Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 7 q3 Week 4 5
Uploaded by
Marwen FernandezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7 q3 Week 4 5
Uploaded by
Marwen FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7
WEEK 4-5
Unit 3 Module 2- Waves Around You
Title: WAVES AS A CARRIER OF ENERGY
Waves around us come in different form; it can be water waves, sound waves and light waves. When you dip you finger
in a basin with water, waves are formed. Playing musical instruments such as guitar, sound waves are produced, and when you
lit a candle during power interruption at night, light waves brighten the room.
A wave is a periodic disturbance that moves away from a source and carries energy with it. Waves that propagate
through solid, liquid and gas are mechanical waves and can be classified as transverse and longitudinal waves.
Anatomy of a wave
a.Crest - the highest point of a wave
b.Trough - the lowest point of a wave
c. Amplitude- the height of a wave
d. Frequency- the number of waves passing a given point
e.Wavelength- the distance between adjacent crest or troughs
LERNING TASK 1:Copy the illustration in a separate sheet of paper and label the parts of a wave
Sound is a longitudinal wave created by object that vibrates and appeal to our auditory system. Humans just like us can
hear sounds with frequency of 20 Hertz to 20 000 Hz.
Sounds with frequencies beyond 20 000 Hz are described as ultrasonic, while infrasonic sounds refer to those with
frequencies of lower than 20 Hz.
Dogs, cats, and bats are some of the animals that can hear sounds that range from 45 Hz to 120 000 Hz.
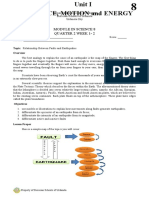
In given figure above, a tuning fork is used to demonstrate the propagation of sound. The vibration produced by the
tuning fork determined the movement of the molecules of air to the right creating compression, the molecules
As the prongs of the tuning fork vibrates, the air molecules moved closer to each other creating compression. As the air
molecules moved apart, thus making up the rarefaction.
Sound is a mechanical wave. It requires a medium to propagate. Without the state of matter, it could not transmit
energy. Sound travels faster in solid than liquid or gas. Look at the figure below, the particles of solid are packed tighter together
thus allowing fast collision of particles and transmission of sounds.
Nature of Particles in different States of Matter
LEARNING TASK 2:Answer the following Questions.
1. How do we hear sounds?____________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. What is an ultrasonic sound? Infrasonic sound? Audible sound? _____________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Do sound waves travel fastest in solids? Prove your answer. ________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
Characteristics of Sound
Sound is described by three characteristics:
a. Pitch
b.Loudness
c. Intensity
Pitch is the highness or lowness of sound. Males have low-pitched voice because their vocal cords are typically
massive and longer than females. Can you name some popular Filipino singers with high-pitched voice? Loudness and Intensity
are closely related.
Intensity of sound refers to the amount of energy of a sound wave. It is measured in decibel.
Loudness on the other hand is subjective. It is a sensation acquired by hearing which depends on how people perceived
sounds. Usually, a high intensity sound produces a louder sound, and a low intensity sound creates a softer sound. As the
intensity becomes higher, the frequency and energy also become high.
LEARNING TASK 3:Read the questions carefully and write your answer in a separate sheet of paper.
1. Differentiate pitch, intensity and loudness. ___________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. How is pitch and wavelength of soundwave related to each other? ________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. How loudness differs with the person? ___________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4. As an ambulance approaches and passes you, how can you explain the sound it produced? ___________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5. Suggest ways on how to protect human ear from noise pollution._________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
LEARNING TASK 4: Fill in the blanks by identifying the appropriate word for each blank. Write the answers on a separate
sheet of paper.
A ________ is a periodic disturbance that moves away from a source and carries energy with it. Waves that propagate
through solid, liquid and gas are ______________ and can be classified as transvers and longitudinal waves. _____ is the
highness or lowness of sound. _______ of sound refers to the amount of energy of a sound wave.___________ is a sensation
acquired by hearing which depends on how people perceived sounds.
You might also like
- Stomp! - Brothers Johnson (Download Bass Transcription and Bass Tab in Best Quality at WWW - Nicebasslines.com)Document5 pagesStomp! - Brothers Johnson (Download Bass Transcription and Bass Tab in Best Quality at WWW - Nicebasslines.com)nicebasslines_com91% (11)
- Lesson Plan in Characteristic of Light (Grade7) by Harrison's GirlDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Characteristic of Light (Grade7) by Harrison's GirlFlorence Ivy Magtanong83% (6)
- SubaruDocument1 pageSubaruIdsaragon Punwun100% (2)
- LeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Diana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 6Document1 pageFormative Assessment 6bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- Q3SCIE7Document6 pagesQ3SCIE7rose ann chavezNo ratings yet
- Cesar E. Vergara Memorial High School: Activity 2: Know Me!Document2 pagesCesar E. Vergara Memorial High School: Activity 2: Know Me!Jonah Santos-PinedaNo ratings yet
- Q3 G7 Science M2Document32 pagesQ3 G7 Science M2arianepatoh2100% (1)
- Name: - Grade & Section: - School: - DateDocument13 pagesName: - Grade & Section: - School: - DateDianneGarciaNo ratings yet
- Learner's Material: ScienceDocument14 pagesLearner's Material: ScienceElma MayNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2: Week 1 - 2Document10 pagesScience: Quarter 2: Week 1 - 2Khiel YumulNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode5 - SLMDocument4 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode5 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q3 W4Document47 pagesScience 6 Q3 W4Anna Antonia PagalanNo ratings yet
- Properties of SoundDocument23 pagesProperties of SoundRichard Estrada100% (3)
- Light and SoundDocument16 pagesLight and SoundMichaelle BunaoNo ratings yet
- Properties of SoundDocument20 pagesProperties of SoundRichard EstradaNo ratings yet
- MEED 2 Midterm LAS 9.2Document3 pagesMEED 2 Midterm LAS 9.2Joemari GalmanNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Q3 Week 7Document11 pagesScience 4 Q3 Week 7monica saturninoNo ratings yet
- Physics Module 3Document36 pagesPhysics Module 3Euann MagtibayNo ratings yet
- G8-W4 WS1 Sound and Waves VocabularyDocument2 pagesG8-W4 WS1 Sound and Waves Vocabularyjohnrobin.amoguisNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Summative Week 4Document1 pageSCIENCE Summative Week 4jannaNo ratings yet
- Waves Unit 6 8Document6 pagesWaves Unit 6 8Jonathan L. CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Science: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDocument16 pagesScience: Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistMaryjane TamparongNo ratings yet
- Las Q3 Module 4 2Document2 pagesLas Q3 Module 4 2Jerome VitalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument6 pagesMathematics, Science, and Technologyfrederick liponNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 8 Quarter 2 Week 1-2: Topic: Relationship Between Faults and EarthquakesDocument9 pagesModule in Science 8 Quarter 2 Week 1-2: Topic: Relationship Between Faults and EarthquakesDanica Feliciano Lorenzo100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesChristine Marquez RamosNo ratings yet
- Speed of Sound in Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument6 pagesSpeed of Sound in Solids, Liquids and GasesMerlpa May AlcardeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SoundDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 SoundSomaya HussienNo ratings yet
- Review For Test On Chapter 10-14Document6 pagesReview For Test On Chapter 10-14Cassie BNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Science 7Document8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Science 7sandra bumalayNo ratings yet
- PAPER ESM SOUND (Group 2)Document18 pagesPAPER ESM SOUND (Group 2)Ainun AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Science 4 3.3Document4 pagesScience 4 3.3Nelson ManaloNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document37 pagesScience 2Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Characteristics of Sound: For Science Grade 4 Quarter 3/week 7Document12 pagesInvestigating The Characteristics of Sound: For Science Grade 4 Quarter 3/week 7Arnel Jumawan100% (1)
- Module 2 in Forensic Photography Chapter 2 (Autosaved)Document9 pagesModule 2 in Forensic Photography Chapter 2 (Autosaved)escasinasjeralyn42No ratings yet
- Text ResourceDocument32 pagesText Resourceapi-235382852No ratings yet
- Sound Energy: Ms. TiffanyDocument32 pagesSound Energy: Ms. TiffanyTiffany ArazaNo ratings yet
- Science Revision NotesDocument13 pagesScience Revision NotesNoaNo ratings yet
- Q 2 Week 3 Day 1 2 Properties of LightDocument24 pagesQ 2 Week 3 Day 1 2 Properties of LightNeil Joseph LandinginNo ratings yet
- G8 Q1 Module-6.LightDocument10 pagesG8 Q1 Module-6.LightMark Christian SanicoNo ratings yet
- Science: Waves: Carriers of EnergyDocument13 pagesScience: Waves: Carriers of EnergyAlethea Aquie100% (1)
- Light Wave PropertiesDocument27 pagesLight Wave PropertiesDom Christian LastNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Q3 Science LASDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Q3 Science LASCharina Sato50% (2)
- Ch-13 Why Do We Fall IllDocument25 pagesCh-13 Why Do We Fall IllSagarika MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Sounds: Propagation & CharacteristicsDocument43 pagesModule 5 Sounds: Propagation & CharacteristicsMasTer CrafT (MasTerCrafT89)No ratings yet
- Light and Illumination Lesson 1Document33 pagesLight and Illumination Lesson 1Victorino Victorino ButronNo ratings yet
- LAS LightDocument2 pagesLAS LightMaricel ValenNo ratings yet
- Mod. 59 - L, H, EDocument46 pagesMod. 59 - L, H, EDaryl LazoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pagesScience 7 Assessment QuestionsLea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument25 pagesSoundsubashini silvaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - Worksheet On SoundsDocument4 pagesGrade 7 - Worksheet On SoundsLavander Blush100% (2)
- How Sound Is Produced and Transmitted Through a MediumDocument14 pagesHow Sound Is Produced and Transmitted Through a MediumOjas SinghNo ratings yet
- Light Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesLight Study Guide Answersapi-240689882No ratings yet
- Siberian Qigong The Hidden Facet of QigongDocument99 pagesSiberian Qigong The Hidden Facet of Qigongeeklşeke kelekşlekNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Unit 1Document8 pagesScience 8 Unit 1miraples siblingsNo ratings yet
- 2eso - MusicDocument110 pages2eso - MusicElena Sánchez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Anatomy of A Wave - How Do You Describe Waves?: BackgroundDocument2 pagesActivity 4 - Anatomy of A Wave - How Do You Describe Waves?: BackgroundShane Catherine BesaresNo ratings yet
- Sound and Light Activities..Document2 pagesSound and Light Activities..rihannah faith mesaNo ratings yet
- Activity Pack Sound Energy ActivityDocument8 pagesActivity Pack Sound Energy ActivityalexNo ratings yet
- DIRON Light and SoundDocument14 pagesDIRON Light and SoundLunaNo ratings yet
- Mail OnlineDocument12 pagesMail OnlineMarwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Mail OnlineDocument12 pagesMail OnlineMarwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- What Is Being AssertiveDocument4 pagesWhat Is Being Assertivejrg.rodriguez100% (1)
- Assert Hand02Document1 pageAssert Hand02MorxiahNo ratings yet
- YTS / YIFY Torrent Sites & ProxiesDocument1 pageYTS / YIFY Torrent Sites & ProxiesTindusNiobetoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Q3 WEEK 3Document2 pagesGrade 7 Q3 WEEK 3Paul Marwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 q3 Week 4 5Document2 pagesGrade 7 q3 Week 4 5Marwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pa4X User Manual v3.1 E PDFDocument1,160 pagesPa4X User Manual v3.1 E PDFGergely HillNo ratings yet
- AW Noel Gallagher Don't Look Back in AngerDocument1 pageAW Noel Gallagher Don't Look Back in AngerrpGIu0998No ratings yet
- 245 Penfold Digital Audio ProjectsDocument95 pages245 Penfold Digital Audio Projectsmanecolooper100% (1)
- TreVoce EQ DSP Series ManualDocument5 pagesTreVoce EQ DSP Series ManualMohammad FamuNo ratings yet
- Custom Iw 106: Product Specification SheetDocument1 pageCustom Iw 106: Product Specification SheetChiluvuri VarmaNo ratings yet
- SFA String Methods Course PlanDocument27 pagesSFA String Methods Course PlanFernando MartinezNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness Exercises PDFDocument7 pagesMindfulness Exercises PDFSimplegirl4uNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Phono CartridgesDocument2 pagesA Guide To Phono CartridgesuthramNo ratings yet
- What's New in Pro Tools 12.8Document42 pagesWhat's New in Pro Tools 12.8Matthew Howe YipNo ratings yet
- Sound System SpecsDocument4 pagesSound System SpecsRey Mark GipulaoNo ratings yet
- JBL Irx112bt Sell Sheet 12-18-19Document2 pagesJBL Irx112bt Sell Sheet 12-18-19Óscar SánchezNo ratings yet
- Audiometry Screening and InterpretationDocument8 pagesAudiometry Screening and InterpretationJuan Sebastián Montaño MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- SY77 Owners ManualDocument268 pagesSY77 Owners ManualIoannis Giannakakis100% (1)
- 10307412-User Manual-Tts 36-ADocument24 pages10307412-User Manual-Tts 36-ADaniel FernandezNo ratings yet
- Stack Noice Control 01Document2 pagesStack Noice Control 01gechaves1No ratings yet
- Physics Give Reason Exam 18Document36 pagesPhysics Give Reason Exam 18apoorvnain15No ratings yet
- MUS1!19!20 Q1 L1 Sound and SilenceDocument17 pagesMUS1!19!20 Q1 L1 Sound and SilenceApril PerezNo ratings yet
- Momus Design CNC Router Manual Version 2.1Document178 pagesMomus Design CNC Router Manual Version 2.1Francisco Teruel100% (8)
- Section 16010Document10 pagesSection 16010وسام اللبديNo ratings yet
- Saffire PRO Range: Dual Unit Support GuideDocument21 pagesSaffire PRO Range: Dual Unit Support GuideMartin BalboaNo ratings yet
- TIM Square-Sine Inter Modulation MeasuringDocument8 pagesTIM Square-Sine Inter Modulation MeasuringGerardo Angel GentileNo ratings yet
- Modulation or Vocal VarietyDocument22 pagesModulation or Vocal VarietyLouie Niel VasquezNo ratings yet
- EGSA Silencer Rating Guide FinalDocument15 pagesEGSA Silencer Rating Guide FinalShiv ChevliNo ratings yet
- AFRICAN MUSICAL TRADITIONSDocument18 pagesAFRICAN MUSICAL TRADITIONSGRAZ SHIEL HARINo ratings yet
- MSC Ga35vbDocument24 pagesMSC Ga35vbLeo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Allen Speakers BrochureDocument3 pagesAllen Speakers BrochureBlanca PantojaNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Lessons W-B Mon 12th OctoberDocument22 pagesInstrumental Lessons W-B Mon 12th OctoberLuca NewmanNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 5: MUSIC (Module) 1 QuarterDocument46 pagesMapeh 5: MUSIC (Module) 1 QuarterIce KuanNo ratings yet