Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grades: 5 - 6: Topic Grade 5 Grade 6
Uploaded by
yitages0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesOriginal Title
4. Mathematics 1-8_Part5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesGrades: 5 - 6: Topic Grade 5 Grade 6
Uploaded by
yitagesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Grades: 5 – 6
Topic Grade 5 Grade 6
Number and Unit 2: Fractions
Unit 1: The divisibility of whole numbers
operation 2.1 Types of Fractions
1.1 The Notion of Divisibility: Divisibility tests
2.2 Operations of fractions
1.2 Multiples and divisors
2.2.1 Addition and subtraction of fractions
1.2.1 Revision on multiples and divisors
2.2.2 Multiplication and division of fractions
1.2.2 Prime and composite numbers
1.2.3 Prime factorization
1.2.4 Common divisors
1.2.5 Common multiples
1.3 Applications
Unit 3: Decimals Unit 2: Conversion of Fractions, decimals and percentage
3.1 Revision of Tenths and hundredths 2.1 The simplification of fraction
3.2 Decimals on number line 2.2. Conversion of fractions to decimals & percentage
3.3 Addition and subtraction of decimals 2.3 Conversion of decimals to fractions & percentage
3.4 Multiplication and division of decimals 2.4 Conversion of percentage to fractions & decimals
3.5 Relate common fractions to decimals 2.5 Comparing and ordering fractions
Unit 4: Percentages Unit 3: Operation on Fraction and Decimals
4.1 Part of a whole as percentages 3.1 Addition of fractions and decimals
4.2 Expressing One quantity as a percentage of another 3.2 Subtraction of fractions and decimals
4.3 Connecting Fractions and Percentages 3.3 Multiplication of fractions and decimals
4.4 Solving percentage application problems 3.4 Division of decimals
Unit 5: Working with variables Unit 4: Linear inequalities and proportionality
Algebra 5.1. Generalization and Formalization of Growth Patterns 4.1 Revision of linear equations
5.2 Algebraic terms and expressions 4.2 Solving linear inequalities by substitution
5.2.1 Variables, algebraic terms and values of terms 4.3 Solving one-step linear inequalities
5.2.2 The value of simple algebraic expression 4.4 Proportionality
5.3. Solving Linear Equations by substitution 4.4.1 Direct proportion
5.4. Solving one-step linear equations 4.4.2 Inverse proportion
5.5. Applications 4.5 Applications of linear inequalities, and proportionality
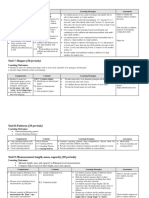
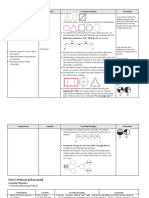
Geometry & Unit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid Shapes Unit 5: Plane and Solid figures
Measurement 7.1 Classify three dimensional shapes according to their properties 5.1 Angles
7.2 Definitions of classes of shapes such as prism, pyramids, spheres 5.2 Triangles
7.3 Compare three dimensional figures based on their definitions 5.3 Four-sided Figures
5.4 Circles
5.5 Solid Figures (vertices, edges and faces)
Unit 8: Lines, Angles and Their Measurement
8.1 Lines
8.1.1 Construction of intersecting and parallel lines
8.1.2 Bisecting a given line segment
8.1.3 Construction of perpendicular lines to a given line
8.2 Angles and the measurement of angles
8.2.1 Angles
8.2.2 Measurement and classification
8.2.3 Bisecting an angle
8.3 Lines of symmetry
8.4 Measurement
8.4.1 The perimeters and areas of squares and rectangles
8.5 Applications of lines, angles and measurement
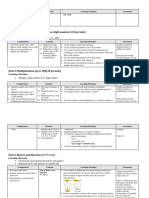
Unit 1: Measurement: -Area and Capacity
1.1. Measuring area of surfaces using square tiles and sheets of paper
1.2 Measuring area of plane figures in 𝑐𝑚2 , 𝑚2 and hectare
1.3 Measuring capacity of objects in cm3, liters and m3
1.4 conversion of areas and volumes of units in mm2, cm2, m2, km2 and
mm3, cm3, m3, km3
1.5 Applications to find the area and volume
Statistics & Unit 6: Data Handling Unit 6: Data Handling
Probability 6.1 Data Collection
6.1. Questions Formulation and Data Collection
6.2 Construction and interpretation of bar graphs and line plots
6.3 Average of numbers 6.2. Organization of Data using Tables
6.4 Simple experiments using coins, lottery, and dice; 6.3 Construction and Interpretation of Graphs
6.4. The Mean, Mode and Median of Data
You might also like
- Argumentative Writing Unit PlanDocument31 pagesArgumentative Writing Unit Planapi-645797970No ratings yet
- Functional Languages: Giving Opinions Using Filter When Responding To QuestionsDocument3 pagesFunctional Languages: Giving Opinions Using Filter When Responding To QuestionsbeauNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Definition: Let: y FX Ab FXDocument25 pagesDifferentiation Definition: Let: y FX Ab FXRazvan Gabriel RizeaNo ratings yet
- 50 Debate PromptsDocument65 pages50 Debate PromptsZmaj bibliotekaNo ratings yet
- 2018 수능특강 영어독해연습Document40 pages2018 수능특강 영어독해연습남창균No ratings yet
- Basic Mathematical SymbolsDocument12 pagesBasic Mathematical SymbolsAllyson Angel IturiagaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Test: Choose Words and Fill in The Blanks. / 6Document2 pagesUnit 9 Test: Choose Words and Fill in The Blanks. / 6Be HajNo ratings yet
- Cat 2007 Quantitative Questions Day Qqad ProblemsDocument24 pagesCat 2007 Quantitative Questions Day Qqad Problemsapi-3830507No ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument44 pagesDifferentiationnaseem113No ratings yet
- Abstraction and SymbolsDocument14 pagesAbstraction and Symbolsflynn riderNo ratings yet
- Useful Language For DiscussionsDocument1 pageUseful Language For DiscussionsEsraNo ratings yet
- A Level Core Pure Maths by Michael Cook PDFDocument188 pagesA Level Core Pure Maths by Michael Cook PDFhpant100% (1)
- Debate TopicsDocument7 pagesDebate TopicsJubal EarlyNo ratings yet
- Study Advice Services: Differentiation 1Document23 pagesStudy Advice Services: Differentiation 1Weldon James WilsonNo ratings yet
- Adjective / Adverb + Past Participle: Compound Adjectives With NumbersDocument5 pagesAdjective / Adverb + Past Participle: Compound Adjectives With NumbersKrishna Veena KosuruNo ratings yet
- Expressing Opinions: Personal Point of ViewDocument6 pagesExpressing Opinions: Personal Point of ViewAyu RanifaNo ratings yet
- 1 SCHR Odinger's Equation: One-Dimensional, Time-Dependent VersionDocument9 pages1 SCHR Odinger's Equation: One-Dimensional, Time-Dependent VersionArpita AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument24 pagesIndefinite IntegrationAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Console ApplicationDocument13 pagesConsole Applicationkomi_dot100% (2)
- Training Pack PDFDocument12 pagesTraining Pack PDFLolTheBobNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers: Key FormulaeDocument7 pagesReal Numbers: Key FormulaeKomanduri Murali SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Math102 Equation SheetDocument0 pagesMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNo ratings yet
- Sentence CompletionDocument9 pagesSentence CompletionMuhammad YasirNo ratings yet
- 2006 Reading and VocabularyDocument21 pages2006 Reading and VocabularyAriunjargal RagchaabazarNo ratings yet
- X With Respect To X The Derived Function Is 2x .: IntegrationDocument15 pagesX With Respect To X The Derived Function Is 2x .: IntegrationAdri EnneNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solutions of The Schrodinger EquationDocument26 pagesNumerical Solutions of The Schrodinger EquationqrrqrbrbrrblbllxNo ratings yet
- Choose Correct ParticipleDocument10 pagesChoose Correct ParticipleAnonymous N71PP0DEnxNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Equations, Inequalities Absolue Value-Student 1617Document22 pages2.0 Equations, Inequalities Absolue Value-Student 1617syahmiNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Maths Division WorksheetDocument3 pagesGrade 3 Maths Division WorksheetRamkishore ChelvinMurugeshNo ratings yet
- Maths Note P1 and P3Document188 pagesMaths Note P1 and P3Afeefa SaadatNo ratings yet
- Aeroplane X: Part One: Expressions (Items 1-15) Choose The Best AnswerDocument21 pagesAeroplane X: Part One: Expressions (Items 1-15) Choose The Best AnswerMacadamia 127No ratings yet
- 50 Debates PromptsDocument64 pages50 Debates PromptssugarlakeofusNo ratings yet
- P6 English 2019 CA1 River Valley Exam PaperDocument23 pagesP6 English 2019 CA1 River Valley Exam PaperiMathGenius100% (1)
- PHIL 25 Methods ReasoningDocument5 pagesPHIL 25 Methods ReasoningJoshfu70No ratings yet
- If You Really Want To Win, Cheat!Document16 pagesIf You Really Want To Win, Cheat!ritamariamartinez100% (1)
- Nouns To Verbs Worksheet 3Document1 pageNouns To Verbs Worksheet 3Kasia KusyNo ratings yet
- ENG 102.material - CompleteDocument85 pagesENG 102.material - CompleteAdil AdilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - Introductionradhika kumarfNo ratings yet
- English Grammar s2Document2 pagesEnglish Grammar s2Muhamad Fajar SidikNo ratings yet
- IntegralesDocument27 pagesIntegralesKevin DgoNo ratings yet
- Geometry 2018.Document9 pagesGeometry 2018.melissaNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Exam For 5th UnitDocument22 pages12th Grade Exam For 5th UnitОогий ОдгэрэлNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Functions Paper 1 With AnswerDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Functions Paper 1 With AnswerJarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- Solving The 15-PuzzleDocument6 pagesSolving The 15-PuzzleJeremyUltraNo ratings yet
- UNIT2.5 - Exercises 49-51Document6 pagesUNIT2.5 - Exercises 49-51lmwummelNo ratings yet
- Symbol Symbol Name Meaning or Definition ExampleDocument6 pagesSymbol Symbol Name Meaning or Definition Examplessrao2211No ratings yet
- ST Olave'S Grammar School Goddington Lane Orpington Br6 9ShDocument8 pagesST Olave'S Grammar School Goddington Lane Orpington Br6 9ShV HNo ratings yet
- 3-Debate Ethics: Should Anorexic or Morbidly Obese Women or Men Be Featured On The Covers of Major Magazines?Document2 pages3-Debate Ethics: Should Anorexic or Morbidly Obese Women or Men Be Featured On The Covers of Major Magazines?camila piranNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic 1. IntegersDocument23 pagesArithmetic 1. IntegersVenkat SabbaniNo ratings yet
- Intermediate French VocabularyDocument6 pagesIntermediate French Vocabularybboy2972No ratings yet
- Two-Variable Linear Inequalities Word ProblemsDocument3 pagesTwo-Variable Linear Inequalities Word ProblemsJoh TayagNo ratings yet
- Master Verbal Analogies with Tips and ExamplesDocument8 pagesMaster Verbal Analogies with Tips and Exampleschristina beyerNo ratings yet
- DIRECTIONSDocument8 pagesDIRECTIONSJulianaHelena SuarezVelasquezNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Equations Inequalities and Absolute ValuesDocument30 pagesTopic 2 Equations Inequalities and Absolute ValuessureinrajahNo ratings yet
- CAT Sentence Completion Strategy GuideDocument35 pagesCAT Sentence Completion Strategy GuidedeepamjyotiroutrayNo ratings yet
- 1.2.11 Practice - Spoken Assignment How Many (Spoken Assignment)Document3 pages1.2.11 Practice - Spoken Assignment How Many (Spoken Assignment)FizzlesNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus BC 2016 Scoring GuidelinesDocument7 pagesAP Calculus BC 2016 Scoring Guidelines고봉기No ratings yet
- To Be Past TenseDocument15 pagesTo Be Past TenseAngela Florez Guisao0% (1)
- G6 Core MathsDocument2 pagesG6 Core MathsKabi MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-02-12 at 8.50.54 AMDocument3 pagesScreenshot 2024-02-12 at 8.50.54 AMzkqgwtjvfhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Sentayehu GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Example: Assume A Public Body Receives From MOFED A Transfer of Birr 100,000 ForDocument32 pagesExample: Assume A Public Body Receives From MOFED A Transfer of Birr 100,000 ForSentayehu GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Sentayehu GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Introduction to FGE AccountingDocument28 pagesIntroduction to FGE Accountingsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5Sentayehu GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Public Chapter 4Document19 pagesPublic Chapter 4samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to FGE AccountingDocument28 pagesIntroduction to FGE Accountingsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Public Chapter 1Document21 pagesPublic Chapter 1samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part33Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part33yitagesNo ratings yet
- Introduction to FGE AccountingDocument28 pagesIntroduction to FGE Accountingsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Measurement-Length, Mass, Capacity (32 Periods)Document2 pagesUnit 6: Measurement-Length, Mass, Capacity (32 Periods)yitagesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part16Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part16yitagesNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Data Handling (16 Periods) : Learning Outcomes: at The End of This Unit, Learners Will Be Able ToDocument2 pagesUnit 7: Data Handling (16 Periods) : Learning Outcomes: at The End of This Unit, Learners Will Be Able ToyitagesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3Enyew AlemawNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Characteristics of Taxation: Public Revenue Sources of Public RevenuesDocument19 pagesMeaning and Characteristics of Taxation: Public Revenue Sources of Public Revenuessamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part27Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part27yitagesNo ratings yet
- Teach multiplication and division up to 1,000Document2 pagesTeach multiplication and division up to 1,000yitagesNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Shapes (20 Periods) : Competencies Learning Strategies Assessment Unit 6: Addition and Subtraction Up To 100Document2 pagesUnit 7: Shapes (20 Periods) : Competencies Learning Strategies Assessment Unit 6: Addition and Subtraction Up To 100yitagesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part23Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part23yitagesNo ratings yet
- Unit 10: Ethiopian Currency (10 Periods) : Learning OutcomesDocument2 pagesUnit 10: Ethiopian Currency (10 Periods) : Learning OutcomesyitagesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part13Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part13yitagesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part15Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part15yitagesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Adding and Subtracting Three-Digit Numbers (34 Periods)Document2 pagesUnit 2: Adding and Subtracting Three-Digit Numbers (34 Periods)yitagesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Fractions and PatternsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Fractions and PatternsyitagesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus: Grades 1 - 12Document2 pagesMathematics Syllabus: Grades 1 - 12yitagesNo ratings yet
- Geometry & Measurement Unit 4: Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures Unit 4: Similarity of FiguresDocument2 pagesGeometry & Measurement Unit 4: Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures Unit 4: Similarity of FiguresyitagesNo ratings yet
- Classify 3D Shapes and Measure Lines, Angles in GeometryDocument2 pagesClassify 3D Shapes and Measure Lines, Angles in GeometryyitagesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part6Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part6yitagesNo ratings yet
- Grades: 5-6: Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4Document2 pagesGrades: 5-6: Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4yitagesNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document5 pagesModule 2Tatsuya ShibaNo ratings yet
- Polygons PropertiesDocument9 pagesPolygons Propertieskarla halninNo ratings yet
- Shanghai Tower FinalDocument53 pagesShanghai Tower FinalAquaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade9Q3 - SimilarityDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Grade9Q3 - SimilarityJusten Mar Lavilla100% (2)
- Unit2 Interior Decoration PDFDocument7 pagesUnit2 Interior Decoration PDFTushar100% (1)
- Analyzing ArtworkDocument3 pagesAnalyzing ArtworkXytle DaskeoNo ratings yet
- CAM LectureDocument31 pagesCAM LectureMuhammad AzamNo ratings yet
- Tessellations Project FinalDocument6 pagesTessellations Project FinalwjmenardNo ratings yet
- G8 - Unit 4 - CP - Where's The Proof - Students' PDFDocument272 pagesG8 - Unit 4 - CP - Where's The Proof - Students' PDFSanye GangwaniNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument17 pagesDraftSHERLITA PINONo ratings yet
- Maths Module 5 Summary NotesDocument23 pagesMaths Module 5 Summary NotesMalack ChagwaNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Shielding Comparison: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3Document16 pagesDielectric Shielding Comparison: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3Diego AriasNo ratings yet
- Emerging Architectonic Forms and Designed Forms: Alpana R. Dongre, S.A. Deshpande, and R.K. IngleDocument13 pagesEmerging Architectonic Forms and Designed Forms: Alpana R. Dongre, S.A. Deshpande, and R.K. IngleAgamemnon KingNo ratings yet
- KBSM Maths Number Patterns TIMSS ItemsDocument14 pagesKBSM Maths Number Patterns TIMSS ItemsbrandontanNo ratings yet
- Advance Technique Creating A Car Model in Google SketchupDocument66 pagesAdvance Technique Creating A Car Model in Google SketchupYasman David50% (2)
- Identify symmetry in shapesDocument9 pagesIdentify symmetry in shapesLouie Raff Michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Area of "My Space" ProjectDocument1 pageArea of "My Space" Projectjnewman85100% (4)
- Modul English For Engineering I (TM2)Document25 pagesModul English For Engineering I (TM2)SenoNo ratings yet
- Revised ECD Checklist Administration GuideDocument24 pagesRevised ECD Checklist Administration GuideDennis Millares Yape100% (2)
- 3700-Article Text-4112-1-10-20200320Document8 pages3700-Article Text-4112-1-10-20200320TANISHA GOYALNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Visual Perceptual Skills TestsDocument76 pagesInterpreting Visual Perceptual Skills TestsKatalin Molnár100% (2)
- Wc-Ece Math Cloak LessonDocument4 pagesWc-Ece Math Cloak Lessonapi-246210596No ratings yet
- Microteaching Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMicroteaching Lesson Planapi-438996430No ratings yet
- Essential Design Elements and PrinciplesDocument20 pagesEssential Design Elements and PrinciplesSubhojit DasNo ratings yet
- The Sorcerer Supreme: Example - Casting A Simple SpellDocument3 pagesThe Sorcerer Supreme: Example - Casting A Simple SpellEmma WarsdaleNo ratings yet
- Kinds-Of-Decorative-Design LESSON 3Document39 pagesKinds-Of-Decorative-Design LESSON 3Pauline Joy ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Tips Tricks and Techniques For CorelDRAWDocument23 pagesTips Tricks and Techniques For CorelDRAWvalentin bajinaru100% (1)
- Powder Coating PDFDocument41 pagesPowder Coating PDFZephrine T MillardNo ratings yet
- ANSI B89.3.1-1972 1979 Measurement of Out - of - RoundnessDocument36 pagesANSI B89.3.1-1972 1979 Measurement of Out - of - Roundness1975.venkat7685100% (1)
- Statistics of Particle Size DistributionDocument21 pagesStatistics of Particle Size DistributionjosefgonzalezmoreyNo ratings yet