Professional Documents
Culture Documents
H Na HO Naoh H: Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
mohit parteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
H Na HO Naoh H: Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
mohit parteCopyright:
Available Formats
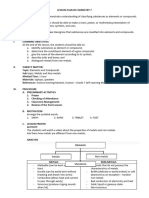
LESSON PLAN
SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS – VIII, D NO. OF PERIODS REQUIRED : 5
LESSON TO BE TAUGHT Chapter : 4 — Metals & Non-Metals
MY FOCUS 1. Physical properties of metals and non-metals (malleability, ductility, etc.)
2. Chemical properties of metals and non-metals (reaction with oxygen, water, acids, bases etc.)
3. Displacement reaction
4. Uses of metals and non-metals
5. Metalloids
STUDENT ACTIVITY 1. Demonstration of displacement reaction between copper sulphate (CuSO4 ) and iron (Fe)
2. Demonstration of reaction of metal (Na) with water to produce sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen gas H 2 .
2 Na 2H 2O 2 NaOH H 2
PRACTICE ASSESSMENT Q1. What do you mean by terms malleability and ductility in metals?
Ans. Malleability is a characteristic property of metals by which they can be beaten into thin sheets .Ductility is the property
of metals by which they can be drawn into thin wires.
Q2. What are metalloids? Give some examples.
Ans. Metalloids are elements having properties of both metals and non-metals. For e.g. Arsenic , Antimony etc.
Q3. What happens when sulphur dioxide is dissolved in water?
Ans. When sulphur dioxide is dissolved in water, sulphurous acid is formed.
Reaction :
SO2 H 2O H 2 SO3
ADDITIONAL 1. Silver conducts electricity better than any other metal.
INFORMATION 2. Aluminium can be recycled over and over again without any loss of quality.
CAN DO STATEMENTS 1. Students are able to differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their physical and chemical properties.
2. Students are able to write word equation for chemical reactions. For e.g. Reactions of metals and non-metals with
oxygen, water, acids etc.
3. Students can explain displacement reaction with the help of examples.
4. Students are able to explain uses of metals and non-metals.
5. Students can explain the term “metalloids” with examples.
You might also like
- Lesson Plan Metals and Non-Metals Class 8Document6 pagesLesson Plan Metals and Non-Metals Class 8sunita mishraNo ratings yet
- H Na HO Naoh H: Lesson PlanDocument1 pageH Na HO Naoh H: Lesson Planmohit parteNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals 10Document28 pagesMetals and Non Metals 10maryam mustafaNo ratings yet
- Semi DLPDocument2 pagesSemi DLPAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series PDFDocument17 pagesThe Reactivity Series PDFVictoria KairooNo ratings yet
- L-3 Metals Non Metals - CBE - RashmiDocument18 pagesL-3 Metals Non Metals - CBE - RashmiPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: Module - 6Document19 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: Module - 6Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 4Document5 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 4SashankNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 4. Metals and Non-MetalsDocument7 pagesCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 4. Metals and Non-MetalsSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- C13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesDocument39 pagesC13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesBasil ChinNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science - CH - 3 - Metals - Non Metals - NotesDocument4 pagesClass 8 - Science - CH - 3 - Metals - Non Metals - Notes8eanjanimaitreyNo ratings yet
- Lalith Castle International SchoolDocument3 pagesLalith Castle International Schoolkashishsoni1011No ratings yet
- Properties of Metals G LudhianaDocument7 pagesProperties of Metals G Ludhianaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Materials Meatls Non MetalsDocument11 pagesMaterials Meatls Non MetalsEmman MalikNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry Lesson Notes, 2nd TermDocument10 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry Lesson Notes, 2nd Termfatima manuel AzarateNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument5 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument2 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Materials Metals and Non MetalsDocument6 pagesNotes On Materials Metals and Non Metalsmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MetalsDocument5 pagesChemistry MetalsBrett Burrows100% (4)
- Metal and Non Metal Class 8Document23 pagesMetal and Non Metal Class 8Ripu Daman SinghNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals QuestionsDocument2 pagesMetals and Non Metals QuestionsraghavNo ratings yet
- Subject: Type of Lesson: Grade: Csec Obj:: Student Instructional MaterialDocument7 pagesSubject: Type of Lesson: Grade: Csec Obj:: Student Instructional MaterialChris McLeanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsBhavesh BhaveshNo ratings yet
- Ryan International School, Noida Extension Session (2021-22) Subject-Science Handouts - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesRyan International School, Noida Extension Session (2021-22) Subject-Science Handouts - Metals and Non-MetalsAashnaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Nonmetals - NotesDocument3 pagesMetals and Nonmetals - NotesARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Shiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of MetalsDocument18 pagesShiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of MetalsHarshit RajputNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Metals and Non Metals Notes VLDocument11 pages8 Science Metals and Non Metals Notes VLShravani BogarNo ratings yet
- St. John'S School Greater Noida WestDocument3 pagesSt. John'S School Greater Noida WestIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Subject Science Chapter 4Document3 pagesClass 8 Subject Science Chapter 4Geetank PugliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter MetalsDocument162 pagesChapter MetalswilliamwilsonlauNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotesmuhammad dawoodNo ratings yet
- 6 - Materials - Metals and Non-Metals - Book Back AnswersDocument7 pages6 - Materials - Metals and Non-Metals - Book Back AnswersSOULSNIPER 15No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesMetals and Non-Metals: Multiple Choice QuestionsAkash SahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3science Solutions Chapter 6 Life ProcessesDocument13 pagesChapter 3science Solutions Chapter 6 Life ProcessessumeshmirashiNo ratings yet
- Metals ReviewerDocument8 pagesMetals ReviewerCyber DomingoNo ratings yet
- Materials: Metal and Non-Metals: Check Point 1Document6 pagesMaterials: Metal and Non-Metals: Check Point 1Renuga DeviNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 and 2 PATTERNSAND PROPERTIES OF METALSDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1 and 2 PATTERNSAND PROPERTIES OF METALSgiselle veneziaNo ratings yet
- Metals: Bonding & Structure Properties Alloys Chemical Reactions Reactivity SeriesDocument23 pagesMetals: Bonding & Structure Properties Alloys Chemical Reactions Reactivity SeriespenguinpowerrrrNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Metals 2023Document26 pagesCH 4 Metals 2023Heidi VagueNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemistryvisheshsingla411No ratings yet
- Metals Worksheet 1Document2 pagesMetals Worksheet 1Sharizah Bte Md Amin100% (1)
- Metals and Non Metals WorksheetDocument7 pagesMetals and Non Metals WorksheetAnwesha SunishkaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Some Aspects of Corrosion: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesMetals and Some Aspects of Corrosion: ObjectivesFree AcxNo ratings yet
- 2 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pages2 Metals and Non-MetalsArmaanNo ratings yet
- Class10 Science Notes Chapte3Document9 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapte3PallaviGupta100% (1)
- C504 - Reactivity SeriesDocument49 pagesC504 - Reactivity Seriesghan02122011No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Periodic OxfordDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Periodic OxfordEyad ELshenawyNo ratings yet
- Experiment n6Document2 pagesExperiment n6Javan Mamogay BrionesNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument4 pagesMetalsJhade YapNo ratings yet
- Barath Kavin Chemistry Project 2Document11 pagesBarath Kavin Chemistry Project 2clockw916No ratings yet
- TextDocument3 pagesTextTaofeek Damilola100% (1)
- Delhi Public School Ranipur, Haridwar Subject-Chemistry Class-ViiiDocument8 pagesDelhi Public School Ranipur, Haridwar Subject-Chemistry Class-ViiiAtharv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- STD 8 CH 4 Metals & Non Metals WK & Extra NotesDocument4 pagesSTD 8 CH 4 Metals & Non Metals WK & Extra NotespvzqjtxfvbNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument2 pagesMetals and Non-Metalsdaffodil joy eres100% (1)
- Activity No 8 Properties of MetalsDocument5 pagesActivity No 8 Properties of MetalsILIVEFOR MONSTA7No ratings yet
- 3.1 Chemistry of Metals FULLDocument41 pages3.1 Chemistry of Metals FULLRenejhon MaquilanNo ratings yet
- Metals Question and Answers Class 8Document3 pagesMetals Question and Answers Class 8brm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- Ionization Potentials: Some Variations, Implications and ApplicationsFrom EverandIonization Potentials: Some Variations, Implications and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Perspectives in Hydrogen in Metals: Collected Papers on the Effect of Hydrogen on the Properties of Metals and AlloysFrom EverandPerspectives in Hydrogen in Metals: Collected Papers on the Effect of Hydrogen on the Properties of Metals and AlloysNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- MasterSpec Consolidated TOCDocument39 pagesMasterSpec Consolidated TOCsheevesNo ratings yet
- Valuable CattleDocument2 pagesValuable CattleGurmeet BrarNo ratings yet
- HINO Cableado ElectricoDocument11 pagesHINO Cableado ElectricoWalter Eduard100% (1)
- Auditor or ManagerDocument7 pagesAuditor or Managerapi-79118648No ratings yet
- Regulator With NRVDocument2 pagesRegulator With NRVBiswanath LenkaNo ratings yet
- Handling of Hygroscopic Products System-TechnikDocument4 pagesHandling of Hygroscopic Products System-TechnikMudassir FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chromatography NotesDocument25 pagesChromatography NotesGeetha AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec V Art 6 2007 (Ingles)Document8 pagesAsme Sec V Art 6 2007 (Ingles)fdvrevtrfvrtfNo ratings yet
- Fick Second LawDocument9 pagesFick Second LawJohnny WoodsNo ratings yet
- 242 Chemistry Resources CH 5 8Document137 pages242 Chemistry Resources CH 5 8Tina Sima88% (8)
- Tsubaki ChainDocument8 pagesTsubaki Chainbmihaiela100% (1)
- Type of Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesType of Chemical ReactionsSAHARAN ANANDNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Not One of The Possible Answers ListedDocument12 pagesExercises: Not One of The Possible Answers ListedSarah ChoiNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Green BiotechnologyDocument9 pagesAdvantages of Green BiotechnologyDanica JuanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Chemical Bonding ICSE Solutions Class 10 ChemistryDocument18 pagesCH 2 Chemical Bonding ICSE Solutions Class 10 ChemistrylionelkenethNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticiDocument29 pagesAntiepilepticiIskraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 07 ADocument3 pagesAssignment 07 AsundusNo ratings yet
- Electrozincados en 10152 (2009)Document18 pagesElectrozincados en 10152 (2009)joaopedrosousaNo ratings yet
- Chem2 Lesson 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument8 pagesChem2 Lesson 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsCarl EscalaNo ratings yet
- Dehydrated Culture MediaDocument92 pagesDehydrated Culture MediaTitan Biotech Ltd.0% (1)
- Raw Materials-IronDocument22 pagesRaw Materials-IronAilson Silva AlvesNo ratings yet
- Biocomposites Guide PDFDocument40 pagesBiocomposites Guide PDFShirah CoolNo ratings yet
- CRC 2-26Document2 pagesCRC 2-26saranNo ratings yet
- Test1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesTest1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (1)
- Microwave Pyrolysis of Polystyrene and Polypropylene Mixtures Using Different Activated Carbon From BiomassDocument14 pagesMicrowave Pyrolysis of Polystyrene and Polypropylene Mixtures Using Different Activated Carbon From BiomassTrisna Kumala DhaniswaraNo ratings yet
- 2014 Online Catlog - PDF MonDocument50 pages2014 Online Catlog - PDF Monjaag2000No ratings yet
- Fardis EC8-3 Member Models - 0Document75 pagesFardis EC8-3 Member Models - 0Wendirad BeshadaNo ratings yet
- Magneto Hydro Dynamic GeneratorDocument19 pagesMagneto Hydro Dynamic GeneratorKarthik ViratNo ratings yet
- Drain Cleaner: Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesDrain Cleaner: Safety Data SheetSuresh SubbuNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Properties of A New Fiber-Reinforced CompositesDocument10 pagesBiomechanical Properties of A New Fiber-Reinforced Compositesazam ahmedNo ratings yet