Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Budget of Works: Imelda National High School Senior High School Department
Budget of Works: Imelda National High School Senior High School Department
Uploaded by
Laarni Antiola Sardea0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Bugdet of Work
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesBudget of Works: Imelda National High School Senior High School Department
Budget of Works: Imelda National High School Senior High School Department
Uploaded by
Laarni Antiola SardeaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
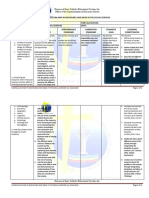
IMELDA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
BUDGET OF WORKS
Level: Senior High School
Subject Group: Specialized Subject
Subject: Discipline and Ideas in Social Sciences
Number of Subject Code
QUARTER Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC) Days
Taught
Quarter I
define Social Sciences as the study of society HUMSS_DIS 11- IIIa-1
distinguish Social and Natural Sciences and Humanities HUMSS_DIS 11- IIIa-2
compare and contrast the various Social Science HUMSS_DIS 11- IIIb-d-3
disciplines and their fields, main areas of inquiry, and
methods
5
trace the historical foundations and social contexts that HUMSS_DIS 11- IIId-4
led to the development of each discipline
Structural-Functionalism 1.1. Structuralism 1.2. determine HUMSS_DIS 11 -IIIe-f-1
manifest and latent functions and dysfunctions of
sociocultural phenomena
Marxism analyze social inequalities in terms of class HUMSS_DIS 11-IIIg-2
conflict
Symbolic Interactionism appraise the meanings that HUMSS_DIS 11-IIIh-3
people attach to everyday forms of interaction in order to
explain social behavior
Psychoanalysis analyze the psychodynamics of the HUMSS_DIS 11-IIIi-5
person’s personality in terms of Id, Ego, and Superego
Rational Choice predict the social consequences of HUMSS_DIS 11-IVa-6
decision making based on scarcity
Institutionalism examine the constitutive nature of HUMSS_DIS 11-IVb-7
informal and formal institutions and their actors and how
it constrains social behavior
Feminist Theory determine the relationship between HUMSS-DIS 11-IVc-8
gender ideology and gender inequality
Hermeneutical Phenomenology analyze significance of HUMSS_DIS 11-IVd-9
data
Human-Environment Systems HUMSS_DIS 11-IVd-10
9.1. distinguish the ways by which human-environment
interactions shape cultural and natural landscapes
9.2. interpret thematic and mental maps to understand
landscape changes and an individual’s sense of place
9.3. explain environmental and social issues through the
analysis of spatial distributions and spatial processes
examine the social ideas of Filipino thinkers starting from HUMSS_DIS 11-IVe-1
Isabelo de los Reyes, Jose Rizal, and other Filipino
intellectuals
value the role of interpersonal relations in Philippine HUMSS_DIS 11-IVe-2
culture
evaluate the person’s personality using the core values of HUMSS_DIS 11-IVf-3
Sikolohiyang Pilipino
explain the significance of using a particular language for HUMSS_DIS 11-IVg-4
discourse
critique dominant approaches using Filipino perspectives HUMSS_DIS 11-IVg-5
determine how Social Science can be used to address HUMSS_DIS 11-IVh-6
social concerns
recognize multidisciplinarity and/or interdisciplinarity as
an approach to looking at society HUMSS_DIS 11-IVh-7
generate an analysis of a social phenomenon using at HUMSS_DIS 11-IVi-j-8
least two approaches from the Social Sciences
Quarter II
examine the social ideas of Filipino thinkers starting from HUMSS_DIS 11-IVe-1
Isabelo de los Reyes, Jose Rizal, and other Filipino
intellectuals
value the role of interpersonal relations in Philippine HUMSS_DIS 11-IVe-2
culture
evaluate the person’s personality using the core values of HUMSS_DIS 11-IVf-3
Sikolohiyang Pilipino
explain the significance of using a particular language for HUMSS_DIS 11-IVg-4
discourse
critique dominant approaches using Filipino perspectives HUMSS_DIS 11-IVg-5
determine how Social Science can be used to address HUMSS_DIS 11-IVh-6
social concerns
recognize multidisciplinarity and/or interdisciplinarity as HUMSS_DIS 11-IVh-7
4
an approach to looking at society
generate an analysis of a social phenomenon using at HUMSS_DIS 11-IVi-j-8
least two approaches from the Social Sciences
Prepared by: LAARNI A. SARDEA Recommending Approval: PAPIAS P. JAYME
Teacher II Assistant Principal II
Approved by: DENNIS D. SILVA, EDD
School Principal IV
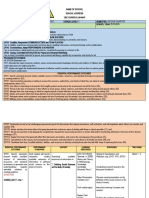
IMELDA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
BUDGET OF WORKS
Level: Senior High School
Subject Group: Specialized Subject
Subject: Discipline and Ideas in the Applied Social Sciences
Numbe Subject Code
Most Essential Learning Competencies r of
QUARTER
(MELC) Days
Taught
Quarter I
COUNSELING clarify the relationships between social sciences and HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ia-1
applied social sciences
cite differences among the applied social sciences HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ia-2
Identify the goals and scope of counseling HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ib-3
demonstrate comprehension of the principles of HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ib-4
counseling
discuss the core values of counseling HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ib-5
show understanding of the roles and functions of HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ic-6
counselors
identify specific work areas in which counselors work HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ic-7
identify career opportunities for counselors HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ic-8
value rights, responsibilities, and accountabilities HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ic-9
distinguish between ethical and unethical behaviors HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ic-10
among counselors
describe the clientele and audience of counseling HUMSS_DIASS 12-Id-11
HUMSS_DIASS 12-Id-12
identify the settings in which counselors are found
HUMSS_DIASS 12-Id-13
illustrate the different processes and methods HUMSS_DIASS 12-Id-14
involved in undertaking counseling
distinguish the needs of individuals, groups, HUMSS_DIASS 12-Id-15
organizations, and communities
SOCIAL WORK identify the goals and scope of social work HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ie-16
demonstrate comprehension of the principles of social HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ie-17
work
discuss the core values of social work HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ie-18
show an understanding of the roles and functions of HUMSS_DIASS 12-If-19
social workers
identify specific work areas in which social workers HUMSS_DIASS 12-If-20
work
identify career opportunities for social workers HUMSS_DIASS 12-If-21
value rights, responsibilities, and accountabilities HUMSS_DIASS 12-If-22
distinguish between ethical and unethical behaviors HUMSS_DIASS 12-If-23
among practitioners
describe the clientele and audience of social work HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ig-24
distinguish the needs of individuals, groups, HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ig-25
organizations and communities
HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ig-26
identify the settings in which social workers are found
illustrate the different processes and methods HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ig-27
involved in undertaking social work
Quarter II
COMMUNICATION identify the goals and scope of communication HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ih-28
demonstrate comprehension of the principles of HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ih-29
communication
discuss the core values of communication HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ih-30
describe the elements and levels of the HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ih-31
communication processes
show understanding of the roles and functions of HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ij-32
communicators and journalists
identify specific work areas in which communicators HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ij-33
and journalists work
identify career opportunities for communicators and HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ij-34
journalists
value rights, responsibilities, and accountabilities HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ij-35
distinguish between ethical and unethical behaviors HUMSS_DIASS 12-Ij-36
among practitioners
describe the clientele and audience of communication HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIa-37
distinguish the needs of individuals, groups, HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIa-38
organizations, and communities
identify the settings in which communicators and HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIa-39
journalists are found
illustrate the different processes and methods HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIa-40
involved in undertaking communication
distinguish the appropriate communication media HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIa-41
channel(s) to use in different settings and situations
explain each of the functions of applied social sciences HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIb-d-
42
identify situations that would require or necessitate HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIb-d-
the performance of the various functions in 43
local/Philippine settings
analyze the effects of applied social sciences HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIe-f-
processes on individuals, groups, and society 44
evaluate the effects of certain program or projects on HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIe-i-
knowledge, attitude, and behavior of individuals, 45
groups, and society
synthesize the learning from the course and its HUMSS_DIASS 12-IIj-46
applications to the learner
Prepared by: LAARNI A. SARDEA Recommending Approval: PAPIAS P. JAYME
Teacher II Assistant Principal II
Approved by: DENNIS D. SILVA, Ed.D.
School Principal IV
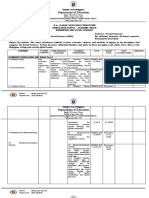
IMELDA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
BUDGET OF WORKS
Level: Senior High School
Subject Group: Specialized Subject
Subject: Introduction to the Philosophy of the Human Person
Number Subject Code
QUARTE Most Essential Learning Competencies
of Days
R (MELC)
Taught
Quarter I
Distinguish a holistic perspective from a partial point of PPT11/12-Ia-1.1
view
Recognize human activities that emanated from PPT11/12-Ib-1.2
deliberate reflection
Realize the value of doing philosophy in obtaining a broad 4 PPT11/12-Ib-1.3
perspective on life
Do a philosophical reflection on a concrete situation from PPT11/12-Ic-1.4
a holistic perspective
Distinguish opinion from truth PPT11/12-Ic-2.1
Analyze situations that show the difference between PPT11/12-Id-2.2
opinion and truth
Realize that the methods of philosophy lead to wisdom PPT11/12-Id-2.3
8
and truth
Evaluate opinions PPT11/12-Ie-2.4
Recognize own limitations and possibilities PPT11/12-If-3.1
Evaluate own limitations and the possibilities for their PPT11/12-Ig-3.2
transcendence
4
Recognize how the human body imposes limits and PPT11/12-Ih-3.3
possibilities for transcendence
Distinguish the limitations and possibilities for PPT11/12-Ii-3.4
transcendence 4
Notice disorder in an environment PPT11/12-Ii-4.1
Notice things that are not in their proper place and PPT11/12-Ii-4.2
organize them in an aesthetic way
20
Show that care for the environment contributes to PPT11/12-Ij-4.3
health, well-being and sustainable development
Quarter II
Realize that “all actions have consequences. 28 PPT11/12-IIa-5.1
Evaluate and exercise prudence in choices PPT11/12-IIa-5.2
Realize that: PPT11/12-IIb-5.3
a. Choices have consequences
b. Some things are given up while others are obtained in
making choices
Show situations that demonstrate freedom of choice and PPT11/12-IIc-5.4
the consequences of their choices
Realize that intersubjectivity requires accepting PPT11/12-IIc-6.1
differences and not to imposing on others
Appreciate the talents of persons with disabilities and PPT11/12-IId-6.1
those from the underprivileged sectors of society and
their contributions to society
PPT11/12-IId-6.3
Explain that authentic dialogue means accepting others
even if they are different from themselves
Perform activities that demonstrate the talents of PPT11/12-Iie-6.4
persons with disabilities and those from the
underprivileged sectors of society
Recognize how individuals form societies and how PPT11/12-IIf-7.1
individuals are transformed by societies
Compare different forms of societies and individualities PPT11/12-IIg-7.2
(eg. Agrarian, industrial and virtual)
Explain how human relations are transformed by social PPT11/12-IIg-7.3
systems
Evaluate the transformation of human relationships by PPT11/12-IIh-7.4
social systems and how societies transform individual
human beings
Recognize the meaning of his/her own life PPT11/12-IIh-8.1
Enumerate the objectives he/she really wants to achieve PPT11/12-IIi-8.2
and to define the projects he/she really wants to do in
his/her life
Explain the meaning of life (where will all these lead to) PPT11/12-IIi-8.3
Reflect on the meaning of his/her own life. PPT11/12-IIi-8.4
Prepared by: LAARNI A. SARDEA Recommending Approval: PAPIAS P. JAYME
Teacher II Assistant Principal II
Approved by: DENNIS D. SILVA, Ed.D.
School Principal IV
You might also like
- Summary of Zaretta L. Hammond's Culturally Responsive Teaching and The BrainFrom EverandSummary of Zaretta L. Hammond's Culturally Responsive Teaching and The BrainNo ratings yet
- The Scholarship of Teaching and Learning In and Across the DisciplinesFrom EverandThe Scholarship of Teaching and Learning In and Across the DisciplinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- From Moment to Meaning: The Art of Scholar-Practitioner InquiryFrom EverandFrom Moment to Meaning: The Art of Scholar-Practitioner InquiryNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Psychology of CrimeDocument2 pagesSyllabus of Psychology of CrimeJabbar0% (1)
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Distinguish Features of Academic WritingDocument15 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Distinguish Features of Academic WritingHellen Dea100% (1)
- Summary of Özlem Sensoy, Robin DiAngelo & James A. Banks's Is Everyone Really Equal?From EverandSummary of Özlem Sensoy, Robin DiAngelo & James A. Banks's Is Everyone Really Equal?No ratings yet
- DLL World Religions - October 2017Document5 pagesDLL World Religions - October 2017edde201077% (13)
- Cot Q3 2021Document4 pagesCot Q3 2021Annie CasquiteNo ratings yet
- CM (Discipline and Ideas in The Social Sciences)Document4 pagesCM (Discipline and Ideas in The Social Sciences)RhaedenNarababYalanib67% (6)
- 21st Century Lit-For COTDocument5 pages21st Century Lit-For COTmyrnaNo ratings yet
- DIASS First Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesDIASS First Quarter ExamElmer Lumague0% (1)
- Budget of Work - DISSDocument3 pagesBudget of Work - DISSJienalyn AgabinNo ratings yet
- HUMSS - Culminating Activity CG - 1 PDFDocument3 pagesHUMSS - Culminating Activity CG - 1 PDFDeanPierreBesanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Lesson Plan - SimilarityDocument4 pagesGrade 10 - Lesson Plan - SimilarityshipradangNo ratings yet
- HUMSS - Culminating Activity CG - 1 PDFDocument3 pagesHUMSS - Culminating Activity CG - 1 PDFJonna Marie Ibuna100% (1)
- The Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesFrom EverandThe Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- HUMSS - Disciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences CG - 1 PDFDocument7 pagesHUMSS - Disciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences CG - 1 PDFAlexander Justin Salvador75% (4)
- LCD DissDocument3 pagesLCD DissLG NiegasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Discipline in Ideas in Social Science Grade 11Document4 pagesCurriculum Map Discipline in Ideas in Social Science Grade 11Raizza Vanizza SiguenzaNo ratings yet
- Diss CGDocument9 pagesDiss CGJessa Tampoya100% (1)
- Social Sciences: The Study of Society: Full Name: Grade 11Document35 pagesSocial Sciences: The Study of Society: Full Name: Grade 11Lawrence LardizabalNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Gadgets: The Cultural Evolution of ThinkingFrom EverandCognitive Gadgets: The Cultural Evolution of ThinkingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- D.I. Session GuideDocument9 pagesD.I. Session GuideMary Grace Morales100% (1)
- Social Pathology: A Systematic Approach to the Theory of Sociopathic BehaviorFrom EverandSocial Pathology: A Systematic Approach to the Theory of Sociopathic BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceHannae pascuaNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument2 pagesPerformance TaskLaarni Antiola SardeaNo ratings yet
- LP For Co PNHSDocument4 pagesLP For Co PNHSgelbert larong100% (1)
- Budget of Works Q 1 &2Document3 pagesBudget of Works Q 1 &2Virginia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: - 11 - : No. Learning Competency Code Date Taught As Indicated in The DLL/DLP Taught/ Not Taught X RemarksDocument2 pagesGrade Level: - 11 - : No. Learning Competency Code Date Taught As Indicated in The DLL/DLP Taught/ Not Taught X RemarksCecilia Narvaez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Ranking Melcs Diss 1st2ndqtrDocument2 pagesRanking Melcs Diss 1st2ndqtrMhay Anne PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Management Plan: Emergence of The Social SciencesDocument6 pagesLesson Management Plan: Emergence of The Social Sciencesarniel catubigNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesDocument8 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciencesjaynnie vigonteNo ratings yet
- Curguide DissDocument9 pagesCurguide DissOlive AsuncionNo ratings yet
- HUMSS - Disciplines and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences CGVVVVDocument7 pagesHUMSS - Disciplines and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences CGVVVVPaul Edward MacombNo ratings yet
- Disciplines & Ideas in Ss PDFDocument7 pagesDisciplines & Ideas in Ss PDFSittie Haynah Moominah BualanNo ratings yet
- DISS - 1ST 2 Positivist Social ScienceDocument6 pagesDISS - 1ST 2 Positivist Social ScienceLennie DiazNo ratings yet
- DISCIPLINES AND IDEAS IN THE SOCIAL SCIENCES Ver. 2018-2019Document6 pagesDISCIPLINES AND IDEAS IN THE SOCIAL SCIENCES Ver. 2018-2019domafecaluyoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map DISSDocument5 pagesCurriculum Map DISSleila lastimaNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesDocument7 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesNorven Dulaugon100% (2)
- SyllabusDocument11 pagesSyllabusMohammad C. DatuganNo ratings yet
- Budgeted Lesson.1st Quarter - DISSDocument5 pagesBudgeted Lesson.1st Quarter - DISSJonalyn BanezNo ratings yet
- Least Mastered DissDocument2 pagesLeast Mastered DissMalen Torres100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceHannae pascuaNo ratings yet
- Diss Q3 W 3 4Document18 pagesDiss Q3 W 3 4ikkajessicaaa1003No ratings yet
- Budgeted Lesson.2nd Quarter - DISSDocument3 pagesBudgeted Lesson.2nd Quarter - DISSJonalyn BanezNo ratings yet
- DISS - 1ST 3 Interpretative Social ScienceDocument6 pagesDISS - 1ST 3 Interpretative Social ScienceLennie DiazNo ratings yet
- Integrative Assessment Form GRADE 11 - SAMPLEDocument6 pagesIntegrative Assessment Form GRADE 11 - SAMPLElynji pedrosaNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Fidp Diss EditedDocument4 pages1st Sem Fidp Diss EditedMarielle AlystraNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY DESIGNDocument6 pagesACTIVITY DESIGNSHAINA DOBLENo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Brgy. 23, National Highway, Gingoog CityDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan: Brgy. 23, National Highway, Gingoog CityJhoan JaneNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesDocument10 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesOlive AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Disciplines and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences 12Document22 pagesModule 1 - Disciplines and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences 12anewor100% (1)
- Instructions in Answering The Community Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship Learning Activity Sheet (Las)Document3 pagesInstructions in Answering The Community Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship Learning Activity Sheet (Las)Jeffrey LozadaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Concept PaperDocument5 pagesEapp Concept PaperRench GarciaNo ratings yet
- Yu, Nericca JaneDocument33 pagesYu, Nericca JaneKaren Roldan RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ssed 223Document9 pagesReviewer Ssed 223Margareth De VillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1Jaynal HussainNo ratings yet
- Diss Final Module Gas-3Document16 pagesDiss Final Module Gas-3Chan BenzNo ratings yet
- Lu V2 Diass M14-Q2Document18 pagesLu V2 Diass M14-Q2Laurence Cañero SelgaNo ratings yet
- Essential Performance OutcomesDocument13 pagesEssential Performance OutcomesArsub Varquez100% (1)
- Budget of Work For DissDocument4 pagesBudget of Work For DissFrancis CaneteNo ratings yet
- Diass TosDocument1 pageDiass TosLaarni Antiola SardeaNo ratings yet
- Diass TosDocument1 pageDiass TosLaarni Antiola SardeaNo ratings yet
- Persuasion DLLDocument5 pagesPersuasion DLLLaarni Antiola SardeaNo ratings yet
- RRL ExampleDocument7 pagesRRL ExampleZenshe F. TabuadaNo ratings yet
- Age and Gender Detection Using PythonDocument4 pagesAge and Gender Detection Using PythonAnil Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and Its ImportanceDocument14 pagesCritical Thinking and Its ImportanceELMUNTHIR BEN AMMAR100% (1)
- D Sulhan AliDocument22 pagesD Sulhan AliMasrurotul AbadiyahNo ratings yet
- Expressive Poetry Assess RubricDocument3 pagesExpressive Poetry Assess Rubriclily claireNo ratings yet
- Lesson Check CH 1Document2 pagesLesson Check CH 1Indah FitriyanaNo ratings yet
- Proposal Oninstractional Leadership Effectivness Edt 2Document55 pagesProposal Oninstractional Leadership Effectivness Edt 2Beka AsraNo ratings yet
- Government Urdu High School Kundur Honnali (T) ACADEMIC YEAR-2021-22Document39 pagesGovernment Urdu High School Kundur Honnali (T) ACADEMIC YEAR-2021-22Vikram GandhaleNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Social Anxiety in The Academic Performance of The Stem 12 Students of Lagro High School S.Y. 2019-2020Document24 pagesThe Effects of Social Anxiety in The Academic Performance of The Stem 12 Students of Lagro High School S.Y. 2019-2020Hana FermaceNo ratings yet
- A Study On Language Disorders in Learners: December 2019Document9 pagesA Study On Language Disorders in Learners: December 2019Wahyu AdamNo ratings yet
- WBCS Preliminary Exam Question Paper 2016 Set ADocument35 pagesWBCS Preliminary Exam Question Paper 2016 Set ASunny RoyNo ratings yet
- Gap ModelDocument21 pagesGap ModelAravind Sai PrasadNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Literature Relevant To Engineering IdentityDocument25 pagesA Review of The Literature Relevant To Engineering IdentityDrake ManNo ratings yet
- Developmental ReadDocument48 pagesDevelopmental ReadMharaTootNo ratings yet
- Myth of ComputerDocument3 pagesMyth of ComputerscribdomminiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Seen Pre-Board - AI - Grade 10 - 2021-22Document7 pagesQuestion Bank For Seen Pre-Board - AI - Grade 10 - 2021-22Moksha WalgudeNo ratings yet
- MOB Chapter 7Document15 pagesMOB Chapter 7Ockouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- PSY 369: Psycholinguistics: Second Language Acquisition: Critical Periods & BilingualismDocument29 pagesPSY 369: Psycholinguistics: Second Language Acquisition: Critical Periods & BilingualismJasper John RoqueNo ratings yet
- ss10 Course OverviewDocument5 pagesss10 Course Overviewapi-328926105No ratings yet
- Secretaría Académica Dirección de Estudios de Nivel Medio SuperiorDocument55 pagesSecretaría Académica Dirección de Estudios de Nivel Medio SuperiorDiegoNo ratings yet
- Social Identity Theory of LeadershipDocument3 pagesSocial Identity Theory of LeadershipJames BryanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Hazards v3Document4 pagesLesson Planning Hazards v3api-262631683No ratings yet
- Understanding PID Control and Loop Tuning Fundamentals - Control Engineering PDFDocument1 pageUnderstanding PID Control and Loop Tuning Fundamentals - Control Engineering PDFrafik1995No ratings yet
- Teaching SpeakingDocument15 pagesTeaching SpeakingRodeliza Jean JapsonNo ratings yet
- Years 11-12 Resilience BuildersDocument5 pagesYears 11-12 Resilience Buildersapi-279426599No ratings yet