Professional Documents
Culture Documents
See 2 P
Uploaded by
marc millisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
See 2 P
Uploaded by
marc millisCopyright:
Available Formats
~r;;:,(f';.':::!'f!"'t\,!:~~;f!',::..
"
';;:I'&.~~t'f':;;J\'J,t...~~;~~1' c:;;..;9,,:1c,"':
';~t~,~~,:;;,'c.:cc, ,,' , , ' . "
gf"~':;f;)"-' 79f'!11""!,:',lr'1J \ ~".; , 5044 8 ° c;
';.
:;::.[':',;\ (
.., a~ infinite,eia'~tic solid (cf, Cambridge and Dublin Mathe- if dX/dx+dY/dy+dZ/d.z-4nl! (,ll+n) = o (50)~~
matical Journal, 1848). , , , , or the density is 4efined by the expression: '~;
, It ~ay be note~ that the de~slty of an Iso~roplc solId, = 1/[ n (m+n)] .(dX/dx+d Y/d +dZ/dz) , ( I) ,~
whIch does not vary wIth the coordInates (x,y, z), IS expressed. I! 4 ~ S ,
, -by the ratio, This specifies the density throughout space of the infinite
I!\=
[(m+n)V2d]/(dX/dx+dY/dy+dZ/dz). (43) iso.tropic soli?, that of the finite solid body in (41) being,;
B t b' t' h D .. unIty per UnIt of volume.
.u y .c't1lssons equa Ion we ave. , .
, .2 To reach IJord KelvIn s result most dIrectly, we let R
, ': , ' V2 V+4n I! =. o I! = -V V/4n (44) denote the resultant of the forces, X, Y; Z, at any point
\ or " 1!=--:.(I/4n)((}2J//(}x2+(}2V/(}y2+(}2V/(}z2), (45) (x,y,z), atthedistancer= V(X2+y2+Z2) from the origin"
"c" , c, By c<?mparing (43) and (45), we find ~hat if a mass whether discontinuous and vanishing in all points outside
,,':of density, , some finite closed surf~ce, or continuous and vanishing at all
c' 0" ' \ ' = 1/[ n (m+n)] .
(~ + ~ + ~ ) (46) infinitely distant points wi~h sufficient convergency to make
I! 4 , dx dy dz Rr converge to o as r Increases to 00, Then the con-
, be distributed throughout space, we may conclude th.at its vergency of Xr, Yr, Z:r t~ zero"when r,is infinite, c~early
potential at (x, y, z) will be identical with the dilatation of ~akes V= o for all InfinItely, dIstant p~l~tS, Accor~lnglyt
; "'the ell\stiqsolid substance: .If S be any. clos,ed sur~ace round t,he ongln 0! coo~dlnate~,
;;c, , , '. d = (} /(} +(},8/(} +(} /(} ( 7) , everywhere InfinItely dIstant from It, the functIon (0- V) IS
.: ., a x :JI r z, 4 zero for all points of it, and satisfies the equationV2(d'- V)
;'". For If we dIvIde (42) by (m+n), and subtract from = o for all points witbin it, Therefore d' = V throughout
:clt the .fir~t of (44), ,we get: ' the infinite isotropic solid,
~~;;,\: ; ; V'd+(dX/dx-+dY/dy+dZ/dz)/(m+n)+ ' Now let X',Y', Z' denote the values of X, Y; Z at any,
!' , -:V'V-4nl! = o (48) point (x,y, z), and by a triple integration throughout all space,
,~,'whicb gives: ' V!(d'- VJ = o (49) we shall have for the potential Vor dilatation 0:
.!~:,;\;" '::" ' ' , +00 +bo +00
'~\""J:.;liiZi';~~j'(J, ~.:if[41f (m+n)]. S S S (dX'/d.:i:'+d Y'/dy'+dZ'/dz')/V[(x~x')2+(y- y')'+(Z-Z'}2] .dx' dy' dz', (52)
[:'c.:\' ,) " :,. , -00-'X>-op
-: "Forthe element of the mass is' I! = I/[4n(ln+n)]'(dX'/dx'+dY'/dy'+dZ'/dz') .(53)
" -,
~:'. 'li.nd?the mutual distances of the elements of mass filling the element of space dxdy dz is
f:l':c~~:/:ic"r~:!;' r = V[(X-x')2+(y-y')2+(Z-Z')2] , \ (54)
,~"' :1':: ' "These expressions may be,rendered more convenient by integrating by parts, and noticing the prescribed con-
!; !dition 0(, convergence, according to which when x' is infinite,
;c:,:: ',;:;':i~~!~':'Zil,.;,::.,\: ;,~".""", +CX) +CX) , ,"
" S SX'/V[(x-x')2+(y-y')2+(z-z')2],dy'dz'=o. (55)'
~:::",~,-.';""'" -~-oo
1:':' And, therefore, 'for the three components of finite value, resolved along the coordinate axes, and integrated throughout
, \ all sp.ace,we have: +CX) +00 +CX) , ,
!,;,i.:J'1';"O =';I/[41f (m+n)l.S ' S S [X' (x-x')+ Y' (y-y')+Z' (z-z')]/V[(X-X')2+(y- y')2+(Z-Z')2] .d.'t"' dy' dz'. (56)
~~~~;:';.i:" : ~; , ~= -00 -CX)
~,i:"~' ,i,;. 'We may integrate each 'of the equations (38) in the same way, for at ,8, r respectively. The result for these
" 'c' I ,
~,:j:.,~isplac~~ents. is: a = u+ lj ,8 = v+ V r == w+ w (57)
~:~;'~here: u;-:v, w, U; II; W denote the potentials at (x, y, z) of distributions of matter through all space of densities respectively
':~":::: ; -:;' (m/41tn) (}d'/(}x (In/4nn) (}0/(}y (tn/4nn) (}d'/(}z X/4nn Y/4nn , Z/4nn , (58)
, " ',
~~,,;ln: pthet
l\" )"Cc;~r.' .~ords the
' functions' .. are such that throughout all space
~\.:;-;~J:'~,:,;'!:):,:,;~'}:;!'~,
: ' y2u,:t-(m/n) ad'/(}x = o V2lj+X/n = o V2v+(11f/n) (}d'/(}.v = o V2 V+ Y/n = 0 ( )
:,':;;p,;"~,;:;>!,~,:~!:;:,:::- , ' " :c, , V2w+(m/n) (}0/(}z = o V'W+Z/n = 0. 59
Y", Z" denote the values of X, Y; Z ,for a. point (x", y", z"), we find
G~~.rq:,;~~~\t;y'f':"i~"::'~',:.
" ::"',.! ' -, +00,+00+00
r;-~;I:):i:~~,t,,:~t~;tti~~:.::',:
L\,~,.;.",. ,~." , c'a
~;!,:\","...,~",J~.,:it'c"",;
,," i:=i:t
/ (I /4'n~ ) S S S(In' (}d"' / 8x" + X" )/ 11[( x-'- X" ) 2+ (Y -'- Y " ) 'l+
,
( z- Z" ) 2] .dx" dt/' dz"
"
:;- ' -:00-:0:;:00 .!
S S S (tn .(}d"' !.(}y" + V")/ V[(.'t"-' x")2 + (y- )1')2~(Z -z")2] .dx" dy" dz" (60)
.-:00-:00-:~ /
l.::::.:~,~;,~~!:;:;;;Li~~:~: ~ ,( I/ 41fn) S S S (,n .(}0"/(}z" +Z")/ V[(x -x")'2+(y- y")2+ (z:- z")2] .dx" dy'dz" .,
~ :::";"i!"J"!,;;t,;l,',;f;;;ll'!'\.~"\'!: ::,;;"~ , ' .;
",'"c".-""(;(f{ f-IT~(."..'""."'~.' , -00-00-00 ,
"~:~,,~-!~;1};.".,:'~'1~';t!i'cC,;;!;:"1,jf,:; , ;',~ : ' .:
You might also like
- Damaskin 1982Document11 pagesDamaskin 1982pescaofritoNo ratings yet
- indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Department of Physics and MeteorologyDocument2 pagesindian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Department of Physics and MeteorologyAnurag MNo ratings yet
- 82 BafaDocument18 pages82 BafaTaarik100% (1)
- ApolloDocument15 pagesApolloPaul RobertoNo ratings yet
- Cape Physics 2012 U2 p1Document15 pagesCape Physics 2012 U2 p1Steve RamlalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory Anna University Question Paper R2013Document23 pagesElectromagnetic Theory Anna University Question Paper R2013kkarthiksNo ratings yet
- Electr Forces Fields2 AkDocument3 pagesElectr Forces Fields2 AkJack JackNo ratings yet
- Partial Complete CVNG3013Document8 pagesPartial Complete CVNG3013Chris BramaoNo ratings yet
- Aml710 Major Sem2 08Document2 pagesAml710 Major Sem2 08donotpanicNo ratings yet
- See 1 BDocument1 pageSee 1 BTorey AmiciNo ratings yet
- Steady and UnsteadyDocument9 pagesSteady and UnsteadyDSddsNo ratings yet
- XCIV The Large Deflection of Simply Supported BeamsDocument8 pagesXCIV The Large Deflection of Simply Supported BeamsFacheng ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Mysha Jain Math Class II ADocument8 pagesMysha Jain Math Class II A29ajayNo ratings yet
- Engg Maths 4 Jan 2018 (2015 Scheme)Document2 pagesEngg Maths 4 Jan 2018 (2015 Scheme)bharath sNo ratings yet
- Cursul 08Document26 pagesCursul 08DarabaGabriellNo ratings yet
- $cho Olnew' - G De: Answer AllquestionsDocument5 pages$cho Olnew' - G De: Answer AllquestionsSandra KhanNo ratings yet
- Atoms PyqDocument26 pagesAtoms PyqAditya Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics National Institute of Technology, TiruchirappalliDocument6 pagesDepartment of Mathematics National Institute of Technology, TiruchirappalliprathikNo ratings yet
- Pub 04Document4 pagesPub 04παπαδοπουλοςNo ratings yet
- Maximum Neatly (You WillDocument7 pagesMaximum Neatly (You WillBobNo ratings yet
- Em Waves + PyqDocument4 pagesEm Waves + Pyqabhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Dirac Deltas and Discontinuous FunctionsDocument6 pagesDirac Deltas and Discontinuous Functionsdiego2591No ratings yet
- Rules and Regulations of SPCA Punjab, 1982Document5 pagesRules and Regulations of SPCA Punjab, 1982Pakistan Animal Welfare SocietyNo ratings yet
- Domestic Help Varification Form2Document3 pagesDomestic Help Varification Form2Rajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Assig #: NmentDocument5 pagesAssig #: NmentsovrinNo ratings yet
- See 2 MDocument1 pageSee 2 Mmarc millisNo ratings yet
- Scan Jul 14, 2021Document17 pagesScan Jul 14, 2021ULTRONOMO PRIMENo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Digital Analog Communication Systems 8th Edition by Answer and ScriptDocument5 pagesSolutions Manual Digital Analog Communication Systems 8th Edition by Answer and ScriptSydney0% (1)
- Task 4part BDocument5 pagesTask 4part BJood KhunjiNo ratings yet
- Common Difference: Ly/.::. 5 Vvu - Jic.. ? - SVJ 'Document5 pagesCommon Difference: Ly/.::. 5 Vvu - Jic.. ? - SVJ 'John MeyersNo ratings yet
- EfrainDocument1 pageEfrainchikas_gwenhwyfarNo ratings yet
- Sem 4Document20 pagesSem 4Kartik Yallappa NamdeNo ratings yet
- R 314, Exam.Document6 pagesR 314, Exam.jennifer_crummNo ratings yet
- Moments of Distribution, Skewness, KurtosisDocument16 pagesMoments of Distribution, Skewness, KurtosisAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2021 SAC 1 PT 2 Revision - SolutionsDocument89 pages2021 SAC 1 PT 2 Revision - SolutionsChamu BatugedaraNo ratings yet
- ./"' (Yji4'Y Ji4'Y J14) ': 1:/I, 1:ii, - C'U 1:it O., (/ (/ Pr/I. R:: Pr/21Document4 pages./"' (Yji4'Y Ji4'Y J14) ': 1:/I, 1:ii, - C'U 1:it O., (/ (/ Pr/I. R:: Pr/21donotpanicNo ratings yet
- Line Integral 2Document24 pagesLine Integral 2Mohamed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Peri :: : ': - : - ' /., /: Energy Density and Classical Average EnergyDocument1 pagePeri :: : ': - : - ' /., /: Energy Density and Classical Average EnergyBen WrightNo ratings yet
- DerivativeDocument143 pagesDerivativebbNo ratings yet
- Math A PrefinalsDocument2 pagesMath A PrefinalshappytohelpNo ratings yet
- Scan 0002Document1 pageScan 0002ntran14No ratings yet
- MRCTC Analytic GeometryDocument6 pagesMRCTC Analytic GeometryJunnar Jay AbañoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 27, 2023Document7 pagesAdobe Scan Oct 27, 2023hmatubu2No ratings yet
- A Shred of Honour: A Markham of the Marines NovelFrom EverandA Shred of Honour: A Markham of the Marines NovelRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (8)
- EMTlec 22Document6 pagesEMTlec 22I190845 Samana NayyabNo ratings yet
- TM Waves in Rectangular W.G.Document12 pagesTM Waves in Rectangular W.G.MANUDEYNo ratings yet
- ) Ans Er: - . 5°5:.2 FN: AN203/ AD303Document5 pages) Ans Er: - . 5°5:.2 FN: AN203/ AD303abhijit99541623974426No ratings yet
- Test 1Document7 pagesTest 1api-3807258No ratings yet
- 21 Stresss AnalysisDocument21 pages21 Stresss AnalysisA ANo ratings yet
- Sedimentation in Tilted VesselsDocument12 pagesSedimentation in Tilted Vessels2306노강민No ratings yet
- Polar BeasrDocument1 pagePolar BeasrsonnynotsonyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29 Jan 2023Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 29 Jan 2023Krish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 2Document11 pagesQuestion Bank 2testing.mugdhNo ratings yet
- lO弋心 弋 lO lO-: e =e =ezx =0Document1 pagelO弋心 弋 lO lO-: e =e =ezx =0allenNo ratings yet
- O Level 2012 Maths D P2 Question 10Document2 pagesO Level 2012 Maths D P2 Question 10Sabbir MasumNo ratings yet
- Baby HitlerDocument2 pagesBaby Hitlerapi-574396440No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exam# (Illustrate Free Body Pressure Distribution Where Applicable) G) Find The Pressure at Point A in The in The Figure BelowDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics Exam# (Illustrate Free Body Pressure Distribution Where Applicable) G) Find The Pressure at Point A in The in The Figure BelowCamille WallaceNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Electrical NotesDocument256 pagesGrade 12 Electrical NotesTim GordashNo ratings yet
- See 2 eDocument1 pageSee 2 emarc millisNo ratings yet
- See 2 MDocument1 pageSee 2 Mmarc millisNo ratings yet
- FF (FFJ: X' (X',-.:-.X') + Y' (Y"-Y') +Z' ($"-S')Document1 pageFF (FFJ: X' (X',-.:-.X') + Y' (Y"-Y') +Z' ($"-S')marc millisNo ratings yet
- Einstein 'S Opponents: More InformationDocument21 pagesEinstein 'S Opponents: More Informationmarc millisNo ratings yet
- See 2 oDocument1 pageSee 2 omarc millisNo ratings yet
- Early Journal Content On JSTOR, Free To Anyone in The WorldDocument52 pagesEarly Journal Content On JSTOR, Free To Anyone in The Worldmarc millisNo ratings yet
- Gravitational WavesDocument18 pagesGravitational Wavesmarc millisNo ratings yet
- Historical Papers Astrophysics Science Journal 3450Document1 pageHistorical Papers Astrophysics Science Journal 3450marc millisNo ratings yet
- CM 21 Ponderomotive ForceDocument4 pagesCM 21 Ponderomotive Forcemarc millisNo ratings yet
- Five Trigonometry Identities ProblemsDocument2 pagesFive Trigonometry Identities ProblemsdibyanshuNo ratings yet
- PlanimeterDocument4 pagesPlanimeterdukenmargaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Chapter 4 - The DSMDocument17 pagesFinite Element Method Chapter 4 - The DSMsteven_gogNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Differential EquationsEricka Mae FedereNo ratings yet
- A. Introduciton: MethodDocument19 pagesA. Introduciton: MethodStrag ChrisNo ratings yet
- 2015 MTAP Reviewer For 4th Year Solution Part 1Document3 pages2015 MTAP Reviewer For 4th Year Solution Part 1Nathaniel Pascua22% (9)
- MATH 195a6 Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesMATH 195a6 Syllabus PDFMarjorie ChanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Relations PDFDocument229 pagesMathematical Relations PDFmars100% (1)
- DILE NO A LA PLANCHA (Kim Jhon Phatti Satto)Document6 pagesDILE NO A LA PLANCHA (Kim Jhon Phatti Satto)Kimsito Al TlvNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Trade TechDocument2 pagesAnswer Key Trade TechPaulojoy BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Formulae For Partially Filled Circular Pipes (Akgiray, 2004) PDFDocument15 pagesHydraulics - Formulae For Partially Filled Circular Pipes (Akgiray, 2004) PDFRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- IMO Level 2 - Class 6 (2013-2014) PDFDocument12 pagesIMO Level 2 - Class 6 (2013-2014) PDFChirag JainNo ratings yet
- As Further Mathematics - CP1 - Vectors MSDocument12 pagesAs Further Mathematics - CP1 - Vectors MSjimNo ratings yet
- Ls Maths8 2ed TR Workbook Answers-2Document60 pagesLs Maths8 2ed TR Workbook Answers-2Hana Mohamed89% (101)
- Math12-1 - Lesson 3 - Trigonometric Functions of AnglesDocument12 pagesMath12-1 - Lesson 3 - Trigonometric Functions of AnglesKobe MartinezNo ratings yet
- 02-Random VariablesDocument38 pages02-Random Variablesmilkiyas mosisaNo ratings yet
- Graduate Functional Analysis Problem Solutions WDocument17 pagesGraduate Functional Analysis Problem Solutions WLuis ZanxexNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Second Order Linear Differential EquationsDocument51 pagesLec 4 Second Order Linear Differential EquationsTarun KatariaNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Computational EngineeringDocument21 pagesLinear Algebra For Computational EngineeringCovenant AdeogoNo ratings yet
- Asymptotes of Rational Functions: X FX X X FX XDocument2 pagesAsymptotes of Rational Functions: X FX X X FX XericaNo ratings yet
- Math4 ST3 Q3Document2 pagesMath4 ST3 Q3Troy Esto VillorenteNo ratings yet
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDocument6 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
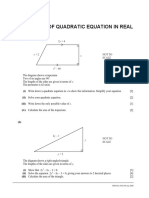
- Application of Quadratic Equation in Real ContextDocument3 pagesApplication of Quadratic Equation in Real ContextMCHNo ratings yet
- HD 13 Numerical Integration of MDOF 2008Document18 pagesHD 13 Numerical Integration of MDOF 2008tanha56313955No ratings yet
- Apeejay School, Panchsheel Park Test PaperDocument11 pagesApeejay School, Panchsheel Park Test PaperRitvik BansalNo ratings yet
- COMPLEX ANALYSIS 1 LATEST (Repaired)Document118 pagesCOMPLEX ANALYSIS 1 LATEST (Repaired)koskeyemmanuel82No ratings yet
- Cryptography Final ProjectDocument10 pagesCryptography Final Projectapi-514261788No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics Course Work Instructions: Attempt All Questions Question OneDocument2 pagesBusiness Mathematics Course Work Instructions: Attempt All Questions Question OneLUMU EMMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Two-Dimensional FormulationDocument18 pagesChapter 7 Two-Dimensional Formulationvivi100% (1)
- Assign. No 1Document7 pagesAssign. No 1getachewbonga09No ratings yet