Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adult Patient Diagnosed With COVID-19: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
Uploaded by
pramodbankhele38450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageOriginal Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageAdult Patient Diagnosed With COVID-19: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
Uploaded by
pramodbankhele3845Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
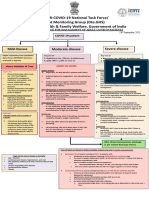
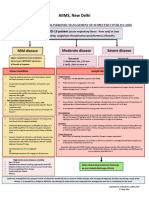
AIIMS/ ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/ Joint Monitoring Group (Dte.
GHS)
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
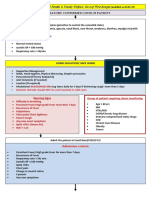
CLINICAL GUIDANCE FOR MANAGEMENT OF ADULT COVID-19 PATIENTS
Revised on 05/01/2023
Adult patient diagnosed with COVID-19
Mild disease Moderate disease Severe disease
Any one of: Any one of:
Upper respiratory tract symptoms 1. Respiratory rate >30/min,
1. Respiratory rate ≥ 24/min,
and/or fever WITHOUT shortness breathlessness
breathlessness
of breath or hypoxia 2. SpO2 < 90% on room air
2. SpO2 : 90% to ≤ 93% on room air
Home Isolation & Care
(Refer to relevant guideline)
ADMIT IN WARD ADMIT IN HDU/ICU
MUST DOs Oxygen Support: Respiratory & Cardiovascular Support:
Target SpO : 94-96% (88-92% in Consider use of NIV (Helmet or face mask
Physical distancing, indoor mask 2
patients with COPD) interface depending on availability) in
use, hand hygiene
patients with increasing oxygen
Symptomatic management Preferred devices for oxygenation: requirement, if work of breathing is LOW
(hydration, anti-pyretics, anti- non-rebreathing face mask Consider use of HFNC in patients with
tussive)
Awake proning encouraged in all increasing oxygen requirement
Monitor temperature and oxygen patients requiring supplemental Intubation should be prioritized in
saturation (by applying a SpO probe oxygen therapy (sequential patients with high work of breathing /if
to fingers)
2 position changes every 2 hours) NIV is not tolerated
Stay in contact with treating Anti-inflammatory or Use institutional protocol for ventilatory
physician immunomodulatory therapy: management when required
Seek immediate medical attention if:
Dexamethasone 6 mg/day or Need for vasopressors to be considered
Difficulty in breathing or SpO2 ≤ 93% equivalent dose of based on clinical situation
methylprednisolone (32 mg in 4
High grade fever/severe cough, divided doses) usually for 5 to 10 Anti-inflammatory or
particularly if lasting for >5 days days or until discharge, whichever is immunomodulatory therapy:
earlier.
A low threshold to be kept for those Dexamethasone 6 mg/day or equivalent
with any of the high-risk features* Patients may be initiated or dose of methylprednisolone (32 mg in 4
switched to oral route if stable divided doses) usually for 5 to 10 days or
and/or improving until discharge, whichever is earlier. No
*High-risk for severe disease or evidence for benefit in higher doses.
There is no evidence for benefit for
mortality systemic steroids in those NOT Anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory
Age > 60 years requiring oxygen supplementation, therapy (such as steroids) can have risk of
or on continuation after discharge secondary infection such as invasive
Cardiovascular disease and CAD
Anti-inflammatory or mucormycosis when used at higher dose
Diabetes mellitus and other immunomodulatory therapy (such or for longer than required
immunocompromised states (such as steroids) can have risk of
as HIV) secondary infection such as invasive Anticoagulation:
Active tuberculosis mucormycosis when used at higher Prophylactic dose of unfractionated
dose or for longer than required heparin or Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Chronic lung/kidney/liver disease (weight based e.g., enoxaparin 0.5mg/kg
Cerebrovascular disease Anticoagulation: per day SC). There should be no
contraindication or high risk of bleeding
Prophylactic dose of unfractionated
Obesity Supportive measures:
heparin or Low Molecular Weight
Unvaccinated Heparin (weight based e.g., Maintain euvolemia (if available, use
enoxaparin 0.5mg/kg per day SC). dynamic measures for assessing fluid
Antibiotics should not be used unless
there is clinical suspicion of bacterial There should be no responsiveness)
infection contraindication or high risk of If sepsis/septic shock: manage as per
Possibility of coinfection of COVID-19 bleeding existing protocol and local antibiogram
with other endemic infections must
be considered Monitoring: Monitoring:
Systemic corticosteroids are not Clinical Monitoring: Respiratory Clinical Monitoring: Work of breathing,
indicated in mild disease Hemodynamic instability, Change in
rate, Hemodynamic instability,
Change in oxygen requirement oxygen requirement
DO NOT USE IN COVID-19
Lopinavir-ritonavir Serial CXR; HRCT chest to be done Serial CXR; HRCT chest to be done ONLY if
ONLY if there is worsening there is worsening
Hydroxychloroquine
Ivermectin Lab monitoring: CRP, D-dimer, Lab monitoring: CRP, D-dimer, blood sugar
Neutralizing monoclonal antibody blood sugar 48 to 72 hrly; CBC, KFT, 48 to 72 hrly; CBC, KFT, LFT 24 to 48 hrly
LFT 24 to 48 hrly
Convalescent plasma
Molnupiravir
Favipiravir
After clinical improvement, discharge
Azithromycin as per revised discharge criteria
Doxycycline
Additionally in moderate or severe disease at Additionally in rapidly progressing moderate
high risk of progression or severe disease
Consider Tocilizumab preferably within 24-48 hours of onset
Consider Remdesivir for up to 5 days (200 mg IV on day 1
followed by 100 mg IV OD for next 4 days) of severe disease/ ICU admission [4 to 6 mg/kg (400 mg in 60
To be started within 10 days of onset of symptoms, in those kg adult) in 100 ml NS over 1 hour] if the following conditions
having moderate to severe disease with high risk of progression are met:
(requiring supplemental oxygen), but who are NOT on IMV or Rapidly progressing COVID-19 not responding adequately
ECMO to steroids and needing oxygen supplementation or IMV
No evidence of benefit for treatment more than 5 days Preferably to be given with steroids
NOT to be used in patients who are NOT on oxygen support or in
home setting Significantly raised inflammatory markers (CRP and/or IL-6)
Monitor for RFT and LFT (remdesivir not recommended if eGFR Rule out active TB, fungal, systemic bacterial infection
<30 ml/min/m2; AST/ALT >5 times UNL) (not an absolute Long term follow up for secondary infections (such as
contraindication) reactivation of TB, flaring of Herpes)
You might also like
- Practical CS ProcessingDocument483 pagesPractical CS ProcessinganAMUstudent100% (2)
- Electric Machinery and Transformers - I. L. Kosow PDFDocument413 pagesElectric Machinery and Transformers - I. L. Kosow PDFzcjswordNo ratings yet
- FLCCC Alliance I RECOVER Management Protocol For Long Haul COVID 19 SyndromeDocument3 pagesFLCCC Alliance I RECOVER Management Protocol For Long Haul COVID 19 SyndromeAizaz ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFDocument15 pagesDrill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFgustavoemir0% (2)
- DD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogDocument46 pagesDD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogAndres Fdo Mora D100% (2)
- COVID Management 17th January 2022 DR Suvrankar Datta AIIMSDocument1 pageCOVID Management 17th January 2022 DR Suvrankar Datta AIIMSWhiteNo ratings yet
- COVID Clinical Management 14012022Document1 pageCOVID Clinical Management 14012022Naina DesaiNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1Document1 pageCOVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1shivani shindeNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of CovidDocument7 pagesAIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of Covidsenthil kumarNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of Covid-19 Cases: (Enter Post Title Here)Document7 pagesAIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of Covid-19 Cases: (Enter Post Title Here)senthil kumarNo ratings yet
- AIIMS/ ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/ Joint Monitoring Group (Dte - GHS) Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of IndiaDocument1 pageAIIMS/ ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/ Joint Monitoring Group (Dte - GHS) Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of IndiaSomnath Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- AIIMS COVID Algorithm 1.5-1 PDFDocument1 pageAIIMS COVID Algorithm 1.5-1 PDFAnutosh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Syndromic ApproachDocument1 pageAIIMS Syndromic ApproachRagul VNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGDocument25 pagesCOVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGMartin PaturlanneNo ratings yet
- WB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)Document49 pagesWB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)El MirageNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGDocument24 pagesCOVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGHouda LaatabiNo ratings yet
- WB COVID19 Latest Treatment ProtocolDocument1 pageWB COVID19 Latest Treatment ProtocolRahul AwasthiNo ratings yet
- FluticasoneDocument3 pagesFluticasoneAmberNo ratings yet
- AIIMS COVID Doc 1.6.1-1Document1 pageAIIMS COVID Doc 1.6.1-1mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- 07 - 10 - 21 Treatment of Covid 19 InfectionDocument26 pages07 - 10 - 21 Treatment of Covid 19 InfectionStonefalconNo ratings yet
- Treatment Protocol Covid-19Document4 pagesTreatment Protocol Covid-19Shiv singhNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Sepsis Topic DiscussionDocument5 pagesPediatric Sepsis Topic Discussionapi-602288180No ratings yet
- Antibiotics-Generation OperationDocument5 pagesAntibiotics-Generation OperationZamzami Ahmad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Covid Drug TherapyDocument35 pagesCovid Drug TherapyNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management Guidelines For Suspected or Confirmed COVID 19 Infection in Adults Version 4 April 2023 MOH NUGDocument94 pagesClinical Management Guidelines For Suspected or Confirmed COVID 19 Infection in Adults Version 4 April 2023 MOH NUGFrozenboy. 1993No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSKhurram NadeemNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Antiviral TX Guidance 4-22-2020Document23 pagesCOVID-19 Antiviral TX Guidance 4-22-2020Lydia IsaacNo ratings yet
- Ventilator: Associated Pneumonia (VAP)Document36 pagesVentilator: Associated Pneumonia (VAP)D. Melba S.S ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Recommendation For The Use of Antibiotics For The Treatment of InfectionDocument5 pagesRecommendation For The Use of Antibiotics For The Treatment of InfectionGem BorjaNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Severe Asthma in PediatricsDocument53 pagesManagement of Acute Severe Asthma in PediatricsAmit AnandNo ratings yet
- Brajac - ProtocolDocument13 pagesBrajac - Protocolthanh ngôNo ratings yet
- COVID MX BsmmuDocument2 pagesCOVID MX BsmmuNuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- Updated National Guidelines of Covid-19 and Important FAQ'sDocument30 pagesUpdated National Guidelines of Covid-19 and Important FAQ'sIshtiaque KhanNo ratings yet
- Critical Care of Patient With Covid 19Document32 pagesCritical Care of Patient With Covid 19Anonymous Kv0sHqFNo ratings yet
- Icu Manag Myesthenia GravisDocument51 pagesIcu Manag Myesthenia GravisparuNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- DIPIRO 9th PHARMACOTHERAPY-PATOPHISIOLOGY APPROACH EDISI 9 (PDF - Io)Document31 pagesDIPIRO 9th PHARMACOTHERAPY-PATOPHISIOLOGY APPROACH EDISI 9 (PDF - Io)NingrumSindayaniNo ratings yet
- GHC Lower Respiratory Tract Antimicrobial Guideline V 3 FinalDocument19 pagesGHC Lower Respiratory Tract Antimicrobial Guideline V 3 FinalNicthe Ruiz RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Guide 2013Document30 pagesAntibiotics Guide 2013Stefani NoviliaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLDocument12 pages2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLSutirtha RoyNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsgailannreyesNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsgailannreyesNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA RestriveraDocument18 pagesASTHMA RestriveraAoi ShinNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneShaira TanNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Isoniazid Induced Bullous Drug ReactionDocument6 pagesA Case Report On Isoniazid Induced Bullous Drug ReactionPutri YingNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Penggunaan Antibiotik Pada PasienDocument5 pagesPedoman Penggunaan Antibiotik Pada PasienErvina Lie100% (1)
- Laboratory Confirmed Covid 19 Patient: Department of Health & Family Welfare, Govt of West BengalDocument2 pagesLaboratory Confirmed Covid 19 Patient: Department of Health & Family Welfare, Govt of West BengalSujoyDeNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Management ProtocolDocument2 pagesPneumonia Management Protocolsky nuts100% (1)
- Adverse Effects of Anti Tubercular Drugs. MDR TBDocument75 pagesAdverse Effects of Anti Tubercular Drugs. MDR TBDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM100% (1)
- Pediatric Acute Sepsis: Physician'S OrdersDocument4 pagesPediatric Acute Sepsis: Physician'S OrdersSughosh MitraNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Disease SeverityDocument7 pagesCOVID-19 Disease SeverityParishan SaeedNo ratings yet
- EVMS Critical Care COVID-19 Protocol PDFDocument18 pagesEVMS Critical Care COVID-19 Protocol PDFGreyWolf1776No ratings yet
- Drug Study No.1 Brand Name: Paracetamol Generic Name: Tempra Classification: Anti-Infectives Dosage: 100mg, 1ml Drops q4hrDocument7 pagesDrug Study No.1 Brand Name: Paracetamol Generic Name: Tempra Classification: Anti-Infectives Dosage: 100mg, 1ml Drops q4hrMary EnsomoNo ratings yet
- 05-05-2021 Covid Guidelines - Coasl and SLCP - Version 7Document14 pages05-05-2021 Covid Guidelines - Coasl and SLCP - Version 7Doctors NewsNo ratings yet
- Risk Factor PneumoniaDocument6 pagesRisk Factor Pneumoniaali subchanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium BromideDocument8 pagesDrug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium Bromidepaupaulala100% (2)
- MethylprednisoloneDocument4 pagesMethylprednisoloneadryananestesiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Management of COVID-19 in Children (Below 18 Years)Document10 pagesGuidelines For Management of COVID-19 in Children (Below 18 Years)Juhi NeogiNo ratings yet
- Query 1 Modified Systematic ApproachDocument3 pagesQuery 1 Modified Systematic ApproachAntoNo ratings yet
- BCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesAlvy SyukrieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsNo ratings yet
- Coins of Chatrapati SambhajiDocument4 pagesCoins of Chatrapati Sambhajipramodbankhele3845No ratings yet
- The World of Labour in Mughal India (c.1500-1750) : S M Centre of Advanced Study in History, Aligarh Muslim UniversityDocument17 pagesThe World of Labour in Mughal India (c.1500-1750) : S M Centre of Advanced Study in History, Aligarh Muslim Universitypramodbankhele3845No ratings yet
- Madhyayugin Bharathatil Rajya Va Samaj: Samasya Ani Sambhavyata (Marathi)Document15 pagesMadhyayugin Bharathatil Rajya Va Samaj: Samasya Ani Sambhavyata (Marathi)pramodbankhele3845No ratings yet
- 1dulla BhattiDocument24 pages1dulla Bhattipramodbankhele3845100% (1)
- Aurangzeb Era Sarvani RevoltDocument18 pagesAurangzeb Era Sarvani Revoltpramodbankhele3845No ratings yet
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- Shaft DeflectionDocument15 pagesShaft Deflectionfreek_jamesNo ratings yet
- 7273X 47 ITOW Mozart PDFDocument3 pages7273X 47 ITOW Mozart PDFAdrian KranjcevicNo ratings yet
- Handbook - European Choral AssociationDocument24 pagesHandbook - European Choral AssociationMonica SaenzNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck SlabDocument29 pagesBubble Deck SlabJhimy Rusbel Gutierrez YanapaNo ratings yet
- NUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsDocument2 pagesNUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsJorge ParraNo ratings yet
- WebMethods System Requirements 8xDocument7 pagesWebMethods System Requirements 8xmaxprinceNo ratings yet
- Toefl StructureDocument50 pagesToefl StructureFebrian AsharNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper DementiaDocument1 pageReaction Paper DementiaElla MejiaNo ratings yet
- Movie Review of THORDocument8 pagesMovie Review of THORSiva LetchumiNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentDocument8 pagesEpidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentRakib HossainNo ratings yet
- Van Daley - Leadership ResumeDocument1 pageVan Daley - Leadership Resumeapi-352146181No ratings yet
- WHITE TOWN GROUP-4 FinalDocument112 pagesWHITE TOWN GROUP-4 Finalaswath manojNo ratings yet
- Electric Valve Actuator Type Car: For 2 & 3-Way Valves Type G/L/M/S 2Fm-T & G/L/M/S 3Fm-T Page 1 of 4 0-4.11.08-HDocument4 pagesElectric Valve Actuator Type Car: For 2 & 3-Way Valves Type G/L/M/S 2Fm-T & G/L/M/S 3Fm-T Page 1 of 4 0-4.11.08-HMuhd Khir RazaniNo ratings yet
- 7 ApportionmentDocument46 pages7 Apportionmentsass sofNo ratings yet
- January 11, 2019 Grade 1Document3 pagesJanuary 11, 2019 Grade 1Eda Concepcion PalenNo ratings yet
- AMX Prodigy Install ManualDocument13 pagesAMX Prodigy Install Manualsundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- Tip Sheet March 2017Document2 pagesTip Sheet March 2017hoangvubui4632No ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document32 pagesLecture 08SusovanNo ratings yet
- No ApprovedDocument154 pagesNo ApprovedAnnaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mathematics Checkpoint Booklet AY 23-24Document270 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics Checkpoint Booklet AY 23-24Arta riaNo ratings yet
- EPA NCP Technical Notebook PDFDocument191 pagesEPA NCP Technical Notebook PDFlavrikNo ratings yet
- Pu3-Mo A1 MoversDocument40 pagesPu3-Mo A1 MoversMiss María José SalasNo ratings yet
- Theben Timer SUL 181DDocument2 pagesTheben Timer SUL 181DFerdiNo ratings yet
- Classical School of Thought: Ms. Salma ShaheenDocument62 pagesClassical School of Thought: Ms. Salma ShaheenQasim Ali100% (1)
- Sharp Product-Catalogue 2019 enDocument48 pagesSharp Product-Catalogue 2019 enMiki di KaprioNo ratings yet