Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STEPS Preparing Business Research Plan
Uploaded by
dr.p.mohan kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesdiscusses about Steps - Business research plan
Original Title
Steps - Business research plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdiscusses about Steps - Business research plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesSTEPS Preparing Business Research Plan
Uploaded by
dr.p.mohan kumardiscusses about Steps - Business research plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
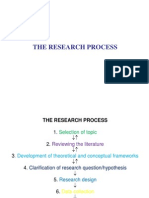
Steps involved in preparing business research plan/proposal
Step 1: Identification of Problem/Opportunity
• The research process starts with the identification of the issues that needs to be
researched.
• In case of basic research conducted by academics an area of interest or some new area
is identified for purpose of research.
Step 2: collection of relevant data
• Helps to develop an initial understanding of the problem
• In case of business problems/opportunity consultation can help in comprehending the
situation.
• In academic research this stage can help in initial understanding of the issue to be
researched.
• Identification of value it has in the
• field of business,
• gaps in existing research,
• contribution the research can make.
Step 3: Statement of Problem
• State the problem, defining the problem with a statement can provide rich benefits.
• Helps in developing clear understanding of
o what issue needs to be resolved,
o it is helpful in clearly laying out the objectives,
o attainment of those would lead to the solution of problem.
• A problem statement is a clear, precise, and succinct statement of question or issue
that is to be investigated with the goal of finding an answer or solution.
Step 4: Detailed Literature Review
• Involves looking for relevant literature in the body of knowledge
• Helps in gaining understanding of variables
• Help in identifying the research design, analytical techniques, sample size and
sampling technique.
• Identifies the significance of factors, evaluates the strength and weaknesses of a
particular issue concern, compares and contrasts information, gives reasons for
selecting a particular factor, links pieces of information and draws appropriate
conclusion.
• Literature review would have helped in gaining detailed understanding of variables,
their characteristics, their effects or how are they affected.
Step 5: Research Hypothesis
• A hypothesis is defined as a logically conjectured relationship between two or more
variables expressed in the form of a testable statement
• Hypothesis that is then tested using an appropriate statistical technique.
Step 6: Research Methodology
• Researcher identifies how the study will be conducted.
• Few questions that a researcher needs to answer while drafting research methodology.
o What is the Unit of Analysis?
o Who are the subjects in the research study?
o What is the sampling technique for the study?
o What is the sample size for the study?
o What statistical techniques would be used for testing hypothesis?
o Which instrument will be used for data collection?
Step 7: Data Collection
• The next step after formulating the research methodology is the collection of data.
• Data can be collected through variety of means that includes telephonic interviews,
personally administered questionnaire, mail questionnaires, face to face interview, and
observation.
• A few issues highlighted in data collection include timing of data collection,
individual collecting the data, and cost associated with the collection of data.
Step 8: Data Entry and Screening
• Entering the data into any statistical software that can help in analysis of data.
• Once the data is entered it is important to screen and clean the data for any anomalies,
failure to do so will result in incorrect results.
• For instance you record, pay for the respondents, and each one answers between
10000 to 100000, but by mistake you enter 1000 instead of 10000, this will result in
wrong interpretation of results.
Step 9: Data Analysis with Appropriate statistical techniques
• There are number of techniques that are applied to analyze the data.
• In order to understand if there exist differences between groups we can use tests to
compare groups (T-Tests, ANOVA),
• to investigate relationship between variables we can use correlation and for prediction
we can use Linear, Multiple and Logistic Regression.
• One of the problems with researchers is that they do not know what test to apply in
what situation, this has been taken care off by identifying the scenarios in which the
test are applicable, plus detailed examples in which the test is appropriate.
Step 10: Interpretation/Presentation of Results
Once the data is analyzed and you have the results on screen, the next step is to
interpret the results, followed by its presentation.
One of the key issues most research face is the interpretation of the results.
The researcher has to determine if the results are significant, does the hypothesis hold
true, and then present the results in a meaning full easy to understand manner.
Discusses in detail the interpretation of the results and how shall they be presented in
the thesis.
Step 11: Discussion
• The Discussion section is a culmination of the research and the most important part of
the paper.
• Most newbies in research simply interpret the results but do not discuss the findings.
• Discussion involves reviewing the research results in light of the existing research.
• This section involves comparing and contrasting the research results with previous
research studies, and it is seen if the results are similar or contradictory to old studies.
• If they are contradictory the researcher needs to look for reasons that are causing this
change.
Step 12: Conclusion
• Final step in a research study is providing a Conclusion.
• It provides an overview of the entire thesis while highlighting the focal points of the
discussion.
• This section provides the findings of the research in a logical form.
• Summarize the main points of research, but do not just list points, try making it
interesting but providing an overall picture that helps in developing understanding of
work.
• Conclude your paper by restating what you have found, acknowledge that there is
more to be explored on the topic and briefly describe the issues that remain.
* * *
You might also like
- Master Resource Book in Physics For JEE Main 2020 by D. B. SinghskksDocument1,425 pagesMaster Resource Book in Physics For JEE Main 2020 by D. B. SinghskksSAHIL YADAV 7825No ratings yet
- Polishing Up On Finishing How To Stay Competitive Due To Optimized Surface FinishingDocument33 pagesPolishing Up On Finishing How To Stay Competitive Due To Optimized Surface Finishingชนพัทธ์ คงพ่วงNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: (Nature of Inquiry and Research)Document31 pagesPractical Research 2: (Nature of Inquiry and Research)pabloNo ratings yet
- Type of Research and Research ProcessDocument75 pagesType of Research and Research ProcessEthiopia NetsanetNo ratings yet
- Reliability & Maintainability Engineering Ebeling Chapter 9 Book Solutions - MaintainabilityDocument13 pagesReliability & Maintainability Engineering Ebeling Chapter 9 Book Solutions - MaintainabilityMiko MilladsNo ratings yet
- Manual Controls C807Document40 pagesManual Controls C807Felipe Aguilar Rivera100% (1)
- Steps of The Research ProcessDocument21 pagesSteps of The Research ProcessAmal IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Steps in Report Writing in Research MethodologyDocument2 pagesSteps in Report Writing in Research Methodologydr.p.mohan kumarNo ratings yet
- Research Design PresentationDocument31 pagesResearch Design PresentationdiksangelNo ratings yet
- FORMULATING RESEARCHDocument12 pagesFORMULATING RESEARCHAesha Upadhyay100% (1)
- Research Methodology & Project Report: Definition: Research Is Defined As Careful Consideration of Study Regarding ADocument19 pagesResearch Methodology & Project Report: Definition: Research Is Defined As Careful Consideration of Study Regarding AAnusha SagarNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument203 pagesResearch Methodologyrohit vermaNo ratings yet
- Research Weeks 1-2 ReviewDocument41 pagesResearch Weeks 1-2 ReviewGlee Gray FrauletheaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology MainDocument33 pagesResearch Methodology MainsteveaustonNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Unit 2Document33 pagesResearch Methodology Unit 2Raghavendra A NNo ratings yet
- RM (Full Notes)Document74 pagesRM (Full Notes)Raveendhar.S -MCA100% (1)
- 0.0.0.0 Lab - Configuring Devices For Use With Cisco Configuration Professional (CCP) 2.5 - InstructorDocument12 pages0.0.0.0 Lab - Configuring Devices For Use With Cisco Configuration Professional (CCP) 2.5 - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-Lesson 13-Writing A Research ReportDocument36 pagesUnit 4-Lesson 13-Writing A Research ReportDale Jose GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Q - 1 Describe Steps in Research Process: Step 1: Identify The ProblemDocument4 pagesQ - 1 Describe Steps in Research Process: Step 1: Identify The ProblemAbu MusaNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH PROCESS STEPSDocument17 pagesRESEARCH PROCESS STEPSNavjot PannuNo ratings yet
- The Process of Research, A Quick GlanceDocument16 pagesThe Process of Research, A Quick GlanceHassaan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ResearchDocument54 pagesIntroduction To ResearchMurgi LalNo ratings yet
- ECN4126 Lecture 2Document45 pagesECN4126 Lecture 2213349No ratings yet
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGYDocument21 pagesRESEARCH METHODOLOGYnithashaindrojuNo ratings yet
- PR 2 TopicsDocument9 pagesPR 2 TopicsJan Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument21 pagesChapter TwoBeka BekoNo ratings yet
- Research Problem FormulationDocument46 pagesResearch Problem Formulationsumathichokkalingam100% (1)
- Research Process StepsDocument11 pagesResearch Process StepsAryan VermaNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics and Research Methodology TheoryDocument39 pagesBusiness Statistics and Research Methodology Theoryshubhamshubhshubh20No ratings yet
- Session2 - Defining The Research ProblemDocument25 pagesSession2 - Defining The Research ProblemjavoleNo ratings yet
- CSC4252 - Lect - 3 - Research Problem - 2018Document28 pagesCSC4252 - Lect - 3 - Research Problem - 2018AhmadNo ratings yet
- NAVR 611 Theory: Additional notes from Practical ResearchDocument20 pagesNAVR 611 Theory: Additional notes from Practical Researchtweetyclarke100% (1)
- RRRRDocument72 pagesRRRRVenkateswara Raju100% (1)
- Assignment of SPSSDocument12 pagesAssignment of SPSSAkshay poplyNo ratings yet
- Process of Research-IDocument30 pagesProcess of Research-IcprableenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Case Study and EthnographyDocument44 pagesLecture 3 Case Study and EthnographyAhmad AltarefeNo ratings yet
- 3 The Charactersitics Processes and Ethics of ResearchDocument51 pages3 The Charactersitics Processes and Ethics of ResearchCedrick AvellanNo ratings yet
- 202Document15 pages202monthlyreportcharhiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Research ProcessDocument9 pagesOverview of Research ProcessKc BaniagaNo ratings yet
- Steps in conducting action researchDocument10 pagesSteps in conducting action researchsanggeethambigai vijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Business Research ProcessDocument3 pagesBusiness Research ProcessMulong CabrillasNo ratings yet
- The Five WsDocument81 pagesThe Five WsHamidullah AminNo ratings yet
- BRM 2018 Process DesignDocument36 pagesBRM 2018 Process DesignMEDISHETTY MANICHANDANANo ratings yet
- Research Process Part 3 PDFDocument8 pagesResearch Process Part 3 PDFjahfarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Research ProcessDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Research ProcessMebruka Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document5 pagesLesson 4HASANUDDIN ASMAD. HASSIMANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2aryoooiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Research MethodsDocument40 pagesIntroduction to Research MethodsMohammed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Research ProcessDocument21 pagesResearch ProcessHruday ChandNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology - Prof. Satya Deo - LUDocument33 pagesResearch Methodology - Prof. Satya Deo - LUkushalkumarheirNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Research and An Overview of The Reserch ProcessDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To Research and An Overview of The Reserch ProcessLiezel NoahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Formulation of The Research ProblemDocument59 pagesChapter 2 - Formulation of The Research ProblemAliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Steps of ResearchDocument2 pagesCharacteristics and Steps of ResearchAlyanna MagroNo ratings yet
- Tomato ProductionDocument29 pagesTomato ProductionjoneforshoNo ratings yet
- .Research Methodology 1660795228000Document36 pages.Research Methodology 1660795228000winniepichoNo ratings yet
- Technical Writing and Research Methodology: Part Two: Research Methodology By: Kuleni Diro (MSC)Document16 pagesTechnical Writing and Research Methodology: Part Two: Research Methodology By: Kuleni Diro (MSC)kuleniNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument24 pagesResearch Methodologylatha gowdaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research First Lesson IntroductionDocument6 pagesPractical Research First Lesson IntroductionEmmanuel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Research Process 11Document12 pagesResearch Process 11Xalu XalManNo ratings yet
- Me 5151 Research Methodology and IprDocument53 pagesMe 5151 Research Methodology and IprKalaiselvan PerumalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Research ProcessDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Research ProcessJohn AgnerNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit-1Document20 pagesBRM Unit-1REDAPPLE MEDIANo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Research Process, Paradigm and OutlineDocument32 pagesLesson 4 Research Process, Paradigm and OutlineAiza San Pedro SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document24 pagesLecture 03Ziaullah KhanNo ratings yet
- The Research Process: CBA 4007 2020 GUIDEDocument91 pagesThe Research Process: CBA 4007 2020 GUIDETafadzwa BhaselaNo ratings yet
- Good QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesGood QuestionnaireSurbhi Rastogi0% (1)
- Strategy ImplementationDocument11 pagesStrategy Implementationdr.p.mohan kumarNo ratings yet
- AttitudeDocument33 pagesAttitudedr.p.mohan kumarNo ratings yet
- AttitudeDocument33 pagesAttitudedr.p.mohan kumarNo ratings yet
- Dania Purnama - 2224190099 - Uji NormalitasDocument4 pagesDania Purnama - 2224190099 - Uji NormalitasDANIA PURNAMANo ratings yet
- Study Scheme & Syllabus Of: IK Gujral Punjab Technical UniversityDocument28 pagesStudy Scheme & Syllabus Of: IK Gujral Punjab Technical UniversityvijiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Goldengate 12c Fundamentals For OracleDocument5 pagesOracle Goldengate 12c Fundamentals For OracleqaleeqNo ratings yet
- Student KitDocument38 pagesStudent KitGautam RastogiNo ratings yet
- 0 Finite DifferenceDocument18 pages0 Finite Differencevisamarinas6226No ratings yet
- Calculate Head Loss in PipesDocument10 pagesCalculate Head Loss in PipesJeffrey Fernandez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Thermocouples - WikaDocument13 pagesThermocouples - WikaJ BagienNo ratings yet
- Bio P3 2007Document7 pagesBio P3 2007Noor ArifinNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Compensating For Emissivity Using Infrared Imaging RadiometersDocument3 pagesMeasuring and Compensating For Emissivity Using Infrared Imaging RadiometersSammoonNo ratings yet
- Rubik Cube Solver ReportDocument11 pagesRubik Cube Solver ReportDarthstarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Sequence Diagrams - v3Document27 pagesLecture 10 - Sequence Diagrams - v3Gautam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gabion Walls Presentation FijiDocument38 pagesGabion Walls Presentation FijiHuy ChungNo ratings yet
- cc1101 p25Document105 pagescc1101 p25fadfadfNo ratings yet
- Finger Pattern Types and Ridge Count AnalysisDocument24 pagesFinger Pattern Types and Ridge Count AnalysisMuhamad Chairul SyahNo ratings yet
- VSBXDocument33 pagesVSBXDylan HenryNo ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel Biology (B) AS-levelDocument28 pagesJune 2018 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel Biology (B) AS-levelbgtes123No ratings yet
- his Life": Λογοτεχνία και διαπολιτισμικές διαδρομές Literature and cross‐cultural routesDocument18 pageshis Life": Λογοτεχνία και διαπολιτισμικές διαδρομές Literature and cross‐cultural routesCharpapathNo ratings yet
- Basson Considerations 2005Document113 pagesBasson Considerations 2005Maxmore KarumamupiyoNo ratings yet
- Master Chemical Engineering 2016 enDocument92 pagesMaster Chemical Engineering 2016 enAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Electro ChemistryDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Electro ChemistryKritika MishraNo ratings yet
- Spyn Audio Catalog-1589913182Document28 pagesSpyn Audio Catalog-1589913182Jose Gregorio Ortega CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle: Solve The Crossword Puzzle, With The Help of Given CluesDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle: Solve The Crossword Puzzle, With The Help of Given CluesAnas Ahmad GhaziNo ratings yet
- GR 80 CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMDocument20 pagesGR 80 CONFIGURATION DIAGRAMAffan fNo ratings yet
- wph13 01 MSC 20200123 PDFDocument11 pageswph13 01 MSC 20200123 PDFfadi baqainNo ratings yet