Professional Documents
Culture Documents
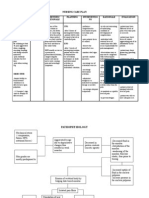
Injury SX Generator MOI Primary Complaint Clinical Presentation Dermatomes/ Myotomes/ DTR's Special Tests/ Examination Interventions
Uploaded by
Megan Ralstin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views6 pagesThis document provides a flowchart to help diagnose various cervical spine injuries and conditions. It outlines common symptoms, mechanisms of injury, clinical presentations, special tests, and treatment interventions for issues such as forward head posture, spondylosis, facet lock, radiculopathy, and disc syndrome. Primary complaints, dermatomal involvement, range of motion restrictions, and neurological changes are noted for each diagnosis. Both conservative and manual therapy approaches are recommended depending on the specific condition.
Original Description:
Original Title
Diagnoses Flowchart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a flowchart to help diagnose various cervical spine injuries and conditions. It outlines common symptoms, mechanisms of injury, clinical presentations, special tests, and treatment interventions for issues such as forward head posture, spondylosis, facet lock, radiculopathy, and disc syndrome. Primary complaints, dermatomal involvement, range of motion restrictions, and neurological changes are noted for each diagnosis. Both conservative and manual therapy approaches are recommended depending on the specific condition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views6 pagesInjury SX Generator MOI Primary Complaint Clinical Presentation Dermatomes/ Myotomes/ DTR's Special Tests/ Examination Interventions
Uploaded by
Megan RalstinThis document provides a flowchart to help diagnose various cervical spine injuries and conditions. It outlines common symptoms, mechanisms of injury, clinical presentations, special tests, and treatment interventions for issues such as forward head posture, spondylosis, facet lock, radiculopathy, and disc syndrome. Primary complaints, dermatomal involvement, range of motion restrictions, and neurological changes are noted for each diagnosis. Both conservative and manual therapy approaches are recommended depending on the specific condition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Diagnoses Flowchart
Injury Sx Generator MOI Primary Clinical Dermatomes/ Special Tests/ Interventions
complaint Presentation Myotomes/ Examination
DTR’s
Forward Head -Weak DNF -Prolonged abnormal -Pain -More common in -Stretch tight muscles
Posture -Lengthened neck posture females -Strengthen weak muscles
extensors -Dull ache -Posture education
-Tight -Non-referring -Soft tissue work
suboccipitals
Upper Crossed -Weak DNF/ -Prolonged abnormal -Pain -More common in -Stretch tight muscles
Syndrome rhomboids/ posture females -Strengthen weak muscles
serratus/ low trap -Dull ache -Posture education
-Tight pecs/ -Non-referring -Soft tissue work
suboccipitals/
levator/upper trap
Spondylosis/OA -Neck -Spectrum of spinal -Pain (not -Spondylosis -Not typically -OA X-ray: narrowing of -Joint protection strategies
-Can feel into arm, degeneration (OA is radicular unless without OA affected joint spaces, osteophytes, (avoid extremes of
upper T-spine, and further progressed) around nerve) radiographic cysts (subchondral), motion)
upper scapular -Stiffness changes: hair loss sclerosis -Mobilize locally and
region (facet patterns, temp -LOM in SB usually first globally
referral) changes on skin, -SB and ROT equally -Strengthen
hyperhidrosis limited > BB -Improve motor control
-OA radiographic -Restore muscular/CT
evidence present in health
90% of people > 60
y/o
-40% of people with
OA are
asymptomatic
Acute Cervical -Meniscoid -Meniscoid is drawn -Sharp, -Reduced rotation -BB, ROT, SB limited -Opening and traction of
Facet Lock into the joint with localized pain ipsilaterally towards painful side the facet to allow
flexion (prolonged -Able to move freely -Palpable paraspinal meniscoid to reduce back
head position) and is into flexion spasm at level of into place
unable to retract with involvement -Indirect technique:
extension -Tender traction and ROT away
-Swelling -Direct technique: traction
and ROT towards
-Maintainence of ROM
gained
-Ice to reduce
inflammation/ pain
modulation
Cervical Facet -Progression of -Repetitive meniscoid -Dull ache in -Not typically
Syndrome facet joint entrapment cervical spine affected but can be
degeneration (microtrauma) -Coupled motion if degeneration
-Neck -DJD restriction (SB, compresses a
-Scapular referral -Facet arthropathy ROT, BB) nerve
-Active trigger -Would cause
points diminished DTR’s,
radiculopathy,
muscle weakness
Cervical -Compression of -Younger: foraminal -Radicular sx -Sx progress central -Diminished -Quadrant +
Radiculopathy nerve root encroachment caused to distal DTR’s -Compression +
by disc herniation -Neck pain -Radicular sx into -Spurling’s +
-Older: stenotic -Decreased cervical arms and hands -Distraction +
(lateral mostly) ROM -Muscle weakness -Test cluster: upper limb
foraminal -Dermatomal, tension test, spurling,
encroachment caused myotomal, and DTR distraction, cervical
by osteophyte changes rotation <60 degrees to
formation ipsilateral side
Cervical Disc -Disc -Disc degradation: -Pain -Dull ache to severe -Disc degredation -C7 60% of all cervical -Traction of cervical spine
Syndrome -Neck disc degrades -Numbness burning depending (herniation): can HNP: weakness in triceps -Mobilization and muscle
-Can feel into arm prematurely after 1 on structures disc compress nerve and finger extensors, energy technique of
injury (30’s – 40’s) contacts and diminish numbness and pain cervical spine
-DDD: normal -Worse in the DTR’s, cause radiating into middle -Soft tissue release
degradation after morning because radiculopathy, and finger -Posture education
multiple injuries disc is rehydrated, muscle weakness -C6 25% of all cervical
(50’s – 60’s) worse at work due to -DDD: can HNP: weakness in biceps
-Acute: some static postures, and encroach on and wrist extensors,
combination of SB, can’t get foramen and numbness and pain
ROT, BB, and/or comfortable at night compress nerve radiating to thumb side of
axial compression and diminish hand (Median nerve
-Chronic: progression DTR’s, cause distribution)
from facet syndrome, radiculopathy, and -C5 3rd most common
exposure to whole muscle weakness cervical HNP: shoulder
body vibration pain and weakness in
deltoid and into upper
arm, not usually
numbness and tingling
-C8 HNP: weakness with
handgrip, numbness and
pain radiating to little
finger side of hand (ulnar
nerve distribution)
Cervical -Spine -Damage to the spinal -Weakness -Flexion makes it -LMN findings at -Weakness and -Traction in flexion if
Myelopathy cord usually C5-C6 -Paresthesias better level of lesion clumsiness in hands tolerated
(spinal cord widest -Pain -Extension makes it -UMN findings -Paresthesias in hand -Neuromuscular re-
and canal narrowest) worse below level of -Decreased cervical education
-Older: osteophyte lesion ROM -HVLAT contraindicated
and ligament -Hyper-reflexia -Weakness or stiffness in -Soft tissue release
thickening causing -Extrasegmental legs -Surgical decompression
central stenosis paresthesias -Unsteady gait
-Younger: central (typical -Pain
HNP dermatomal -Slight hesitancy on
-Sudden onset: MVA, patterns not always urination
axial load evident) -Lhermitte’s sign
-Quadrant +
-Compression +
-Spurling’s +
-Distraction: could
alleviate or provoke
-Babinski
-Hoffman’s not as
common
-Test cluster: abnormal
gait, Babinski, Hoffman,
Inverted supinator sign, >
45 y/o
Whiplash -Cervical muscles: -MVA -Neck pain -Fatigue -Altered muscle -Conservative approach
SCM, semispinalis -Athletic injuries and/or occipital -Vertigo recruitment patterns: fatty -Protective
and splenius -Trauma headaches -Visual disturbances infiltration -Bed rest 2-3 days
capitis, upper trap -Falls -Neck stiffness -Depression -Sensorimotor: joint -Modalities
-Cervical -Insomnia repositioning errors, -Pain-free ROM
ligaments: alar, -Hyper-irritability balance disturbance, -Gentle isometrics
transverse, -WAD: pain > 3 dizziness
tectorial, months -Sensory hypersensitivity
interspinous -WAD I: neck pain,
-Disc stiffness, tenderness,
-Facet: contusion, no signs
occult fracture, -WAD II: neck pain,
recurrent stiffness, tenderness,
meningeal nerve, some point
meniscoid tenderness or LOM
-CNS/PNS -WAD III: neck
pain, stiffness,
tenderness,
neurological signs
-WAD IV: neck
pain, fracture or
dislocation
Cervical Fractures -Neck -Compression: pure - Middle column can -Spinal cord injury -Depends on extent of
flexion (failure of the protrude into the possible leading to damage to ligaments
anterior column) canal, resulting in UMN signs (PLL), disc and/or none
-Burst: intense axial paralysis or death -Extrasegmental -We will see after
load (failure of paresthesias, stabilizstion
anterior, middle, and hyper-reflexia
posterior columns)
Thoracic Facet -Facet -Trauma -Localized pain -Not typically -Common patterns: -Stretching
Syndrome -Associated rib -Posture -Possible facet affected but can be -T1 extension restriction -Mobilization
(costotransverse referral pain if degeneration due to forward head -HVLAT
joint positional compresses a posture -Muscle energy technique
fault) nerve -T3-T7 flexion (basically PNF contract-
restriction/rib dysfunction relax or hold-relax)
-T8-T12 extension
restriction
T4 Syndrome -T4 -Unknown -Headache -Hand clumsiness -Altered -AROM/PROM WNL -Traction: cervical and
-Onset may coincide -Pain, pins, -Heaviness in upper dermatomes and pain-free thoracic
with new job that and/or needles extremities although not -Neurological findings -PA mobs
requires frequent into hands typical thoracic negative -Thoracic HVLAT above
stooping or bending spine presentation -Pas stiff mid T spine and below T4
-Hands feel and may -Hot or cold hands to -Postural correction
objectively be tough
swollen -Tender mid T spine
-T2-T7 dull, -Deviation/prominence of
intermittent mid SPs (not just because
back pain skinny, actual
-Headache morphological changes)
-Glove distribution
pain or pins and
needles
-Worse at night and
better changing
position or getting
up
Peripheral Nerve -Nerve -Compression -Paresthesias -Pain progresses to -Diminished
Entrapment -Traction -Muscle anesthesia DTR’s
-Friction weakness -Numbness constant -Radicular sx
-Anoxia -Motor weakness -Muscle weakness
-Cutting progresses to muscle
wasting
-Warm, flushed skin
progresses to cold,
white skin
-Scaly skin
progresses to thin,
smooth, shiny skin
-Dry, brittle nails
-Loss of sweat
glands
Thoracic Outlet -Neurovascular -Trauma -Diffuse pain -Worse with arm -Possible -Adson’s test for tight -Treat the cause of TOS
Syndrome bundle as it exits -Repetitive overhead -Paresthesia elevation diminished DTR’s, scalenes or cervical rib (can’t treat cervical rib)
through thoracic activities -Numbness -Hand/arm doesn’t radicular sx, and -Costoclavicular test for -Reduce pain and
outlet -Developmental: -Weakness feel like their own muscle weakness elevated 1st rib inflammation
-Feel sx in arm, scapula descends -Heaviness -Unusual fatigue when sx provoked -Hyperabduction/Wright -Avoid cervical traction
shoulder, head, pulling on soft tissue -Fatigue with elevated test can also be used for -Postural correction
chest, axilla and causing -Swelling positions elevated 1st rib and tight -OMT: mob 1st rib,
peripheral nerve -Discoloration -Changes in skin pec minor scapulothoracic mobility,
entrapment temperature -Roos test for general scapular
(involved vs. TOS test strengthening/motor
uninvolved side) control exercises
-Pec stretch
-Surgery (try to avoid if
possible): cervical and 1st
rib excision, scalene
release
Thoracic -Spine -Hyperflexion -Severe pain -Hyperkyphosis -T9-T11 most common -Alleviate pain with
Compression -Axial compression -Risk factors: -X-ray: increased graded return to loading
Fractures -Fractures as a result -Older female radiolucency, thinning of -Engage stabilizing
of metabolic bone -Estrogen deficiency cortical margin, musculature (back, abs,
disease (osteoporosis) -Poor diet trabeculae number and diaphragm)
-Alcoholism thickness decreased
-Smoking -Possible reduced -Early movement to
-Sedentary lung/heart capacity prevent secondary
-Chronic steroid use -Cervical hyperextension impairments (ex:
compensation pneumonia)
-Painful ambulation -Avoid extension
(can’t dissipate forces -Increase loading
properly due to -Increase aerobic
spinal/pelvic endurance
malalignment) -Increase strength
-Light traction above and
below fracture
Rib Fracture -Rib -Direct blow -Localized -Evidence of trauma -Difficult to assess on x- -Protection with bracing
-Severe coughing tenderness -Pain with ray, callus often first to help reduce rib
(geriatrics) -Pain on deep movement evidence excursion and
-Overuse (golf, inspiration -PA tenderness/pain approximate bones
baseball high rotation -Relative rest
forces) -Analgesics
Scheuermann’s -Spine -Defect of ring -Diffuse back -Hyperkyphosis -Sharp angulation of -Anterior stretching (pecs,
Disease apophysis of pain kyphosis with trunk FB abdominals)
vertebral body in -Additional -Extensor strengthening
adolescents made complications include -Severe cases: bracing or
noticeable from: burst fracture, spinal fusion
-Axial loading of compression fracture,
spine (ex: heavy associated scoliosis,
backpack) Schmorl’s nodes
-Obesity (vertebral body
-Possible multiple degeneration allowing
microtrauma to disc to extend into body)
epiphysis (ex: heavy
lifting, high contact
sports like football,
lacrosse, soccer)
Scoliosis -Spine -Functional: habitual -Structual Idiopathic: -Non-structural: correct
poor posture, pain assess if there are cause of scoliosis
and muscle spasm, fractures, other structural -Strucutral: refer to
leg length impingements/occlusions, orthopedic surgeon,
discrepancy (actual visceral organs impaired, perform regular
shortening or nerves impaired, check assessment, and treat what
apparent shortening leg length you can typically after
from pelvic obliquity) -Adam’s Test: check for surgery
-Structural Acquired: rib hump -Scoliosis 20-40 degrees:
osteopathic – bracing
fractures, thoracic -Scoliosis > 50 degrees:
surgery, rickets, spinal fusion
osteomalacia;
neuropathic – polio,
paraplegia,
Friedreich’s ataxia
-Structural
Congenital:
osteopathic –
hemivertebrae,
osteogenesis
imperfecta;
neuropathic – spina
bifida,
neurofibromatosis;
myopathic –
amyotonia congenita
-Structural Idiopathic
You might also like
- Study Guide PCE Shane Mrsic Toma 2014Document137 pagesStudy Guide PCE Shane Mrsic Toma 2014Nidhi Katyal100% (3)
- Differential Diagnosis MSK PathoDocument13 pagesDifferential Diagnosis MSK PatholizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan-Herniated Nucleus PulposusJasmin Jacob67% (3)
- Foundations Adult Health Nursing 8th Cooper Test BankDocument15 pagesFoundations Adult Health Nursing 8th Cooper Test BankRaadqqqNo ratings yet
- Cyriax ConceptDocument26 pagesCyriax ConceptMeenakshiputraeashwarprasad MacherlaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Surgery NotesDocument3 pagesOrthopedic Surgery NotesJoel Salu100% (1)
- Spine PDFDocument7 pagesSpine PDFDRAHMEDFAHMYORTHOCLINIC100% (1)
- Bedah 2Document204 pagesBedah 2Muhammad Sobri MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Tiss 28Document12 pagesTiss 28Ubaid RahamanNo ratings yet
- Injury NotesDocument15 pagesInjury NotesJaden MusclowNo ratings yet
- Neuro RehabilitationDocument58 pagesNeuro Rehabilitationsyafaat164No ratings yet
- MSK Ncm106lecDocument50 pagesMSK Ncm106lecJASTINE JOY PEREZNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cervical Spine & TMJDocument5 pages3.1 Cervical Spine & TMJAIREN MARGARET MAGDALENANo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Orthopedics: ManojDocument3 pagesUpper Limb Orthopedics: ManojManoj PakalapatiNo ratings yet
- Ortho. CompDocument51 pagesOrtho. CompSakshi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PT3 Postural AnalysisDocument5 pagesPT3 Postural Analysisim. EliasNo ratings yet
- GFHDocument34 pagesGFHaisa mutiaraNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument2 pagesOsteoarthritisapi-518311936No ratings yet
- Cancer Epidemiology Pathogenesis Lab/Gross Clinical Features Prognosis/TxDocument7 pagesCancer Epidemiology Pathogenesis Lab/Gross Clinical Features Prognosis/TxCaryn RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff Tears IhoqkuDocument2 pagesRotator Cuff Tears IhoqkuKeefe TanNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic!Document15 pagesOrthopaedic!bowelprepcolonNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems in AdolescentDocument11 pagesCommon Health Problems in Adolescent2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Concept MapDocument2 pagesDay 2 Concept Mapkyle frascoNo ratings yet
- ELBOWDocument7 pagesELBOWPhoebe DemegilloNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation ARSDocument4 pagesShoulder Dislocation ARSBambang Ulan AeiyuNo ratings yet
- Hip Disorders SummaryDocument2 pagesHip Disorders SummarybhnsboshkashNo ratings yet
- Sports MedicineDocument32 pagesSports Medicinersimranjit100% (1)
- Wrist Injuries (Orthopedics)Document2 pagesWrist Injuries (Orthopedics)Kimmybee GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unlock - (PESERTA) BEDAH 2 - Mantap Februari 2018Document202 pagesUnlock - (PESERTA) BEDAH 2 - Mantap Februari 2018Selvi AristinaNo ratings yet
- Underlying Process Umum AkhirnyaDocument3 pagesUnderlying Process Umum AkhirnyaannyNo ratings yet
- Ortho NotesDocument283 pagesOrtho NotesGaushinee VallimanalanNo ratings yet
- W7 CTSDocument4 pagesW7 CTSStevanie SesiliaNo ratings yet
- OrthopaediDocument87 pagesOrthopaediGalihNo ratings yet
- DegenerativeDiskDisease (HNP) IDocument2 pagesDegenerativeDiskDisease (HNP) Iapi-3822433No ratings yet
- Bedah 2 Batch 3 2018Document87 pagesBedah 2 Batch 3 2018Meiza Ihsan FakhriNo ratings yet
- Final Year SyllabusDocument4 pagesFinal Year SyllabusAanchal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document3 pagesChapter 36Samantha QuintoNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular Joint: Structure, Function, Dysfunction and Treatment Chris KeatingDocument34 pagesTemporomandibular Joint: Structure, Function, Dysfunction and Treatment Chris KeatingHichem SeghierNo ratings yet
- Head Neck Spine Conditions SummaryDocument5 pagesHead Neck Spine Conditions SummaryDominic c. CastañedaNo ratings yet
- CA II Prefinal Neuro 1Document4 pagesCA II Prefinal Neuro 1emilyfaye.nebabNo ratings yet
- Bedah Menejemen FrakkturDocument53 pagesBedah Menejemen FrakkturvitaNo ratings yet
- Toxins 10 00018Document27 pagesToxins 10 00018Dana DumitruNo ratings yet
- Back Spine ConditionsDocument2 pagesBack Spine ConditionsNinjaNo ratings yet
- 116A PrelimsDocument6 pages116A PrelimsKimjin MallareNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic FinalDocument858 pagesOrthopedic Finalhashmf180% (10)
- (Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-2 Batch 3 2018 SalinanDocument200 pages(Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-2 Batch 3 2018 SalinantikaNo ratings yet
- Dislokasi Catatan Unas Myn Van ZarDocument6 pagesDislokasi Catatan Unas Myn Van ZardewiswahyuNo ratings yet
- Dylan Sciara Catergory 1Document4 pagesDylan Sciara Catergory 1api-508474347No ratings yet
- Mnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureDocument6 pagesMnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Zuku Visual Flashnotes Cruciate ExtendedDocument3 pagesZuku Visual Flashnotes Cruciate ExtendedMargarita BrownNo ratings yet
- Radio - MusculoskeletalDocument20 pagesRadio - MusculoskeletalVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Fracture Dislocation LesionsDocument14 pagesFracture Dislocation LesionsReichelle Reine LisingNo ratings yet
- Mus Culo SkeletalDocument7 pagesMus Culo SkeletalJessica Abella SohNo ratings yet
- Management of Chronic Pain With Interventional TechniqueDocument40 pagesManagement of Chronic Pain With Interventional TechniqueRovika RovikaNo ratings yet
- Spodylolysthes IsDocument70 pagesSpodylolysthes IsshravaniNo ratings yet
- Hip ConditionsDocument2 pagesHip ConditionsseemaNo ratings yet
- Patellofemoral Arthralgia Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)Document4 pagesPatellofemoral Arthralgia Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD)Carlos GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Aging Spine: A Degenerative Cascade: TH STDocument4 pagesAging Spine: A Degenerative Cascade: TH STChristi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Rheuma (Gout, CPD, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis)Document2 pagesRheuma (Gout, CPD, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis)Jezreel Yanah De LeonNo ratings yet
- Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesFrom EverandLength Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy TechniquesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Pharmacology AbbreviationsDocument1 pagePharmacology AbbreviationsMegan RalstinNo ratings yet
- Patient Case 5 Mr. Chlif-Chronic Heart FailureDocument67 pagesPatient Case 5 Mr. Chlif-Chronic Heart FailureMegan RalstinNo ratings yet
- Ringworm: Morgan Giacobazzi, Megan RalstinDocument8 pagesRingworm: Morgan Giacobazzi, Megan RalstinMegan RalstinNo ratings yet
- Timed Up and Go: Lauren Walters SPT, Megan Ralstin, SPT, Marissa Taylor, SPTDocument14 pagesTimed Up and Go: Lauren Walters SPT, Megan Ralstin, SPT, Marissa Taylor, SPTMegan RalstinNo ratings yet
- Hormone Responses To ExerciseDocument4 pagesHormone Responses To ExerciseMegan RalstinNo ratings yet
- SHCDocument58 pagesSHCElizabethmike100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP)Aaron ArceNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARY ACTIVITY of Module 1Document3 pagesPRELIMINARY ACTIVITY of Module 1Casio, Anthony MaryNo ratings yet
- 2.2 First Aid - Basic First Aid and Resuscitation - Participant HandoutDocument3 pages2.2 First Aid - Basic First Aid and Resuscitation - Participant HandoutEva ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Covid GuidelinesDocument1 pageCovid Guidelinesapi-509452068No ratings yet
- Bmi Lab Viva QuestionDocument7 pagesBmi Lab Viva QuestionnijafancyNo ratings yet
- Demodex Infestation Requires Immediate, Aggressive Treatment by Doctor, Patient - Primary Care Optometry NewsDocument5 pagesDemodex Infestation Requires Immediate, Aggressive Treatment by Doctor, Patient - Primary Care Optometry NewsΔιονύσης ΦιοραβάντεςNo ratings yet
- Medication - Chart ADHD PDFDocument2 pagesMedication - Chart ADHD PDFaayceeNo ratings yet
- Biographic Data: Nursing Health HistoryDocument14 pagesBiographic Data: Nursing Health HistoryMae Jane AuzaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 3rd Term English Question 2078Document8 pagesGrade 7 3rd Term English Question 2078Deependra SilwalNo ratings yet
- Rmu Surgery OspesDocument110 pagesRmu Surgery OspesHumna YounisNo ratings yet
- Daftar Sampel ReadyDocument6 pagesDaftar Sampel ReadydindaNo ratings yet
- World Sight Day-Activity Report - 2022-PICO PakistanDocument5 pagesWorld Sight Day-Activity Report - 2022-PICO Pakistanjibran khanNo ratings yet
- What Is High Blood PressureDocument3 pagesWhat Is High Blood PressureShekarNo ratings yet
- Gastro POMDocument63 pagesGastro POMLionell Castillo100% (1)
- WedDocument6 pagesWedPratiwi IkaNo ratings yet
- Mispa Count Plus 1Document2 pagesMispa Count Plus 1Tony DanartoNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument60 pagesCopdRizqy Shofianingrum100% (1)
- Body Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Study Notes: BloodDocument7 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Study Notes: BloodTUSHAR DASHNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of NewbornDocument15 pagesHemolytic Disease of Newborncyphochilus100% (1)
- DuchenneDocument13 pagesDuchennejenika studiesNo ratings yet
- Diane Kazer Loving On Our LymphDocument22 pagesDiane Kazer Loving On Our LymphKátia BárbaraNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Conventional Tube Test and Gel Technique in Evaluation of Direct Antiglobulin TestDocument5 pagesA Comparison of Conventional Tube Test and Gel Technique in Evaluation of Direct Antiglobulin TestYunita RapaNo ratings yet
- Osteomielitis Akut Edit MeiDocument9 pagesOsteomielitis Akut Edit MeiRaja DarmawanNo ratings yet
- ISC236 Abnormal PsychologyDocument2 pagesISC236 Abnormal PsychologyGregNo ratings yet
- TESTDocument22 pagesTESTjuniati samparaNo ratings yet
- Retic MethodDocument18 pagesRetic MethodFaty DearNo ratings yet
- 37 - Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument1 page37 - Acute Rheumatic FevernasibdinNo ratings yet