Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2
Uploaded by
Aritra SahaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2
Uploaded by
Aritra SahaCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment.........
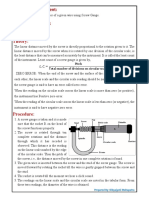
Aim of the Experiment:To determine the diameter of a wire using a screw gauge.
Apparatus Required:
Screw gauge and wire
Theory and working formulae:
Screw gauge is an instrument which consists of two scales.One fixed scale called linear scale or main
scale ( in mm) and one circular scale ( 100 div or 50 div).
Pitch and least count of a Screw gauge:
The pitch of a Screw gauge is the linear distance moved by its Screw on the main scale when the
circular scale is given one complete rotation.
Least count of Screw gauge is the least distance which can be measured by a Screw gauge.
L.C =Pitch of the Screw gauge/Total number of divisions on its circular scale.
If circular scale has 100 divisions then L.C=1mm/100 =0.01mm=0.001cm
If circular scale has 50 divisions then L.C= 1/2mm/50=1/100 =0.01mm= 0.001cm
( For 50 div pitch =1/2 mm)
Zero error:
If the zero on the circular scale coincides with the zero mark on the base line of main scale on
bringing the Screw in contact with stud,the instrument is said to be free from zero error. But in case
both the zeroes do not coincide with each other due to any defect or mechanical error the
instrument is said to have zero error.
There are two types of zero error:
1) Positive zero error and
2) Negative zero error .
Observation table:
S.No M.S.R C.S.R×L.C Total D
Here M.S.R = Main scale reading ( in cm)
V.S.R= Vernier scale reading ( in cm)
Total D = Total diameter ( in cm)
Calculations :
Mean diameter of the wire = Total diameter /5
=.........cm
Result:
The diameter of a given wire =.......cm
Precautions:
1) We should not hold the wire tightly in between stud and screw head
2) While taking measurements move the Screw in one direction to avoid backlash error.
You might also like
- Screw GaugeDocument19 pagesScrew GaugeMohammad Rashik ZamanNo ratings yet
- Dcep 112 & Dmep 112Document21 pagesDcep 112 & Dmep 112aneeqNo ratings yet
- Measure Particle Size with LaserDocument106 pagesMeasure Particle Size with Laserjeroldscd100% (1)
- Vernier Caliper FinalDocument7 pagesVernier Caliper FinalRajesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document3 pagesExperiment 2Gurdeep Singh SagguNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals - R - RecDocument26 pagesClass Xi - Practicals - R - RecDivyashekogNo ratings yet
- Measure Dimensions Using Micrometer Screw GaugeDocument6 pagesMeasure Dimensions Using Micrometer Screw GaugeFarhana Sabrin0% (1)
- Screw GaugeDocument2 pagesScrew GaugeABHISEK SAHUNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - Practicals 2024Document24 pagesClass Xi - Practicals 2024pillisathwik2No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual BY: Muhammad Hassan MaqsoodDocument32 pagesPhysics Lab Manual BY: Muhammad Hassan MaqsoodMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Measure Wire Diameter with Screw GaugeDocument4 pagesMeasure Wire Diameter with Screw GaugeBeAsT HYdrA GamingNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Error AnalysisDocument6 pagesMeasurements and Error AnalysisJoice Krystel RañoaNo ratings yet
- AP - Lab 02 - Measurement Using Screw GuageDocument3 pagesAP - Lab 02 - Measurement Using Screw GuagesalihaNo ratings yet
- Phy Lab ReadingsDocument31 pagesPhy Lab ReadingsMuhammad Hassan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Measure Wire Diameter and Sheet ThicknessDocument3 pagesMeasure Wire Diameter and Sheet ThicknessỮΜΔIŘ ҜĦΔŇNo ratings yet
- Screw Gauge by FirojDocument2 pagesScrew Gauge by FirojRahulNo ratings yet
- Screw Gauge by FirojDocument2 pagesScrew Gauge by FirojRahulNo ratings yet
- Physics Labwork: For MechanicsDocument24 pagesPhysics Labwork: For MechanicsSang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Practical Experiments 1 To 7Document9 pagesPractical Experiments 1 To 7Moses Samuel SukdularyNo ratings yet
- Least CountDocument8 pagesLeast CountPutri Citra DewiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics LabDocument31 pagesDynamics LabỮΜΔIŘ ҜĦΔŇNo ratings yet
- Object: Experiment 1 MeasurementDocument7 pagesObject: Experiment 1 MeasurementAnonymous PhtjQvnZzNo ratings yet
- Physics ExperimentDocument9 pagesPhysics ExperimentgapuzsawalNo ratings yet
- Class 11 ExperimentsDocument25 pagesClass 11 ExperimentsSoham Nag100% (1)
- Measurement of Lenght - Volumetime and MassDocument23 pagesMeasurement of Lenght - Volumetime and MassnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Measuring Tools ExplainedDocument7 pagesMeasuring Tools ExplainedDea Salsabila siregarNo ratings yet
- Metrology: Nri Institute of TechnologyDocument55 pagesMetrology: Nri Institute of TechnologyKasijanto JantoNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Experiment: Apparatus Required:: Prepared By: Dibyajyoti MahapatraDocument3 pagesAim of The Experiment: Apparatus Required:: Prepared By: Dibyajyoti MahapatraAnant SahNo ratings yet
- Vernier Scale Reading Vernier Division Coinciding With Main Scale Division × Least Count (In CM) Total Reading Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale Reading I.e., Diameter (In CM)Document30 pagesVernier Scale Reading Vernier Division Coinciding With Main Scale Division × Least Count (In CM) Total Reading Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale Reading I.e., Diameter (In CM)Cdt varun rana 44No ratings yet
- Jannatul Kawnine Ikra - Id: 233022712: Date: 24/02/24Document8 pagesJannatul Kawnine Ikra - Id: 233022712: Date: 24/02/24nahianrahman0011No ratings yet
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument7 pagesMeasuring Instrumentslindobuhledandelion0No ratings yet
- 01 Phy Quant 2 (Length & Time) (9jan8)Document26 pages01 Phy Quant 2 (Length & Time) (9jan8)Sagar JathanNo ratings yet
- 21 Me 435,435,435,435Document40 pages21 Me 435,435,435,435Faisal MehrbanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document110 pagesLecture 02Getachew G/AmlakNo ratings yet
- Workshop: University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore (FSD Campus)Document7 pagesWorkshop: University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore (FSD Campus)mjunaidNo ratings yet
- Metrology NotesDocument7 pagesMetrology NotesDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics XI Experiment 2Document3 pagesPhysics XI Experiment 2saumyayayNo ratings yet
- Measure volume with vernier caliper and screw gaugeDocument16 pagesMeasure volume with vernier caliper and screw gaugeKanika SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vernier Calliper Screw Gauge and SpherometerDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Vernier Calliper Screw Gauge and SpherometerAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Measure and Error Analysis Lab 1Document7 pagesMeasure and Error Analysis Lab 1RexRuNo ratings yet
- MEASURING INSTRUMENTSDocument13 pagesMEASURING INSTRUMENTSheartmelt slimesNo ratings yet
- DIMENSIONALDocument16 pagesDIMENSIONALEslam MansourNo ratings yet
- Measure Diameter and Volume Using Vernier CalipersDocument40 pagesMeasure Diameter and Volume Using Vernier CalipersHunter OfficialNo ratings yet
- Screw GuageDocument3 pagesScrew GuageHarini PriyaNo ratings yet
- Ensc 102L Lab ExperimentsDocument19 pagesEnsc 102L Lab ExperimentsgapuzsawalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2Document4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2Me Being RandomNo ratings yet
- METROLOGY LAB MANUALDocument30 pagesMETROLOGY LAB MANUALSanju JohnNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual (Screw Gauge) PDFDocument4 pagesLab Manual (Screw Gauge) PDFKashif Ali100% (2)
- CH - 2 - Measurement of Length, Volume, Time and Mass PDFDocument6 pagesCH - 2 - Measurement of Length, Volume, Time and Mass PDFNcnagesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Experiment (2) MeasurementsDocument10 pagesExperiment (2) MeasurementsAbha NawafNo ratings yet
- JJ204 Workshop Technology Semester 2Document150 pagesJJ204 Workshop Technology Semester 2Ye ChonnNo ratings yet
- Metrology: Nri Institute of TechnologyDocument55 pagesMetrology: Nri Institute of TechnologySavantNo ratings yet
- Screw Gauge (Micrometer) : Determination of Thickness/dameter of Thin Sheet/wire. Important FormulaeDocument2 pagesScrew Gauge (Micrometer) : Determination of Thickness/dameter of Thin Sheet/wire. Important Formulaevishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document3 pagesExperiment 2Shubhra Nil DeyNo ratings yet
- Measure Wire, Sheet, & Irregular Object DimensionsDocument7 pagesMeasure Wire, Sheet, & Irregular Object DimensionsSHAIK ISMAIL BASHANo ratings yet
- Introduction of Micrometer Screw GaugeDocument8 pagesIntroduction of Micrometer Screw Gaugesamar karemoreNo ratings yet
- DATE:8 JUNE 2022 Screw Gauge 1Document4 pagesDATE:8 JUNE 2022 Screw Gauge 1Anuj KiniNo ratings yet
- Physics - Practical Record Writing - Class XIDocument83 pagesPhysics - Practical Record Writing - Class XISara Wolf100% (1)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- M-Caps-01: Physics: NEET - XI StudyingDocument12 pagesM-Caps-01: Physics: NEET - XI StudyingAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument2 pagesBiology ProjectAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Bangali Gamer 01No ratings yet
- English 2 Specimen QP 2021Document4 pagesEnglish 2 Specimen QP 2021Dipankar Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3Aritra SahaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Bangali Gamer 01No ratings yet
- ISC Physics PDFDocument22 pagesISC Physics PDFAmanAdhikari007NEonNo ratings yet
- 20 ISC BiologyDocument22 pages20 ISC BiologyBran strongNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Bangali Gamer 01No ratings yet
- Salvatore - The Story: As As Rail" Acts As A Nursemaid To His Brothers, Ever Watchful of Their Safety andDocument5 pagesSalvatore - The Story: As As Rail" Acts As A Nursemaid To His Brothers, Ever Watchful of Their Safety andAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- ISC Physics PDFDocument22 pagesISC Physics PDFAmanAdhikari007NEonNo ratings yet
- 20 ISC BiologyDocument22 pages20 ISC BiologyBran strongNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Polymers ISC Project 2014Document94 pagesSynthetic Polymers ISC Project 2014Ash P KumarNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Questions Answers From Passages of The Tempest Act 1 Scene 1Document4 pagesQuestions Answers From Passages of The Tempest Act 1 Scene 1Aritra SahaNo ratings yet
- The DolphinsDocument5 pagesThe DolphinsAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- The Gift of India: Short Questions Part - 1Document10 pagesThe Gift of India: Short Questions Part - 1Aritra Saha0% (1)
- Physics ProjectDocument3 pagesPhysics ProjectAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument2 pagesBiology ProjectAritra SahaNo ratings yet