Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orbital Cavity & Oral Cavity Anatomy
Uploaded by
حوراء عارف الموسويOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orbital Cavity & Oral Cavity Anatomy
Uploaded by
حوراء عارف الموسويCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 7&8 Anatomy
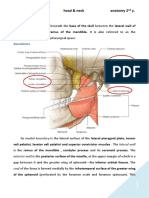
Orbital cavity:
It is the eye socket. It is pyramidal in shape with anterior base and posterior apex. It has:
- Superior surface or roof.
- Inferior surface or floor.
- Medial wall.
- Lateral wall.
- Superior margin.
- Inferior margin.
Roof of the orbit is formed by orbital plate of frontal bone and lesser wing of sphenoid
bone. The lateral wall is formed by zygomatic bone and greater wing of sphenoid bone.
The medial wall formed by frontal process of maxilla, lacrimal and orbital plate of
ethmoid. The floor is formed by maxilla, palatine and zygomatic bones.
Superior orbital margin contains supra-orbital notch or foramen. Infra-orbital foramen
situated below the inferior margin of the orbit.
The orbit contains posteriorly the optic canal for the passage of optic nerve. Superior
orbital fissure for the passage of 3rd , 4th and 6th cranial nerves that supplied the recti
muscles of the eye. Inferior orbital fissure separates between lateral and floor of the
orbit for the passage of infra-orbital nerve, artery and vein. The orbit also contains the
lacrimal fossa and inferior orbital groove.
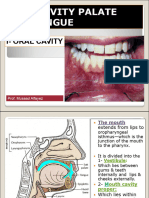
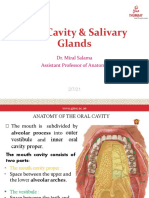
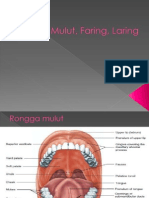
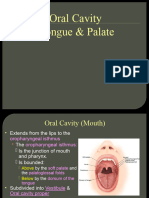
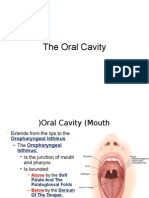
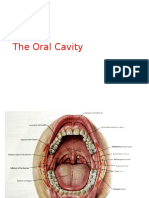
Oral cavity or the mouth:
It can be divided into oral vestibule and oral cavity proper. The oral vestibule lies
between the lips and cheek and teeth. The oral cavity proper is bounded anteriorly and
laterally by the teeth, superiorly by the palate (soft and hard palate), inferiorly by the
tongue and floor of the mouth and posteriorly by oropharyngeal isthmus. Labial and
buccal frenum situated between lips and cheek and teeth. The sub-lingual region
contains the orifice of sub-mandibular gland, lingual frenum, sub-lingual papilla, sub-
lingual fold and in the ventral surface of the tongue there are deep lingual veins.
Blood supply of the mouth: in general the blood supply is derived from branches of
maxillary artery, branches of facial artery and lingual artery.
Lymphatic drainage through sub-mental, sub-mandibular and deep cervical lymph
nodes.
The palate: or roof of the mouth which consists of hard palate and soft palate. Hard
palate lies anteriorly and forms 2/3rd of the palate. It is covered by keratinized mucosa.
The soft palate situated posteriorly and contains muscles. That means soft palate is a
movable structure. The blood supply of the palate comes from greater and lesser
palatine arteries branches of maxillary artery, ascending palatine branch of facial artery
and ascending pharyngeal artery a branch of external carotid artery.
The tongue: it is a muscular organ and covered with mucus membrane. It has two
surfaces; dorsal and ventral surfaces. The dorsal surface is divided by a v-shaped
structure into anterior 2/3rd and posterior 1/3rd . the anterior 2/3rd contains villi form
papillae, fungiform papillae and valate papillae. The posterior 1/3rd contains lingual
tonsils. There is a shallow longitudinal sulcus in the dorsal surface of the tongue called
medial sulcus of the tongue.
Muscles of the tongue: there are extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue. The
intrinsic muscles lie within the mass of the tongue and these are: superior and inferior
longitudinal muscles. Vertical and transverse muscles. The extrinsic muscles are:
- Styloglossus: originates from styloid process and inserts in the tongue.
- Hyoglossus: originates from hyoid bone and inserts in the tongue.
- Genioglossus: originates from genial tubercle and inserts in the tongue.
- Palatoglossus: originates from the palate and inserts in the tongue.
Blood supply of the tongue: mainly from lingual artery and secondary from tonsillar
branch of facial artery and the ascending pharyngeal artery. Venous drainage through
dorsal lingual and deep lingual veins.
Innervation of the tongue: Sensory innervation of the anterior 2/3rd of the tongue via
lingual nerve a branch of mandibular division of trigeminal nerve. The posterior 1/3 rd via
glossopharyngeal nerve. Chorda tympani a branch of facial nerve gives taste fibers to
anterior 2/3rd of the tongue.
All muscles of the tongue are supplied by hypoglossal nerve except palatoglossus which
is innervated by vagus nerve.
Lymphatic drainage of the tongue: this is via sub-mandibular (body and lateral border
of the tongue) and the tip of the tongue drains into the sub-mental lymph nodes.
Posterior 1/3rd is drained into deep cervical lymph nodes.
You might also like
- Role of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTDocument18 pagesRole of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTashoorocksNo ratings yet
- Digestive System at Head and NeckDocument8 pagesDigestive System at Head and NeckArinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- L1) Oral Cavity, Palate and TongueDocument39 pagesL1) Oral Cavity, Palate and Tongue3amroooni.a.aNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity Salivary GlandsDocument36 pagesOral Cavity Salivary GlandsSaifNo ratings yet
- 14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalDocument50 pages14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalSudeep DhakalNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument98 pagesOral CavitynicewanNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyAdeleye John AdebolaNo ratings yet
- Nasal Anatomy OverviewDocument23 pagesNasal Anatomy OverviewArchanaShenoyNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity and PharynxDocument6 pagesOral Cavity and PharynxStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 14 Oral CavityDocument41 pages14 Oral Cavityhamokimo65No ratings yet
- TONGUE SeminarDocument82 pagesTONGUE SeminarArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Tongue Intrinsic Muscles: Frenulum LinguaeDocument1 pageTongue Intrinsic Muscles: Frenulum LinguaeBogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- Oropharynx Ppt VigneshDocument39 pagesOropharynx Ppt VigneshsakthimuruganaravindNo ratings yet
- 3 PharyngologyDocument86 pages3 PharyngologyWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument44 pagesTongueSidhartha BordoloiNo ratings yet
- The TongueDocument7 pagesThe Tonguemanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- Mouth & Oral CavityDocument28 pagesMouth & Oral CavityButool FatimaNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument36 pages14-Oral CavitykavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Anatomy First YearDocument8 pagesLecture 7 Anatomy First Yearspo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- Mulut, Faring, LaringDocument76 pagesMulut, Faring, LaringNiddy Rohim FebriadiNo ratings yet
- Amirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral CavityDocument27 pagesAmirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral Cavityamirhossein vaeziNo ratings yet
- 1 RHINOLOGY NoseDocument116 pages1 RHINOLOGY NoseWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Palate, Palatine Tonsils PDFDocument10 pagesTongue, Palate, Palatine Tonsils PDFChristopher PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity AnatomyDocument40 pagesOral Cavity AnatomyharisNo ratings yet
- EarDocument6 pagesEarDr.Mahesh kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and TongueDocument40 pagesAnatomy of Nose and TongueDanial SharizulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyBkas GrgNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity NursingDocument38 pagesOral Cavity NursingRiya AktarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyArjun SainiNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of Mouth and PharynxDocument4 pages1 Anatomy and Physiology of Mouth and Pharynxyq24w9p85sNo ratings yet
- Pivotal Role of Tongue in Prosthodontic TreatmentDocument13 pagesPivotal Role of Tongue in Prosthodontic TreatmentAkshayaa BalajiNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument59 pagesOral CavityshaisidroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of NoseDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Noserizgah jawas100% (1)
- NOSEDocument6 pagesNOSEAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- The MouthDocument13 pagesThe MouthAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- 1: Sinuses: 1 2 3 1. Orbit and Ocular Adenexa 4 A OrbitDocument26 pages1: Sinuses: 1 2 3 1. Orbit and Ocular Adenexa 4 A OrbitMuhammed AbdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- W2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFDocument69 pagesW2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Tongue and PalateDocument103 pagesTongue and PalateHeba S RadaidehNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Upper DigestionDocument16 pagesAnatomy of The Upper DigestionNabilla MahyendaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System of OxDocument14 pagesThe Respiratory System of OxHemant JoshiNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument162 pagesTongueDevendra ChhonkarNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument46 pagesTonguedeepak mauryaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs - NoseDocument24 pagesSensory Organs - Noseapi-324160601No ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity Anatomy Structures Functions Blood Supply Paranasal Sinuses OpeningsDocument41 pagesNasal Cavity Anatomy Structures Functions Blood Supply Paranasal Sinuses OpeningsGuo YageNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of The EarDocument8 pagesAnatomy Physiology of The EargheaastridgayatriNo ratings yet
- External Nose Anatomy NotesDocument4 pagesExternal Nose Anatomy NotesNia IarajuliNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity & Oropharynx (GIT-A-001) by MedicneticDocument14 pagesOral Cavity & Oropharynx (GIT-A-001) by MedicneticMuhammad Hammad ZiaNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: DissectionDocument23 pagesPharynx: DissectionrajtanniruNo ratings yet
- 7 Infratemporal FossaDocument7 pages7 Infratemporal FossaAaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 44 - Masticatory ApparatusDocument6 pagesLecture 44 - Masticatory ApparatusleahbayNo ratings yet
- Anat NotesDocument94 pagesAnat NotesCarineHugz (CarineHugz)No ratings yet
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (18)
- TongueDocument72 pagesTongueDrRj SameenNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) : Leukocyte Extravasation (Document5 pagesLeukocytes (White Blood Cells) : Leukocyte Extravasation (حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Lec 1Document24 pagesNervous System Lec 1حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Digestive Tract: Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus and ItsDocument10 pagesDigestive Tract: Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus and Itsحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 1)Document6 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 1)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Blood Filmالملخص 2Document2 pagesBlood Filmالملخص 2حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument3 pagesIron-Deficiency Anemia Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Treatmentحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- دي ام تقرير كورس اول PDFDocument6 pagesدي ام تقرير كورس اول PDFحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Check List AnatomyDocument7 pagesCheck List Anatomyحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 2)Document5 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 2)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Blood Physio 3Document9 pagesBlood Physio 3حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- x - ray سمنارDocument11 pagesx - ray سمنارحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Vitamins Are Organic Compounds That People Need in Small QuantitiesDocument1 pageVitamins: Vitamins Are Organic Compounds That People Need in Small Quantitiesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument10 pagesVitaminsحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 2)Document5 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 2)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument10 pagesVitaminsحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 2)Document5 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 2)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 1)Document6 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 1)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- سمنار فارماDocument12 pagesسمنار فارماحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 1)Document6 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 1)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- سمنار فارماDocument12 pagesسمنار فارماحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes (Part 2)Document5 pagesDrugs For Diabetes (Part 2)حوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Quiz on Grammar, Vocabulary and ComprehensionDocument36 pagesQuiz on Grammar, Vocabulary and ComprehensionprasannaNo ratings yet
- Beginning Chi Manipulation TechniqueDocument3 pagesBeginning Chi Manipulation Techniqueellemistery100% (1)
- Maths Paper 2Document8 pagesMaths Paper 2pantmukul100% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris SMP Kelas 8 Soal PG SMT GanjilDocument7 pagesBahasa Inggris SMP Kelas 8 Soal PG SMT GanjilNanda Dwi KusumaningrumNo ratings yet
- Quiz Questions on Vocabulary and GrammarDocument25 pagesQuiz Questions on Vocabulary and GrammarRasyidy 'Eddy' AliasNo ratings yet
- U4c1 VocabDocument3 pagesU4c1 Vocabapi-308919474No ratings yet
- BIO 103 - All Notes-1 - Copy (2) - 1Document27 pagesBIO 103 - All Notes-1 - Copy (2) - 1judikidNo ratings yet
- Market Forms of PoultryDocument23 pagesMarket Forms of PoultryEvangeline De OcampoNo ratings yet
- D&D 3.0 Savage Species Web EnhancementDocument6 pagesD&D 3.0 Savage Species Web EnhancementStephen CameronNo ratings yet
- Aztec MythologyDocument10 pagesAztec Mythologysalamanderwolf100% (3)
- The Hare and Pineapple - WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Hare and Pineapple - WorksheetSelam AmanielNo ratings yet
- Verbalanalogies 130625071031 Phpapp01Document6 pagesVerbalanalogies 130625071031 Phpapp01Reno Miranda EnticoNo ratings yet
- English Context Clues and Modals WorksheetsDocument3 pagesEnglish Context Clues and Modals WorksheetsLarracas CristineNo ratings yet
- Beetons Book of Poultry and Domestic Animals-Showing How To Rear and Manage Them-1870Document528 pagesBeetons Book of Poultry and Domestic Animals-Showing How To Rear and Manage Them-1870te.iubesc777No ratings yet
- The 12 Cranial NervesDocument11 pagesThe 12 Cranial Nervesapi-306342919No ratings yet
- Collection of University Question Papers 1990-2015: Microbiology Paper IDocument41 pagesCollection of University Question Papers 1990-2015: Microbiology Paper IGanesh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Course OverviewDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Course OverviewPatrick PoculanNo ratings yet
- Distinction Between Poisonous and NonDocument9 pagesDistinction Between Poisonous and NonمحمدأميندماجNo ratings yet
- Microorganism Effects Form 5 Science ChapterDocument33 pagesMicroorganism Effects Form 5 Science Chapterjaivin2002No ratings yet
- Surgery 421Document218 pagesSurgery 421AshNo ratings yet
- Charlottes Web FinalDocument43 pagesCharlottes Web Finalapi-4299410240% (2)
- Tle Agriculture AnimalsDocument2 pagesTle Agriculture AnimalsRonel Sayaboc AsuncionNo ratings yet
- YDS practice test provides SEO-optimized titleDocument14 pagesYDS practice test provides SEO-optimized titleCeyhun Güler ☾☆No ratings yet
- The Wyrms TaleDocument64 pagesThe Wyrms TaleMichael WelkerNo ratings yet
- Full Companion Planting GuideDocument9 pagesFull Companion Planting GuidesticklesNo ratings yet
- Kuvings Whole Slow Juicer ManualDocument24 pagesKuvings Whole Slow Juicer ManualandreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Joints: Mr. Saihou SannehDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Joints: Mr. Saihou Sannehflex gyNo ratings yet
- Zoo - Minimum Dimension of EnclosuresDocument14 pagesZoo - Minimum Dimension of Enclosuressalman672003No ratings yet
- Stepenuvanje Pridavki PDFDocument2 pagesStepenuvanje Pridavki PDFOlivera JordanovaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Apheresis in VeterinaryDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Apheresis in VeterinaryEliDavidNo ratings yet