Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Present Perfect Tense
Uploaded by
Andrea SaldañaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Present Perfect Tense
Uploaded by
Andrea SaldañaCopyright:
Available Formats
Present Perfect Tense
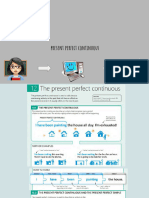
The present perfect tense refers to an action or state that either occurred at an
indefinite time in the past (e.g., we have talked before) or began in the past and
continued to the present time (e.g., he has grown impatient over the last hour).
This tense is formed by: Subject + have/has + the past participle of the main
verb.
The construction of this verb tense is straightforward. The first element is have or
has, depending on the subject the verb is conjugated with. The second element is
the past participle of the verb, which is usually formed by adding -ed or -d to the
verb’s root (e.g., walked, cleaned, typed, jumped, laughed, sautéed) although
English does have quite a few verbs that have irregular past participles (e.g., done,
said, gone, known, won, thought, felt, eaten).
Use of Present Perfect
▪ puts emphasis on the result
Example: She has written five letters.
▪ action that is still going on
Example: School has not started yet.
▪ Action that stopped recently
Example: She has cooked dinner.
▪ finished action that has an influence on the present
Example: I have lost my key.
▪ action that has taken place once, never or several times before the
moment of speaking
Example: I have never been to Australia.
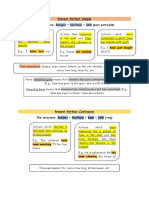
Form of Present Perfect
Positive Negative Question
I / you / we / the I have spoken. I have not spoken. Have I spoken?
y
he / she / it He has spoken. He has not spoken. Has he spoken?
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Bahsa Inggris TensesDocument15 pagesBahsa Inggris TensesNaufal RafiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument9 pagesPresent Perfect TenseDost JanNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveKiara Fajardo matusNo ratings yet
- Lesson - TenseDocument31 pagesLesson - Tenseneel_103No ratings yet
- FULL GUIDE - Present Perfect Passive (2020)Document11 pagesFULL GUIDE - Present Perfect Passive (2020)Mary JerilNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH BAHASA INGGIRS - CopyDocument19 pagesMAKALAH BAHASA INGGIRS - CopyFarhan GustamaNo ratings yet
- Basic English: 1. The Present SimpleDocument11 pagesBasic English: 1. The Present SimpleRaina FemmeNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: The Tense of A Verb Tells You When A Person Did Something or When Something Existed or Happened.Document7 pagesObjectives:: The Tense of A Verb Tells You When A Person Did Something or When Something Existed or Happened.deidreanne pataweNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense: Definition, Rules and Useful ExamplesDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Tense: Definition, Rules and Useful ExamplesAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense: Have or Has, Depending On The Subject The Verb Is Conjugated With. TheDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect Tense: Have or Has, Depending On The Subject The Verb Is Conjugated With. TheThairones SantosNo ratings yet
- Grammar Rule - 8 - Verb Tenses - Present TenseDocument3 pagesGrammar Rule - 8 - Verb Tenses - Present TenseMlles HoneyNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR 4 - Present Perfect Tense - Parte 1Document4 pagesGRAMMAR 4 - Present Perfect Tense - Parte 1Gonzalo Díaz-LetelierNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandoutDocument10 pagesGrammar Handoutstonegrave68No ratings yet
- I Finished My Homework Last Night. I Traveled To Spain in 1985. I Got Up at Seven This MorningDocument11 pagesI Finished My Homework Last Night. I Traveled To Spain in 1985. I Got Up at Seven This MorningjahazielbdNo ratings yet
- Handout in Verb TensesDocument5 pagesHandout in Verb TensesZarah CaloNo ratings yet
- Inglês 10ºanoDocument5 pagesInglês 10ºanoDANIELA TEIXEIRANo ratings yet
- FULL GUIDE - Present Perfect Passive (2020)Document11 pagesFULL GUIDE - Present Perfect Passive (2020)Melany OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Exposición Sobre Los Tiempos VerbalesDocument13 pagesExposición Sobre Los Tiempos VerbaleselisannamartinezNo ratings yet
- Students' Book SCPSCDocument19 pagesStudents' Book SCPSCmdemadulislam41No ratings yet
- What Is A Verb TenseDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Verb TenseArchie BermoyNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple X ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Simple X ContinuousMaria MouraNo ratings yet
- Review of English TensesDocument8 pagesReview of English TensesSyifaa' NajibNo ratings yet
- Seldom For This Company.: Simple Present TenseDocument2 pagesSeldom For This Company.: Simple Present TenseLailatul Rohma HadiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Simple Present Tense: Subject + Verb 1 (Base/Present Form)Document4 pages1 - Simple Present Tense: Subject + Verb 1 (Base/Present Form)Ria RianaNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument6 pagesVerb TensesnornNo ratings yet
- Present Progressive TenseDocument5 pagesPresent Progressive TenseObaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument19 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousValNo ratings yet
- Guía de Estudio InglésDocument8 pagesGuía de Estudio Ingléspauc27mNo ratings yet
- FCE - Grammar Lesson 1Document3 pagesFCE - Grammar Lesson 1NORMA ZOGHEIBNo ratings yet
- Self-Study GuideDocument4 pagesSelf-Study GuideALex Ruiz SandovaalNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Written By: Faris Arifiansyah Class: Xi TKJ-B School: SMKN 1 CimahiDocument11 pagesEnglish Tenses: Written By: Faris Arifiansyah Class: Xi TKJ-B School: SMKN 1 CimahiFaris ArifiansyahNo ratings yet
- Wolfgang Admired The Way The Light Glinted Off His Silver MedalDocument12 pagesWolfgang Admired The Way The Light Glinted Off His Silver MedalEjona NuhiuNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple, Present Perfect ContDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Simple, Present Perfect ContNik RashaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Tenses ReportDocument13 pagesGrammar Tenses ReportAlberto Emiliano Montoya OlivoNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument24 pagesPresent Tensearyasaputra7333No ratings yet
- Catholic University of Mozambique: Vidalmiro Da Alzira AdolfoDocument4 pagesCatholic University of Mozambique: Vidalmiro Da Alzira AdolfoVidal Miro AdolfoNo ratings yet
- 5 Pertemuan VDocument11 pages5 Pertemuan VNumpy PandasNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect TenseFederico Effendy Sañz100% (1)
- Simple Present: InglêsDocument4 pagesSimple Present: Inglêsjurgute2000No ratings yet
- English Homework Name: Course: Date:: Structure Present PerfectDocument4 pagesEnglish Homework Name: Course: Date:: Structure Present PerfectJuanchoNo ratings yet
- Presentation EnglishDocument49 pagesPresentation EnglishribasdNo ratings yet
- Traditiile Romei AnticeDocument13 pagesTraditiile Romei AnticeAnonymous XsOfDozHauNo ratings yet
- What Is The Present Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Present Perfect TenseGareth JoseNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple TheoryDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect Simple TheoryÁngela Naranjo GómezNo ratings yet
- A Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilDocument77 pagesA Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilSofia RaheelNo ratings yet
- Support Handout For EnglishDocument20 pagesSupport Handout For EnglishLuis Julio Carlos PiresNo ratings yet
- Catatan:: VERB) - Perfect Tense Menggunakan VERB 3Document3 pagesCatatan:: VERB) - Perfect Tense Menggunakan VERB 3Rezky SyabaniNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument31 pagesTensesVanshNo ratings yet
- BSN1 F - Eng100 Group2Document31 pagesBSN1 F - Eng100 Group2Jerreca DasasNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument20 pagesConditional SentencesBelinha FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses PresentationDocument14 pagesBasic Tenses PresentationDuvan JadyNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishAntoaneta StancuNo ratings yet
- Principal Parts and Tenses of The VerbsDocument35 pagesPrincipal Parts and Tenses of The Verbs1900248No ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument2 pagesPresent Perfectapi-296199660No ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouiseNo ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouiseNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument12 pagesPresent Perfectleonor marcelaNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument4 pagesPresent TenseAnggun GrechiaNo ratings yet
- Cours Anglais Général 01Document17 pagesCours Anglais Général 01AmoyeNo ratings yet