Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circular Motion Investigation
Uploaded by
Maan PatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circular Motion Investigation
Uploaded by
Maan PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
TASK PLANNER
LEARNING AREA Science
TEACHER S.Panjwani
YEAR / SUBJECT 12 Physics
TASK NAME Circular Motion Design Investigation
DRAFT DUE DATE
DUE DATE
LEARNING DESIGN
Using the equipment provided, design an investigation to explore how one variable (applied force, radius
of circular path or mass of object) affects the period of an object undergoing uniform circular motion.
To complete this task, you will have to complete the following:
Part A: Design Modification
In your group, discuss the factors that could affect the uniform circular motion of the stopper. As a
group, and modifying the given method, select one of these factors to test. You may choose to use the
template provided to guide your planning.
Part B: Conduct the experiment
Undertake the chosen investigation. You will work together safely and collaboratively to collect data.
Part C: Scientific report
Individually, you will write a report with the following:
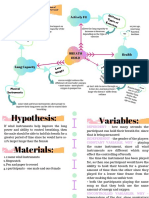
introduction with relevant physics concepts, a hypothesis and variables
materials/apparatus*
method/procedure that outlines the steps to be taken*
identification and management of safety and/or ethical risks*
results*
analysis of results, identifying trends, and linking results to concepts
evaluation of procedures and data, and identifying sources of uncertainty
conclusion, with justification.
The written report should be a maximum of 1500 words.
*The five asterisked sections of materials/apparatus, method/procedures, risks and results are excluded
from the word count.
PROVIDED EQUIPMENT Ideal
position
of
rotation
r
Actual
rotation
al
Alligator position
clip/tape
M
g
Figure 1: Diagrams of available equipment.
PROCEDURE
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in Figure 1. The alligator clip/tape is used as an indicator to fix the
radius of rotation of the string.
2. Record the mass m of the rubber stopper and length of string from the end of the tube to the
approximate centre of mass of the rubber stopper. Record this as r.
3. Record the mass M of the suspended mass.
4. Holding the tube firmly, spin the rubber stopper steadily so that the alligator clip/tape remains just
below the position at which it touches the end of the tube.
5. Time 20 revolutions of the stopper and use this to calculate its period. Record this result. Repeat the
measurement to record 3 separate times.
6. Calculate the average period of the stopper.
7. Vary one of the following variables: the mass M suspended vertically (and thus the applied force), the
radius r or the mass of the rubber stopper m.
8. Through considering equations for the force causing the centripetal acceleration and the speed of the
stopper, suggest the expected relationship between the period of the stopper and the chosen variable.
Test this relationship with the aid of a suitable graph.
ASSESSMENT
Parts A and B: Design modification/conduct the experiment
To be completed by end of lesson Friday Week 8 Term 1 (20/03/2020)
Part C: Scientific report
Draft due date: Monday Week 10 Term 1 (30/03/2020)
Due date: Monday Week 1 Term 2 (27/04/2020)
This is a summative practical investigation that will assess students primarily on Science Inquiry Skills and
Uniform Circular Motion (Topic 1.3). The practical investigation will assess student ability against the
following performance standards:
IAE2 Obtaining, recording, and representation of data, using appropriate conventions and formats.
IAE3 Analysis and interpretation of data and other evidence to formulate and justify conclusions.
IAE4 Evaluation of procedures and their effect on data.
KA1 Demonstration of knowledge and understanding of physics concepts.
KA4 Communication of knowledge and understanding of physics concepts and information, using
appropriate terms, conventions and representations.
An assessment rubric has been provided on the following page.
Performance Standards for Stage 2 Physics
- Investigation, Analysis and Evaluation Knowledge and Application
A Designs a logical, coherent, and detailed Demonstrates deep and broad knowledge
physics investigation. and understanding of a range of physics
concepts.
Obtains, records, and represents data, using
appropriate conventions and formats Develops and applies physics concepts
accurately and highly effectively. highly effectively in new and familiar
contexts.
Systematically analyses and interprets data
and evidence to formulate logical Critically explores and understands in depth
conclusions with detailed justification. the interaction between science and society.
Critically and logically evaluates procedures Communicates knowledge and
and their effect on data. understanding of physics coherently, with
highly effective use of appropriate terms,
conventions, and representations.
B Designs a well-considered and clear physics Demonstrates some depth and breadth of
investigation. knowledge and understanding of a range of
physics concepts.
Obtains, records, and represents data, using
appropriate conventions and formats mostly Develops and applies physics concepts
accurately and effectively. mostly effectively in new and familiar
contexts.
Logically analyses and interprets data and
evidence to formulate suitable conclusions Logically explores and understands in some
with reasonable justification. depth the interaction between science and
society.
Logically evaluates procedures and their
effect on data. Communicates knowledge and
understanding of physics mostly coherently,
with effective use of appropriate terms,
conventions, and representations.
C Designs a considered and generally clear Demonstrates knowledge and understanding
physics investigation. of a general range of physics concepts.
Obtains, records, and represents data, using Develops and applies physics concepts
generally appropriate conventions and generally effectively in new or familiar
formats with some errors but generally contexts.
accurately and effectively. Explores and understands aspects of the
Undertakes some analysis and interpretation interaction between science and society.
of data and evidence to formulate generally Communicates knowledge and
appropriate conclusions with some
justification. understanding of physics generally
effectively, using some appropriate terms,
Evaluates procedures and some of their conventions, and representations.
effect on data.
D Prepares the outline of a physics Demonstrates some basic knowledge and
investigation. partial understanding of physics concepts.
Obtains, records, and represents data, using Develops and applies some physics
conventions and formats inconsistently, concepts in familiar contexts.
with occasional accuracy and effectiveness. Partially explores and recognises aspects of
Describes data and undertakes some basic the interaction between science and society.
interpretation to formulate a basic
conclusion. Communicates basic physics information,
using some appropriate terms, conventions,
Attempts to evaluate procedures or suggest and/or representations.
an effect on data.
E Identifies a simple procedure for a physics Demonstrates limited recognition and
investigation. awareness of physics concepts.
Attempts to record and represent some data, Attempts to develop and apply physics
with limited accuracy or effectiveness. concepts in familiar contexts.
Attempts to describe results and/or interpret Attempts to explore and identify an aspect
data to formulate a basic conclusion. of the interaction between science and
society.
Acknowledges that procedures affect data.
Attempts to communicate information about
physics.
ASSESSMENT OUTLINE (DO NOT ATTACH TO REPORT)
Key points to include Description Comments
IAE2 Obtaining, recording, and representation of data, using appropriate conventions and formats.
Summary of results Table(s) used to summarise data with appropriate use of
headings, symbols, units and significant figures.
Sample calculations shown where appropriate.
Graph(s) used to summarise data with appropriate axes
labels, units and trend line. Trend line equation displayed
when appropriate.
Calculation of Calculation of unknown variables showing logical working
unknown variables and appropriate units.
IAE3 Analysis and interpretation of data and other evidence to formulate and justify conclusions.
Critical analysis of the Identification of trends, linking results to concepts.
results. A comment Justification of whether results are consistent with
on the accuracy and expected theory.
precision of the Explanation of how accuracy and precision of results were
results based on identified.
evidence.
Conclusion A clear statement of how the results relate to the aim of
the experiment. Was the hypothesis supported?
Do the results lead to a definite conclusion/are there any
limitations on the conclusion and why?
IAE4 Evaluation of procedures and their effect on data.
Discussion of all likely A description and classification of the possible errors (e.g.
sources of errors and systematic or random - at least 2 for each type). Discuss
their effects on the how they affected the data and how effectively the
data. procedure minimised their effects.
Reliability and validity Comment on the reliability and validity of the experiment.
KA1 Demonstration of knowledge and understanding of physics concepts.
Key ideas and Demonstrates a deep and broad knowledge and
background theory understanding of the physics concepts surrounding the
experiment.
Hypothesis A prediction of the results or relationship between
variables based on physics theory.
Variables Identification of independent, dependent, controlled and
uncontrollable variables.
Justification of variables (e.g. how they are controlled, why
they impact the dependent variable)
Safety and ethical At least three possible hazards and appropriate
considerations precautions.
Materials listed Apparatus to be used for investigation. Specific quantities
and measurements provided.
KA4 Communication of knowledge and understanding of physics concepts and information, using appropriate terms,
conventions and representations.
Correct referencing in Effective use and selection from a variety of sources.
the collection of data Clear referencing (in-text and bibliography).
from a variety of
sources
Report should be Use concise language and graphics to present scientific
logical, clear and information in the correct report format. Captions to
scientific identify tables and figures.
Maximum of 1500 words (Introduction, Discussion and
Conclusion).
Grade:
You might also like
- Task Sheet Electromagnets Criteria A DDocument3 pagesTask Sheet Electromagnets Criteria A DSahana PotatoNo ratings yet
- MYP Unit PlannerDocument16 pagesMYP Unit Plannerzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- HSC Assessment Physics Task 1 2015Document5 pagesHSC Assessment Physics Task 1 2015pixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 PhysicsDocument67 pagesGrade 12 PhysicsTishaSuperableNo ratings yet
- 2b Scientific Models CTLDocument13 pages2b Scientific Models CTLapi-460570858No ratings yet
- 2019 Higher School Certificate Year 11 Yearly Examination PhysicsDocument11 pages2019 Higher School Certificate Year 11 Yearly Examination PhysicsSyed Hasan100% (1)
- Assessmen and Evaluation - Amado (MAED-PED ESSU MAIN BORONGAN, EASTERN SAMARDocument23 pagesAssessmen and Evaluation - Amado (MAED-PED ESSU MAIN BORONGAN, EASTERN SAMARAmado M Cadiong100% (1)
- Yr8 Unit PlanDocument8 pagesYr8 Unit Planapi-334786948No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics (30S) : A Course For Independent StudyDocument50 pagesGrade 11 Physics (30S) : A Course For Independent StudyLeeyah YoungNo ratings yet
- Forces Revision Booklet PDFDocument4 pagesForces Revision Booklet PDFVaggelis KøtrønisNo ratings yet
- Myp Physics Student ChecklistsDocument12 pagesMyp Physics Student ChecklistsVardan BajajNo ratings yet
- North Atlanta High School: Chemistry SyllabusDocument7 pagesNorth Atlanta High School: Chemistry Syllabusapi-325710836No ratings yet
- MYP - 1 - Unit - 2 - The - Properties - of - Matter - Part - 1Document28 pagesMYP - 1 - Unit - 2 - The - Properties - of - Matter - Part - 1vandana giriNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainNo ratings yet
- Wave and Wave PhenomenaDocument71 pagesWave and Wave PhenomenaPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Analyzing a Chemistry Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAnalyzing a Chemistry Lesson PlanUmi YasifunNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 17 - Year 10s PhysicsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 17 - Year 10s Physicsapi-352881693No ratings yet
- Section 1 - IB Lesson: Inquiry: Establishing The Purpose of The UnitDocument7 pagesSection 1 - IB Lesson: Inquiry: Establishing The Purpose of The Unit吴双鑫100% (1)
- Y10 Science Semester 2 Exam Paper 2014Document28 pagesY10 Science Semester 2 Exam Paper 2014Joshua JohnNo ratings yet
- J P Sinha IitDocument107 pagesJ P Sinha IitShaharukh Nadaf0% (1)
- Physics 2a Assignment1Document25 pagesPhysics 2a Assignment1api-357692508No ratings yet
- Understanding Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Physical and Chemical ChangesAnchal Chadha100% (1)
- Physics 11 Energy Unit PlanDocument38 pagesPhysics 11 Energy Unit PlanNicole FurutaniNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Physical Quantities & Units 1.2 Scalars and Vectors: (1 Hour) (2 Hours)Document56 pages1.1 Physical Quantities & Units 1.2 Scalars and Vectors: (1 Hour) (2 Hours)elty TanNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Inquiry QuestionsDocument7 pagesKey Concept Inquiry Questionsapi-477189194No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics (2020)Document15 pagesGrade 10 Physics (2020)Mikail MoorajNo ratings yet
- DP Unit Planner Fields and ForcesDocument4 pagesDP Unit Planner Fields and ForcesDr-Salah JaradatNo ratings yet
- Physics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument21 pagesPhysics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Unit Plan 2014-03-26Document3 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Unit Plan 2014-03-26sk112No ratings yet
- Space Quest Teachers Page Final-2Document10 pagesSpace Quest Teachers Page Final-2api-265230795No ratings yet
- Week 12 Myp 4 HWDocument2 pagesWeek 12 Myp 4 HWAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- EDST544 Science Curriculum Teaching 2Document21 pagesEDST544 Science Curriculum Teaching 2tongsuiNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Dna 2Document7 pagesUnit Plan Dna 2api-513750879No ratings yet
- 2015 Year 7 Properties Chemical Sciences ProgramDocument4 pages2015 Year 7 Properties Chemical Sciences Programapi-222503660No ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics Revision GuideDocument29 pagesAQA GCSE Physics Revision GuideGkongNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan G10 Speed of Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesUnit Plan G10 Speed of Chemical ReactionsoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Gulzar Hina 5 6 Lesson Plan AnalysisDocument8 pagesGulzar Hina 5 6 Lesson Plan Analysisapi-300665697No ratings yet
- Myp Pedigree Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMyp Pedigree Lesson Planapi-257190713No ratings yet
- AP Physics B Notes - Kinematics in One DimensionDocument8 pagesAP Physics B Notes - Kinematics in One DimensionAndy He100% (1)
- Equations Involving Algebraic Fractions Lesson PlanDocument1 pageEquations Involving Algebraic Fractions Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Changes Unit PlanDocument6 pagesChanges Unit PlanAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Experiment Relationship between Mass and TimeDocument5 pagesCircular Motion Experiment Relationship between Mass and TimeSubesh ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- East Irondequoit Middle School Sciences 7.2 Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems EcologyDocument10 pagesEast Irondequoit Middle School Sciences 7.2 Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems EcologyMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- California State Science Fair 2007 Project SummaryDocument18 pagesCalifornia State Science Fair 2007 Project Summarysome_set18No ratings yet
- Standard Mathematics Unit Outline - Algebra - 16188655 - Sheenal ChandDocument38 pagesStandard Mathematics Unit Outline - Algebra - 16188655 - Sheenal Chandapi-408516407No ratings yet
- Electroscope Activity Cep LPDocument10 pagesElectroscope Activity Cep LPapi-285382578No ratings yet
- Yr 8 SRPDocument6 pagesYr 8 SRPapi-205793004No ratings yet
- Synchronous Learning Plan Temperature Feb 24 2021Document6 pagesSynchronous Learning Plan Temperature Feb 24 2021Jassien Moring FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 Chemistry Last WeekDocument2 pagesMYP 4 Chemistry Last Weekwama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Sample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Document20 pagesSample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science Unit Outline For EnergyDocument3 pagesYear 8 Science Unit Outline For Energyapi-297560946No ratings yet
- Unit Planner Dynamic SC f2Document8 pagesUnit Planner Dynamic SC f2zuliana1No ratings yet
- Mechanics All p4Document316 pagesMechanics All p4Joumana WalidNo ratings yet
- Standards - Based Instruction and Assessment Rubric For Chemistry Content StandardsDocument20 pagesStandards - Based Instruction and Assessment Rubric For Chemistry Content Standardsjamz_s100% (1)
- Year 11 Physics ProgramDocument7 pagesYear 11 Physics ProgrampamelahamptonNo ratings yet
- Subject Report May Z1 2019Document34 pagesSubject Report May Z1 2019Anil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Chapter 6 - Life ProcessesDocument15 pagesClass 10 - Chapter 6 - Life ProcessesScALLyWagNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Stichiometry.Document8 pagesUnit Plan Stichiometry.Muntha AnilNo ratings yet
- 4PH1 Grade Characteristics FINALDocument7 pages4PH1 Grade Characteristics FINALJasonNo ratings yet
- 2023 Stage 1 Chemsitry Design Practical Acid RainDocument3 pages2023 Stage 1 Chemsitry Design Practical Acid RainRory WallaceNo ratings yet
- Actively Fit: SmokingDocument4 pagesActively Fit: SmokingMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Student Task Planner - English Independent Reading TasksDocument2 pagesStudent Task Planner - English Independent Reading TasksMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- 12 Spec Maths Student Timeline 2021Document2 pages12 Spec Maths Student Timeline 2021Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Compare The Waysin Which Anthony Burgess in A Clockwork Orange and Michael Radfordin 1984 Use The Features of Their Text Types To Explore The Effect of Oppressive Governments OnDocument5 pagesCompare The Waysin Which Anthony Burgess in A Clockwork Orange and Michael Radfordin 1984 Use The Features of Their Text Types To Explore The Effect of Oppressive Governments OnMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- 12 Spec Maths Student Timeline 2021Document2 pages12 Spec Maths Student Timeline 2021Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Biology Practical Easwar AlladaDocument6 pagesBiology Practical Easwar AlladaMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Year 9 English Drama Text Response Text: Play Script Adaptation of Bram Stoker's Dracula Genre: Gothic/HorrorDocument5 pagesYear 9 English Drama Text Response Text: Play Script Adaptation of Bram Stoker's Dracula Genre: Gothic/HorrorMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- GallipoliDocument2 pagesGallipoliMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- YEAR 10A EXTENDED MATHEMATICS MID-YEAR EXAM REVIEWDocument7 pagesYEAR 10A EXTENDED MATHEMATICS MID-YEAR EXAM REVIEWMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- How to Write a Synopsis: A Guide to Crafting a Story SummaryDocument1 pageHow to Write a Synopsis: A Guide to Crafting a Story SummaryMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Reading AssignmentDocument2 pagesReading AssignmentMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- The Scenario: How Humans Affect The Control and Spread of Infectious DiseaseDocument3 pagesThe Scenario: How Humans Affect The Control and Spread of Infectious DiseaseMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Round Table Intro Letter 2Document1 pageRound Table Intro Letter 2Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper For The 2018 Semester 2 9EXT Common TestDocument7 pagesPractice Paper For The 2018 Semester 2 9EXT Common TestMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Radiometric Sources DemonstrationDocument2 pagesRadiometric Sources DemonstrationMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Reacting Acid PracticleDocument1 pageReacting Acid PracticleMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 3 (A Grade)Document4 pagesExemplar 3 (A Grade)Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Scienceworld: Stannard WilliamsonDocument53 pagesScienceworld: Stannard WilliamsonMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Reacting Acid PracticleDocument1 pageReacting Acid PracticleMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Round Table Intro Letter 2Document1 pageRound Table Intro Letter 2Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Pop PracticleDocument2 pagesPop PracticleMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 2 (A+ Grade)Document6 pagesExemplar 2 (A+ Grade)Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Lady Stripped Bare by Tracey Spicer Explore The Idea of Female Beauty Standards?Document4 pagesLady Stripped Bare by Tracey Spicer Explore The Idea of Female Beauty Standards?Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 3 (A Grade)Document4 pagesExemplar 3 (A Grade)Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 2 (A+ Grade)Document6 pagesExemplar 2 (A+ Grade)Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 2 (A+ Grade)Document6 pagesExemplar 2 (A+ Grade)Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exponents: Reactions of Acids Aim: To Investigate The Reactions of Acids With Metal and With MetalDocument2 pagesExponents: Reactions of Acids Aim: To Investigate The Reactions of Acids With Metal and With MetalMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Lady Stripped Bare by Tracey Spicer Explore The Idea of Female Beauty Standards?Document4 pagesLady Stripped Bare by Tracey Spicer Explore The Idea of Female Beauty Standards?Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 3 (A Grade)Document4 pagesExemplar 3 (A Grade)Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Work Example 3Document1 pageWork Example 3Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Tech Acceptance, Granic 2019 PDFDocument22 pagesTech Acceptance, Granic 2019 PDFAhmad Ridwan Bin Osman Hussin IPGKTAANo ratings yet
- BRM 9e PPT CH 13 - Measurement and ScaleDocument23 pagesBRM 9e PPT CH 13 - Measurement and Scalexueting MaNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument52 pagesThesisBechay PallasigueNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Validity StudyDocument9 pagesReliability and Validity StudyNour SarhanNo ratings yet
- Brand Management in Higher Education - The University Brand Personality ScaleDocument10 pagesBrand Management in Higher Education - The University Brand Personality ScaleSolitude WorksNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Work Environment, Work Discipline and Motivation On The Performance of Civil Servants at The Ministry of Home AffairsDocument9 pagesThe Influence of Work Environment, Work Discipline and Motivation On The Performance of Civil Servants at The Ministry of Home AffairsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Master Syllabus Social Work 3810 (3 Credit Hours)Document18 pagesMaster Syllabus Social Work 3810 (3 Credit Hours)api-282881075No ratings yet
- Practical Research (APP 006)Document5 pagesPractical Research (APP 006)Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- Project Paper GuidelinesDocument22 pagesProject Paper GuidelinesRobin CalifNo ratings yet
- The Structured Interview An Alternative To The Assessment Center?Document15 pagesThe Structured Interview An Alternative To The Assessment Center?Raymond BaileyNo ratings yet
- Can Charisma Be Taught?Document24 pagesCan Charisma Be Taught?Manuel Hugo Luarte JaraNo ratings yet
- Digital Platforms and SMEs' Business Model Innovation Exploring The Mediating Mechanisms of Capability ReconfigurationDocument13 pagesDigital Platforms and SMEs' Business Model Innovation Exploring The Mediating Mechanisms of Capability ReconfigurationdewyekhaNo ratings yet
- HLS EU Q 47 CalculationDocument23 pagesHLS EU Q 47 CalculationAfri Kesling Document'sNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Adult Development and Aging 8th EditionDocument25 pagesTest Bank For Adult Development and Aging 8th EditionEunice Hatfield100% (35)
- Cape Communication Studies ProgrammeDocument34 pagesCape Communication Studies ProgrammeAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- Sociology Canadian 9th Edition Macionis Test BankDocument26 pagesSociology Canadian 9th Edition Macionis Test BankWilliamThomasbpsg100% (43)
- Scriven - 1991 - Evaluation Thesaurus PDFDocument183 pagesScriven - 1991 - Evaluation Thesaurus PDFJuan Pablo Correa100% (1)
- Developing Assessment For Speaking: Yenny Rahmawati & ErtinDocument12 pagesDeveloping Assessment For Speaking: Yenny Rahmawati & ErtinAstarothNo ratings yet
- Journal of Clinical Child PsychologyDocument9 pagesJournal of Clinical Child PsychologyYudha Alfian HaqqiNo ratings yet
- Proposal Dian Narulita FixDocument61 pagesProposal Dian Narulita FixFebri YantoNo ratings yet
- Good Psychometric PropertiesDocument44 pagesGood Psychometric PropertiesPamela joyce c. santosNo ratings yet
- Internal Validity in Research/DissertationDocument7 pagesInternal Validity in Research/DissertationSTAR ScholarsNo ratings yet
- JPGN-17-205 The Pediatric Eating Assessment Tool PDFDocument7 pagesJPGN-17-205 The Pediatric Eating Assessment Tool PDFNina SalinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Research MethodologyDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Research MethodologyAdeniji OlusegunNo ratings yet
- Partial Least Squares Structural Equation ModelingDocument16 pagesPartial Least Squares Structural Equation ModelingSteven adiNo ratings yet
- HSBH 1007 - Week 1 Lecture AJC 2008Document52 pagesHSBH 1007 - Week 1 Lecture AJC 2008alichizariNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Guiding Principles in The Assessment of LearningDocument26 pagesActivity No. 1 Guiding Principles in The Assessment of LearningJude SanchezNo ratings yet
- Research Chapter I-Iii-1Document19 pagesResearch Chapter I-Iii-1Grace Kelly TabandaNo ratings yet
- 8604 Assignment 2Document19 pages8604 Assignment 2Ruhaan TanvirNo ratings yet
- Applying Career Competencies in Career ManagementDocument344 pagesApplying Career Competencies in Career ManagementdmarisenthilNo ratings yet