Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roger's Report - Production Guide For Calopo
Uploaded by
Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roger's Report - Production Guide For Calopo
Uploaded by
Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.Copyright:
Available Formats
I.
AGRONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Calopo
(Calopogonium mucunoides
Desv.) is a vigorous, hairy
annual or short-lived
perennial trailing legume. It
can reach several meters in
length and form a dense,
tangled mass of foliage, 30-
50 cm deep. It is an annual
creeper of 0:3-0.5 m height.
Stem is succulent, covered with long brown hairs. Its lower part
becomes creeper while upper part turns to twiner. The leaves are up to
16 cm long and trifoliate. The hairy leaflets are 4-10 cm long x 2-5 cm
broad, ovate to elliptical. The inflorescence is a slender hairy raceme
that may be up to 20 cm long and bears 2 to 12 blue or purple small
flowers. The pod is hairy, yellowish-brown. 4-5 cm long. It contains 4-8
seeds. There are 73,000 seeds in 1 kg.
Calopo is mainly used as cover crop, alone or in mixture with
other legumes, especially in rubber, oil palm or in young forest
Submitted by: plantations. Calopo is a pioneer species: it provides soil protection
ROGER Y. IBAÑEZ, JR.
PhD in Animal Science Student against erosion, reduces soil temperature, improves soil fertility and
controls weeds (Cook et al., 2005; Chin Chen Peng et al., 1997).
Submitted to:
DR. DANILO L. LAMELA
Professor
Republic of the Philippines
DR. EMILO B. ESPINOSA SR. MEMORIAL STATE
COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Poblacion, Cawayan, Masbate
II. DISTRIBUTION distance should be 1.2 to 1.8 m. It can also be propagated by planting
the rooted slips.
It is a native of tropical South America but distributed naturally
in Malaya and Indonesia. It was introduced in 1930 as a cover crop in Seed Management
India. Now widespread throughout the tropics. To break the dormancy the seeds are to be treated through any
of the following methods (i) Concentrated sulphuric acid (S.G. 1.8) for
20 minutes or with 24 or 36 N sulphuric acid for 7 min. then wash and
III. CULTURAL MANAGEMENT dry. (ii) hot water treatment (3 minutes at 75ºC).
Climatic Requirement Reproductive development
It has shown excellent performance under wide range of climate Flowering is initiated by short days (14 hours), depending on
preferably hot, humid tropics with an annual rainfall in excess of 1525 accession. Calopo is self-fertile and seeds freely. May act as an annual
mm. It is moderately drought and shade tolerant. in seasonally dry environments.
Soil requirements Fertilizer Management
Grows on a wide range of soil types, but prefers clay soils with It responds well to phosphorus application and recommended
pH 4.5-5.0. In tropical America, grows well on acid soils with high Al fertilizer dose is 20 kg N + 60 kg P + 30 kg K/ha. On acid soils in the
saturation. Poor tolerance of salinity. Pantanal, Brazil, productivity was improved by fertilizer application using
20 kg/ha P, 20 kg/ha S, 60 kg/ha K and 1 t/ha dolomitic limestone.
Temperature Requirements
Grows best at 32ºC maximum and 24ºC minimum daily Disease Management
temperatures, with outer limits of 36ºC maximum and 18ºC minimum.
Susceptible to the root-knot nematode. For conventional farming
Prefers humid-tropical, low elevations but will grow up to altitudes of
systems, soil solarization, alone or in combination with organic
2,000 m asl.
amendments, was found effective towards Meloidogyne javanica
Land Preparation
Companion Species
One deep ploughing with disc plough followed by two discings
and planking are sufficient. Grasses: Excellent compatibility with tall, erect grasses such as
Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana ), pangola grass (Digitaria eriantha ) and
Planting distance
setaria (Setaria sphacelata ), because it is little eaten. However, its low
It is sown at the beginning of rainy season through broadcasting the palatability can lead to calopo dominance. Sometimes oversown into
seeds @ 6-8 kg/ha and then covered with soil but in line sowing the signal grass (Brachiaria decumbens ) pastures in Brazil.
Legumes: As cover crop in tree plantations in southeast Asia, Magnesium g/kg DM 3.7 1.1 2.7 6.3 10
often planted in a species mixture with one or more of the species C. Manganese mg/kg DM 44 38 49 2
caeruleum , Pueraria phaseoloides , Centrosema molle , and Desmodium Zinc mg/kg DM 33 30 36 2
ovalifolium . Copper mg/kg DM 9 9 9 2
Iron mg/kg DM 557 525 590 2
IV. NUTRIENT CONTENTS Secondary metabolites Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb
Calopo (Calopogonium mucunoides), aerial part, fresh Tannins (eq. tannic acid) g/kg DM 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 3
Tannins, condensed (eq. g/kg DM 1.0 1
catechin)
Ruminant nutritive Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb
Main analysis Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb values
Dry matter % as fed 33.1 10.6 21.0 54.5 13 OM digestibility, % 60.4 *
Crude protein % DM 12.8 5.0 3.8 22.9 17 Ruminant
Crude fibre % DM 34.8 5.3 22.4 43.2 15 Energy digestibility, % 57.7 *
NDF % DM 54.4 7.7 45.0 63.7 4 ruminants
ADF % DM 41.5 6.0 33.9 50.6 6 DE ruminants MJ/kg DM 10.8 *
Lignin % DM 9.7 2.2 6.8 12.9 7 ME ruminants MJ/kg DM 8.6 *
Ether extract % DM 2.9 1.4 1.4 6.3 13 ME ruminants (gas MJ/kg DM 7.1 1
production)
Ash % DM 8.8 3.2 5.7 19.1 17
Gross energy MJ/kg DM 18.7 *
Calopo (Calopogonium mucunoides), aerial part, dry
Minerals Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb
Calcium g/kg DM 11.1 5.0 4.4 21.8 15
Phosphorus g/kg DM 2.0 1.7 0.9 8.1 15
Potassium g/kg DM 9.3 5.0 3.6 20.7 10
Main analysis Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb
Sodium g/kg DM 0.6 1
Dry matter % as fed 88.3 1
Crude protein % DM 18.3 1 VI. UTILIZATION
NDF % DM 55.6 1
Calopo can be grazed or cut and fed fresh. It can yield up to 14
ADF % DM 33.9 1
t DM/ha if it is harvested in a single cut when pods are already mature.
Lignin % DM 6.8 1 When cut every 9-12 weeks, DM yields are about 4-6 t/ha (Chin Chen
Ether extract % DM 3.4 1 Peng et al., 1997). When calopo is grown as a perennial, DM yields
Ash % DM 10.4 1 decrease over years (FAO, 2011; Cook et al., 2005). It is recommended
Minerals Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb to graze it rotationally with rest periods of 8 to 12 weeks (Chin Chen
Calcium g/kg DM 7.1 0.6 6.7 7.7 3 Peng et al., 1997). Calopo is rarely made into hay or ensiled, though this
Phosphorus g/kg DM 1.4 0.5 0.9 1.9 3 is possible. It may be used as deferred feed to combat drought but has
Potassium g/kg DM 7.0 1
a low nutritive value (Cook et al., 2005). It becomes an important part
of the diet during the dry season when other species have disappeared
Magnesium g/kg DM 2.0 0.2 1.8 2.2 3
(Giller, 2001).
Zinc mg/kg DM 22 18 26 2
Copper mg/kg DM 11 10 11 2 It is used as a fodder crop and is less palatable at early stage but
Iron mg/kg DM 224 208 239 2 after flowering it becomes more palatable. Being fast grower, it is good
for soil conservation purposes. In new mixed pasture, the Calopo can be
Ruminant nutritive Unit Avg SD Min Max Nb
sown after the grasses get established. It fixes 3.8 mg N/day per plant
values and 87 per cent of the fixed N is transferred to the top. It is frost and
drought susceptible but is an excellent flood tolerant and grows well in
ME ruminants (gas MJ/kg DM 7.1 1
production) acid soils.
VII. STORAGE / CONSERVATION
V. SUSTAINABLE USE It is usually cut by hand and is seldom conserved as hay or silage.
It gives full cover in 2-3 months and can be harvested at 8 weeks Whether grazed or cut and fed, calopo is often refused by cattle
intervals after establishment. Grazing can also be done rotationally at although they eat it less reluctantly during the dry season.
interval of 8-12 weeks
You might also like
- SWEET PEA Production GuideDocument11 pagesSWEET PEA Production GuidemelchieNo ratings yet
- Organic Production of Some Agronomic Crops: Basmati Rice, Cotton, Red Gram and SugarcaneFrom EverandOrganic Production of Some Agronomic Crops: Basmati Rice, Cotton, Red Gram and SugarcaneNo ratings yet
- k0199 70Document2 pagesk0199 70bingus sNo ratings yet
- About Arachis Pintoi Krap. (L C D I)Document8 pagesAbout Arachis Pintoi Krap. (L C D I)Dinh xuan BaNo ratings yet
- Calopogonium Mucunoides: Tropical ForagesDocument12 pagesCalopogonium Mucunoides: Tropical ForagesRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Fast-Growing Commercial and Native Philippine Tree SpeciesDocument25 pagesFast-Growing Commercial and Native Philippine Tree SpeciesEvelyn VergaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document14 pagesAssignment 2Roman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Juglans Neotropica DielsDocument2 pagesJuglans Neotropica DielsJesus BobadillaNo ratings yet
- LuffaDocument24 pagesLuffapjagath62No ratings yet
- 10958-NARI Guyana Production de Boulanger (Aubergine) Au Guyana (Angl)Document17 pages10958-NARI Guyana Production de Boulanger (Aubergine) Au Guyana (Angl)christopher alleyneNo ratings yet
- SRE 613 Jatropha A Multipurpose Plant With Considerable Potential For The TropicsDocument9 pagesSRE 613 Jatropha A Multipurpose Plant With Considerable Potential For The Tropicssasi kumar RNo ratings yet
- Mesta 1.0Document5 pagesMesta 1.0Sharath.H sharuNo ratings yet
- Macadamia Organic Nuts in Guatemala Nov 10 2014Document24 pagesMacadamia Organic Nuts in Guatemala Nov 10 2014Rafael MerchanNo ratings yet
- Bottlt Gourd - ReviewDocument5 pagesBottlt Gourd - ReviewspandanaNo ratings yet
- Clitoria Ternatea PDFDocument5 pagesClitoria Ternatea PDFJohn Mark Fernandez DanlagNo ratings yet
- Plant Community Structure: Types and CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesPlant Community Structure: Types and CharacteristicsRichard Bannor MensahNo ratings yet
- Lycopodium Clavatum LinnDocument5 pagesLycopodium Clavatum LinnDayashankarNo ratings yet
- Cardamom CultivationDocument6 pagesCardamom CultivationNuur Yusuf Sheikh OmarNo ratings yet
- Potato Production presentationDocument7 pagesPotato Production presentationsaunyamatashinga32No ratings yet
- Acacia ModestaDocument13 pagesAcacia ModestaAkshay BoobathiNo ratings yet
- Potato Production ZimDocument7 pagesPotato Production ZimStanley OtienoNo ratings yet
- A Review On SagwanDocument4 pagesA Review On SagwanSujit KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Amadumbe Amadumbe: Agriculture, Forestry & FisheriesDocument2 pagesAmadumbe Amadumbe: Agriculture, Forestry & FisheriesPhumakimi0% (1)
- Tea NotesDocument4 pagesTea NotesNurul Emira ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Cultivation Practices of Banana: Course: B.Sc. Agriculture Subject: Principles of Horticulture Unit:4Document21 pagesCultivation Practices of Banana: Course: B.Sc. Agriculture Subject: Principles of Horticulture Unit:4pfdc GuwahatiNo ratings yet
- Katambora Rhodes Grass Fact SheetDocument1 pageKatambora Rhodes Grass Fact SheetMB ManyauNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Tanaman Pakan Teramnus LabialisDocument25 pagesIlmu Tanaman Pakan Teramnus LabialisGoodlike GoodNo ratings yet
- Genipa americana: The marmalade box treeDocument5 pagesGenipa americana: The marmalade box treevitazzoNo ratings yet
- Andropogon GayanusDocument10 pagesAndropogon GayanusSophia Mitz Aya-ayNo ratings yet
- Gerbera: On April 1, 2010, In, by AdminDocument3 pagesGerbera: On April 1, 2010, In, by Adminratna606No ratings yet
- Seaweed Culture: Kappaphycus Alvarezii, Eucheuma Denticulatum, Gracilaria Verrucusa, Porphyra SP., Codium SPDocument3 pagesSeaweed Culture: Kappaphycus Alvarezii, Eucheuma Denticulatum, Gracilaria Verrucusa, Porphyra SP., Codium SPLaila UbandoNo ratings yet
- Sunflower 2Document20 pagesSunflower 2Aastha DubeyNo ratings yet
- BagalungaDocument10 pagesBagalungajohn doeNo ratings yet
- Cassava and Yam Production and Management TecnoguideDocument16 pagesCassava and Yam Production and Management TecnoguideEric D. ValleNo ratings yet
- GrasshopperDocument10 pagesGrasshopperMaynard PascualNo ratings yet
- Bamboo: Dendrocalamus Letiflorus SpeciesDocument68 pagesBamboo: Dendrocalamus Letiflorus SpeciesRi La LeNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Sorghum For GrainDocument33 pagesCultivation of Sorghum For GrainAditya DagarNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY OF JASMINEDocument13 pagesPRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY OF JASMINEViji ThulasiramanNo ratings yet
- GrassesDocument10 pagesGrasseskenken211210% (1)
- Banana Crop GuideDocument1 pageBanana Crop GuideDeep LahaneNo ratings yet
- Production of Cassava Fufu FlourDocument69 pagesProduction of Cassava Fufu Flourjerson100% (1)
- Cryptomeria JaponicaDocument5 pagesCryptomeria JaponicaFitzgerald BillyNo ratings yet
- Adaptations in Plants and Animals of Xerophytic Condition: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument43 pagesAdaptations in Plants and Animals of Xerophytic Condition: Biology Investigatory ProjectSezzal KujurNo ratings yet
- PERSIMMON Giovanni MarconeDocument15 pagesPERSIMMON Giovanni Marconeabyutza100% (1)
- A2026993635 - 22695 - 23 - 2019 - UNI - IV Sericulture PDFDocument40 pagesA2026993635 - 22695 - 23 - 2019 - UNI - IV Sericulture PDFSaurabh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Major Insect Pests of DrumstickDocument32 pagesMajor Insect Pests of DrumstickNavneet MahantNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Plants Species Found in Southern NigeriaDocument14 pagesTerrestrial Plants Species Found in Southern NigeriaENIME CALEBNo ratings yet
- Description: para Grass Is A Vigorous, Semi-: FabaceaeDocument5 pagesDescription: para Grass Is A Vigorous, Semi-: FabaceaeJethro MinanoNo ratings yet
- Mungbean PDFDocument12 pagesMungbean PDFJulie teppangNo ratings yet
- Spondias Mombin: Anacardiaceae LDocument5 pagesSpondias Mombin: Anacardiaceae LMaria José PradoNo ratings yet
- Mango Production and ManagementDocument13 pagesMango Production and ManagementFranklin Cruz LechugasNo ratings yet
- Mathan kumar R Horticulture student pptxDocument25 pagesMathan kumar R Horticulture student pptxmathanramanathan2005No ratings yet
- 04_Soya_beanDocument7 pages04_Soya_beanNk MeenaNo ratings yet
- Rahul Crop production-WPS OfficeDocument31 pagesRahul Crop production-WPS OfficeKapil DangauraNo ratings yet
- Moringaoleifera Nature Is Most Nutritious and MultiPurpose Tree - Golden Leash Pet ProductsDocument5 pagesMoringaoleifera Nature Is Most Nutritious and MultiPurpose Tree - Golden Leash Pet ProductsMoringa Customer CareNo ratings yet
- DeodaraDocument12 pagesDeodaraNE e-SportsNo ratings yet
- MUNGBEANDocument9 pagesMUNGBEANFrancis Jay HalligNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3233516764599185387Document5 pagesInbound 3233516764599185387hlaingnweni29No ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Crop Suitability Assessment RepairedDocument5 pagesExercise 5 Crop Suitability Assessment RepairedJessa PalbanNo ratings yet
- Rice cropping calendar moduleDocument3 pagesRice cropping calendar moduleRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Ibañez Roger Module6Document1 pageIbañez Roger Module6Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
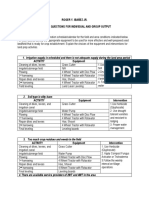
- Roger Y. Ibañez, Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group OutputDocument1 pageRoger Y. Ibañez, Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group OutputRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Roger Y. Ibañez Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group OutputDocument2 pagesRoger Y. Ibañez Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group OutputRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Roger Y. Ibañez Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group Output Exercise 1Document2 pagesRoger Y. Ibañez Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group Output Exercise 1Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Roger Y. Ibañez JR.: Exercise ADocument3 pagesRoger Y. Ibañez JR.: Exercise ARoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Project Work Plan and Budget Matrix: Ipil National High SchoolDocument1 pageProject Work Plan and Budget Matrix: Ipil National High SchoolRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- 1st in P.E 2nd SEM.Document12 pages1st in P.E 2nd SEM.Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Roger Y. Ibañez Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group OutputDocument2 pagesRoger Y. Ibañez Jr. Exercise Questions For Individual and Group OutputRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- 2 Quiz in Physical EducationDocument11 pages2 Quiz in Physical EducationRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Critical Reading and Thinking StrategiesDocument3 pagesCritical Reading and Thinking StrategiesRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesNarrative ReportRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Rizal's Life - Exile and DeathDocument14 pagesModule 5 - Rizal's Life - Exile and DeathRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- A Brief History of Philippine ArtDocument3 pagesA Brief History of Philippine ArtRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Rizals Life - FAMILY, CHILDHOOD AND EARLY EDUCATIONDocument15 pagesMODULE 3 - Rizals Life - FAMILY, CHILDHOOD AND EARLY EDUCATIONRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Module 1 - HISTORICAL BACKGROUND AND CONTEXT OF RA 1425Document10 pagesModule 1 - HISTORICAL BACKGROUND AND CONTEXT OF RA 1425Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Heroes worth emulatingDocument12 pagesHeroes worth emulatingDaryl Cloyd EstanteNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: A. Fill The Blanks. Write Your Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument1 pageExercise 1: A. Fill The Blanks. Write Your Answer On The Space ProvidedRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Breed of Native ChickenDocument2 pagesBreed of Native ChickenRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- The Philippine Setting in The 19 Century Learning Outcomes:: Page - 1Document11 pagesThe Philippine Setting in The 19 Century Learning Outcomes:: Page - 1Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Agricultural Pest Management ReviewDocument3 pagesAgricultural Pest Management ReviewRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Module 1. Curriculum Concepts Nature And-1Document9 pagesModule 1. Curriculum Concepts Nature And-1Shiela castroNo ratings yet
- Introductionto ResearchDocument25 pagesIntroductionto ResearchMichael IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Major 7 - Syallbus (Curriculum Development in Agricultural Education)Document6 pagesMajor 7 - Syallbus (Curriculum Development in Agricultural Education)Roger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Methods of ResearchDocument4 pagesMethods of ResearchRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
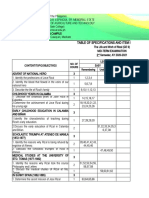
- Table of Specifications and Item PlacementDocument15 pagesTable of Specifications and Item PlacementRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Agricultural Pest Management ReviewDocument3 pagesAgricultural Pest Management ReviewRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- LET Reviewers for Agriculture and Fishery Arts ExamsDocument7 pagesLET Reviewers for Agriculture and Fishery Arts ExamsRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Republic of the Philippines Agricultural Education CurriculumDocument7 pagesRepublic of the Philippines Agricultural Education CurriculumRoger Yatan Ibañez Jr.No ratings yet
- Effect of Zinc Application On Growth and Yield of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.)Document6 pagesEffect of Zinc Application On Growth and Yield of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.)Oliver TalipNo ratings yet
- 6-row Manual Rice TransplanterDocument6 pages6-row Manual Rice TransplanterRamnatha Reddy50% (2)
- Eth Fruit Crops Production and Management StudentDocument144 pagesEth Fruit Crops Production and Management StudentWaseem AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Visual properties of plants: Forms and shapesDocument61 pagesVisual properties of plants: Forms and shapesBushra Ateyyeh100% (1)
- Kakawate - GliricidiaDocument6 pagesKakawate - GliricidiaRojiebouy RantaelNo ratings yet
- Alphabet of Flowers, Dean & Son's, Coloured Six-Penny BooksDocument16 pagesAlphabet of Flowers, Dean & Son's, Coloured Six-Penny BooksIngrid Vance Steighner100% (1)
- Anubias Barteri Caladiifolia: Plants Difficulty Level: EasyDocument25 pagesAnubias Barteri Caladiifolia: Plants Difficulty Level: EasyMohammed KareemNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lab Exam IIDocument17 pagesReviewer Lab Exam IIblueNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology: Germination: Dela Cena, Patricia Beatrice S. Student, City of Mandaluyong Science High SchoolDocument18 pagesPlant Physiology: Germination: Dela Cena, Patricia Beatrice S. Student, City of Mandaluyong Science High SchoolBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Floating Raft Hydroponics: Sixth Grade Garden LessonDocument3 pagesFloating Raft Hydroponics: Sixth Grade Garden LessonBayyinah HydroponicNo ratings yet
- How Low Temperatures Induce Flowering in PlantsDocument3 pagesHow Low Temperatures Induce Flowering in PlantsEvan Jane JumamilNo ratings yet
- Wolie PPT OrobancheDocument19 pagesWolie PPT OrobancheWolie GebreegziherNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Business Communication Developing Leaders For A Networked World 3rd Edition Peter CardonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Business Communication Developing Leaders For A Networked World 3rd Edition Peter CardonRebeccaLarsonqxsd100% (42)
- Taxonomy of Solanum Sect. Solanum in South AmericaDocument22 pagesTaxonomy of Solanum Sect. Solanum in South AmericaMountains Forest MpedraceaeNo ratings yet
- Weeds of Rice in AsiaDocument120 pagesWeeds of Rice in AsiaZahid IhsanNo ratings yet
- Manual Arado y Surcador BCS 90103113 - 10-2015 - Aratri - e - AssolcatoriDocument39 pagesManual Arado y Surcador BCS 90103113 - 10-2015 - Aratri - e - AssolcatoriJuan Carlos Benavides VargasNo ratings yet
- Seed TestingDocument4 pagesSeed TestingMae Joy SoteNo ratings yet
- Ethnobotany of HawaiiDocument48 pagesEthnobotany of HawaiiAngel Eduardo Moreno AlboresNo ratings yet
- 100 Dangerous PlantsDocument19 pages100 Dangerous PlantsShybe ElrikNo ratings yet
- ShippersDocument3 pagesShippersmari poseaNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument4 pagesBotanySesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Tim Ekberg Co-Ordinator PH 0357273931 Mobile 0427573535: 96 Milawa-Bobinawarrah RD, Milawa, Victoria, 3678Document5 pagesTim Ekberg Co-Ordinator PH 0357273931 Mobile 0427573535: 96 Milawa-Bobinawarrah RD, Milawa, Victoria, 3678api-25932006No ratings yet
- Forage Crops WORDDocument15 pagesForage Crops WORDmichael hobayanNo ratings yet
- Edible BerriesDocument35 pagesEdible BerriesSofia RheiNo ratings yet
- Catalogue EEE BooksDocument174 pagesCatalogue EEE Bookshemjo67No ratings yet
- The Induction of Shoots On Leaf Explants of Jatropha Curcas L. With Cytokinins: BAP and KinetinDocument27 pagesThe Induction of Shoots On Leaf Explants of Jatropha Curcas L. With Cytokinins: BAP and Kinetinivan araNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Starting A Garden in A Smarter Way ComDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 Starting A Garden in A Smarter Way ComApril Noreen Briz100% (1)
- Grade - 10 Plant Science - Floriculture and Nursery ManagementDocument115 pagesGrade - 10 Plant Science - Floriculture and Nursery ManagementAnup HamalNo ratings yet
- Turgor-Pressure Plant-Cell Pritchard 2003Document3 pagesTurgor-Pressure Plant-Cell Pritchard 2003Melissa Giorgi OrtizNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Secondary Growth PDFDocument3 pagesLab 9 - Secondary Growth PDFRio Ruby LloviaNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsFrom EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignFrom EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Green Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsFrom EverandGreen Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsNo ratings yet
- Climate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingFrom EverandClimate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualFrom EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Pipeline Planning and Construction Field ManualFrom EverandPipeline Planning and Construction Field ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Experiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated TemperaturesFrom EverandExperiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated TemperaturesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Engineering for Kids: Building and Construction Fun | Children's Engineering BooksFrom EverandEngineering for Kids: Building and Construction Fun | Children's Engineering BooksRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresFrom EverandAdvanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Piezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringFrom EverandPiezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresFrom EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Building Support Structures, 2nd Ed., Analysis and Design with SAP2000 SoftwareFrom EverandBuilding Support Structures, 2nd Ed., Analysis and Design with SAP2000 SoftwareRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsFrom EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbFrom EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Offshore Pipelines: Design, Installation, and MaintenanceFrom EverandOffshore Pipelines: Design, Installation, and MaintenanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Built: The Hidden Stories Behind Our StructuresFrom EverandBuilt: The Hidden Stories Behind Our StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (27)