagesEcosystemSunil 2doNo ratings yet
- Kajima's Three PolicyDocument2 pagesKajima's Three PolicyBe Seang SeNo ratings yet
- Form Discussion 1 Problem Based Learning Faculty:FEB Class:ICB-A Group:HG-01Document2 pagesForm Discussion 1 Problem Based Learning Faculty:FEB Class:ICB-A Group:HG-01RadityaNo ratings yet
- EIA EMP of MJDocument234 pagesEIA EMP of MJagarwal.rmNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-Trends & Issues in SSDocument3 pagesChap 1-Trends & Issues in SSMicheleNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF The Environment and You 3rd Edition by Norm Christensen PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF The Environment and You 3rd Edition by Norm Christensen PDFapril.hooks896100% (37)
- 2006 OHCRSCReportfinalDocument141 pages2006 OHCRSCReportfinaluncleadolphNo ratings yet
- G12 Ucsp Q2 Module-6Document16 pagesG12 Ucsp Q2 Module-6Daniel MadagascarNo ratings yet
- TLE-Agri Crop Production Three: Learning Area Grade Level Seven/Eight Quarter DateDocument5 pagesTLE-Agri Crop Production Three: Learning Area Grade Level Seven/Eight Quarter DateÁthymosNo ratings yet
- Final White PaperDocument8 pagesFinal White Paperapi-610470569No ratings yet
- Global Warming CollageDocument1 pageGlobal Warming CollageSiddharth ShankarNo ratings yet