Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHASE (E-LEARNING) : 1,2,2A, 3 & 4: Weekly Test - 1
Uploaded by
Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHASE (E-LEARNING) : 1,2,2A, 3 & 4: Weekly Test - 1
Uploaded by
Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEKLY TEST - 1
JEE(Advanced)
16-08-2020
JEE(Main+Advanced) : NURTURE COURSE
PHASE (E-LEARNING) : 1,2,2A,3 & 4
HINT – SHEET
then at x = 1 y will be maximum
PART-1 : PHYSICS
y = 5 – (1 – 1)2 = 5
SECTION-I 4. 1
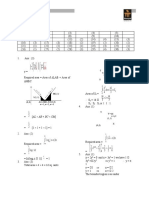
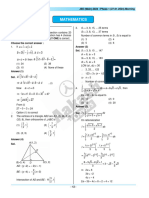
1. (3) d= (6 – a)2 + (8 – 4)2
2. (1)
3. (4) (5)2 = (6–a)2 + 16
4. (1) (6 – a)2 = 9
5. (2) 6–a=3
6. (2) a = 3 cm
7. (4) 5. 0
8. (3) PART-2 : CHEMISTRY
9. (4)
SECTION-I
10. (2)
21. (1)
11. (1)
[Kr]36 5s1
12. (2)
Last electron enters in s-subshell, so it belongs
13. (2) to s-block.
14. (1) For s-block group number = number of valence
15. (2) electron(s).
16. (1) 22. (3)
17. (1) mass of sodium
18. (3) % of Na = × 100
molecular mass
19. (1)
11. (1) 23
Þ 7= ´ 100
y = cos x3 M
dy 23 ´ 100
= – sin x3 (3x 2 ) = –3x2 sinx3 M= = 328.6
dx 7
SECTION-II 23. (3)
1. 2 32
= 0.2
2. 2 2x + 3y
3. 5
92.8
y = 5 – (x – 1)2 = 0.4
3x + 4y
dy Hence x = 56 & y = 16.
= –2 (x – 1) = 0
dx 24. (1)
25. (2)
d2 y
<0 Sn4+ > In+ > Sn > In
dx2
26. (1)
WT # 1 E-1
JEE (Advanced) 2022/NURTURE COURSE/16-08-2020
27. (1) SECTION-II
28. (1) 1. 3
29. (1)
2. 1
30. (3)
BiI5 does not exists because of I – being very 4A + 2B + 3C A4B2C3
strong reducing agent. So it reduces Bi5+ to Bi3+ Initial mole 2 1.2 1.44 0
and forms BiI3. final mole 0 0.48
31. (2)
C is limiting reagent.
Across the period size decreases and down the
group size increases. So, Cs is largest ionic \ moles of A4B2C3 is 0.48.
radius. 3. 1
32. (2) 4. 4
O+ is smaller than parent atom while anion is
bigger than parent atom. O 2– and N 3– are r2 (2)2
Bohr radius = = =4
isoelectronic species. So ionic size µ r1 (1)2
5. 4
1
. (visible lines = 4 6 ® 2, 5 ® 2, 4 ® 2, 3 ® 2)
nuclear ch arg e
Hence the correct order is O+ < O2– < N3– .
33. (1) PART-3 : MATHEMATICS
Atomic radii of zero group elements are
SECTION-I
expressed as their vander Waal's radii.
rvan der Waal's > rcovalent. 41. (4)
34. (1) 10 é 1ù
Due to stable half filled electronic configuration y =3 + Î ê -7, - ú
of outer most shell of N, it has higher ionisation
( sin q - 2) ë 3û
energy than O which has partially filled electron 42. (B)
configuration of outer most shell. cos A cosC - sin A sin C
cos 2B =
35. (1) cos A cos C + sin A sin C
As elements are ionized of the proton to electron 1 - tan A tan C
ratio increases, so the attraction between valence cos 2B =
1 + tan A tan C
shell electron and nucleus increases and as a
Using 'C' and 'D'
result the size decreases. Therefore, the removal
of electron from smaller cation requires higher 1 - cos 2B
= tan A tan C
energy. Hence the second ionisation energy is 1 + cos 2B
higher than its first ionisation energy. Þ tan2B = tanA tanC
36. (3) 43. (D)
As size of atom increases, the distance between
nucleus and outer most electrons increases. So 2cot a + cosec 2a = 2 cot a + 1 + cot 2 a
the attraction between the nucleus and outer
( cot a + 1)
2
most electron decreases. As a result the =
ionisation energy decreases.
cos a
37. (3) = cot a + 1 = +1
38. (2) sin a
39.
40.
(3)
(3) =-
( cos a + sin a ) ì 3p ü
í < a < pý
According to Mulliken's, the electronegativity = sin a î4 þ
44. (A)
Ionisation energy + Electron affinity 23° + 44° = 67°
2 tan23º + tan44º = tan67º – tan44º
tan23º + 2tan44º = tan67º
E-2 WT # 1
JEE (Advanced) 2022/NURTURE COURSE/WEEKLY TEST/PHASE-1,2,2A,3 & 4/16-08-2020
45. (A) 52. (1)
æ p ö æpö 2n - 1
sin 22005. ç 2006 ÷ sin ç ÷ Tn =
è2 ø = è2ø 3.5.7.... ( 4n - 5 )( 4n - 1)
æ p ö æ p ö
22005 sin . ç 2006 ÷ 2 2005.sin ç 2006 ÷
è2 ø è2 ø 1é ( 4n - 1) - 1 ù
Tn = ê ú
æ p ö 2 ëê 3.5.7.... ( 4n - 5 )( 4n - 1 ) ûú
= 2 -2005.cosec ç 2006 ÷
è2 ø
46. (B) 1é 1 1 ù
Tn = ê - ú
3
1 4 cos 10° + 4 sin 20° 3 2 ëê 3.5.7.... ( 4n - 5 ) 3.5.... ( 4n - 5 )( 4n - 1 ) ûú
4 cos10° + sin 20° put n = 2,3,4........
1 æ cos 30° + 3 cos10° + 3 sin 20° - sin 60° ö
= ç ÷ 1 æ1 ö 1 1 æ1 ö 1 3 1
4è cos10° + sin 70° ø S¥ = T1 + = + = . =
2 çè 3 ÷ø 3 2 çè 3 ÷ø 3 2 2
3
= 53. (2)
4
47. (2)
(a / r)
3 é1 ù
sin 6 x + cos6 x = 1 - sin 2 2x Î ê , 1ú
S¥ =
1-r
(
Þ a = 4 r - r2 )
4 ë4 û
48. (4) é1 æ 1ö ù
2
a = 4 ê -çr - ÷ ú
sin2A + sin2B + sin2C = 4sinAsinBsinC êë 4 è 2 ø úû
in DABC.
49. (C) 54. (1)
a, b, c > 0
S=
(
10. 1049 - 1 ) AM > HM
9 a+b+c 3
50. (B) ³
3 1 1 1
12 – 32 + 52 – 72+.......upto 50 terms + +
a b c
= (1 – 3) (1 + 3) + (5 – 7) (5 + 7)+.......
a b c
= –2[1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + ......50 terms] , ,
= –2.(50)2 = –5000 b c a
AM > GM
51. (B)
1 a b c
Tn = n ( n + 1)( n + 2 )( n + 3 ) éë ( n + 4 ) - ( n - 1 ) ùû + + ³3
5 b c a
1
Tn = n ( n + 1)( n + 2 )( n + 3)( n + 4 ) 55. (3)
5 1
1 1
1 ( 64 )
1+ + +.....¥ Þ ( 64 )1- 1
- ( n - 1) n ( n + 1)( n + 2 )( n + 3 ) 7 49
7
5
1 1 7 7
Þ ( 2)
6´
T1 = .1.2.3.4.5 - ´ 0 Þ ( 64 ) 6 6 =128
5 5
1 1 56. (3)
T2 = .2.3.4.5.6 - .1.2.3.4.5 A.M. > G.M.
5 5
1 æa b cö
Tn = n ( n + 1)( n + 2 )( n + 3 )( n + 4 ) çb + c + a÷
1
5 è ø ³ æ a . b . c ö3
3 çb c a÷
1 è ø
- ( n - 1) n ( n + 1)( n + 2 )( n + 3)
5 a b c
1 + + ³3
Sn = n ( n + 1)( n + 2 )( n + 3 )( n + 4 ) b c a
5
WT # 1 E-3
JEE (Advanced) 2022/NURTURE COURSE/16-08-2020
57. (1) 2. 7
p 5p p
æaö æbö æcö Use + =
2 ç ÷ + 3 ç ÷ + 4 ç ÷ = 18 7 14 2
è2ø è3ø è4ø
2 3 4
for maximising a b c we use AM > GM. æp ö
& sin ç - q ÷ = cos q
a b c è2 ø
equality occurs when = =
2 3 4 ( )
ƒ ( x ) + g ( x ) = sin x cos x cos 2 x + sin 2 x = sin x cos x
a b c a + b + c 18
Q = = = = æpö æpö p p
2 3 4 2+3+4 9 ƒ ç ÷ + g ç ÷ = sin .cos
Þ a = 4; b = 6; c = 8. è7ø è7ø 7 7
58. (1)
æ p 5p ö æ p 5p ö
log1/ 2 x 2 < log1/ 2 x Þ x2 > x > 0 = sin ç - ÷ cos ç - ÷
Þ x2 – x > 0 Þ x(x – 1) > 0 Þ x > 1 è 2 14 ø è 2 14 ø
59. (2) 5p 5p
log1/5 7 < log1/56
= cos sin
14 14
log35 < log37
60. (2) æ 5p ö æ 5p ö
= gç ÷ + ƒç ÷
3 è 14 ø è 14 ø
cos x + cos y = 3. 2
2
æx+yö æx-yö 3
2 cos ç ÷ cos ç ÷= Q log 2- x2 6 > - log x2 -2x + 3 6
è 2 ø è 2 ø 2 2
p æx-yö 3
2 cos cos ç ÷= \ log 2-x2 6 > - log(x-1)2 +2 6 (always negative)
6 è 2 ø 2
2
æx-yö 3
cos ç ÷= \ inequality holds when log 2-x 2 6 is defined.
è 2 ø 2 2
p
( -x + y) = (Q y > x) 2 - x2 2 - x2
3 Þ >0 & ¹1
2 2
p Þ
y= ,x=0 x Î ( - 2, 2) ~ {0}
3
4. 4
SECTION-II We have x,A1,A3....A9,2y x in A.P
1. 2 2y - x
LHS < 1 d=
100
cos12x = 5sin3x + (9tan2x + cot2x)
4x + 2y
RHS = min. when 5sin3x = –5 A 20 = x + 20d =
5
and 9tan2x + cot 2x = 6(AM > GM)
2x, H1,H2.......H95 are in A.P.
cotx = 3tanx
y - 2x
1 d=
tan2 x = 100
3
1 1 8x + y
tan x = or tan x = - A '20 = 2x + 20d ' =
3 3 5
x = 30º, 210º x = 150º, 330º Now, A20 = H20 (Given)
sin3x = –1 x = 330º From 1 and 2 we get required solution.
general solution is 5. 3
7p 11p Use AM, GM
x = 2np + ,n Î I or x = 2np + ;n Î I
6 6
E-4 WT # 1
You might also like
- Aws G2 3Document112 pagesAws G2 3Mhand AmsNo ratings yet
- RC DESIGN-ColumnsDocument29 pagesRC DESIGN-Columnsdilnessa azanawNo ratings yet
- NEET Test SeriesDocument4 pagesNEET Test SeriesAbir Dn100% (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- IIT JEE 2008 Solution Paper 1Document53 pagesIIT JEE 2008 Solution Paper 1anon-973002No ratings yet
- Eulerian and Mixture Multiphase Models in ANSYS Fluent: Surya Deb Ansys Inc. November 21, 2019Document43 pagesEulerian and Mixture Multiphase Models in ANSYS Fluent: Surya Deb Ansys Inc. November 21, 2019umair35No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rotating Machines: Solution ManualDocument116 pagesDynamics of Rotating Machines: Solution ManualHassen M OuakkadNo ratings yet
- UT FSRG2 Test-3 Code-A2 SolDocument4 pagesUT FSRG2 Test-3 Code-A2 SolKrishna NayakNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2019 Jan 09 Slot 1Document9 pagesJEE Mains 2019 Jan 09 Slot 1cbsegirlsaipmtNo ratings yet
- Mathematics JEE Solutions 2022Document6 pagesMathematics JEE Solutions 2022Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) Online Exam (09-01-2020) Shift-II (Physics) PDFDocument12 pagesJEE (Main) Online Exam (09-01-2020) Shift-II (Physics) PDFABHIROOP REDDYNo ratings yet
- JEE - Main - Online Exam - 9-01-2020 - Shift-II PDFDocument34 pagesJEE - Main - Online Exam - 9-01-2020 - Shift-II PDFApoorv SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains August 27 2021 Shift2Document45 pagesJee Mains August 27 2021 Shift2Atharva Sheersh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ellipse Narayana Pyq Sol 2Document7 pagesEllipse Narayana Pyq Sol 2vallabha kaustubhaNo ratings yet
- 152040-24!01!23 Mathematicss Paper+With+Answer MorningDocument11 pages152040-24!01!23 Mathematicss Paper+With+Answer Morningmr.anbhbNo ratings yet
- MA112 Test 1 Semester 2 2018Document3 pagesMA112 Test 1 Semester 2 2018Tusanita MapuolaNo ratings yet
- Basic Math - EXERCISE-1Document17 pagesBasic Math - EXERCISE-1Rajat AnandNo ratings yet
- Vpts 12Document12 pagesVpts 12MARSHMALLOW GAMINGNo ratings yet
- MAT2691 Assignment 01-2023-S1Document11 pagesMAT2691 Assignment 01-2023-S1Carole-ann de BeerNo ratings yet
- Mat102 - Scheme-A-2021Document4 pagesMat102 - Scheme-A-2021ashwinharikumar56No ratings yet
- Mathematics v2 PDFDocument15 pagesMathematics v2 PDFVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- 8696Document3 pages8696Mohd Mohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 30 01 2023 - Evening Shift 2 PDFDocument24 pagesAnswer and Solutions - JEE - Main 2023 - PH 1 - 30 01 2023 - Evening Shift 2 PDFunidentified incognitoNo ratings yet
- X 2ifx 2: ETS - 5 MathematicsDocument4 pagesX 2ifx 2: ETS - 5 MathematicsPradyumna ParthakudiNo ratings yet
- 22 Mathematics Paper With Solution EveningDocument8 pages22 Mathematics Paper With Solution EveningAISHA AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Pre-Board Examination (First) 2021-22 Class: Xii Subject: MathematicsDocument8 pagesMarking Scheme Pre-Board Examination (First) 2021-22 Class: Xii Subject: MathematicsChhavi DhimanNo ratings yet
- Cbse Term - Ii Full Test-1: FiitjeeDocument9 pagesCbse Term - Ii Full Test-1: FiitjeeSwastik PandeyNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument15 pagesMathematicsAnmol PuriNo ratings yet
- MA112 Test 2 Semester 2 2018Document4 pagesMA112 Test 2 Semester 2 2018Kaushal KumarNo ratings yet
- AnsSol JEEMain 2023 PH 2-10-04 2023 Evening PaperDocument23 pagesAnsSol JEEMain 2023 PH 2-10-04 2023 Evening Paperviswanath100% (1)
- WWW Aimstutorial inDocument58 pagesWWW Aimstutorial inAakashNo ratings yet
- TN 11th-maths-model-question-paper-EM-2018 - WWW - Governmentexams.co - inDocument6 pagesTN 11th-maths-model-question-paper-EM-2018 - WWW - Governmentexams.co - inmeshaNo ratings yet
- (6881) DPP 7 9 Ja (01 To 03) Module 1 BDocument11 pages(6881) DPP 7 9 Ja (01 To 03) Module 1 Bdeepak123456789abcNo ratings yet
- Maths Pre-Board 1 Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesMaths Pre-Board 1 Marking SchemePoonam RoyNo ratings yet
- (Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Document13 pages(Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Resonance EduventuresNo ratings yet
- Prac 3 BsolDocument3 pagesPrac 3 BsolDorwinNeroNo ratings yet
- KVPY Stream SB SX Solved Sample Paper 2015 Paper 1Document37 pagesKVPY Stream SB SX Solved Sample Paper 2015 Paper 1CG13698No ratings yet
- A RK y (First T Exam Nation 2015-2016) : Nswe e ErmDocument9 pagesA RK y (First T Exam Nation 2015-2016) : Nswe e ErmSangeeta BansalNo ratings yet
- DPP No. 7: PhysicsDocument3 pagesDPP No. 7: PhysicsUddhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2027-3.0 Hour Review Test-1-SOLUTION - FinalDocument9 pages2027-3.0 Hour Review Test-1-SOLUTION - FinalROHANNo ratings yet
- 01.05.2019 - It-1 Nur - P I - Iit-Jee (M+a)Document12 pages01.05.2019 - It-1 Nur - P I - Iit-Jee (M+a)priyanshukumawat227No ratings yet
- Solutions - Maths Workbook - 2 - Complex NumbersDocument101 pagesSolutions - Maths Workbook - 2 - Complex NumbersravimcanitNo ratings yet
- MA112 Test 1 2017 PDFDocument3 pagesMA112 Test 1 2017 PDFTusanita MapuolaNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Mathematics P1 (ENG) NOV Question PaperDocument7 pagesGr10 Mathematics P1 (ENG) NOV Question PaperthovhakalepatienceNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths - DPP 07 (Extra) - Arjuna NEET Fastrack 2024Document3 pagesBasic Maths - DPP 07 (Extra) - Arjuna NEET Fastrack 2024barnikbanerjee11No ratings yet
- Kunci Jawaban Uas Xii Sem 1 K-13Document2 pagesKunci Jawaban Uas Xii Sem 1 K-13Anindya SyahwaNo ratings yet
- Nda (Maths) Mock Test - 62 (Solution)Document7 pagesNda (Maths) Mock Test - 62 (Solution)Gurpreet GabaNo ratings yet
- Ans & Sol - JEE (Main) - 2022 - Phase-2 - 26-07-2022 - Evening - (Physics)Document6 pagesAns & Sol - JEE (Main) - 2022 - Phase-2 - 26-07-2022 - Evening - (Physics)Ashish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Companion-Soln bk5Document6 pagesCompanion-Soln bk5samthegofNo ratings yet
- 3001 Mathematics Paper+With+Answer Morning PDFDocument4 pages3001 Mathematics Paper+With+Answer Morning PDFNishkarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Answer Advance Calculus BEEU 2033 Chapter 2-5Document16 pagesTutorial Answer Advance Calculus BEEU 2033 Chapter 2-5nurfazlinda123No ratings yet
- 65ae0d61bd3885001816ced2 - ## - Mock Test 09 (Hints & Solution) JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2024Document13 pages65ae0d61bd3885001816ced2 - ## - Mock Test 09 (Hints & Solution) JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2024myownwork8678No ratings yet
- MATHS SAT PAPER 03 Solution (431103)Document7 pagesMATHS SAT PAPER 03 Solution (431103)hiNo ratings yet
- DPP No.3 English PC Zhk7lY0Document7 pagesDPP No.3 English PC Zhk7lY0m2595jn9d9No ratings yet
- Ans and Sol JEE Main 2024 PH 1-01-02 2024 Morning Actual PaperDocument30 pagesAns and Sol JEE Main 2024 PH 1-01-02 2024 Morning Actual Paperpriyanshusharmaps9833No ratings yet
- (Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Document11 pages(Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Resonance EduventuresNo ratings yet
- UT FSRG2 Test-2 Code-A2 Sol 09.07.2023Document4 pagesUT FSRG2 Test-2 Code-A2 Sol 09.07.2023Skull GNo ratings yet
- NR 10102 Mathematics I CDocument8 pagesNR 10102 Mathematics I CSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- DPP (13-15) 11th J-Batch MathsDocument11 pagesDPP (13-15) 11th J-Batch MathsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 5..aod 21.05.21 Ans&solDocument9 pages5..aod 21.05.21 Ans&solKovid AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Maths 27 January Shift 1 ByjusDocument6 pagesJee Main Maths 27 January Shift 1 Byjusakshayrajhans053No ratings yet
- Jee Main 2024 Shift1 Maths Jan27Document6 pagesJee Main 2024 Shift1 Maths Jan27neerajbhayal3456No ratings yet
- Solutions: JEE Main - 2020 - 9 January 2020 (Evening) PhysicsDocument13 pagesSolutions: JEE Main - 2020 - 9 January 2020 (Evening) PhysicsRaghav MadanNo ratings yet
- Cosmos College of Management & Technology: Tutepani (Near Satdobato), Lalitpur Tel: 01-5151419 / 2151806Document4 pagesCosmos College of Management & Technology: Tutepani (Near Satdobato), Lalitpur Tel: 01-5151419 / 2151806Rahul RouniyarNo ratings yet
- PHASE (E-LEARNING) : 1,2,2A, 3 & 4: Weekly Test - 2Document7 pagesPHASE (E-LEARNING) : 1,2,2A, 3 & 4: Weekly Test - 2Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IntroductionDocument15 pagesChemistry IntroductionScience 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- SS (Phase-03) Test Planner 2021 22Document1 pageSS (Phase-03) Test Planner 2021 22Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- States of Matter 1Document7 pagesStates of Matter 1Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- AIATS Planner For SS - 2122Document3 pagesAIATS Planner For SS - 2122Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Ray Optics and OpticalDocument44 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Ray Optics and OpticalScience 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- Machinability of Gray Cast Irons - AFS - Modern Castings - WebOnly0305Document17 pagesMachinability of Gray Cast Irons - AFS - Modern Castings - WebOnly0305crazy dNo ratings yet
- YSS Cold Working Die PDFDocument11 pagesYSS Cold Working Die PDFHoang Le VuNo ratings yet
- Members in Compression - IVDocument38 pagesMembers in Compression - IVFatin FalconNo ratings yet
- Borehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangDocument7 pagesBorehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangJose Leo MissionNo ratings yet
- Bingham Model For Pumpable ConcreteDocument11 pagesBingham Model For Pumpable ConcreteYogendra SINGH PATELNo ratings yet
- Timken-Engineering-Manual 10424Document8 pagesTimken-Engineering-Manual 10424panji hastawirataNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Standardization of Flanged and Flued Expansion Joint DesignDocument32 pagesOptimization and Standardization of Flanged and Flued Expansion Joint DesignPankaj SinglaNo ratings yet
- Dye Sensitized Solar Cells For The Building Integrated Photovoltaic MarketDocument4 pagesDye Sensitized Solar Cells For The Building Integrated Photovoltaic MarketRui GarciaNo ratings yet
- VI. Auxiliary FunctionsDocument21 pagesVI. Auxiliary FunctionsAnshu Kumar Gupta100% (4)
- Ncyclopedia of Iron, Steel, and Their Alloys - Austempered Ductile Cast IronDocument21 pagesNcyclopedia of Iron, Steel, and Their Alloys - Austempered Ductile Cast IronPranoy BaruaNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument17 pagesFuel CellsSameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Formation of Energy Bands in Solids.: ConductorDocument16 pagesUnit-Iv Formation of Energy Bands in Solids.: ConductorBellala ParimalaNo ratings yet
- Gas Phase Embrittlement and Time Dependent Cracking of Nickel Based Super AlloysDocument48 pagesGas Phase Embrittlement and Time Dependent Cracking of Nickel Based Super AlloysgtrdcNo ratings yet
- ProQuestDocuments 2024 04 04Document2 pagesProQuestDocuments 2024 04 04Theodøros D' SpectrøømNo ratings yet
- Phy Assignment03E PDFDocument25 pagesPhy Assignment03E PDFBhawna SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDF Card - Ni - CR - Fe - 00-035-1375Document1 pagePDF Card - Ni - CR - Fe - 00-035-1375mohammed sabeehNo ratings yet
- CHE425: Problem SetDocument9 pagesCHE425: Problem SetJack AndreasNo ratings yet
- Solid State Assignment-1 Answer KeyDocument4 pagesSolid State Assignment-1 Answer KeyShibashis PaulNo ratings yet
- Line Single PhaseDocument2 pagesLine Single PhasehussamNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnandha BabuNo ratings yet
- Flashing LiquidsDocument31 pagesFlashing LiquidsAmerNo ratings yet
- Solutions D-02 Applied Mechanics: (June 2003)Document19 pagesSolutions D-02 Applied Mechanics: (June 2003)AdzLinkBalaoangNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Precipitators: (Nazaroff & Alvarez-Cohen, Pages 447-453 + Added Material)Document10 pagesElectrostatic Precipitators: (Nazaroff & Alvarez-Cohen, Pages 447-453 + Added Material)jonnelNo ratings yet
- 5 Lead-Tin Phase Diagrams Using Cooling CurvesDocument2 pages5 Lead-Tin Phase Diagrams Using Cooling CurvesOliver TabellNo ratings yet
- INTERNDocument21 pagesINTERNSahil Shah100% (1)