Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 1 CHN Concepts
Uploaded by
juice0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views3 pages1. Community health nursing involves promoting health, preventing illness, and maintaining health at various levels including individuals, families, communities, and populations.
2. It utilizes a philosophy that considers multiple health determinants, encourages active client participation, and values interdependence among health team members to address community needs.
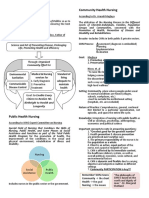
3. Key principles of community health nursing include focusing on the community as the unit of care, prioritizing community needs, working as an equal partner with the community, and focusing on primary prevention through environmental strategies and optimal resource use.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHN Lec - M1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Community health nursing involves promoting health, preventing illness, and maintaining health at various levels including individuals, families, communities, and populations.
2. It utilizes a philosophy that considers multiple health determinants, encourages active client participation, and values interdependence among health team members to address community needs.
3. Key principles of community health nursing include focusing on the community as the unit of care, prioritizing community needs, working as an equal partner with the community, and focusing on primary prevention through environmental strategies and optimal resource use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views3 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 1 CHN Concepts
Uploaded by
juice1. Community health nursing involves promoting health, preventing illness, and maintaining health at various levels including individuals, families, communities, and populations.
2. It utilizes a philosophy that considers multiple health determinants, encourages active client participation, and values interdependence among health team members to address community needs.
3. Key principles of community health nursing include focusing on the community as the unit of care, prioritizing community needs, working as an equal partner with the community, and focusing on primary prevention through environmental strategies and optimal resource use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
NCM113 Prelims - GMJ
Lecture - Module 1 CHN Concepts
DEFINITION OF TERMS - The study of the distribution and determinants of health-
1. Community related states or events in specified populations and the
- A collection of people who interact with one another and application of this study to the prevention and control of
whose common interests or characteristics form the basis health problems.
for a sense of unity or belonging (Allender et.al, 2009) 10. Health Statistics
- A group of people who share common interests, who - They refer to the numbers that summarize information
interact with each other and who function collectively related to health which are collected by researchers,
within a defined social structure to address common experts from government, private, non-profit agencies,
concern (Clark, 2008). and organizations. They are often used to learn about
- A group or collection of individuals interacting in social public health and health care.
units ns sharing common interests, characteristics, values 11. Health INDICATORS
and goals (Maurer and Smith, 2013). - A list of information that would determine the health of a
2. Community Health particular community or country.
- The health status of a community and the organized 12. Population Group
responsibilities of public health, school health, - A group of people who share common characteristics,
transportation, safety and other tax-supported functions developmental stage or common exposure to
with voluntary and private actions to promote and protect environmental factors, and common health problems,
the health of local population identified as communities. issues, and concerns (Maglaya, 2009).
3. Community Health Nursing (ANA, 1980) - Population groups are the usual targets or beneficiaries of
- A synthesis of nursing practice and public health applied social services and health programs.
to promoting and preserving the health of the populations.
PHILOSOPHY OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
- The focus of community health nursing:
o prevention of illness A philosophy is defined as a system of beliefs that
o promotion of health provides a basis for and guide action.
o maintenance of health It provides the direction and describe the whats, the whys
4. Community Health Nursing and the hows of activities within a profession.
- It is service rendered by a professional nurse to o Humanistic values of the nursing profession.
communities, groups, families, and individuals at home, o Unique and distinct component of health care
in health centers, in clinics, in schools, and in places of o Multiple factors of health considered
work for the promotion of health, prevention of illness, o Active participation of clients is encouraged
care of the sick at home, and rehabilitation. (Ruth B. o Nurse considers availability of resources
Freeman) o Interdependence among health team members is
5. Community Health Nursing (Dr. Araceli Maglaya) practiced
- The utilization of the Nursing Process in the different o Scientific and up to date
levels of clientele-individuals, families, population groups o Tasks of community health nurse vary with time
and communities, concerned with the promotion of health,
and place
prevention of disease and disability and rehabilitation.
o Independence or self-reliance of the people is the
6. Community Development
end goal
- An organized effort of people to improve the conditions
o Connectedness of health and development
of community life and the capacity of the people for
participation, self-direction, and integrated efforts in PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
community affairs (Jimenez, 2008).
7. Community Development 1. The focus is the community as the unit of care -
- A process where community members come together to the responsibility of the nurse is to the community as
take collective action and generate solutions to common a whole
problems. Community wellbeing (economic, social, 2. Give priority to the community needs - the CHN
environmental, and cultural) often evolves from this type nurse should develop skills in nursing process and
of collective action being taken at a grassroots level. population-focused skills to help the community
8. Community Organizing identify their needs and produced benefits for the
community; Demographics and vital statistics are the
- A process consists of steps or activities that instill and
tools used by the Community Health Nurse to
reinforce the people’s self-confidence on their own
achieve this benefit.
collective strengths and capabilities (Manalili, 1990).
3. Work with the community as an equal partner of
- A process of educating and mobilizing members of the
the health team - client is considered as an active
community to enable them to resolve community
partner, not a passive recipient of care. Team
problems.
approach and partnership between the health care
- A means to build the community’s capacity to work for
worker and the community produce effective and
the common good in general and health goals (Famorca et
sustainable results.
al, 2013).
4. In selecting appropriate activities, focus on
primary prevention - strategies implemented are
9. Epidemiology
focused on achieving optimal health, prevent diseases
and disability.
5. Promote a healthful physical and psychosocial Constructs of HBM:
environment - health team should focus on Severity
designing strategies that focus on environmental PERCEIVED Susceptibility
determinants of health such as education, Benefits of Treatment
socioeconomic status, physical environment, and Barriers
social supports. 2. Milio’s Framework for Prevention
6. Promote optimum use of resources - effective - by Nancy Milio (1976)
usage of community resources for strategies that will - Complements the HBM and provides mechanism for
produce long term effects. directing and examining opportunities for nursing
7. Collaborate with others working in the interventions at the population level.
community - nurse must work with a variety of - Proposed that health deficits often result from an
sectors to settle issues that affect health, which is imbalance between a population’s health needs and its
considered as a product of multiple health health-sustaining resources
determinants. - Milio’s framework encourages the nurse to understand
health behaviors in the context of their societal milieu
FEATURES OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
Application of Milio’s Framework in CHN:
Milio’s Proposition Population Health
Population health deficits I and F living in poverty have
result from deprivation poorer health status compared
and/or excess of critical with middle- and upper-class
health resource. individuals
Individual choices related Choices and behavior of
to health promotion or individuals are strongly
health damaging behaviors influenced by desires, values,
are influenced by efforts and beliefs. (E.g. Use of
to maximize valued illegal drugs by adolescents is
resources. often dependent on peer
pressure and the need for
Community Health Nurse - it is the job of a community acceptance, love and
health nurse to help and keep the community health problems belonging.
under control (Mona, 2015) Alteration in patterns of Some behaviors such as
a) serve direct care behavior resulting from smoking have been difficult to
b) advocate for health improvement decision making of a maintain due to company
c) educate individuals or the public significant number of policies and laws
d) perform research in community health people in a population can implemented.
FEATURES OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING result in social change
Behavior of populations Positive and negative lifestyle
It is a specialty field of nursing
result from selection from choices (e.g. smoking, alcohol
Its practice combines public health with nursing
limited choices (to include use, regular exercise, diet) are
It is population based.
actual and perceived dependent on culture,
It emphasizes on wellness and other than disease or
options available, beliefs, socioeconomic status and
Illness.
expectations resulting educational level.
It involves inter-disciplinary collaboration.
from socialization,
It increases client’s responsibility and self-care.
education, and experience)
FUNCTIONS OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
Without the availability of Addressing persistent health
1. Identification of community culture and resources (key
alternative health problems (e.g. HPN) is
factor in HCDS)
promoting options hindered because most people
2. Evaluate community health conditions, health risks and
are aware of what causes the
problems
problem but reluctant to make
3. Plan and implementation of comprehensive community
lifestyle changes to prevent or
health interventions, care, services, and program.
reverse the condition.
4. Develop health policy at the local community level
THEORIES AND APPROACHES (COMMUNITY
HEALTH NURSING PRACTICE)
1. Health Belief Model (HBM)
3. Pender’s Health Promotion Model
- Developed by social psychologists in1958 to explain why
- Developed by Nola Pender in 1980s and revised in 1996
people failed to participate in screening for TB.
- Explores may biopsychosocial factors that influence
- Provide the basis for current health education and health
individuals to pursue health promotion activities.
promotion practices.
- Depicts the multidimensional factors with which people
- HBM has been used to explain behavior change and
interact as they work to achieve optimum health.
maintenance of behavior change and to guide health
promotion interventions (janz et. Al. 2002)
- Major limitation of HBM – burden of action is on the
client
4. PRECEDE-PROCEED MODEL
- Developed by Dr. Lawrence W. Green and colleagues
- Provides a model for community assessment, health
education, planning and evaluation.
- In this model, predisposing factors refer to people’s
characteristics that motivate them towards health-related
behaviors.
- Enabling factors refer to conditions in people and the
environment that facilitate or impede health related
behavior.
You might also like
- Module 1 Overview of Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesModule 1 Overview of Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesKristil Chavez50% (2)
- Level 2 Major Subjects 2Document86 pagesLevel 2 Major Subjects 2Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- CHN IntroDocument29 pagesCHN IntroaugiejanenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document11 pagesLesson 2John Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- CHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentDocument33 pagesCHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentSVPSNo ratings yet
- CPH Week 1Document6 pagesCPH Week 1Jabez MatigaNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesCommunity Health NursingMae CalicaNo ratings yet
- CHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentDocument33 pagesCHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentSVPSNo ratings yet
- CHN Rle ReviewerDocument10 pagesCHN Rle ReviewerKenneth Fe AgronNo ratings yet
- CHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1Document13 pagesCHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1SVPSNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 CHN and GeronDocument14 pagesTopic 1 CHN and GeronAngela Patricia TuyNo ratings yet
- NUR153 SAS Session1Document7 pagesNUR153 SAS Session1Abegyl Nicole Figura0% (1)
- NSG 101 Community Health NursingDocument7 pagesNSG 101 Community Health NursingAl-mathar L. TingkahanNo ratings yet
- CHN IiDocument33 pagesCHN IiAila Hinlog100% (1)
- CHN Lecture - 2Document13 pagesCHN Lecture - 2HANNAH LEAL RENDAJE SHARIFFNo ratings yet
- CHN Long Quiz Rev 1Document8 pagesCHN Long Quiz Rev 1Princess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- CHN (Reviewer)Document6 pagesCHN (Reviewer)Louise Andrea OdulioNo ratings yet
- ALL SUBJECTS PRELIM TO MIDTERM HANDOUTS CompressedDocument117 pagesALL SUBJECTS PRELIM TO MIDTERM HANDOUTS CompressedRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- CHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1Document12 pagesCHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1SVPSNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Principles of Community Health NursingDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts and Principles of Community Health NursingElgen B. AgravanteNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Topic 1 & 2 Hassiman, Hasanuddin A. BSN 3EDocument2 pagesAssignment On Topic 1 & 2 Hassiman, Hasanuddin A. BSN 3EHASANUDDIN ASMAD. HASSIMANNo ratings yet
- NCM 113 - CHN ConceptDocument5 pagesNCM 113 - CHN ConceptLorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- NCM 222 CHN Lesson 1Document5 pagesNCM 222 CHN Lesson 1Krishane JustaleroNo ratings yet
- CHN PointersDocument18 pagesCHN PointersDjayNo ratings yet
- Public Health Nursing Community Health NursingDocument23 pagesPublic Health Nursing Community Health NursingJorge Danielle100% (1)
- CHN PointersDocument18 pagesCHN PointersDjayNo ratings yet
- Lesson CHNDocument4 pagesLesson CHNPrincess Shaniel Marzo BugarNo ratings yet
- CHN Reviewer Final Na ToDocument27 pagesCHN Reviewer Final Na ToDESSA GALOSONo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument10 pagesCommunity Health NursingBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- NRG 302 Lec - Prelim ReviewerDocument46 pagesNRG 302 Lec - Prelim ReviewerEmmy Flor ValmoriaNo ratings yet
- CHN FinalDocument3 pagesCHN FinalMañoza, MarifeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Primary Health CareDocument5 pages3 - Primary Health CareLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNo ratings yet
- CHN Week 1: Definition of Community Health Nursing Principles of Community Health NursingDocument22 pagesCHN Week 1: Definition of Community Health Nursing Principles of Community Health NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document58 pagesCHN 2Cristelle Joy RebocaNo ratings yet
- CHN - Nursing ConceptsDocument5 pagesCHN - Nursing ConceptsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Maglaya Community Health Nursing NotesDocument2 pagesMaglaya Community Health Nursing NotesMaria Bernadette Manumbas60% (5)
- CHN 2 LectureDocument44 pagesCHN 2 Lectureandrea.maungca.mnlNo ratings yet
- CPH Lec - Week 1Document9 pagesCPH Lec - Week 1tuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument15 pagesFINALSmayangernszNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Community Health Nursing ConceptsDocument4 pagesModule 1: Community Health Nursing ConceptsAno NymousNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument5 pagesCommunity Health NursingKamilNo ratings yet
- NUR153 IG Session1Document5 pagesNUR153 IG Session1ira GenelazoNo ratings yet
- Overview of PHNDocument14 pagesOverview of PHNariel camusNo ratings yet
- CHN Midterms NotesDocument11 pagesCHN Midterms NotesKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community Health NursingDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Community Health NursingFredrick WedderburnNo ratings yet
- CHN Chapter 6Document6 pagesCHN Chapter 6Paulo Marie TanNo ratings yet
- COMMUNIT Y HEALTH NURSING 2 Reviewer (Week 1-4)Document7 pagesCOMMUNIT Y HEALTH NURSING 2 Reviewer (Week 1-4)Angelica Marie MacaslingNo ratings yet
- HO An Overview of CHNDocument3 pagesHO An Overview of CHNdenNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Concepts: Overview of The LessonDocument24 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Concepts: Overview of The LessonKASSANDRA THERESE G. DAITOLNo ratings yet
- CPH LecDocument46 pagesCPH LectuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- Add Topics For Prelim and MidtermDocument6 pagesAdd Topics For Prelim and MidtermRy LlanesNo ratings yet
- CHN 1Document10 pagesCHN 1keiemorayaNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Module 1m-2mDocument84 pagesNCM 104 Module 1m-2mJr CaniaNo ratings yet
- Comhen220 Prelim (Transcribe)Document8 pagesComhen220 Prelim (Transcribe)Orongan CarmelaNo ratings yet
- 1.Chn Introduction and FamilyDocument7 pages1.Chn Introduction and FamilyLuzie Mae SuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 CHNDocument5 pagesLecture 1 CHNFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 CHN 2Document9 pagesStudy Guide 1 CHN 2Hilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.No ratings yet
- Dental Public HealthDocument8 pagesDental Public HealthR ENo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument4 pagesCommunity Health NursingDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan: Submitted ToDocument7 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: Submitted TojuiceNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2: Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesMODULE 2: Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticejuiceNo ratings yet
- Droplet and Contact 1Document38 pagesDroplet and Contact 1juiceNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument3 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ RLE - Module 2 III DisorderDocument4 pagesPrelims - GMJ RLE - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- MEASLES Case DiscussionDocument21 pagesMEASLES Case DiscussionjuiceNo ratings yet
- Related To Vomiting As Evidence by Muscle Weakness and FatigueDocument3 pagesRelated To Vomiting As Evidence by Muscle Weakness and FatiguejuiceNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene Protocol RevisedDocument13 pagesHand Hygiene Protocol RevisedjuiceNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs and Intake/Output Form: GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJDocument1 pageVital Signs and Intake/Output Form: GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJ GMJjuiceNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ SL - Module 1 Fluids & Electrolytes: Lactated Ringers, D5 Water, Plain Normal SalineDocument3 pagesPrelims - GMJ SL - Module 1 Fluids & Electrolytes: Lactated Ringers, D5 Water, Plain Normal SalinejuiceNo ratings yet
- Sheilla M. Trajera, RN, MN, LPT, Phd. O-Jay B. Jimenez, RN, MNDocument44 pagesSheilla M. Trajera, RN, MN, LPT, Phd. O-Jay B. Jimenez, RN, MNjuiceNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ RLE - Module 2 III DisorderDocument1 pagePrelims - GMJ RLE - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- M1 - ABG InterpretDocument2 pagesM1 - ABG InterpretjuiceNo ratings yet
- M1 - Urinary DisordersDocument2 pagesM1 - Urinary DisordersjuiceNo ratings yet
- M1 - F&eDocument2 pagesM1 - F&ejuiceNo ratings yet
- Individualized Learning Plan IlpDocument16 pagesIndividualized Learning Plan Ilpapi-572860282No ratings yet
- Sampath SamhithaDocument2 pagesSampath Samhithasampath yadavNo ratings yet
- Book Review FormatDocument3 pagesBook Review FormatJayson MercadoNo ratings yet
- Determine Criteria For Site Selection - Local Initiatives Support CorporationDocument5 pagesDetermine Criteria For Site Selection - Local Initiatives Support CorporationbenonyNo ratings yet
- L3 Reading Year 4 PKPDocument1 pageL3 Reading Year 4 PKPvikneswaranNo ratings yet
- Quiz L1-2Document11 pagesQuiz L1-2tayrayrmp68No ratings yet
- World English 3e Level 3 Grammar Activities Unit 11 Lesson CDocument1 pageWorld English 3e Level 3 Grammar Activities Unit 11 Lesson CJesus Calizaya SabinoNo ratings yet
- How To Write & Publish A Critical Literature Review?: Professor Khaled Hussainey Plymouth University 7 February 2014Document30 pagesHow To Write & Publish A Critical Literature Review?: Professor Khaled Hussainey Plymouth University 7 February 2014mahgoub2005No ratings yet
- Ucla EssayDocument7 pagesUcla Essayapi-666363922No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 LastDocument34 pagesAssignment 2 Lastapi-455660717No ratings yet
- Research Logs 1-6Document7 pagesResearch Logs 1-6api-541028245No ratings yet
- Leica Builder Series BrochureDocument6 pagesLeica Builder Series Brochurebbutros_317684077No ratings yet
- HajinLim CVDocument4 pagesHajinLim CVHajin LimNo ratings yet
- Agama - Sarvajnanottara Agama - (Yoga Pada) PDFDocument99 pagesAgama - Sarvajnanottara Agama - (Yoga Pada) PDFtseekerNo ratings yet
- FS2 CompilationDocument31 pagesFS2 CompilationsleighNo ratings yet
- Action Plan Tutor Tutee 2018Document3 pagesAction Plan Tutor Tutee 2018lennie veranoNo ratings yet
- Caro Camp ContentsDocument4 pagesCaro Camp ContentsGreta DuqueNo ratings yet
- Mohsin Ki ZamanatDocument2 pagesMohsin Ki ZamanatAshar MalikNo ratings yet
- Lee Harvey Oswald FinalDocument7 pagesLee Harvey Oswald FinalAudrée Mathieu-LarocheNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge For Ielts Writing Task 2 Volume 2Document141 pagesGeneral Knowledge For Ielts Writing Task 2 Volume 2Faridahmad AziziNo ratings yet
- HALO HALO - For MergeDocument9 pagesHALO HALO - For MergeJuluis TrasmilNo ratings yet
- English 4 - EJE 6 - Week 14Document4 pagesEnglish 4 - EJE 6 - Week 14duseche4No ratings yet
- The Brain That Changes ItselfDocument12 pagesThe Brain That Changes Itselfronaldricardo_ladiesman0150% (10)
- ResumeDocument1 pageResumeapi-425218133No ratings yet
- Eng4 TG U2Document117 pagesEng4 TG U2leetolbean50% (2)
- CDR GuidelinesDocument2 pagesCDR GuidelinesBasit AliNo ratings yet
- CSA Standard W178.2-01: Certification of Welding InspectorsDocument2 pagesCSA Standard W178.2-01: Certification of Welding InspectorsramalingamNo ratings yet
- Intro To Machine Learning GoogleDocument4 pagesIntro To Machine Learning GoogleSudip MitraNo ratings yet
- KelompokDocument17 pagesKelompokEristia AyuNo ratings yet
- Moving To A New Country British English Student Ver2Document4 pagesMoving To A New Country British English Student Ver2Paula LyrioNo ratings yet