Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meropenem Meropenem: (Lexi-Drugs Multinational)
Uploaded by
Jhoann JamanilaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Meropenem Meropenem: (Lexi-Drugs Multinational)
Uploaded by
Jhoann JamanilaCopyright:
Available Formats
Search Lexicomp !
User Guide Log Out
Home Trissel's IV Compatibility Interactions Drug I.D. Patient Education Calculators More Clinical Tools
$
" Back To Search ! Find in document Jump to Section # Print Help
Meropenem (Lexi-Drugs Multinational)
Outline Expand All Monograph Images Adult Patient Education Pediatric Patient Education
Antibiotic, Carbapenem
Brand Names:
International
Dosing: Adult
International Note: Infusion method: Dosing is presented based on the traditional infusion method over 30 minutes,
Nonproprietary Names unless otherwise specified.
(INN)
Usual dosage range:
Brazilian Nonproprietary
Traditional intermittent infusion method (over 30 minutes): IV: 500 mg every 6 hours or 1 to 2 g
Names (DCB)
every 8 hours; 500 mg every 6 hours achieves comparable pharmacokinetic and
Japanese Accepted Name pharmacodynamic parameters to 1 g every 8 hours (Kuti 2003; Lodise 2006).
(JAN) Extended infusion method (off-label): IV: 1 to 2 g every 8 hours over 3 hours. May give a loading
Anatomic Therapeutic dose of 1 to 2 g over 30 minutes, especially when rapid attainment of therapeutic drug
Chemical (ATC) concentrations is desired (eg, sepsis) (Crandon 2011; SCCM [Rhodes 2017]).
Classification Continuous infusion method (off-label): IV: 2 g every 8 hours over 8 hours or 3 g every 12 hours
over 12 hours (Venugopalan 2018). May give a loading dose of 1 to 2 g over 30 minutes,
Pharmacologic Category
especially when rapid attainment of therapeutic drug concentrations is desired (eg, sepsis)
Dosages (SCCM [Rhodes 2017]).
Dosing: Adult Note: Extended and continuous infusion methods are based largely on pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic modeling data (Crandon 2011; Dulhunty 2015; Yu 2018). A prolonged
Dosing: Geriatric
infusion strategy has a greater likelihood of attaining pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic
Dosing: Renal
targets and may offer clinical benefit in patients with severe infections or less susceptible
Impairment: Adult
pathogens (Yu 2018). Meropenem stability (admixed with NS at a concentration of 20 mg/mL)
Dosing: Hepatic at room temperature for >1 hour or under refrigeration for >15 hours is not supported by the
Impairment: Adult
manufacturer. Data exist supporting stability for extended and continuous infusion when
Dosing: Obesity: Adult admixed with NS at a concentration of 14.3 mg/mL at room temperature for ≤7 hours (Fawaz
Dosing: Pediatric 2019) and at a concentration of 20 mg/mL under refrigeration for ≤24 hours (Patel 1997).
Dosing: Renal Pharmacokinetic data support the use of an admixture of 10 mg/mL in NS as stable at room
Impairment: Pediatric temperature for an infusion duration ≤12 hours (Venugopalan 2018).
Dosing: Hepatic
Impairment: Pediatric Indication-specific dosing:
Calculations Anthrax (off-label use): Note: Consult public health officials for event-specific
Uses recommendations.
Systemic (meningitis excluded), treatment (alternative agent): IV: 2 g every 8 hours as part of
Clinical Practice
an appropriate combination regimen for 2 weeks or until clinically stable, whichever is
Guidelines
longer (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Administration and Meningitis, treatment: IV: 2 g every 8 hours as part of an appropriate combination regimen for
Storage Issues 2 to 3 weeks or until clinically stable, whichever is longer (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Medication Safety Issues Note: Antitoxin should also be administered. Following the course of IV combination therapy
for systemic anthrax infection (including meningitis), patients exposed to aerosolized
Warnings & Precautions spores require oral monotherapy to complete a total antimicrobial course of 60 days (CDC
[Hendricks 2014]).
Reproduction, Pregnancy,
& Lactation Bloodstream infection (gram-negative bacteremia) (off-label use): For empiric therapy of
known or suspected gram-negative organisms (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa) or
Adverse Reactions
pathogen-directed therapy for organisms resistant to other agents.
Interactions IV: 1 g every 8 hours (IDSA [Mermel 2009]); for empiric therapy in patients with neutropenia,
severe burns, sepsis, or septic shock, give as part of an appropriate combination regimen
Patient & Therapy (Kanj 2019a; Moehring 2019a; SCCM [Rhodes 2017]). Note: For critical illness or infection
Management
with an organism with an elevated minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), some experts
Preparations prefer the extended or continuous infusion method and/or increasing the dose to 2 g
every 8 hours (Del Bono 2017; Moehring 2019a; SCCM [Rhodes 2017]).
Pharmacology & Duration of therapy: Usual duration is 7 to 14 days depending on the source, pathogen, extent
Pharmacokinetics
of infection, and clinical response; a 7-day duration is recommended for patients with
Dental Information uncomplicated Enterobacteriaceae infection who respond appropriately to antibiotic
therapy (Moehring 2019a; Yahav 2018). Note: If neutropenic, extend treatment until
Pearls & Related afebrile for 2 days and neutrophil recovery (ANC ≥500 cells/mm3 and increasing) (IDSA
Information [Freifeld 2011]). For P. aeruginosa bacteremia in neutropenic patients, some experts treat
for a minimum of 14 days and until recovery of neutrophils (Kanj 2019b).
References
Cystic fibrosis, acute pulmonary exacerbation (off-label use): For empiric or targeted
Brand Names: US therapy for P. aeruginosa or other gram-negative bacilli.
Brand Names: Canada IV: 2 g every 8 hours, most often given as part of an appropriate combination regimen (Chmiel
This site uses cookies. By continuing to use
2014; Flume 2009).this site
Note: Someyou areprefer
experts agreeing to our
the extended use of infusion
or continuous cookies.
method to optimize exposure (Delfino 2018; Kuti 2004; Simon 2019).
Continue or find out more.
Duration of therapy: Duration is usually 10 days to 3 weeks or longer based on clinical response
You might also like
- Antiemetic Drug Use in Children What The.3Document6 pagesAntiemetic Drug Use in Children What The.3Zafitri AsrulNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime: Drug Information: Special AlertsDocument18 pagesCefuroxime: Drug Information: Special Alertsminhmap90_635122804No ratings yet
- Ceftazidime and Avibactam - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument16 pagesCeftazidime and Avibactam - Drug Information - UpToDateMarius PapuricaNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument47 pagesAmoxicillin - Drug Information - UpToDateMikaela lNo ratings yet
- Meropenem - Drug Information - UpToDate-2Document8 pagesMeropenem - Drug Information - UpToDate-2Vh TRNo ratings yet
- Meropenem - Drug Information - UpToDate-2Document8 pagesMeropenem - Drug Information - UpToDate-2Vh TRNo ratings yet
- COVID Clinical Management 14012022Document1 pageCOVID Clinical Management 14012022Naina DesaiNo ratings yet
- National Task Force Clinical Guidance for Managing Adult COVID-19 PatientsDocument1 pageNational Task Force Clinical Guidance for Managing Adult COVID-19 PatientsWhiteNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics-Generation OperationDocument5 pagesAntibiotics-Generation OperationZamzami Ahmad FahmiNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneShaira TanNo ratings yet
- FlagylDocument3 pagesFlagylAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1Document1 pageCOVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1shivani shindeNo ratings yet
- Drug Information Response: January 30, 2023Document10 pagesDrug Information Response: January 30, 2023api-661456802No ratings yet
- Medical Treatment of Endometriosis-Related PainDocument24 pagesMedical Treatment of Endometriosis-Related PainAgung SentosaNo ratings yet
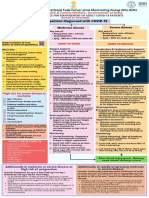
- Adult Patient Diagnosed With COVID-19: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of IndiaDocument1 pageAdult Patient Diagnosed With COVID-19: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of Indiapramodbankhele3845No ratings yet
- Penicillin G (Intravenous and Short-Acting Intramuscular) - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument29 pagesPenicillin G (Intravenous and Short-Acting Intramuscular) - Drug Information - UpToDateMikaela lNo ratings yet
- Bmj-2021-069211.full Reduce Unnecessary Use of Proton Pump InhibitorsDocument7 pagesBmj-2021-069211.full Reduce Unnecessary Use of Proton Pump InhibitorsYo MeNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Puncak Alam Campus Faculty of Health SciencesDocument9 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Puncak Alam Campus Faculty of Health SciencesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- Needle Temperature and PainDocument5 pagesNeedle Temperature and PainCici PatresiaNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin - Drug Information - UpToDate PDFDocument56 pagesClarithromycin - Drug Information - UpToDate PDFNaztasia 'ola' Flowerin BNo ratings yet
- Yovita - The Role of Clinical Pharmacist On Safe Administration AntibioticDocument48 pagesYovita - The Role of Clinical Pharmacist On Safe Administration AntibioticRois HasyimNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Terapi ImunoglobulinDocument13 pagesTerapi ImunoglobulinMochammad Arsyi GNo ratings yet
- Impétigo Revisión SistemáticaDocument21 pagesImpétigo Revisión SistemáticaDanielNo ratings yet
- SHC SMUG RibavirinDocument2 pagesSHC SMUG RibavirinMario BulaciosNo ratings yet
- Mount Carmel Medication Management Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesMount Carmel Medication Management Pocket GuideWOSU100% (1)
- 3.effects of Zingiber Officinalis (WILLD.)Document6 pages3.effects of Zingiber Officinalis (WILLD.)adil.shanuNo ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Anti Tubercular Drugs. MDR TBDocument75 pagesAdverse Effects of Anti Tubercular Drugs. MDR TBDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (1)
- Recommendation For The Use of Antibiotics For The Treatment of InfectionDocument5 pagesRecommendation For The Use of Antibiotics For The Treatment of InfectionGem BorjaNo ratings yet
- Dexmedetomidine - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument21 pagesDexmedetomidine - Drug Information - UpToDateRicardo Ortiz NovilloNo ratings yet
- Eptinezumab in Episodic Migraine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (PROMISE-1)Document14 pagesEptinezumab in Episodic Migraine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (PROMISE-1)JUAN MANUEL CERON ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Student medication interactionsDocument26 pagesStudent medication interactionsLila DanielsNo ratings yet
- Dr._Nataraj__EJCM-132-1888-1893-2023Document7 pagesDr._Nataraj__EJCM-132-1888-1893-2023vithz kNo ratings yet
- PHN AnalgesikDocument9 pagesPHN AnalgesikAhmad Isyai RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Efficacyof Ceftriaxone 1 Gdaily Versus 2 Gdailyfor The Treatmentof Community Acquired Pneumonia ASystematic Reviewwith Meta AnalysisDocument12 pagesEfficacyof Ceftriaxone 1 Gdaily Versus 2 Gdailyfor The Treatmentof Community Acquired Pneumonia ASystematic Reviewwith Meta AnalysisChristine LilyanaNo ratings yet
- A Randomized Comparative Trial of Two Low-Dose Oral Isotretinoin Regimens in Moderate To Severe Acne VulgarisDocument8 pagesA Randomized Comparative Trial of Two Low-Dose Oral Isotretinoin Regimens in Moderate To Severe Acne VulgarisKadir KUCUKNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Provides Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesDrug Study Provides Nursing Care PlanMenard VelascoNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@S0140 67362032544 7Document10 pages10.1016@S0140 67362032544 7Omar Nassir MoftahNo ratings yet
- Penicilina G Benzatínica - DynaMedDocument3 pagesPenicilina G Benzatínica - DynaMedMedipackNo ratings yet
- Gulati 2020Document14 pagesGulati 2020Anisha MDNo ratings yet
- Emerging Treatment Strategies For Impetigo in Endemic and Nonendemic Settings: A Systematic ReviewDocument21 pagesEmerging Treatment Strategies For Impetigo in Endemic and Nonendemic Settings: A Systematic Reviewnurul hidayatiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Paracetamoldamtere71% (7)
- TB PosterDocument1 pageTB PosterSucie 1997No ratings yet
- GavisconDocument8 pagesGavisconletisha mamaNo ratings yet
- FluticasoneDocument3 pagesFluticasoneAmberNo ratings yet
- Tribute TrialDocument9 pagesTribute TrialMr. LNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGDocument25 pagesCOVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGMartin PaturlanneNo ratings yet
- New Drugs: Self-Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesNew Drugs: Self-Test QuestionscNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Cinnarizine Versus Sodium Valproate in Migraine ProphylaxisDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Cinnarizine Versus Sodium Valproate in Migraine ProphylaxisALINENo ratings yet
- Grant 2002Document13 pagesGrant 2002MarsalitaIrinePNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Guide 2013Document30 pagesAntibiotics Guide 2013Stefani NoviliaNo ratings yet
- Dexmedetomidine: Pediatric Drug InformationDocument15 pagesDexmedetomidine: Pediatric Drug InformationАлексей НиколаевNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome in ChildhoodDocument5 pagesNephrotic Syndrome in ChildhoodJessica SilaenNo ratings yet
- Top Trials in Gastroenterology & HepatologyFrom EverandTop Trials in Gastroenterology & HepatologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Garlic (Allium sativum): Monograph on a herb reputed to be medicinalFrom EverandGarlic (Allium sativum): Monograph on a herb reputed to be medicinalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacoepidemiology, Pharmacoeconomics,PharmacovigilanceFrom EverandPharmacoepidemiology, Pharmacoeconomics,PharmacovigilanceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Buttercup Grownup GreenDocument1 pageButtercup Grownup GreenJhoann JamanilaNo ratings yet
- DOH National Antibiotic Guidelines 2017Document264 pagesDOH National Antibiotic Guidelines 2017Degee O. Gonzales67% (3)
- Caregiving NC IIDocument110 pagesCaregiving NC IIflomar22100% (4)
- Reteplase (MIRel)Document23 pagesReteplase (MIRel)Jhoann JamanilaNo ratings yet
- Caregiving NC IIDocument110 pagesCaregiving NC IIflomar22100% (4)
- Love Scale Strenberg 1997Document23 pagesLove Scale Strenberg 1997javier_sanz_6100% (1)
- ICRU Report 89 Prescribing Recording and Reporting Brachytherapy For Cancer of The Cervix PDFDocument260 pagesICRU Report 89 Prescribing Recording and Reporting Brachytherapy For Cancer of The Cervix PDFFlor Zalazar100% (1)
- 10th Public Exam Question Paper 2012 Science MarchDocument7 pages10th Public Exam Question Paper 2012 Science MarchRavi balanNo ratings yet
- Supplements Who Needs Them?: A Behind The Headlines Report June 2011Document34 pagesSupplements Who Needs Them?: A Behind The Headlines Report June 2011Sa AsNo ratings yet
- Presentation For Music Therapy CourseDocument13 pagesPresentation For Music Therapy CourseRodney HarrisNo ratings yet
- Transfusion UpdateDocument342 pagesTransfusion UpdateAdrian Puscas100% (2)
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesReview of Related LiteratureAlfred Jayson RuizNo ratings yet
- PTLS BrochureDocument2 pagesPTLS BrochuremomhoppNo ratings yet
- Definitions: The Social Determinants of Health. SummaryDocument4 pagesDefinitions: The Social Determinants of Health. SummaryS VaibhavNo ratings yet
- J Parenter Enteral Nutr - 2017 - Worthington - When Is Parenteral Nutrition AppropriateDocument54 pagesJ Parenter Enteral Nutr - 2017 - Worthington - When Is Parenteral Nutrition AppropriateToño ZsucaritasNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Ethmoidectomy - FESS - Surgical TechniqueDocument29 pagesEndoscopic Ethmoidectomy - FESS - Surgical TechniquekityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- Obat antithiroid: New England Medical Journal review of antithyroid drugsDocument52 pagesObat antithiroid: New England Medical Journal review of antithyroid drugsYeyen MusainiNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy Toolbox Study GuideDocument44 pagesOccupational Therapy Toolbox Study GuideKristian ShumateNo ratings yet
- Karma MudraDocument10 pagesKarma Mudramanuelborgefenix1362No ratings yet
- Nurse Collaborates With Jimmy to Reach Anxiety GoalDocument162 pagesNurse Collaborates With Jimmy to Reach Anxiety GoalAnn Claudette SyNo ratings yet
- Ob Final Exam Review Summary Maternity NursingDocument40 pagesOb Final Exam Review Summary Maternity NursingVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyDocument34 pagesDermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyAzry Mustapa100% (1)
- Ms DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesDocument9 pagesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesMs DiabetesLariza LopegaNo ratings yet
- Aldrin C. Sebastian Mapeh 10 X - Galileo Health (Module 1) : What I Know What's inDocument2 pagesAldrin C. Sebastian Mapeh 10 X - Galileo Health (Module 1) : What I Know What's inLei Andrea SebastianNo ratings yet
- RAdiology Related Infratemporal Fossa, Pterygo Palatine Fossa, Parapharyngeal SpaceDocument11 pagesRAdiology Related Infratemporal Fossa, Pterygo Palatine Fossa, Parapharyngeal SpacehaneefmdfNo ratings yet
- Bio Fs IndDocument20 pagesBio Fs IndalvinkoyNo ratings yet
- Infection Control NHS PolicyDocument12 pagesInfection Control NHS PolicyYahya Salem100% (1)
- Rh-Pregnancy 202240 184928Document2 pagesRh-Pregnancy 202240 184928siddharthNo ratings yet
- Mosquito Net SpecificationDocument12 pagesMosquito Net SpecificationManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Marshall Community Letter: Person at Middle School Tests Positive For CoronavirusDocument1 pageMarshall Community Letter: Person at Middle School Tests Positive For CoronavirusJoy M. HosfordNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study GentamicinDocument3 pagesDrugs Study Gentamicinahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Glucemic IndexDocument52 pagesGlucemic IndexMayra de CáceresNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Molecular Mechanisms of Aluminum Neurotoxicity: Update On Adverse Effects and Therapeutic StrategiesDocument31 pagesHHS Public Access: Molecular Mechanisms of Aluminum Neurotoxicity: Update On Adverse Effects and Therapeutic Strategiesfajriana anggun putri amranNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis of Knee: Presented By: DR Dipendra Maharjan 2 Yr Resident, MS Orthopaedics NAMS, Bir HospitalDocument25 pagesTuberculosis of Knee: Presented By: DR Dipendra Maharjan 2 Yr Resident, MS Orthopaedics NAMS, Bir HospitalshravaniNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Chronic Neck Pain Alters Muscle Activation Patterns To Sudden Movements (D. Falla)Document11 pages2015 - Chronic Neck Pain Alters Muscle Activation Patterns To Sudden Movements (D. Falla)romiromiromi123No ratings yet