Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 10 Performance Task
Uploaded by
Brandz Dojenias RonquilloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science 10 Performance Task
Uploaded by
Brandz Dojenias RonquilloCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE 10
PERFORMANCE TASK
At this point, we are quite aware that our country is susceptible to different disaster such as
earthquakes, Volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis. Therefore, it is a must for us to prepare and ensure our
safety and survival when these disaster strike.
For this activity, your goal is to help your family prepare for an impending emergency. Your task
is to prepare an emergency kit for the whole family. Decide what items should be in your emergency kit
and present it by taking picture on how it is being used.
(Use ¼ illustration board)
The scoring rubric below will be used in assessing your kit.
2 points 4 points 6 points 8 points
Survival kit Items None of the items A few of the items At least 8 items At least 10 items
are necessary for are clearly are clearly are clearly
survival during or necessary for necessary for necessary for
after the disaster. survival during or survival during or survival during or
after the disaster. after the disaster. after the disaster.
Labels and Uses None of the items A few of the items At least 8 of the At least 10 items
are labelled are labelled items are labelled are labelled
properly and properly and a properly and a properly and a
there is no reason reason for each reason for each reason for each
for including it in item is included item is included item is stated on
the survival kit. on a separate on a separate a separate sheet
sheet of paper. sheet of paper. of paper.
Neatness and The kit is not The kit is The kit is done The kit is neatly
Effort Exerted organized. It somewhat well with some organized and
looks like the organized and it organization and labelled as
student threw it looks like the labelling. It necessary. Much
together at the student ran out of appears the time and effort
last minute time or didn’t take student worked were put into
without much care of the hard on it. creating projects.
care. project.
Name: _______________________________ Score: _________
Year and Section: ______________________ Date: __________
Summative test in Science 10
Direction: Encircle the correct answer.
1. Volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur in the Philippines because it is ___________
A. Volcanic Origin C. Composed of many islands
B. Located in the Equator D. located in the Pacific Ring of Fire
2. Where does the first motion of an earthquake occur?
A. Continents C. fault
B. Epicenter D. Focus
3. Earthquakes generally occur in areas where _________________
A. Rocks are found C. force on rocks is weak
B. Force on rocks are greatest D. magnetic pull is greatest
4. What is epicenter of an earthquake?
A. A seismic wave that travels along the surface of the earth
B. The last place that motion in an earthquake is detected
C. The point on Earth’s surface is directly above the earthquake’s focus
D. The location along a fault where first motion of an earthquake occurs
5. Which of the following is NOT a landform?
A. Volcano C. Ocean
B. Plateau D. Mountain Range
6. What Philippine volcano with latest eruption last January 12, 2020?
A. Mount Hilong Hilong C. Mount Pinatubo
B. Mount Taal D. Mount Mayon
7. Which of the following statement is NOT TRUE about active volcano?
A. Associated with earthquake C. Presence of hot spring
B. Changes elevation of volcano D. May not erupt
8. How are earth’s structures being formed?
A. Movement of magma C. Earthquake Activity
B. Elevation of Volcano D. Sediments from eroded continents
9. It is where most volcanoes and mountain ranges can be found?
A. Circum-Pacific Belt C. Eurasian Belt
B. Pacific Belt D. None of these
10. Why do earthquakes usually occur at plate boundaries?
A. The rock on the edges of the plates are soft
B. The rocks near the plates experience little stress
C. The rocks near the plates experience great pressure
D. The boundaries between plates have been active for many years.
11. Landforms on Earth’s crust were formed as a result of ________________
A. Earth’s Rotation C. movements of tectonic plates
B. Many bodies of water D. division of the lithosphere into plates
12. The theory used to explain the formation of the earth’s crust and its movement is called _______.
A. Continental drifts C. plate tectonics
B. Magnetic polarity D. sea floor spreading
13. Tectonic plates are made up of rocks that are part of the ________
A. Asthenosphere C. Inner core
B. Lithosphere D. Outer Core
14. Which of these is TRUE about the crustal plate?
A. Has the same thickness everywhere B. Vary thickness
C. Include the crust and upper mantle D. Thickest in the mountain region
15. The movement of the lithospheric plates is facilitated by soft, weak and plastic-like layer. Which of
the following layer is described in the statement?
A. Asthenosphere B. Lithosphere C. Atmosphere D. Mantle
16. A motion beneath the earth that causes the crustal plates to move which results different
landforms?
A. Subduction B. Convection C. Emission D. Collision
17. Plate Tectonics are said to be called _______________
A. Lithospheric Plates B. Asthenospheric Plates C. Subduction plates D. Oceanic Plates
18. Which of the following effects of plate movement cannot be located in the Mindanao region?
A. Cagwait White Beach C. Tinuy-an Falls of Bislig
B. Blue Lagoon of Cantilan D. Mountain Ridge of Cebu
19. These plates have the ability to move _______________ by gliding over the asthenosphere.
A. Horizontally B. Vertically C. Constant D. back and forth
20. Which of the following is a long term effect of plate movement?
A. Volcanoes B. Mountain Ranges C. Earthquakes D. Movement of entire continents
21. What is the average density of the earth’s crust?
A. 2.8 g/cm3 B. 2.6 g/cm3 C. 2.0 g/cm3 D. 1.8 g/cm3
22. What layers of Earth make up the lithosphere?
A. The crust and lower mantle C. The crust and upper mantle
B. The continental crust and oceanic crust D. The upper mantle and lower mantle
23. Earth’s lithosphere is part of the _________
A. Crust B. Asthenosphere C. Mantle D. Core
24. Which of the following occurs because of convection currents?
A. Tectonic plates on the crust move C. The mantle increases sizes
B. Pressure in the crust increases D. Pressure in the crust decreases
25. Which one of the following statements does NOT apply to the lithosphere?
A. It comprises the crust and upper mantle
B. Earthquakes mainly occur in this layer
C. It has the average thickness of 7 kilometers
D. It is rigid/brittle layer
Name: _______________________________ Score: _________
Year and Section: ______________________ Date: __________
Summative test in Science 8
Direction: Encircle the correct answer.
1. What do you call the energy in motion?
a. mechanical energy c. kinetic energy
b. potential energy d. heat energy
2. Which law states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed?
a. Law of acceleration c. Law of Conservation of Energy
b. Law of inertia d. Law of Conservation of Work
3. Which of the following form of energy is associated with an objects’ position?
a. mechanical energy c. kinetic energy
b. potential energy d. heat energy
4. What is the kinetic energy of a 100kg falcata log, if it rolls down the hill at a speed of 15 m/s?
a. 11 250 J c. 112.5 J
b. 1125 J d. 11.25 J
5. A cyclist is pedalling a bicycle down the hill at a speed of 25 m/s. The bicycle has what form of
energy?
a. mechanical energy c. kinetic energy
b. potential energy d. heat energy
6. According to Newton’s First Law of Motion,
a. An object in motion eventually comes to a stop.
b. An object at rest eventually begins to move.
c. An object at rest always remains at rest.
d. An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by a net force.
7. The greater the mass of an object,
a. The easier the object starts moving. c. The more space it takes up
b. The greater its inertia d. The more balanced it is
8. The tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion is known as
a. Balance b. Force c. Inertia d. Mass
9. Mass of the object is quantitative measure of its inertia stated law is Newton’s
a. First law b. Second law c. Third law d. Fourth law
10. Which of these bests describes the concept of inertia?
a. a force that attracts objects with mass
b. the tendency of an object to float in water
c. a force created when surfaces are in contact
d. the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion.
11. Two people pull on a rope in a tug-of-war. Each pull with a 400 N force. What is the tension in the
rope?
a. 0 b. 400 N c. 600 N d. 800 N
12. A block is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 6
N. What is the frictional force between the block and the surface?
a. less than 6 N b. 6 N c. more than 6 N d. Needs more information to say.
13. As a 500 N lady sits on the floor, the floor exerts a force on her is equal to ____.
a. 1000 N b. 500 N c. 250 N d. 50 N
14. How does acceleration of an object change in relation to its mass? It is _____
a. Directly proportional c. Inversely proportional
b. Acceleration doesn’t depend on its mass d. Neither A nor B
15. Which will accelerate faster?
a. A 1000 tons truck c. A fully loaded bus
b. An overloaded jeepney d. A race car
16. What happens when liquid substance turns into solid?
a. It loses energy equal to its latent heat of fusion.
b. It absorbs energy equal to its latent heat of fusion.
c. It losses energy equal to its latent heat of vaporization.
d. It absorbs energy equal to its latent heat of vaporization.
17. Heat is the transfer of ________ from one object to another due to a difference in temperature.
a. Time c. Force
b. Velocity d. Energy
18. What happens when the substance get hotter?
a. Shrinks c. The same
b. Expands d. cannot be identified
19. What is called when two objects touching each other eventually reach the same temperature?
a. Expansion c. Equilibrium
b. Conduction d. All of these
20. What happens to the molecules of a substance as it gets cooler?
a. Shrink c. Move faster
b. Expand d. Move slower
21. When an action force occurs, the reaction force is always___________.
a. In the same direction as the action force.
b. Equal and opposite of the action force.
c. Applied to the same object as the action force.
d. none of the above
22. When you stand on the floor, the force of your body pushing down on the floor is_______.
a. Matched by the floor pushing up on your body.
b. Less than the reaction force applied by the floor.
c. A reaction to the floor pushing up.
d. none of the above
23. When a kangaroo jumps, the kangaroo‟s action force acts on the ground and the reaction
force________.
a. Is equal to the exerted force. c. Acts on the kangaroo.
b. Is greater than the action force. d. two of the above
24. An archer shoots an arrow. The action force is the bowstring against the arrow, the reaction force is
________.
a. Air resistance against the bow c. Arrow‟s push against the bowstring
b. Grip of the archer‟s hand on the bow d. All of the above
25. According to Newton‟s third law of motion, when a hammer strikes and exerts force on a nail, the
nail ________.
a. Creates a friction with the hammer.
b. disappears into the wood
c. Exerts an equal force back on the hammer.
d. Moves at a constant speed
Name: _______________________________ Score: _________
Year and Section: ______________________ Date: __________
SCIENCE 8
Answer the following questions on the space provided. (5 points each)
1. If an elephant were chasing you, its enormous mass would be most threatening. But if you
zigzagged, its mass would be to your advantage. Why?
2. Why is it easier to walk on a carpeted floor than on a smooth, polished floor?
3. How do the laws of motion apply to everyday life?
4. How do Newton’s laws solve common life problems?
You might also like
- Soil Bearing Capacity for Shallow FoundationsDocument78 pagesSoil Bearing Capacity for Shallow FoundationsSweet Boy100% (1)
- St. Bridget College Assessment for Non-Mendelian InheritanceDocument8 pagesSt. Bridget College Assessment for Non-Mendelian InheritancePang ChixxNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency Directory in Science 9 (Quarter 1) : Inopacan National High SchoolDocument4 pagesLearning Competency Directory in Science 9 (Quarter 1) : Inopacan National High SchoolYbur Hermoso-MercurioNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 BOLDocument7 pagesGrade 10 BOLJesselyn Dacdac Llantada-Bautista100% (3)
- DLL Science Grade 8 Week 1Document3 pagesDLL Science Grade 8 Week 1AbramBarangan78% (18)
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEMaverick ShadeNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument2 pagesDLPEldie Ocariza100% (1)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Science 10 Quarter 4, Week 3-4, June 21-25, June 28-July 2, 2021Document5 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan Science 10 Quarter 4, Week 3-4, June 21-25, June 28-July 2, 2021kaycin DuzonNo ratings yet
- Please provide a concise, SEO-optimized title for the document using 40 characters or lessDocument4 pagesPlease provide a concise, SEO-optimized title for the document using 40 characters or lessJackie Lou AriasNo ratings yet
- Integration of ValuesDocument7 pagesIntegration of Valuesapi-340406981No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Continental & Oceanic CrustDocument22 pagesLesson 1 - Continental & Oceanic CrustKatana MistNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science Lesson on Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesPhilippine Science Lesson on Plate Tectonicsjohann reyes50% (2)
- Learning Activity4.1 (Science Grade 8) : Name: Grade/Score: Year and Section: DateDocument2 pagesLearning Activity4.1 (Science Grade 8) : Name: Grade/Score: Year and Section: DateMa LouNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science - Volcano ClassificationDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Science - Volcano ClassificationGellie Mae Badilla Dacay67% (3)
- DLL Endogenic Geologic ProcessesDocument2 pagesDLL Endogenic Geologic ProcessesGivby DollenteNo ratings yet
- Science Month MemoDocument6 pagesScience Month MemoLorraine Calvez DonioNo ratings yet
- SEARCH FOR EINSTEIN OF THE YEARDocument4 pagesSEARCH FOR EINSTEIN OF THE YEARMorena AbayonNo ratings yet
- Reading Selection in ScienceDocument4 pagesReading Selection in ScienceBenes Salamanca BolascoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory ExplainedDocument3 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory ExplainedJR Pellejera0% (1)
- Activity Sheet 12 Drifted SupercontinentDocument2 pagesActivity Sheet 12 Drifted SupercontinentPangangan NHS100% (2)
- Performance Task 1Document3 pagesPerformance Task 1Jellie May RomeroNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPDocument13 pagesGrade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- LEAST MASTERED LEARNING COMPETENCIES Science 10-First QuarterDocument1 pageLEAST MASTERED LEARNING COMPETENCIES Science 10-First QuarterNenbon NatividadNo ratings yet
- DLP IDEA G10 Week 8Document5 pagesDLP IDEA G10 Week 8Arlene Diokno100% (1)
- Deworming Report Forms for SchoolsDocument17 pagesDeworming Report Forms for SchoolsNaddy RetxedNo ratings yet
- SIM - Nucleic Acid - For PublicationDocument16 pagesSIM - Nucleic Acid - For PublicationAdrienne Nicole100% (1)
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes Lesson: Causes and Effects in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesEarthquakes and Volcanoes Lesson: Causes and Effects in 40 CharactersBlythe RabacioNo ratings yet
- ORTEGA-Science G7-LP-Effects of Changes in The Abiotic FactorsDocument1 pageORTEGA-Science G7-LP-Effects of Changes in The Abiotic FactorsIsabel R OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 9-3rd WeekDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 9-3rd WeekJohnRenzoMolinar100% (1)
- Performance Task 2: Plate BoundariesDocument8 pagesPerformance Task 2: Plate BoundariesArmel AbarracosoNo ratings yet
- New E Class Record GRADE 7 10 SCIENCEDocument22 pagesNew E Class Record GRADE 7 10 SCIENCEArthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- Sci - DamaDocument12 pagesSci - DamaJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- Locating Epicenters Using TriangulationDocument2 pagesLocating Epicenters Using TriangulationMaribel Tan-Losloso Nayad100% (2)
- Tos Science 9 - 4thDocument8 pagesTos Science 9 - 4thJay Ronnie PranadaNo ratings yet
- Typhoon Renee Speed and MovementDocument1 pageTyphoon Renee Speed and MovementAlvin Gultia67% (3)
- 2nd-Quarter - DLL Grade 9Document42 pages2nd-Quarter - DLL Grade 9STEPHEN MILANNo ratings yet
- 7e's - Electron ConfigurationDocument5 pages7e's - Electron ConfigurationVea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- Grade 10first TQDocument3 pagesGrade 10first TQJerbs PacundoNo ratings yet
- The Learners Shall Be Able To: : GRADE 1 To 10 Teaching Dates and TimeDocument3 pagesThe Learners Shall Be Able To: : GRADE 1 To 10 Teaching Dates and TimeDanica DabanNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior DLLDocument2 pagesEarth's Interior DLLGivby Dollente100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 10 - 3rd WeekDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 10 - 3rd WeekJohnRenzoMolinar100% (2)
- Grade 10 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 1-2Document10 pagesGrade 10 Activity Sheets Quarter 1 Week 1-2Nexie JunsayNo ratings yet
- Locating Epicenters and Plate BoundariesDocument28 pagesLocating Epicenters and Plate BoundariesyamikoNo ratings yet
- Glee Club Action PlanDocument3 pagesGlee Club Action PlanAdon Mike CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Mr. Arsenio Ladiero Junior High School PrincipalDocument1 pageMr. Arsenio Ladiero Junior High School PrincipalClanetie CollaNo ratings yet
- Science Teacher Science Department Head PrincipalDocument3 pagesScience Teacher Science Department Head PrincipalJelly MendozaNo ratings yet
- DLL SampleDocument6 pagesDLL SampleJenny Domincel PrudenteNo ratings yet
- Seismic Waves Provide Insights Into Earth's InteriorDocument2 pagesSeismic Waves Provide Insights Into Earth's InteriorEllen DispoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 MDL L3 Week 4-5 PRINTEDDocument3 pagesScience 9 MDL L3 Week 4-5 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument34 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDainielle Marie PascualNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Science 10 7es Lesson Plan Quarter 3 Week 3 Topic The Reproductive System PRDocument3 pagesToaz - Info Science 10 7es Lesson Plan Quarter 3 Week 3 Topic The Reproductive System PRJinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet MbaDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheet MbaMubashir AliNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Earthquake Epicenters Using Triangulation Method: Example: Chicago 18 Seconds 153 Seconds 135 SecondsDocument3 pagesModule 3: Earthquake Epicenters Using Triangulation Method: Example: Chicago 18 Seconds 153 Seconds 135 SecondsJakecob Mejillano JacobNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentJoanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- Q1-Week 4 - Major and Minor PlatesDocument2 pagesQ1-Week 4 - Major and Minor Plateskumi100% (1)
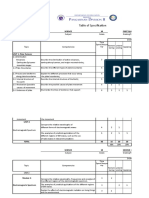
- Table of Specifications: Science Quarterly Grading PeriodsDocument24 pagesTable of Specifications: Science Quarterly Grading PeriodsMarvin ObraNo ratings yet
- Activity Additional Faulty SetupDocument1 pageActivity Additional Faulty SetupJoselle Niebres Reyes100% (1)
- Grade 10 Activity Sheet On Electricity and Magnetism Activity 1: Magnetic Field Mapping ObjectivesDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Activity Sheet On Electricity and Magnetism Activity 1: Magnetic Field Mapping ObjectivesJudarlyn Madria100% (1)
- Template For Unpacking of Science 10 Melcs: Grade Level:10/2 QuarterDocument2 pagesTemplate For Unpacking of Science 10 Melcs: Grade Level:10/2 Quarterjuliusleo martin100% (2)
- Science g8 q2 Module 1 WK 1 PDF FreeDocument26 pagesScience g8 q2 Module 1 WK 1 PDF FreeRaffy cel ZafraNo ratings yet
- Science G8-Q2-MODULE 1-WK-1Document26 pagesScience G8-Q2-MODULE 1-WK-1Choie Gumera50% (2)
- Science g8 q2 Module 1 WK 1Document26 pagesScience g8 q2 Module 1 WK 1Arlene PajaresNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument3 pagesEnvironmental ScienceBrandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Grapes Module in TLEDocument30 pagesGrapes Module in TLEBrandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesDigestive SystemBrandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Application GrapesDocument1 pageApplication GrapesBrandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Teacher Reports on Home-Based WorkDocument9 pagesTeacher Reports on Home-Based WorkBrandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Science 7Document3 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 7Brandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- K12 TLE Curriculum Cookery Grade 7 - 10Document33 pagesK12 TLE Curriculum Cookery Grade 7 - 10Macqz Numlock Abas Kudto88% (8)
- Sample Questionnaire For Science Grade 7Document5 pagesSample Questionnaire For Science Grade 7mj Canilang100% (1)
- S8 - Q2 - Week 4Document6 pagesS8 - Q2 - Week 4Brandz Dojenias Ronquillo100% (2)
- President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityDocument7 pagesPresident Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Torsion Chapter 6Document43 pagesTorsion Chapter 6venkeeku100% (1)
- Assignments 2Document2 pagesAssignments 2Alok RanjanNo ratings yet
- ME 010 506 Thermodynamics: Noel Joseph GomezDocument11 pagesME 010 506 Thermodynamics: Noel Joseph GomezmujeebNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Underpass RCC BridgeDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of Underpass RCC Bridgekashi BhojiaNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Potential ConceptsDocument11 pagesElectric Field and Potential ConceptsAyman HalimeNo ratings yet
- PPLATO - Basic Mathematics - Gradients and Directional DerivativesDocument4 pagesPPLATO - Basic Mathematics - Gradients and Directional Derivativesbitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- Surge Tank Design Considerations ForDocument14 pagesSurge Tank Design Considerations ForPatricio Muñoz Proboste100% (1)
- New Correlations of Single-Phase Friction Factor For Turbulent Pipe Flow and Evaluation of Existing Single-Phase Friction Factor CorrelationsDocument7 pagesNew Correlations of Single-Phase Friction Factor For Turbulent Pipe Flow and Evaluation of Existing Single-Phase Friction Factor CorrelationsHernán GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer ThicknessDocument23 pagesBoundary Layer ThicknessPridhar ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- RMPH 2017 PT3 QuestionDocument4 pagesRMPH 2017 PT3 QuestionAndrei FlorinNo ratings yet
- Beam Reinforcement CalculationDocument8 pagesBeam Reinforcement CalculationAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Picket Fence Freefall LabDocument4 pagesPicket Fence Freefall Labasdf100% (1)
- GR 11 Physical Sciences P1 (English and Afrikaans) November 2022 Possible AnswersDocument10 pagesGR 11 Physical Sciences P1 (English and Afrikaans) November 2022 Possible Answersyoungmarley457No ratings yet
- MRI Safety TrainingDocument20 pagesMRI Safety TrainingYuda Fhunkshyang100% (1)
- Heat Conductivity of Gases and Liquids Vargaftik Filippov, Tarzimanov, YurchakDocument202 pagesHeat Conductivity of Gases and Liquids Vargaftik Filippov, Tarzimanov, YurchakodormicchiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Convection Heat and Mass Transfer in Inclined Rectangular DuctsDocument10 pagesMixed Convection Heat and Mass Transfer in Inclined Rectangular DuctsSouadHadjadjNo ratings yet
- Part 02 Question (528 - 541)Document16 pagesPart 02 Question (528 - 541)rudrakshengg.No ratings yet
- Line sizing for gas flow from PCV to flare headerDocument2 pagesLine sizing for gas flow from PCV to flare headerlutfi awnNo ratings yet
- CC03 Report Lab 10 Group 08 1Document8 pagesCC03 Report Lab 10 Group 08 1ANH GIAN QUỲNH PHƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- 1 EXP Mechanical Vibration (Corrected)Document4 pages1 EXP Mechanical Vibration (Corrected)AbhiNo ratings yet
- Designing a 20W Stirling EngineDocument92 pagesDesigning a 20W Stirling EngineShafiq MahadiNo ratings yet
- Energy Recovery Ventilators: For Today'S Indoor Environmental Quality RequirementsDocument16 pagesEnergy Recovery Ventilators: For Today'S Indoor Environmental Quality RequirementsChess Servin PerezNo ratings yet
- Productdisassemblychart 1Document2 pagesProductdisassemblychart 1api-450114937No ratings yet
- Delta Versus Wye Connected Capacitor Banks PDFDocument3 pagesDelta Versus Wye Connected Capacitor Banks PDFFady MegalaNo ratings yet
- Undamped Vibration Absorber - v3Document14 pagesUndamped Vibration Absorber - v3prem_chaurasiyaaNo ratings yet
- Motionmountain Volume3Document445 pagesMotionmountain Volume3MensijanacNo ratings yet
- Impact of VSC Control Strategies and Incorporation of Synchronous Condensers On Distance Protection Under Unbalanced FaultsDocument10 pagesImpact of VSC Control Strategies and Incorporation of Synchronous Condensers On Distance Protection Under Unbalanced FaultspouyanNo ratings yet