Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer in Food Risk Mngmnt. (GTHRSKMT)
Uploaded by
cherrymae balueta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views6 pagesREVIEWER IN FOOD RISK MNGMNT.
Original Title
Reviewer_ Risk Mgt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentREVIEWER IN FOOD RISK MNGMNT.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views6 pagesReviewer in Food Risk Mngmnt. (GTHRSKMT)
Uploaded by
cherrymae baluetaREVIEWER IN FOOD RISK MNGMNT.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
REVIEWER IN FOOD RISK MNGMNT.
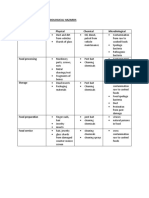
Erderly and Child Care, Nursing
Homes
(GTHRSKMT)
Military Bases, Prison Jails
Transportation with Food Service
Facilities
Foodborne Disease Outbreak
Occurs when 2 or more people
become ill after eating common Foodborne Illness
food.
- Commonly known as food
Food Industry poidoning, caused by eating food
that is contaminated by
America’s largest enterprise
bacteria/harmful substances
Made up of businesses that
produce, manufacture, transport Foodborne disease cause
and distribute food for people.
- 76 M illnesses
Food Production - 325 TH hospitalization
- 5 K Deaths
Activities that occurs on farms,
ranches, orchards, and fishing MAJOR ECONOMIC IMPACT
operations.
Medical expenses
Food Manufacturing Loss of work
Reduced productivity
Takes the raw materials harvested
Legal fees
by producer and converts them into
Punitive damages
forms suitable for distribution and
Loss of business
sale.
Loss of reputation
Retail Distribution System Increased insurance premium
Consist of many food operations, COST OF FOODBORNE ILLNESS
provide for human consumption.
Loss of customers and sales
Loss of prestige and reputation
Lawsuits resulting in lawyer and
TYPES OF FOOD ESTABLISHMENTS
court fees
Full service Restaurant Increased insurance premium
Quick service/Fastfood Lowered employee morale
Convenience Stores Employee absentism
Caterers/Food Concessions Need for retraining employee
Lodging and Accommodation area Embarrassment
Schools/Universities Cafeteria
CAUSES OF FOODBORNE ILLNESS IN FOOD WASH HANDS ……after…
ESTABLISHMENTS
- After using restroom
Poor Personal Hygiene - Touching your face, hair, boy
- Before and after handling raw foods
- Transferring pathogens from body to
- Taking out garbage
food
- Sneezing
Cross-Contamination - Handling chemicals
- Smoking, using e cigarettes, chewing
- Transferring pathogens from one
gum etc.
surface to another.
- Eating or drinking
Time Temperature Abuse
- Letting food stay too long at
USING A HANDWASHING SINK
temperatures that are good for
pathogen growth. - DO NOT use hwsink for other things
- Never dump dirty water in them
Poor Cleaning and Sanitizing
- Never prepared food in them
- Incorrectly cleaned surfaces to food. - Never wash tools and equipment.
- Neber do tgese things in the
following areas in Food handling
YOU’RE ROLE IN KEEPING FOOD SAFE areas and food storage area
- Wash hands properly Glove Use
- Prevent ill employees from working
- Use to cover burn, cut or rash
- Maintenance general personal
- Fingernails, rings, bandage
cleanliness
- single used glove shall not be
- Observe strict rules for eating,
washed
drinking, and smoking.
- only use once
Temperature Danger Zone
HOW AND WHEN TO WASH YOUR HANDS
- pathogens can grow in this range
- Handwashing is a critical step for and cause foodborne illness
avoiding food contamination - 135 F to 43 F
- Take 20 seconds
Store refrigerated food
- Wet, Apply, Scrub, Rinse, Dry
- designated hand wash sink - 41F – 5 C lower
Keep food frozen solid
- 0 F to 18C lower
What should you look when inspecting a - Quality date
delivery vehicle? - Product is still safe to eat past this
date after the quality date but the
- Overall condition of the vehicle
quality was lessen.
- Condition of the product
- Sign of pests in the vehicle Use-By Date
- Door lock sand seals are functioning
- The last day recommended for the
- Correct truck temperature
product while at peak quality. Still
Temperature Logs safe
- First food safety documents other Expiration Date
Department of Health request
- Do not distribute infant formula,
during an inspection.
baby food or vitamins after the
Storing food safety expiration date.
- Store food only in designated areas FEFO
- Six inches off the ground
- First expired, first out
- Away from walls
- Ready to eat food above uncooked Discard cans if they have these problems
food.
- Severe dent in can seams
Store cleaning products and chemicals - Crushed cons that are not stackable
- Deep dents in body of can
- Label cleaning products
- Missing labels
- Keep away from food areas
- Unreadable labels
- Store in designated areas for
- Swollen or bulging ends
cleaning products and chemicals
- Rust that will not wipe off
- Bleach, paint, etc. should not be
- Holes or leaking
stored in the same area.
Discard commercially packaged dry food
Sell-By Date
with these problems
- Also called pull date
- Unlabeled or not correctly labeled
- The store must sell those products
- Unreadable label
before the code date and often
- No code dates
donates these foods when they are
- Signs of pest (gnaw marks,
closed to date ex. Eggs, lunch meat.
droppings, insects)
Packing or Manufacturing Date - Wet, damaged, or stained
- Open packaging
- Not an expiration date
- The day that the food was package, Prepare delivery vehicles to protect food
ex. Crackers, canned foods, spices. from contamination.
Best-By or Best if used by date
- Clean inside of the vehicles at least - Scales
once per week as often as necessary - Prep tables in clean rooms
- Make sure vehicles are pest free - Sorting tables
- Never deliver food in vehicles used - Scoops
to haul garbage.
HANDLING GARBAGE
- Do not bring pets when delivering
food - Remove garbage as quickly as
- Keep items that could contaminate possible
food separate from the delivery - Be careful not to contaminate food
- Lock and seal delivery vehicles when or surfaces when removing garbage
they are not being unloaded or - Clean the inside and outside of
loaded. garbage containers often
- Do not clean garbage containers in
When loading and transporting food
clean rooms or food storage areas
- Keep refrigerated food at 41F (5C) or - Close the lids on outdoor containers
lower during transport - Keep indoor containers covered
- Keep frozen food at temperature when they are not in use
that will keep it frozen.
Trends in Food consumption and choices
- Keep food cold in unrefrigerated
vehicles - Menus reflect changing appetite
- Always cover refrigerated and frozen among diners
food with thermal blankets - People have a wide of variety food
- Or place coolers with icepacks to choose from.
- Load ref. and frozen food so air can
CAUSES OF FOODBORNE ILLNESS
circulate around it.
Shiga Toxin – producing Escherichia
Cleaning
coli bacteria in lettuce and
- Removes food and other dirt from a unpasteurized apple juice.
surface Salmonella Spp. In alfalfa sprouts,
ice creams and dry cereal
Sanitizing
Hepatitis – a virus in raw and lightly
- Reduce pathogens on a surface to cooked oysters
safe levels Listeria Monocytogenes – in hotdogs
and luncheon meats.
Cleaning and sanitizing surfaces
- All surfaces must be cleaned and
rinsed
- Walls and floors
Contamination
- Storage shelves
- Garbage containers
- --Any surfaces that touches food
- Is the presence of substances or Edema of the face, tongue, eyelids,
conditions in the food that can be mouth
harmful to humans Skin rashes – itchy eyes
Respiratory – bronchitis, tightness of
Sources of contamination
the chest
- Soil, oil, water, air, plants, animals, Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
humans. Anaphylactic shock
Bacterial Contamination THE EIGHT PRINCIPAL FOODS THAT MAKE
UP 90% OF ALL ALLERGIC REACTIONS.
- The principle cause of food
poisoning is the direct - Tree nuts
contamination of high risk foods - Peanuts
- Harmful bacteria may also - Milk
contaminate food by means of a - Fish
vehicle or route of contamination - Wheat
- Soy
TYPES AND FORMS OF BACTERIA
- Shellfish
Pathogenic Bacteria - Egg products
- Harmful bacteria responsible for HIGH RISK FOODS
food related illness.
- Which if contaminated with
- Reproduce by Binary Fission in 10-20
pathogenic bacteria and given ideal
mins.
conditions for the bacteria.
Spoilage Bacteria
Types of foods that associated with high
- Responsible for the decomposition risk foods
of foods.
- Cooked meats
- Rotting food, slime on meet,
- Cooked meat products with gravies
Beneficial Bacteria and stocks
- Cooked rice
- Involved in fermentation
- Shellfish/seafood
process/food supplement.
- Cooked eggs and products prepared
-
with eggs.
FOOD ALLERGENS
FORMS OF HEAT TREATMENT PROCESS
Allergy is an immunological
- Pasteurization
response to certain foods, food
- Sterilization
additives and colorings that can
- UHT Treatments
cause respiratory reactions and
other symptoms THE FOLLOWING DETAILS ARE IMPORTANT
TO ASCERTAIN THE INCIDENT (F.POISON)
- Name, address, and contact details
- Date and time of recovery
- Has anyone shown any sign of illness
- Date and time of the meal
- Medical details
- Has family members unwell?
- Date and timings of onset, man
symptoms and details
- Date such as place of food
consumption over the previous 2
days
- Has any family member returned
from overseas?
Microorganisms
- Most common type of food
contamination/ includes bacteria,
viruses and parasites.
Microbes
- Everywhere around us—in soil,
water, air, plants etc.
The Food Flow
- Consist of food products, and
ingredients, used to make them as
they flow through a food
establishment.
HACCP
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control
Points
- Identifies hazard within the flow of
food
- Receive – Store – Prepare – Cook –
Hold – Cool – Reheat.
You might also like
- Food Handler's Manual: StudentFrom EverandFood Handler's Manual: StudentNo ratings yet
- Microbial Hazard Identification in Fresh Fruits and VegetablesFrom EverandMicrobial Hazard Identification in Fresh Fruits and VegetablesNo ratings yet
- Risk Management ReviewerDocument8 pagesRisk Management ReviewerMark Lemuel AmanoNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and Sanitation ManagementDocument71 pagesFood Safety and Sanitation Managementshielad_4100% (1)
- Chapter4&7 - Intro To Food SafetyDocument29 pagesChapter4&7 - Intro To Food SafetyadillaaazmiNo ratings yet
- What Is GMP?: GMP Refers To Good Manufacturing PracticesDocument27 pagesWhat Is GMP?: GMP Refers To Good Manufacturing PracticesDawrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Foodsafety 140116092441 Phpapp02Document53 pagesFoodsafety 140116092441 Phpapp02gizachewyohannesgtgNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Notes For Safety QuizDocument2 pagesHospitality Notes For Safety QuizMuadh KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 (Part 1)Document28 pagesLesson 2 (Part 1)Yisu HimaaNo ratings yet
- 1 Food HygieneDocument43 pages1 Food Hygienemirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Sanitation Day 2 HandoutsDocument95 pagesSanitation Day 2 HandoutsKath Bonavente DacaraNo ratings yet
- Case-Study Group-4 TM102 TPDocument6 pagesCase-Study Group-4 TM102 TPSteff GarciaNo ratings yet
- Food SafetyDocument24 pagesFood SafetyPHELLIPPEqueirozNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Sanitation-2015Document22 pagesFood Safety Sanitation-2015listy anjaniNo ratings yet
- ServSafe Study Guide - SynergyDocument8 pagesServSafe Study Guide - SynergyMike Weihrauch100% (2)
- Rale Day 5Document4 pagesRale Day 5SheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- Food Safety: at Non-Profit Temporary EventsDocument2 pagesFood Safety: at Non-Profit Temporary Eventsjclark13010No ratings yet
- Safe Food HandlingDocument44 pagesSafe Food HandlingBrunoNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and SanitationDocument5 pagesFood Safety and SanitationKong KrcNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Lesson 1 - Food Safety Basic PDFDocument41 pagesRisk Management Lesson 1 - Food Safety Basic PDFJPNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and SanitationDocument15 pagesFood Safety and SanitationJohn Armand EstrososNo ratings yet
- GMP in Bakeries 1629053886Document75 pagesGMP in Bakeries 1629053886Mohamed azarudeen100% (6)
- Nutrition + Life: Jahdielle Keemmah B. Kitane, RNDDocument39 pagesNutrition + Life: Jahdielle Keemmah B. Kitane, RNDRuvelyn Lenares100% (1)
- Food-and-Milk SanitationDocument70 pagesFood-and-Milk SanitationJora Marie Alcantara100% (1)
- Effect of Structure and Type of Produce On RespiraDocument65 pagesEffect of Structure and Type of Produce On RespiraShonnia SiminNo ratings yet
- Hygienic and Sanitary Practices For Bakery - Basic LevelDocument76 pagesHygienic and Sanitary Practices For Bakery - Basic LevelTrishitmandas100% (2)
- SITXFSA001 Use Hygienic Practices For Food SafetyDocument10 pagesSITXFSA001 Use Hygienic Practices For Food SafetyTikaram GhimireNo ratings yet
- CGMP HandoutDocument7 pagesCGMP HandoutMary Joyce JosonNo ratings yet
- Principles of Food SanitationDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Food Sanitationbmmr.071791No ratings yet
- Principles of Food Sanitation, Safety & Hygiene: A Lecture CompilationDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Food Sanitation, Safety & Hygiene: A Lecture CompilationOliver FabonNo ratings yet
- Nisus DSV LabelDocument24 pagesNisus DSV LabelwilliamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Safety Lecture # 1: Prepared by Miss Sidra-Tul-Muntaha Department: Food Science and TechnologyDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Food Safety Lecture # 1: Prepared by Miss Sidra-Tul-Muntaha Department: Food Science and TechnologymuqaddasNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Physical Hazard:: InsectsDocument2 pagesDatasheet: Physical Hazard:: InsectsDharanibalan PNo ratings yet
- Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security and Sanitation - CLSUDocument95 pagesRisk Management As Applied To Safety, Security and Sanitation - CLSUSheena Harrien86% (7)
- Occupational Safety HazardDocument44 pagesOccupational Safety Hazardapril joy manzanillaNo ratings yet
- Packaging Food - Feb 1 BROCHURESDocument2 pagesPackaging Food - Feb 1 BROCHURESOneil LewinNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For ServSafe® Manager 6th Edition PDFDocument27 pagesStudy Guide For ServSafe® Manager 6th Edition PDFvasty.overbeek100% (1)
- Food Tec HSC SummaryDocument33 pagesFood Tec HSC SummarySia GuptaNo ratings yet
- Warehouse 2013Document93 pagesWarehouse 2013Gilbert GillNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Potentially Hazardous Food - Breakout SessionDocument2 pages2.1 Potentially Hazardous Food - Breakout SessionAnn LysterNo ratings yet
- SafetyDocument3 pagesSafetykrizelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Food SafetyDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Food SafetycesNo ratings yet
- MSDS Famotidine Oral Sus - Jan 2010Document5 pagesMSDS Famotidine Oral Sus - Jan 2010Kannan Arumugam ANo ratings yet
- FOOD SAFETY TRAINING 2017 Updated 3 2 17Document28 pagesFOOD SAFETY TRAINING 2017 Updated 3 2 17Hamid AliNo ratings yet
- Coursemodulegensspdf 120730072618 Phpapp02Document43 pagesCoursemodulegensspdf 120730072618 Phpapp02JAHALAN GAZZINGANNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Food SafetyDocument24 pagesBab 1 Food SafetyAini MunirahNo ratings yet
- Foreign Objects Personnel DatasheetDocument2 pagesForeign Objects Personnel DatasheetDharanibalan PNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Pre Production ProcessingDocument26 pagesModule 3 - Pre Production ProcessingMaickol Rafael Sanchez LegerNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Illness What Consumers Need To KnowDocument4 pagesFoodborne Illness What Consumers Need To KnowAnthony MoralesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Food Sanitation, Safety & HygieneDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Food Sanitation, Safety & HygieneMohamed Laghouasli92% (24)
- Chapter 1 Food ContaminantsDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Food ContaminantsBlakeNo ratings yet
- TrainingDocument147 pagesTrainingMelesNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Food Safety and HygieneDocument85 pagesLevel 3 Food Safety and HygieneNikade Confidence100% (2)
- Food Sanitation, Safety and Hygiene: 1. Dangers of Foodborne IllnessDocument4 pagesFood Sanitation, Safety and Hygiene: 1. Dangers of Foodborne IllnessMarifelGelayLascoñaNo ratings yet
- Food SafetyDocument38 pagesFood SafetyMichael Jr ZeuqirneNo ratings yet
- Hygiene and Sanitation in Food Sector - HmhubDocument12 pagesHygiene and Sanitation in Food Sector - HmhubLohith ShivannaNo ratings yet
- Danitol Insecticide: Emulsifiable Concentrate Insecticide - MiticideDocument19 pagesDanitol Insecticide: Emulsifiable Concentrate Insecticide - MiticideRam SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Food Safety SystemDocument81 pagesModule 6 - Food Safety SystemJung-jung Acosta LacuataNo ratings yet
- Presentationt - GCSE Revision Notes (Food Exam)Document34 pagesPresentationt - GCSE Revision Notes (Food Exam)Essay MaintenantNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document4 pagesCase 1Myles JustineNo ratings yet
- Global Economic Integration Is One of The Most Important and Complicated Issues of Our TimeDocument1 pageGlobal Economic Integration Is One of The Most Important and Complicated Issues of Our Timecherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Hazard and Its ExampleDocument1 pageBasic Concept of Hazard and Its Examplecherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- Do You in Favor of Enactment of Law As A Means To Settle The Controversy of The Place Where The First Mass in The Philippines Was HeldDocument1 pageDo You in Favor of Enactment of Law As A Means To Settle The Controversy of The Place Where The First Mass in The Philippines Was Heldcherrymae balueta60% (5)
- Do You Think Jose Rizal Made RetractionDocument1 pageDo You Think Jose Rizal Made Retractioncherrymae balueta100% (1)
- Gymnastics Powerpoint VideoDocument9 pagesGymnastics Powerpoint Videocherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Food Risk Mngmnt. (GTHRSKMT)Document6 pagesReviewer in Food Risk Mngmnt. (GTHRSKMT)cherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- Self Awareness and Values DelopmentDocument32 pagesSelf Awareness and Values Delopmentcherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- About: GymnasticsDocument11 pagesAbout: Gymnasticscherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- CONTINUATION FROM PRELIM (Number Patterns in Mathematics)Document3 pagesCONTINUATION FROM PRELIM (Number Patterns in Mathematics)cherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemical and Biological HazardsDocument2 pagesPhysical Chemical and Biological Hazardscherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument3 pagesHACCPcherrymae baluetaNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Casesheet 086 Siwertell Hermasa Brazil Grain Unloader TerminalDocument2 pagesCasesheet 086 Siwertell Hermasa Brazil Grain Unloader TerminalersNo ratings yet
- Techgig Open Round CompetitionDocument6 pagesTechgig Open Round CompetitionAnil Kumar GodishalaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Speed StudyDocument55 pagesTraffic Speed StudyAnika Tabassum SarkarNo ratings yet
- Surface News - 20130704 - Low Res PDFDocument9 pagesSurface News - 20130704 - Low Res PDFYoko GoldingNo ratings yet
- Phet Body Group 1 ScienceDocument42 pagesPhet Body Group 1 ScienceMebel Alicante GenodepanonNo ratings yet
- Application Problems 1 Through 3Document5 pagesApplication Problems 1 Through 3api-4072164490% (1)
- Basics Stats Ti NspireDocument7 pagesBasics Stats Ti NspirePanagiotis SotiropoulosNo ratings yet
- Br2e Int Readingfile10 PDFDocument2 pagesBr2e Int Readingfile10 PDFSanti RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Civpro RevDocument102 pagesCivpro RevJocelyn Baliwag-Alicmas Banganan BayubayNo ratings yet
- TM9-238 Deepwater Fording of Ordnance Materiel PDFDocument35 pagesTM9-238 Deepwater Fording of Ordnance Materiel PDFdieudecafeNo ratings yet
- 201183-B-00-20 Part ListDocument19 pages201183-B-00-20 Part ListMohamed IsmailNo ratings yet
- MIami Beach City Attorney's DenialDocument7 pagesMIami Beach City Attorney's DenialDavid Arthur WaltersNo ratings yet
- Bemts-I (A) : Air Uni IsbDocument11 pagesBemts-I (A) : Air Uni IsbUmair AzizNo ratings yet
- Sahara International Petrochemical Company (SIPCHEM)Document2 pagesSahara International Petrochemical Company (SIPCHEM)shahbaz1979No ratings yet
- CIVREV!!!!Document5 pagesCIVREV!!!!aypod100% (1)
- Resume (Suyash Garg)Document1 pageResume (Suyash Garg)Suyash GargNo ratings yet
- DTDC Rate Quotation-4Document3 pagesDTDC Rate Quotation-4Ujjwal Sen100% (1)
- UK LL M Thesis - Builders' Liability in UK Law Under TortDocument16 pagesUK LL M Thesis - Builders' Liability in UK Law Under TortRajan UppiliNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Implementation of Green Procurement: Empirical Evidence From Indonesian Educational InstitutionDocument12 pagesFactors Affecting The Implementation of Green Procurement: Empirical Evidence From Indonesian Educational InstitutionYeni Saro ManaluNo ratings yet
- LG LCD TV 32lp1dc - Al-04ca Service ManualDocument47 pagesLG LCD TV 32lp1dc - Al-04ca Service ManualJavin GallardoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Guide - Broad Crested WeirDocument18 pagesExercise Guide - Broad Crested Weirvipul anandNo ratings yet
- A Study On Impact of Smartphone AddictioDocument4 pagesA Study On Impact of Smartphone AddictiotansuoragotNo ratings yet
- Pfmar SampleDocument15 pagesPfmar SampleJustin Briggs86% (7)
- 032017Document107 pages032017Aditya MakwanaNo ratings yet
- IMS DB Interview Questions: Beginner LevelDocument19 pagesIMS DB Interview Questions: Beginner LevelsudhakarcheedaraNo ratings yet
- CH 2 How LAN and WAN Communications WorkDocument60 pagesCH 2 How LAN and WAN Communications WorkBeans GaldsNo ratings yet
- 1491559890CL 0417 PDFDocument48 pages1491559890CL 0417 PDFCoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- Aircraft MaintenanceDocument32 pagesAircraft MaintenanceTateNo ratings yet
- Enabling Trade Report 2013, World Trade ForumDocument52 pagesEnabling Trade Report 2013, World Trade ForumNancy Islam100% (1)