Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Configuration Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)
Uploaded by
Didier SepulvedaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Configuration Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)
Uploaded by
Didier SepulvedaCopyright:
Available Formats
SingleRAN
Configuration Management
Feature Parameter Description
Issue 01
Date 2020-03-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2020. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: https://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description Contents
Contents
1 Change History.........................................................................................................................1
1.1 SRAN16.1 01 (2020-03-30)..................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 SRAN16.1 Draft A (2020-01-20)........................................................................................................................................ 1
2 About This Document.............................................................................................................3
2.1 General Statements................................................................................................................................................................ 3
2.2 Applicable RAT......................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2.3 Features in This Document.................................................................................................................................................. 4
3 Overview....................................................................................................................................5
3.1 Definition....................................................................................................................................................................................5
3.2 Application Scenarios............................................................................................................................................................. 5
3.3 Architecture............................................................................................................................................................................... 5
3.3.1 NEL............................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
3.3.2 EMS........................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.3.3 NMS.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.4 Configuration Security........................................................................................................................................................... 7
4 Typical Application Scenarios............................................................................................... 8
4.1 Network Deployment............................................................................................................................................................ 8
4.2 Network Adjustment........................................................................................................................................................... 10
4.3 Feature Activation.................................................................................................................................................................13
4.4 Network Optimization........................................................................................................................................................ 13
4.5 Network Maintenance........................................................................................................................................................ 14
5 Related Documentation.......................................................................................................17
6 FAQ........................................................................................................................................... 18
7 Glossary................................................................................................................................... 20
8 Reference Documents...........................................................................................................21
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 1 Change History
1 Change History
This chapter describes changes not included in the "Parameters", "Counters",
"Glossary", and "Reference Documents" chapters. These changes include:
● Technical changes
Changes in functions and their corresponding parameters
● Editorial changes
Improvements or revisions to the documentation
1.1 SRAN16.1 01 (2020-03-30)
This issue includes the following changes.
Technical Changes
None
Editorial Changes
Revised descriptions in this document.
1.2 SRAN16.1 Draft A (2020-01-20)
This issue introduces the following changes to SRAN15.1 01 (2019-06-06).
Technical Changes
Change Description Parameter Change
Changed the name of U2020 to None
MAE-Access and the name of CME to
MAE-Deployment.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 1 Change History
Editorial Changes
Reorganized this document using a new template.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 2 About This Document
2 About This Document
2.1 General Statements
Purpose
Feature Parameter Description documents are intended to acquaint readers with:
● The technical principles of features and their related parameters
● The scenarios where these features are used, the benefits they provide, and
the impact they have on networks and functions
● Requirements of the operating environment that must be met before feature
activation
● Parameter configuration required for feature activation, verification of feature
activation, and monitoring of feature performance
This document only provides guidance for feature activation. Feature deployment and
feature gains depend on the specifics of the network scenario where the feature is
deployed. To achieve the desired gains, contact Huawei professional service engineers.
Software Interfaces
Any parameters, alarms, counters, or managed objects (MOs) described in Feature
Parameter Description documents apply only to the corresponding software
release. For future software releases, refer to the corresponding updated product
documentation.
Trial Features
Trial features are features that are not yet ready for full commercial release for
certain reasons. For example, the industry chain (terminals/CN) may not be
sufficiently compatible. However, these features can still be used for testing
purposes or commercial network trials. Anyone who desires to use the trial
features shall contact Huawei and enter into a memorandum of understanding
(MoU) with Huawei prior to an official application of such trial features. Trial
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 2 About This Document
features are not for sale in the current version but customers may try them for
free.
Customers acknowledge and undertake that trial features may have a certain
degree of risk due to absence of commercial testing. Before using them, customers
shall fully understand not only the expected benefits of such trial features but also
the possible impact they may exert on the network. In addition, customers
acknowledge and undertake that since trial features are free, Huawei is not liable
for any trial feature malfunctions or any losses incurred by using the trial features.
Huawei does not promise that problems with trial features will be resolved in the
current version. Huawei reserves the rights to convert trial features into
commercial features in later R/C versions. If trial features are converted into
commercial features in a later version, customers shall pay a licensing fee to
obtain the relevant licenses prior to using the said commercial features. If a
customer fails to purchase such a license, the trial feature(s) will be invalidated
automatically when the product is upgraded.
2.2 Applicable RAT
This document applies to GSM, UMTS, LTE FDD, LTE TDD, NB-IoT, and NR.
For definitions of base stations described in this document, see section "Base
Station Products" in SRAN Networking and Evolution Overview Feature Parameter
Description.
2.3 Features in This Document
This document describes the following features.
Feature ID Feature Name Chapter/Section
MRFD-210301 Configuration 3 Overview
Management
LBFD-004007 Configuration
Management
MLBFD-12000407 Configuration
Management
TDLBFD-004007 Configuration
Management
FBFD-010025 Configuration
Management in Basic
O&M Package
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 3 Overview
3 Overview
3.1 Definition
Configuration management allows users to manage configuration data of
network devices. This controls the running status of network devices and provides
effective network O&M.
3.2 Application Scenarios
A configuration management system is required throughout the network's entire
O&M cycle to allow users to perform the following:
● During network deployment, users can initialize configuration data and
configure network device data.
● During network adjustment and optimization, a configuration management
system allows users to rapidly and accurately modify configuration data for
scenarios such as new feature activation, network capacity expansion,
transmission reconstruction, base station migration, and wireless network
performance optimization.
● During network maintenance, users can monitor, compare, analyze, and
modify configuration data.
3.3 Architecture
Radio access networks (RANs) are divided into three layers:
● Network element layer (NEL)
● Element management layer (EML)
● Network management layer (NML)
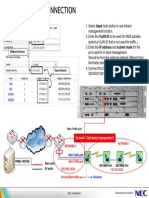
Accordingly, as shown in Figure 3-1, the configuration management architecture
consists of three layers.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 3 Overview
Figure 3-1 Configuration management architecture
3.3.1 NEL
NEL allows users to modify single-NE configuration parameters through a man-
machine language (MML) interface of the local maintenance terminal (LMT), an
MML client integrated with the MAE, or the MAE-Deployment integrated with the
MAE.
● Base stations provide both RAN non-real-time (RAN-NRT) and RAN real-time
(RAN-RT) functions.
Base Station Deployment
Figure 3-2 shows the configuration model. Base stations provide a unified O&M
channel for configuration management.
Figure 3-2 NEs in the traditional base station deployment
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 3 Overview
3.3.2 EMS
EMS allows users to modify and manage single-subnet configuration parameters.
Huawei provides the professional configuration solution MAE-Deployment to
implement EMS-layer configuration management. The MAE-Deployment centrally
manages a SingleRAN network and provides man-machine interaction wizards
and scenario-based designs to efficiently adjust networks in complex scenarios. It
also provides the northbound interface (Itf-N) for integration with an upper-layer
NMS. In principle, all configuration operations are recommended to be performed
on the MAE-Deployment.
The Itf-N is an open interface between the Huawei's EMS and a telecom operator's upper-
layer NMS.
3.3.3 NMS
NMS involves configuration management for the entire network with a focus on
connection to multiple vendors' EMSs. Huawei MAE-Deployment is connected to a
telecom operator's NMS through the Itf-N. An NMS usually has a network
planning system. After making parameter modification decisions, the network
planning system sends parameter modification information to the MAE-
Deployment through the Itf-N. The MAE-Deployment then modifies parameters.
3.4 Configuration Security
Configuration management provides a series of security measures to protect
configuration data. For details, see OM Security Feature Parameter Description.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
4 Typical Application Scenarios
4.1 Network Deployment
Introduction
Configuration management in this scenario specifies configuring data for newly
deployed base station controllers or base stations.
For example, the deployment of new NodeBs or eNodeBs is further divided into
the following three sub-scenarios according to the quantity of new base stations
and configuration data differences between the new and existing base stations:
● Either a small number of base stations will be deployed or no base station
has been deployed on the live network.
● A large number of base stations will be deployed and significant differences
exist between new and existing base station configuration data.
● A large number of base stations will be deployed and slight differences exist
between new and existing base station configuration data.
Recommended Configuration Functions
To deploy a new base station controller, users can perform MML batch
configuration on the LMT or MAE. Alternatively, users can configure data using
the MAE-Deployment general configuration window, device panel, and transport-
and radio-layer planning data.
To deploy a new base station, it is recommended that the MAE-Deployment be
used. Table 4-1 describes the recommended configuration functions.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Table 4-1 Recommended configuration functions for new base station deployment
Scenario Configuration Function Description
Either a small number of Single base station Create the first base
base stations will be deployment using the station and use its
deployed or no base wizard configuration data as a
station has been template for batch
deployed on the live deployment of the
network. remaining base stations.
A large number of base Batch base station Use the template for
stations will be deployed deployment by identical configuration
and significant customizing a summary data among base
differences exist between data file stations and customize
new and existing base configuration data that
station configuration is different among the
data. base stations.
A large number of base Batch base station Apply the sample base
stations will be deployed deployment using a station data for identical
and slight differences summary data file based configuration data
exist between new and on the exported and among base stations and
existing base station customized managed manually customize
configuration data. object class (MOC) configuration data that
is different among base
stations.
Process
Figure 4-1 shows the single base station deployment process using the wizard.
Figure 4-1 Single base station deployment using the wizard
Figure 4-2 shows the batch base station deployment process by customizing a
summary data file.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Figure 4-2 Batch base station deployment by customizing a summary data file
Figure 4-3 shows the batch base station deployment process using a summary
data file based on the exported and customized MOC.
Figure 4-3 Batch base station deployment using a summary data file based on the
exported and customized MOC
4.2 Network Adjustment
Introduction
Configuration management in this scenario specifies adjusting networks in which
services are not evenly distributed. Network adjustment involves the following
scenarios:
● Device capacity expansion
For example, adding a service processing board or interface board for an
existing base station or base station controller.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
● Transmission adjustment
This includes transmission capacity expansion and transmission
reconstruction. For example, adjusting the clock unit and virtual local area
network (VLAN).
● Cell or carrier capacity expansion
For example, changing the NodeB configuration from 3x1 to 3x2.
● Base station reconstruction
The typical scenarios include radio access technology (RAT) addition and co-
MPT base station reconstruction.
– RAT addition refers to adding new RATs to a co-MPT base station. For
example, add LTE to a co-MPT G*U base station to make it a co-MPT
G*U*L base station.
– Co-MPT base station reconstruction refers to changing a separate-MPT
base station to a co-MPT base station. For example, change a separate-
MPT G&U base station to a co-MPT G*U base station.
● Other complex scenarios
Complex network adjustment scenarios may simultaneously involve device,
transport, and radio data adjustment, such as base station migration, BSC
node redundancy, and RNC pool configuration.
Recommended Configuration Functions
Table 4-2 describes the recommended configuration functions for network
adjustment.
Table 4-2 Recommended functions for network adjustment
Scenario Configuration Function Description
Device Base stations: Import and -
capacity export of batch configuration
expansion data on the MAE-Deployment
Base station controllers: Use
the MAE-Deployment general
configuration window and the
device panel
Transmission Base stations: Import and -
adjustment export of batch configuration
data on the MAE-Deployment
Base station controllers:
Import and export of Abis or
Iub batch configuration data
on the MAE-Deployment
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Scenario Configuration Function Description
Cell or carrier Single base station: Radio -
capacity data configuration using the
expansion carrier resource management
(CRM)
Batch base stations: Import
and export of adjusted radio
frequency data
RAT addition Single base station: NE -
shortcut menu on the MAE-
Deployment graphical user
interface (GUI)
Batch base stations:
Customized summary data
files using the MAE-
Deployment as well as import
and export of batch
configuration data
Co-MPT base Data configuration conversion Co-MPT base station
station wizard for co-MPT base reconstruction involves device,
reconstruction station reconstruction on the transport, and radio data
MAE-Deployment conversion.
Radio data reconstruction only
involves radio, remote radio
unit (RRU), and baseband
processing unit (BBP) data
conversion.
Base station MAE-Deployment migration During a base station
migration wizard migration within a BSC/RNC or
across BSCs/RNCs, users only
need to plan transport
parameters and certain radio
parameters. The MAE-
Deployment can automatically
adjust the relations among the
source BSCs/RNCs, destination
BSCs/RNCs, and neighboring
NEs. No manual operation is
required.
BSC node BSC node redundancy The MAE-Deployment
redundancy configuration on the MAE- supports batch changes from
Deployment single-homed GBTSs/eGBTSs
to dual-homed GBTSs/eGBTSs
or dual-homed GBTSs/eGBTSs
to single-homed GBTSs/
eGBTSs and data checks.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Scenario Configuration Function Description
RNC pool RNC pool configuration on the The MAE-Deployment
configuration MAE-Deployment supports batch changes from
single-homed NodeBs to dual-
homed NodeBs or dual-homed
NodeBs to single-homed
NodeBs and data checks.
4.3 Feature Activation
Introduction
Configuration management in this scenario specifies configuring data to activate a
new feature on a legacy network, such as, the Carrier Aggregation feature after
the deployment of an eNodeB.
Recommended Configuration Functions
Recommended configuration functions on the MAE-Deployment include feature
status query, batch feature activation, and validity checks. For details, in MAE-
Deployment Product Documentation, see MAE-Deployment Management >
MAE-Deployment Guidelines > MAE-Deployment Feature Description >
Feature OM Management.
4.4 Network Optimization
Introduction
Configuration management in this scenario specifies adjusting parameters of a
running network to provide better network services. Compared with network
adjustment, network optimization focuses more on radio-layer parameter
adjustment.
The MAE-Deployment supports the following tasks for network optimization:
● Batch adjustment of frequencies or scrambling codes in a cell
● Batch adjustment of neighboring cells or neighboring cells' BCCH allocation
(BA) data
● Batch algorithm parameter adjustment for cells, carriers, and channels
● Data reconfiguration of certain service features, such as reconstructing a cell
that uses High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) and changing the operator to
which a cell belongs in a multi-operator core network (MOCN)
Recommended Configuration Functions
Table 4-3 describes multiple batch data modification methods using the MAE-
Deployment.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Table 4-3 Recommended functions for network optimization
Configuration Description Application Scenario
Function
Importing data To quickly adjust data in This method is
from data batches, export a summary applicable if users
planning files data file, modify the data, and configure different
import the file. values for multiple
objects. The MAE-
Deployment provides
multiple data planning
files for different
network optimization
tasks.
Modifying data in Select some or all of the This method is
batches by using configuration parameters for applicable if users
the wizard an object as a reference and configure parameters to
apply these parameters to the same value for a
another object. single type of objects.
Reconfiguring The MAE-Deployment provides N/A
data for some a configuration wizard that
service features supports one-click
configuration for an object.
Importing data After the data is configured, This method is
from XML files the MAE-Deployment exports applicable if the MAE-
through the configuration data files in Deployment is connected
northbound either MML or XML format for to the 3GPP R6-
interface each NE. Users can use the compliant northbound
script executor provided by the interface of the telecom
MAE-Deployment to remotely operator's NMS.
deliver and activate the
configuration data files to each
NE through the MAE.
4.5 Network Maintenance
Introduction
Configuration management in this scenario specifies implementing routine
inspection on configuration parameters for a running network, including
parameter browsing, checks, and analysis. Configuration parameters are not
modified and the services on the live network are not affected.
Recommended Configuration Functions
Table 4-4 describes the recommended configuration functions for network
maintenance.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Table 4-4 Recommended configuration functions for network maintenance
Scenario Configuration Description
Function
Paramete Global data The data browsing and search functions help
r browsing users effectively locate required information
browsing and prepare for the next step in planning and
adjustment.
The MAE-Deployment provides the global data
browsing and data search functions. Users can
browse configuration information about
different objects, such as port usages of each
interface board and the number of neighbor
relationships configured for each cell. In
addition, users can search for required objects
by defining search criteria.
Configuration The MAE-Deployment provides configuration
reports reports for various scenarios during network
maintenance. The reports can be saved in
multiple formats, where users can view data for
different versions of multiple NEs on the live
network. In addition, the MAE-Deployment
allows for statistics collection on the entire
network.
Paramete Global data check A network generates a large amount of data
r check and the correlations between configuration
objects are complex.
The MAE-Deployment checks the integrity,
redundancy and consistency of configuration
data, and generates an error report. It also
automatically recovers certain data according
to check results.
Configuration The MAE-Deployment allows users to compare
change history NE configuration parameters at different times
management and export NE configuration parameters at a
specified time.
Paramete Parameter During the initial phase of network
r analysis comparison construction, algorithm parameters use the
system default baseline data. During network
maintenance and optimization, users can
modify certain algorithm parameters according
to network performance.
The MAE-Deployment provides comparison
between the actual values of the algorithm
parameters for a base station, controller, or cell
with the default values or configuration
baseline data for subsequent adjustment.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 4 Typical Application Scenarios
Scenario Configuration Description
Function
Parameter filter The MAE-Deployment provides default
parameter sets, also known as parameter
filters, according to different NEs and versions
to help users quickly select the parameters to
be compared. In addition, users can customize
parameter filters.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 5 Related Documentation
5 Related Documentation
The NE configuration management documentation is as follows:
● Product documentation: Initial Configuration Guide, Reconfiguration Guide,
MML Command Reference, and MO and Parameter Reference
● Feature documentation: Feature Parameter Description
● Release documentation: MML Command Changes, MO and Parameter
Changes, Reserved Parameter List, and Disuse Parameter List
● Northbound documentation: Northbound Parameter Changes and
Northbound Parameter List
The configuration management tool documentation is as follows:
● LMT: LMT User Guide
● MAE: MAE MBB Network Management System Product Documentation
● MAE-Deployment: MAE-Deployment Product Documentation
The preceding documentation can be obtained from http://support.huawei.com.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 6 FAQ
6 FAQ
Definition
A parameter involves attributes of an NE configuration object, while a parameter
value is configured for each attribute.
Each parameter has multiple fields, such as Parameter ID, Parameter Name, NE,
MML Command, Meaning, and IsKey. For detailed attribute lists, see parameter
references.
Setting Modes
● Manual settings: Parameter values are manually planned and adjusted.
● Automatic setting: Configuration data is automatically generated. For
example, boards are automatically added after addition of a subrack, or
parameter values are automatically generated using the self-organizing
network (SON).
Branch Parameters
Branch parameters take effect only when certain conditions are met. If certain
conditions are not met, a system cannot obtain a parameter value and the branch
parameter does not take effect. Parameter Relationship in parameter references
provides parameter relationship with conditions.
Mandatory attributes of a branch parameter are configured according to the
following principles:
● If a branch parameter is mandatory and in a default branch relationship,
Mandatory is set to YES.
● Otherwise, Mandatory is set to NO.
For example, if a branch parameter is not in a default branch relationship, Mandatory
is set to NO regardless that the parameter is mandatory under the branch
relationship.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 6 FAQ
Northbound Parameter Disuse
The status of northbound parameters during a disuse period (N to N+2 versions)
is shown in Figure 6-1.
Figure 6-1 Northbound parameter disuse
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 7 Glossary
7 Glossary
For the acronyms, abbreviations, terms, and definitions, see Glossary.
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
SingleRAN
Configuration Management Feature Parameter
Description 8 Reference Documents
8 Reference Documents
None
Issue 01 (2020-03-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
You might also like
- Iu Flex (RAN16.0 - 01)Document74 pagesIu Flex (RAN16.0 - 01)hekriNo ratings yet
- Fault Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Document49 pagesFault Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Trace Server Parameter SettingsDocument5 pagesTrace Server Parameter SettingssostashkinNo ratings yet
- High Speed Mobility (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Document160 pagesHigh Speed Mobility (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Denmark WilsonNo ratings yet
- Cell Management Feature Parameter Description: Eran TDDDocument90 pagesCell Management Feature Parameter Description: Eran TDDJuanNo ratings yet
- GBSS14.0 Optional Feature DescriptionDocument359 pagesGBSS14.0 Optional Feature DescriptionDhananjay ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- SUM-SB-SPE-0425 - WUB - 325C304G9 - C304 - Tanjung AruDocument146 pagesSUM-SB-SPE-0425 - WUB - 325C304G9 - C304 - Tanjung AruIzzatullahAryasatya0% (1)
- v16 5g-AusfDocument50 pagesv16 5g-Ausfkk lNo ratings yet
- Useful Tips For EMS - V3.1Document62 pagesUseful Tips For EMS - V3.1arinal09100% (1)
- Gu Hlr9820 v900r006c03 16 - Training Slides On Sdmt-2010325-B-1.0Document28 pagesGu Hlr9820 v900r006c03 16 - Training Slides On Sdmt-2010325-B-1.0Syed TassadaqNo ratings yet
- Guide To Obtaining BSC6900 InformationDocument49 pagesGuide To Obtaining BSC6900 InformationSunny HaqNo ratings yet
- Iu Flex (RAN15.0 - 02)Document97 pagesIu Flex (RAN15.0 - 02)Firmansyah HermanaNo ratings yet
- 3G CBSDocument44 pages3G CBSOrgilbayar PurevkhuuNo ratings yet
- Summary of Resolved Issues in BTS3900 V100R012C10SPC320 (eGBTS)Document82 pagesSummary of Resolved Issues in BTS3900 V100R012C10SPC320 (eGBTS)richardo simanullangNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 Communication Matrix (V900R019C10 - 04) (XLS) - ENDocument47 pagesBSC6900 Communication Matrix (V900R019C10 - 04) (XLS) - ENwaelq2003No ratings yet
- HUAWEI BSC6000 Hardware Structure and System Description For V900R003-20071106-A-3.0Document87 pagesHUAWEI BSC6000 Hardware Structure and System Description For V900R003-20071106-A-3.0inf018No ratings yet
- GSM R Hlr9820Document0 pagesGSM R Hlr9820futronoNo ratings yet
- ZTE GU NetNumen M31 (RAN) Product DescriptionDocument45 pagesZTE GU NetNumen M31 (RAN) Product DescriptionMutasem Younes100% (2)
- Hlr9h LST Sub ResultDocument270 pagesHlr9h LST Sub ResultPhillip Ramirez0% (1)
- SJ-20150919164026-001-ZXUN IEPC (V1.15.10) Integrated Evolved Packet Core Product DescriptionDocument38 pagesSJ-20150919164026-001-ZXUN IEPC (V1.15.10) Integrated Evolved Packet Core Product DescriptionK OuertaniNo ratings yet
- Huawei CG9812Document520 pagesHuawei CG9812mike100% (1)
- ATN 910I Product Brochure PDFDocument4 pagesATN 910I Product Brochure PDFricardo bendita laricoNo ratings yet
- IManager M2000 V200R013 Optional Feature Description (GSM&UMTS<E)Document203 pagesIManager M2000 V200R013 Optional Feature Description (GSM&UMTS<E)SokratesNo ratings yet
- UE Distance EricssonDocument188 pagesUE Distance EricssonVan-Bien TaNo ratings yet
- Base Station OMCH Self-Recovery (SRAN12.1 - 01)Document30 pagesBase Station OMCH Self-Recovery (SRAN12.1 - 01)anthonyNo ratings yet
- Licensed Assisted Access (eRAN12.1 - 06)Document103 pagesLicensed Assisted Access (eRAN12.1 - 06)waelq2003No ratings yet
- R8854S2600.User Manual Part 3 3787010Document22 pagesR8854S2600.User Manual Part 3 3787010Ivan StevkovskiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers (eRAN17.1 - 02)Document65 pagesDynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers (eRAN17.1 - 02)Por HengNo ratings yet
- c03 - bsc6900 Umts v900r016c00spc650 Release NotesDocument380 pagesc03 - bsc6900 Umts v900r016c00spc650 Release NotesMuntazir MehdiNo ratings yet
- Base Station OMCH Self-Recovery (SRAN18.1 - 02)Document32 pagesBase Station OMCH Self-Recovery (SRAN18.1 - 02)VVL1959No ratings yet
- ELTE2.3 DBS3900 LTE TDD Basic Feature DescriptionDocument92 pagesELTE2.3 DBS3900 LTE TDD Basic Feature DescriptioneuniceikaNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 23.216Document67 pages3GPP TS 23.216VeaceslavRomanNo ratings yet
- Smart Deployment Toolkit Propaganda Slides (V1R2) : Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Huawei ConfidentialDocument19 pagesSmart Deployment Toolkit Propaganda Slides (V1R2) : Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Huawei ConfidentialHerdi KNo ratings yet
- GU - NetNumen U31 R18 V12.18 Test Guide - Distributed - R1.0Document300 pagesGU - NetNumen U31 R18 V12.18 Test Guide - Distributed - R1.0Mohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- RAN18.1 Capacity Monitoring Guide (BSC6910-Based) (03) (PDF) - enDocument82 pagesRAN18.1 Capacity Monitoring Guide (BSC6910-Based) (03) (PDF) - enAnonymous iAYcAhNo ratings yet
- License Control Item Lists (5G RAN2.1 - Draft A)Document8 pagesLicense Control Item Lists (5G RAN2.1 - Draft A)Mohammed Mokhtar100% (1)
- 8DG43091JAAA - V1 - 1350 OMS OIS TMF814 CORBA Interface Specification, 12.3, Issue 1Document552 pages8DG43091JAAA - V1 - 1350 OMS OIS TMF814 CORBA Interface Specification, 12.3, Issue 1Yves MarianoNo ratings yet
- BSC6910 Configuration Principle (Global) (V100R018C10 01) (PDF) - enDocument116 pagesBSC6910 Configuration Principle (Global) (V100R018C10 01) (PDF) - enFrans RapetsoaNo ratings yet
- ECore V100R018C50 Product OverviewDocument34 pagesECore V100R018C50 Product OverviewRegisNo ratings yet
- 02-NB-IoT Air Interface ISSUEDocument90 pages02-NB-IoT Air Interface ISSUEThang DangNo ratings yet
- Soft-Synchronized Network (GBSS16.0 01)Document122 pagesSoft-Synchronized Network (GBSS16.0 01)Wael AlkodamiNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Sharing of Multimode Base Station Co-Transmission (SRAN18.1 - 01)Document72 pagesBandwidth Sharing of Multimode Base Station Co-Transmission (SRAN18.1 - 01)monem777No ratings yet
- 2-ACP SSB Coverage Optimization (Based DT) - 202203Document29 pages2-ACP SSB Coverage Optimization (Based DT) - 202203Emerson Eduardo RodriguesNo ratings yet
- ZXUR 9000 GSM Radio Parameter: Operator LogoDocument18 pagesZXUR 9000 GSM Radio Parameter: Operator LogoHasanNo ratings yet
- Mobility Management in Connected Mode (ERAN3.0 - 07)Document359 pagesMobility Management in Connected Mode (ERAN3.0 - 07)Sergio BuonomoNo ratings yet
- OWG000203 MSOFTX3000 Local Office Data Configuration ISSUE 1.2Document45 pagesOWG000203 MSOFTX3000 Local Office Data Configuration ISSUE 1.2Hoàng Quốc VươngNo ratings yet
- Cell Broadcast (GBSS22.1 - 03)Document43 pagesCell Broadcast (GBSS22.1 - 03)Danilo HuamaniNo ratings yet
- HedEx Lite V200R003C30 Upgrade GuideDocument11 pagesHedEx Lite V200R003C30 Upgrade Guidehilal288No ratings yet
- Access Control Based On 802.1x (SRAN18.1 - 02)Document29 pagesAccess Control Based On 802.1x (SRAN18.1 - 02)VVL1959No ratings yet
- Dopra Linux OS Security (SingleRAN - 20)Document57 pagesDopra Linux OS Security (SingleRAN - 20)waelq2003No ratings yet
- Du Lieu Dong Bo Tham So 4GDocument391 pagesDu Lieu Dong Bo Tham So 4GHa ThanhNo ratings yet
- Oss License DescDocument173 pagesOss License Deschawdang nuree100% (1)
- BTS3900 V100R012C00 ENodeBFunction Used Reserved Parameter List Draft B (2016!08!08)Document34 pagesBTS3900 V100R012C00 ENodeBFunction Used Reserved Parameter List Draft B (2016!08!08)phonephreak100% (1)
- UGW9811 V900R011C00SPC200 Upgrade GuideDocument81 pagesUGW9811 V900R011C00SPC200 Upgrade GuideCheikh Ahmet Tidiane DiengNo ratings yet
- RAN Sharing Huawei GBSS RAN12Document19 pagesRAN Sharing Huawei GBSS RAN12ambroserfNo ratings yet
- Configuration Management (SRAN16.1 01)Document22 pagesConfiguration Management (SRAN16.1 01)VVLNo ratings yet
- Performance Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Document26 pagesPerformance Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier Sepulveda100% (1)
- Uplink Data Compression (ERAN18.1 - 01)Document21 pagesUplink Data Compression (ERAN18.1 - 01)monem777No ratings yet
- Inventory Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Document20 pagesInventory Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- PASOLINKV3Document56 pagesPASOLINKV3Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- 0-Safety PasolinkV4Document6 pages0-Safety PasolinkV4Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- NOKIA INSTRUCIONESHow To Create Q1-ch Over DXX - 030901Document18 pagesNOKIA INSTRUCIONESHow To Create Q1-ch Over DXX - 030901Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- 1.2-Appx Measurement Proc (S460754e) PasolinkV4Document30 pages1.2-Appx Measurement Proc (S460754e) PasolinkV4Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Net CFG ToolDocument209 pagesNet CFG ToolDidier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Catalog 051007 1Document2 pagesCatalog 051007 1Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- AN-RFC2544 Ethernet TestingDocument2 pagesAN-RFC2544 Ethernet TestingDidier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- 2-TRP Eq Descr (S460557e) PasolinkV4Document52 pages2-TRP Eq Descr (S460557e) PasolinkV4Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- 02 - LCT - OptionCard - FPGA Data - Update - ProcedureDocument14 pages02 - LCT - OptionCard - FPGA Data - Update - ProcedureDidier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Flexi Zone Micro BTSDocument51 pagesTroubleshooting Flexi Zone Micro BTSDidier Sepulveda100% (1)
- NMS in - BandDocument1 pageNMS in - BandDidier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Performance Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Document26 pagesPerformance Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier Sepulveda100% (1)
- Configuracion Ancho de Banda Servicios Eth HUAWEIDocument8 pagesConfiguracion Ancho de Banda Servicios Eth HUAWEIDidier Sepulveda0% (1)
- Fma (Sran16.1 02)Document92 pagesFma (Sran16.1 02)Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- WCDMA DBS3900 Estructura de HardwareDocument40 pagesWCDMA DBS3900 Estructura de HardwareWilson PerezNo ratings yet
- User Manual RADWIN 2000 PDFDocument503 pagesUser Manual RADWIN 2000 PDFDario Campos AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- User Manual 2+Document276 pagesUser Manual 2+Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- User Manual 5Document252 pagesUser Manual 5Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Document20 pagesInventory Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Software Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Document18 pagesSoftware Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- User Manual RADWIN 2000 PDFDocument503 pagesUser Manual RADWIN 2000 PDFDario Campos AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- User Manual 5Document252 pagesUser Manual 5Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- User Manual 2+Document276 pagesUser Manual 2+Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide: RADWIN 5000Document75 pagesInstallation Guide: RADWIN 5000Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- User Manual 1 RadwinDocument376 pagesUser Manual 1 RadwinMustre_saxNo ratings yet
- MIB ReferenceDocument97 pagesMIB ReferenceDidier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide: RADWIN 5000Document75 pagesInstallation Guide: RADWIN 5000Didier SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- User Manual 1 RadwinDocument376 pagesUser Manual 1 RadwinMustre_saxNo ratings yet
- Deathsmiles ManualDocument11 pagesDeathsmiles ManualJotamideNo ratings yet
- HTML Advancedtables, Lists & Links - Chapter 6 TOPIC - 1 Lists and Links Objective Type QuestionsDocument38 pagesHTML Advancedtables, Lists & Links - Chapter 6 TOPIC - 1 Lists and Links Objective Type QuestionsVikas ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Exchange 2010 Q&ADocument87 pagesExchange 2010 Q&Akunwar_sdNo ratings yet
- Instalación y Configuración de MailWatcahDocument6 pagesInstalación y Configuración de MailWatcahLuis Miguel HDNo ratings yet
- 8230e DELL Vostro 3350 Wistron Nirvana 13 PDFDocument104 pages8230e DELL Vostro 3350 Wistron Nirvana 13 PDFanh_sao_dem_92No ratings yet
- DBC Format 2007Document17 pagesDBC Format 2007thoroftedal100% (1)
- Enhancing An End User Development in Database Design Using Entity Relationship Diagram MapperDocument12 pagesEnhancing An End User Development in Database Design Using Entity Relationship Diagram MapperHussain Al-A'aliNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance Claim Management SystemDocument14 pagesHealth Insurance Claim Management SystemTaj SNo ratings yet
- COD4 CrackDocument1 pageCOD4 CrackRalph Kervie Stephen ChanNo ratings yet
- HTML TheoryDocument43 pagesHTML TheorySagarMaherNo ratings yet
- USB Interfaced Ultra-High Speed Low Cost Universal Device ProgrammerDocument2 pagesUSB Interfaced Ultra-High Speed Low Cost Universal Device ProgrammerImran ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Design of Analytical Model and Algorithm For Optimal Roadside Ap Placement in VanetsDocument11 pagesDesign of Analytical Model and Algorithm For Optimal Roadside Ap Placement in VanetsArash AziminejadNo ratings yet
- BL-1300 Um 374GB GB WW 1123-1Document308 pagesBL-1300 Um 374GB GB WW 1123-1Ramon Cavaco0% (1)
- OPC XML-DA Demonstration DOKU v10 eDocument34 pagesOPC XML-DA Demonstration DOKU v10 eSergiogranjeiroNo ratings yet
- Advanced SQL Lab 2Document2 pagesAdvanced SQL Lab 2Nyaboke OlyviahNo ratings yet
- Piratenation PDFDocument237 pagesPiratenation PDFsunilNo ratings yet
- A First Step Towards Understanding Popularity in Youtube: Gloria Chatzopoulou, Cheng Sheng, Michalis FaloutsosDocument6 pagesA First Step Towards Understanding Popularity in Youtube: Gloria Chatzopoulou, Cheng Sheng, Michalis Faloutsosbeepee14No ratings yet
- A Literature Review of The Use of Web 2.0 Tools in Higher Education by Conole - Alevizou - 2010Document111 pagesA Literature Review of The Use of Web 2.0 Tools in Higher Education by Conole - Alevizou - 2010Kangdon LeeNo ratings yet
- Baby Thesis Chapter 1Document6 pagesBaby Thesis Chapter 1rebeccabordescambridge100% (2)
- Evaluation of Online Tools: Dos and Don'ts: Unit 4Document28 pagesEvaluation of Online Tools: Dos and Don'ts: Unit 4DANNY PAUCARNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TrainingDocument1 pageBluetooth TrainingsyedtNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quizz - Exec HMDocument5 pagesTake Home Quizz - Exec HMbeshfrend'z0% (1)
- 7 VK 61Document18 pages7 VK 61api-241473079No ratings yet
- BHEL Spec For VFD and Dry Type TransformerDocument93 pagesBHEL Spec For VFD and Dry Type TransformerKarthikeyan GuruNo ratings yet
- (B0566) P. Hodgeson - Quenching and Carburising-Maney Materials Science (1993) PDFDocument319 pages(B0566) P. Hodgeson - Quenching and Carburising-Maney Materials Science (1993) PDFZerina ČustovićNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling and Virtual Manufacturing of A Machine Component Using CATIA V5 and MASTERCAMDocument2 pages3D Modeling and Virtual Manufacturing of A Machine Component Using CATIA V5 and MASTERCAMHIMANSU SEKHAR BEHERANo ratings yet
- Internal - Audit - Manual - World Intellectual PropertyDocument25 pagesInternal - Audit - Manual - World Intellectual PropertyEric AnastacioNo ratings yet
- LogDocument2 pagesLogMohd WaqarNo ratings yet
- Social Media Cyberspace Bangalore UniversityDocument43 pagesSocial Media Cyberspace Bangalore UniversityRupesh Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Hair Salon Management SystemDocument3 pagesHair Salon Management SystemRahul Jalavadiya33% (3)