Professional Documents
Culture Documents
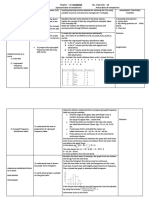
Scores of Students in 50-Item Test: Data Range Frequency 1 - 10 1 11 - 20 4 21 - 30 6 31 - 40 3 41 - 50 2
Uploaded by
Christopher Cabanag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageA histogram is a graph that shows the distribution of data within equal intervals by displaying the frequency of data ranges. It differs from a bar graph by showing frequency ranges rather than individual data points. To create a histogram, the data is grouped into intervals called bins, the frequency of each bin is determined, and bars are drawn next to each other without gaps to represent each bin's frequency. An example demonstrates grouping test scores into bins of equal width and determining the frequency in each bin to construct the histogram.
Original Description:
Original Title
Histogram
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA histogram is a graph that shows the distribution of data within equal intervals by displaying the frequency of data ranges. It differs from a bar graph by showing frequency ranges rather than individual data points. To create a histogram, the data is grouped into intervals called bins, the frequency of each bin is determined, and bars are drawn next to each other without gaps to represent each bin's frequency. An example demonstrates grouping test scores into bins of equal width and determining the frequency in each bin to construct the histogram.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageScores of Students in 50-Item Test: Data Range Frequency 1 - 10 1 11 - 20 4 21 - 30 6 31 - 40 3 41 - 50 2
Uploaded by
Christopher CabanagA histogram is a graph that shows the distribution of data within equal intervals by displaying the frequency of data ranges. It differs from a bar graph by showing frequency ranges rather than individual data points. To create a histogram, the data is grouped into intervals called bins, the frequency of each bin is determined, and bars are drawn next to each other without gaps to represent each bin's frequency. An example demonstrates grouping test scores into bins of equal width and determining the frequency in each bin to construct the histogram.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
HISTOGRAM. It is a graph that shows frequencies of data within equal intervals.
The main difference
between a normal bar graph and a histogram is that a bar graph shows you the frequency of each element in a
set of data, while a histogram shows you the frequencies of a range of data. Unlike the bars on a bar graph, the
bars on the histogram are next to each other without a gap, unless there is an interval that has a frequency of
zero.
To make a histogram: (1) Draw and label the horizontal axis and the vertical axis. The horizontal axis
shows the intervals; the vertical axis shows the frequencies. (2) Use the least and greatest values in the data
to choose a sensible scale for the frequencies. Use intervals of the same size
throughout the scale. (3) Label equal spaces along the horizontal axis. (4) Data Frequency
Draw bars without any gaps in between to show the frequency of each Range
interval. Do not omit any interval, even if an interval has a frequency of 0. 1 – 10 1
(5) Write a title for the graph. 11 – 20 4
Example 4: Take the following scores of 16 students in a 50-item test:
3,11,12,12,19, 22, 23, 24, 25, 27, 29, 35, 36, 37,45, 49.
21 – 30 6
Solution: 31 – 40 3
41 - 50 2
Scores of Students in 50-item Test First, we group
the data into convenient
7
6 ranges, called bins. In this
5 example we are going to
Frequency
4 group the data in bins with
3 a width of 10 each.
2 Changing the size of the
1
bin will change the
0
1 – 10 11 – 20 21 – 30 31 – 40 41 - 50 appearance of the graph.
Scores Next, we draw a frequency
table with the data range
divided in the different
bins. Then we tally the data, placing it in the correct bin.
Finally, we can draw the histogram by placing the bins on the horizontal axes and the frequency on
the vertical axes.
You might also like
- Scores of Students in 50-Item TestDocument2 pagesScores of Students in 50-Item TestChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE HistogramDocument2 pagesEXAMPLE HistogramCy SyNo ratings yet
- HistogramDocument1 pageHistogramCy SyNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Continuous VariablesDocument13 pagesStatistics: Continuous VariablesmchstpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BFC34303Document104 pagesChapter 1 BFC34303alipNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Frequency Distribution: HistogramDocument13 pagesGraphs of Frequency Distribution: HistogramRajNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Chapter 22U Statistics 2023Document12 pagesYr10 Chapter 22U Statistics 2023SplashMixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BFC34303 (Lyy)Document104 pagesChapter 1 BFC34303 (Lyy)shahrull1996No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Data DescriptionDocument93 pagesChapter 7 Data DescriptionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document17 pagesLecture 04Abdur RafayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2,3 - Chapter 2 - Organizing and Graphing DataDocument46 pagesLecture-2,3 - Chapter 2 - Organizing and Graphing DataZafar Ibn Kader 2013819030No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BFC34303Document104 pagesChapter 1 BFC34303F100% (1)
- Module 13 - Organizing DataDocument14 pagesModule 13 - Organizing DataXyrelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- IX StatisticDocument3 pagesIX StatisticVenkatachalam KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument49 pagesLecture 1 PDFPorkkodi Sugumaran0% (1)
- Measures of Spread 2Document8 pagesMeasures of Spread 2Jattawee MarkNo ratings yet
- Module in Statistic Data RepresentationDocument12 pagesModule in Statistic Data RepresentationCarmela UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems On Data Analysis: What Is Your Favorite Class?Document8 pagesSample Problems On Data Analysis: What Is Your Favorite Class?ainaNo ratings yet
- PRESENTATION OF DATA-sampling TechniquesDocument9 pagesPRESENTATION OF DATA-sampling TechniquesMARIA ABIGAIL PAMAHOYNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics in Business & Economics: David P. Doane and Lori E. SewardDocument57 pagesApplied Statistics in Business & Economics: David P. Doane and Lori E. SewardMinh Anh HoangNo ratings yet
- Week 5 WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 5 WorksheetJennifer MooreNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation and OrganizationDocument40 pagesData Presentation and OrganizationGina Mangco-SantosNo ratings yet
- AMSG 20 Statistics PDFDocument13 pagesAMSG 20 Statistics PDFSubordinating ConjunctionNo ratings yet
- Stat Lecture 2Document5 pagesStat Lecture 2bayabaohalim8No ratings yet
- Histograms Questions Worksheets and Revision MMEDocument1 pageHistograms Questions Worksheets and Revision MMEfarzadfar441No ratings yet
- 2005 United States Conference On Teaching Statistics (USCOTS) 27Document3 pages2005 United States Conference On Teaching Statistics (USCOTS) 27Onil PagutayaoNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument23 pagesStatisticsMohana RomanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Three - Graphical Data Analysis v3Document38 pagesChapter - Three - Graphical Data Analysis v3Sahar SanaNo ratings yet
- MATH 7-WEEK 3 Q4 - Organized Data in A Frequency TableDocument11 pagesMATH 7-WEEK 3 Q4 - Organized Data in A Frequency TableAngela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12: Illustrations/Sketches of Graph, Powerpoint PresentationDocument3 pagesGrades 1 To 12: Illustrations/Sketches of Graph, Powerpoint PresentationVIRGEL CABUNGCALNo ratings yet
- LAS 4th Quarter M3Document7 pagesLAS 4th Quarter M3Mark Anthony MolinaNo ratings yet
- 2 Frequency Distribution and GraphsDocument4 pages2 Frequency Distribution and GraphsJay SerdonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Final of FinalDocument158 pagesChapter 2 Final of Finalgeletaw mitawNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Lesson NotesDocument35 pagesResearch Methods Lesson NotesCarol SoiNo ratings yet
- Representing Data: 1. This Table Represents The Number of Coloured Balls in A BagDocument12 pagesRepresenting Data: 1. This Table Represents The Number of Coloured Balls in A Bagshaima ahmedNo ratings yet
- Frequency DistributionDocument24 pagesFrequency DistributionzieNo ratings yet
- CH 14 StatisticsDocument3 pagesCH 14 StatisticsKarthikeya R SNo ratings yet
- Math 10: Quarter 4Document1 pageMath 10: Quarter 4jaredboncales349No ratings yet
- Rfewrf 34 F 34 F 3 WDocument6 pagesRfewrf 34 F 34 F 3 WTiago CostaNo ratings yet
- 22 Chapter 4 Data ManagementDocument75 pages22 Chapter 4 Data ManagementYan YanNo ratings yet
- Assignment: MBA 1 Semester Statistics For Management (Mb0040)Document10 pagesAssignment: MBA 1 Semester Statistics For Management (Mb0040)Niranjan VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 2nd-TopicDocument19 pagesStatistics 2nd-TopicTriscia Joy NocilladoNo ratings yet
- Aj Ka KaamDocument21 pagesAj Ka KaamAnonymous fg4ACqNo ratings yet
- 02 Grouped Discrete Data Continuous DataDocument22 pages02 Grouped Discrete Data Continuous DataCatalina ParNo ratings yet
- Chi Squire NoteDocument21 pagesChi Squire NoteTesfisha AltasebNo ratings yet
- Frequency Polygon NotesDocument2 pagesFrequency Polygon Notesaliesha cassasolaNo ratings yet
- All LecturesDocument53 pagesAll LecturesKevin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Frequancy of DistributionDocument17 pagesFrequancy of DistributionSaudulla Jameel JameelNo ratings yet
- Add Math StatisticsDocument14 pagesAdd Math Statisticskamil muhammadNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 6 v1Document72 pagesScheme of Work Maths Stage 6 v1amos.ndhlovuNo ratings yet
- Population Estimation (Handout)Document4 pagesPopulation Estimation (Handout)Sibiri SilamNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Data PresentationDocument9 pagesModule 3 Data PresentationHannah BarralNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distributions: Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral SciencesDocument45 pagesFrequency Distributions: Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral SciencesOshratNo ratings yet
- SM 1Document125 pagesSM 1Amit YadavNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation of DataDocument6 pagesGraphical Representation of DataJustine Louise Bravo FerrerNo ratings yet
- Marj Line Graph FinalDocument13 pagesMarj Line Graph FinalJamaica Jhoy MedinaNo ratings yet
- 11 StatisticsDocument27 pages11 StatisticsviswanathNo ratings yet
- 12 StatisticsDocument27 pages12 StatisticsviswanathNo ratings yet
- Bar Graph: Favorite FruitDocument1 pageBar Graph: Favorite FruitChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- Daily Number of Customers of XY Convenience StoreDocument2 pagesDaily Number of Customers of XY Convenience StoreChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- PIE Graph: Favorite Movie Genre of Grade 7 StudentsDocument2 pagesPIE Graph: Favorite Movie Genre of Grade 7 StudentsChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- OgiveDocument1 pageOgiveChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- Favorite Movie Genre of Grade 7 Students: Math 7 Quarter 4 Week 4 Graphs To Represent Organized DataDocument1 pageFavorite Movie Genre of Grade 7 Students: Math 7 Quarter 4 Week 4 Graphs To Represent Organized DataChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- OgiveDocument1 pageOgiveChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- Favorite Fruit: FruitsDocument1 pageFavorite Fruit: FruitsChristopher CabanagNo ratings yet
- Introduction To E-Business and E-CommerceDocument27 pagesIntroduction To E-Business and E-CommerceThư AnhNo ratings yet
- I S Eniso3834-5-2015Document24 pagesI S Eniso3834-5-2015Ngoc BangNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument1 pageCover LetterJobJobNo ratings yet
- Shannon Diversity IndexDocument2 pagesShannon Diversity IndexlinubinoyNo ratings yet
- Torrent Downloaded FromDocument2 pagesTorrent Downloaded FromshitmasterNo ratings yet
- Methanation CatalystDocument4 pagesMethanation CatalystBạch Trung Phú100% (2)
- Analysis of The Trollaukin Bind.Document6 pagesAnalysis of The Trollaukin Bind.EdwardNo ratings yet
- Property 261Document4 pagesProperty 261lynNo ratings yet
- Cost Comp - MF UF Vs TraditionalDocument8 pagesCost Comp - MF UF Vs TraditionalahanraNo ratings yet
- Watching in The Wild 2Document1 pageWatching in The Wild 2api-293358997No ratings yet
- Cal Fire Carr Fire ReportDocument18 pagesCal Fire Carr Fire ReportFOX40 NewsNo ratings yet
- National Conference: Indo Asian Academy Degree College Indo Asian Women'S Degree CollegeDocument2 pagesNational Conference: Indo Asian Academy Degree College Indo Asian Women'S Degree CollegeajaxNo ratings yet
- Degree of Crystallinity of Well-Known Polymers (I.e., Nylon 6,6, LDPE, and HDPE) UsingDocument12 pagesDegree of Crystallinity of Well-Known Polymers (I.e., Nylon 6,6, LDPE, and HDPE) Usingselva_raj215414No ratings yet
- Aiyaz Sayed Khaiyum ThesisDocument5 pagesAiyaz Sayed Khaiyum Thesisafbtbakvk100% (2)
- OCOM FTA ReviewerDocument5 pagesOCOM FTA ReviewerJulluis DagoNo ratings yet
- 8 4 Function NotationDocument16 pages8 4 Function Notationapi-233527181No ratings yet
- Laws of Limiting FactorsDocument22 pagesLaws of Limiting FactorsRajdeep YadavNo ratings yet
- AbsenteeismsmawfinalDocument13 pagesAbsenteeismsmawfinalJohn Ray VelascoNo ratings yet
- Water Resources HandoutsDocument4 pagesWater Resources HandoutsPhilip Jayson L. LestojasNo ratings yet
- Yamamoto KuwaharaDocument15 pagesYamamoto KuwaharapravinsuryaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Resume-2Document2 pagesTeaching Resume-2api-490943277No ratings yet
- Simplified Remote Restart White PaperDocument33 pagesSimplified Remote Restart White Paperch herlinNo ratings yet
- Light SensorDocument27 pagesLight SensorDevilal Dewanda90% (10)
- Configuring NIS Services in LinuxDocument8 pagesConfiguring NIS Services in Linuxapi-3736383100% (1)
- Grade 6 Mathematics Week 12 Lesson 4 - 2021 - Term 2Document6 pagesGrade 6 Mathematics Week 12 Lesson 4 - 2021 - Term 2MARK DEFREITASNo ratings yet
- TELEphone Automatic AnsweringDocument5 pagesTELEphone Automatic AnsweringOpeoluwa AreolaNo ratings yet
- Noun in English Grammar With Examples With PDFDocument9 pagesNoun in English Grammar With Examples With PDFhemisphereph2981No ratings yet
- A Paradox in The Interpretation of Group Comparisons: Frederic M. LordDocument2 pagesA Paradox in The Interpretation of Group Comparisons: Frederic M. Lordajax_telamonioNo ratings yet
- Book Exams With Invensis LearningDocument7 pagesBook Exams With Invensis LearningValan In-My VeinsNo ratings yet
- Pareto DiagramDocument1 pagePareto DiagramvirtualbobNo ratings yet