Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro Watertreatment English
Uploaded by
SenthilKumar SubramanianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro Watertreatment English
Uploaded by
SenthilKumar SubramanianCopyright:
Available Formats
WATER TREATMENT
UNIT OPERATIONS IN WATER TREATMENT
What is water treatment?
The unit operations... ...and the appropriate GUNT unit
Water is changed in its characteristics through domestic Water treatment can also be used to make water usable
use or industrial processes. Used water (wastewater) for a specific purpose. Examples of this are the production
Mechanical Processes
can’t be discharged directly to a watercourse. Wastewater of drinking water or process water in industry.
Flotation CE 587 Dissolved Air Flotation
must first be treated so that it no longer poses a hazard to
the environment. If organically polluted wastewater enters Sedimentation HM 142 Separation in Sedimentation Tanks
a watercourse, microorganisms will degrade the organic
matter, consuming large amounts of oxygen. This may
reduce the oxygen level enough to kill fish. Filtration CE 579 Depth Filtration
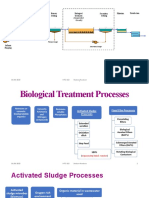
Biological Processes
Aerobic Processes CE 701 Biofilm Process
CE 705 Activated Sludge Process
What unit operations are employed in water treatment?
There are a number of unit operations for water treatment. The key unit operations can be classified accordingly as
The choice of unit operations depends primarily on the follows:
Anaerobic Processes CE 702 Anaerobic Water Treatment
substances needing to be removed.
Adsorption CE 583 Adsorption
Undissolved Dissolved Substances
Physical/Chemical Processes
Substances
Membrane Separation Processes CE 530 Reverse Osmosis
(Solids) Organic Substances
Inorganic
Organic Substances Ion Exchange CE 300 Ion Exchange
Inorganic Biodegradable Non-Biodegradable
Precipitation / Flocculation CE 586 Precipitation and Flocculation
Mechanical
Biological Processes Physical/Chemical Processes
Processes
Chemical Oxidation CE 584 Advanced Oxidation
Flotation Aerobic Processes Adsorption
Sedimentation Anaerobic Processes Membrane Separation Processes
Filtration Ion Exchange
Precipitation / Flocculation
Chemical Oxidation
Combined unit operations... ...and the appropriate GUNT unit
Removal of undissolved substances (solids) is effected domestic wastewater by wastewater treatment plants. By Filtration
by mechanical processes. Dissolved substances can be contrast, anaerobic processes exclude oxygen. Anaerobic Adsorption CE 581 Water Treatment Plant 1
removed by either biological or physical/chemical proc- processes are used in the treatment of heavily organi- Ion Exchange
esses. cally polluted wastewater e.g. from industries like food
processing and paper manufacturing. Filtration
The aim of biological processes is to remove organic, Ion Exchange CE 582 Water Treatment Plant 2
biodegradable substances. Microorganisms use such Non-biodegradable organic and inorganic substances can
substances as a source of nutrition, thereby degrad- be removed by means of physical /chemical processes.
ing them. If this process takes place in the presence Examples of this are water softening by ion exchange and
of dissolved oxygen, they are termed aerobic. They the adsorption of chlorinated hydrocarbons on activated
include the activated sludge process and biofilm proc- carbon.
ess. Their main field of application is in the treatment of
You might also like
- WWT7 - Physical TreatmentDocument17 pagesWWT7 - Physical TreatmentHelder MbidiNo ratings yet
- "Effluent Treatment Using Biodegradable Material": Design Engineering - IIBDocument19 pages"Effluent Treatment Using Biodegradable Material": Design Engineering - IIBUnknown SoulNo ratings yet
- NPTEL Civil Engineering - Water and Waste Water EngineeringDocument2 pagesNPTEL Civil Engineering - Water and Waste Water EngineeringRushan LakdimuthuNo ratings yet
- Treatment ProcessesDocument28 pagesTreatment ProcesseskietNo ratings yet
- TAHIRI - Biogas - Boues STEP - PARTIE4 - 2021Document24 pagesTAHIRI - Biogas - Boues STEP - PARTIE4 - 2021ELGUERCHENo ratings yet
- Irjet V7i9619Document6 pagesIrjet V7i9619ani putkaradzeNo ratings yet
- Unit7-6 Biosolids&Residuals PDFDocument58 pagesUnit7-6 Biosolids&Residuals PDFnickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Industrial Wastewater Treatment ProcessDocument63 pagesChapter 4-Industrial Wastewater Treatment ProcessFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment OperationsDocument10 pagesWastewater Treatment OperationsAnne TayongNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment TechnologyDocument17 pagesWaste Water Treatment TechnologygulfamNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering: Changing Face of Chemical IndustryDocument20 pagesBiochemical Engineering: Changing Face of Chemical IndustrykiramNo ratings yet
- Outotec Mesotherm Biox Process: BenefitsDocument2 pagesOutotec Mesotherm Biox Process: BenefitsJose Heli Vallejos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa Sanitasi Dan Lingkungan: Pengelolaan Air LimbahDocument38 pagesRekayasa Sanitasi Dan Lingkungan: Pengelolaan Air LimbahUnef YamamotoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Waste-Water: Parth Naik ICT, MumbaiDocument48 pagesPharmaceutical Waste-Water: Parth Naik ICT, MumbaiShraddha MalveNo ratings yet
- Unit7-3-WWT-Biological Treatment PDFDocument85 pagesUnit7-3-WWT-Biological Treatment PDFnickNo ratings yet
- SPS 370S - 2024 - Chapter 3.1Document38 pagesSPS 370S - 2024 - Chapter 3.1ziziphomkosana2003No ratings yet
- WTC 102 GemsDocument15 pagesWTC 102 GemsAyoub Mohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument20 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSajib IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Treatment TechnologiesDocument35 pagesTreatment TechnologiesnareshnallaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment AssignmentDocument14 pagesWastewater Treatment AssignmentKanishka JayalathNo ratings yet
- STP Comparision of ProcessDocument11 pagesSTP Comparision of Processwd100% (1)
- Esterilizacion in Situ-1Document16 pagesEsterilizacion in Situ-1juanNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument16 pagesSludge Treatment and Disposalsandhya bhattiNo ratings yet
- 00 - WWT EngineeringDocument188 pages00 - WWT EngineeringFaisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- CHAPT 3-Water SupplyDocument74 pagesCHAPT 3-Water SupplyJamal MohamedNo ratings yet
- Biological Waster TreatmentDocument17 pagesBiological Waster TreatmentAwes OmarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Treatment System (Iets) - Technician Training 2Document42 pagesIndustrial Treatment System (Iets) - Technician Training 2Iqbal Hakeem100% (2)
- Water & Wastewater TR EatmentDocument28 pagesWater & Wastewater TR EatmentMuhammad NidhomNo ratings yet
- Bio Filtration OverviewDocument5 pagesBio Filtration OverviewLarry BothamNo ratings yet
- Strategy For The Treatment of Industrial Wastewaters by Coupling of Chemical Oxidation and Biodegradation ProcessesDocument50 pagesStrategy For The Treatment of Industrial Wastewaters by Coupling of Chemical Oxidation and Biodegradation ProcessesLyNo ratings yet
- Presentation - MBBR-Fair Electronics (Samsung) by ShakibDocument32 pagesPresentation - MBBR-Fair Electronics (Samsung) by Shakibshakib nazmus0% (1)
- 7 - D21WW - Wastewater Treatment BDocument48 pages7 - D21WW - Wastewater Treatment BDominic WaldronNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreastmentDocument16 pagesWaste Water TreastmentMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Textile EffluentDocument8 pagesTextile EffluentargentevesNo ratings yet
- Biological Nutrient Removal: Sneha G K 4SU17CV039 VIII Sem, Civil Engg SDM I T, UjireDocument23 pagesBiological Nutrient Removal: Sneha G K 4SU17CV039 VIII Sem, Civil Engg SDM I T, Ujireವಿನಯ್ ಎಮ್. ಆರ್No ratings yet
- Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated S PDFDocument23 pagesAnaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated S PDFnawajhaNo ratings yet
- GEA Process Engineering IncDocument31 pagesGEA Process Engineering IncElif UsluNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Wastewater Biological TreatmentDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Wastewater Biological Treatmentalvaro.roldan1No ratings yet
- Biofiltration Nitrification Design OverviewDocument62 pagesBiofiltration Nitrification Design OverviewHiep le HuuNo ratings yet
- GWES - Sludge HandlingDocument1 pageGWES - Sludge HandlingHarvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- More Development Wastewater Treatment ProcessDocument6 pagesMore Development Wastewater Treatment ProcessEudkrenutNo ratings yet
- Ngec23.04.2012 22.31.57sciDocument10 pagesNgec23.04.2012 22.31.57sciazerfazNo ratings yet
- Presentation Waste Water TreatmentDocument69 pagesPresentation Waste Water TreatmentAkilaNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations & Processes in Waste Water TreatmentDocument16 pagesUnit Operations & Processes in Waste Water Treatmentbefkadu ayalkieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WWDocument22 pagesIntroduction To WWOmaya TariqNo ratings yet
- Brochure DE NORA TETRA ABF 650 0316Document4 pagesBrochure DE NORA TETRA ABF 650 0316Khang TrầnNo ratings yet
- Municipal Sewage Industry: Centre of ExcellanceDocument1 pageMunicipal Sewage Industry: Centre of ExcellanceAli AhsanNo ratings yet
- Water: Removal of Cod and So From Oil Refinery Wastewater Using A Photo-Catalytic System-Comparing Tio and Zeolite EDocument14 pagesWater: Removal of Cod and So From Oil Refinery Wastewater Using A Photo-Catalytic System-Comparing Tio and Zeolite Epattan madhuNo ratings yet
- 04 Biological Anaerobic SystemDocument24 pages04 Biological Anaerobic SystemDina rodianaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementDocument27 pagesWaste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementSujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental ManagementDocument7 pagesJournal of Environmental Managementsarath6142No ratings yet
- Final - STP ReportDocument39 pagesFinal - STP ReportSatyavijet Chilakapati100% (1)
- Presentation On Waste WaterDocument37 pagesPresentation On Waste WaterDebashish RoyNo ratings yet
- Aguas ResidualesDocument35 pagesAguas ResidualesHenry VilchezNo ratings yet
- CE-311 Lecture On CharacterizationDocument69 pagesCE-311 Lecture On CharacterizationakashNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment: Chapter One: Introduction To Wastewater TreatmentDocument21 pagesSewage Treatment: Chapter One: Introduction To Wastewater Treatmentmarshet berhanNo ratings yet
- Wabag Bioden: Nitrate Removal Biological Denitrifi Cation of Ground WaterDocument6 pagesWabag Bioden: Nitrate Removal Biological Denitrifi Cation of Ground WaterNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Separation Processes: 1.0 Instructional ObjectivesDocument30 pagesSeparation Processes: 1.0 Instructional Objectivesv0578775No ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Boards of Directors of Centurion Bank of Punjab and Lord Krishna Bank Approve MergerDocument2 pagesThe Boards of Directors of Centurion Bank of Punjab and Lord Krishna Bank Approve MergerSenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- General Information - Bombay Stock Exchange: BSE SensexDocument5 pagesGeneral Information - Bombay Stock Exchange: BSE SensexSenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Scheme Name NAV (RS) NAV Date Return 1 WK (%) Return 1 M (%) Return 3 M (%) Return 12 M (%)Document6 pagesScheme Name NAV (RS) NAV Date Return 1 WK (%) Return 1 M (%) Return 3 M (%) Return 12 M (%)SenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- SEBI - Introduction: The Basic Objectives of The Board Were Identified AsDocument5 pagesSEBI - Introduction: The Basic Objectives of The Board Were Identified AsSenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Tannin BasedDocument5 pagesTannin BasedSenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- 3D Chest WorkoutDocument7 pages3D Chest WorkoutSenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Energy From Solid and Liquid Wastes - IIDocument20 pagesEnergy From Solid and Liquid Wastes - IIMukul NarayanNo ratings yet
- Fka Uitm Pahang - (Lab Manual) - Ecw351: Title TEST 11: Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) - Level 1Document2 pagesFka Uitm Pahang - (Lab Manual) - Ecw351: Title TEST 11: Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) - Level 1WHfamilyNo ratings yet
- 4 7 pp.110 115Document7 pages4 7 pp.110 115Xyrile Inguillo100% (1)
- Eluru DPR - ULB On 17-09-2022Document10 pagesEluru DPR - ULB On 17-09-2022Sasidhar KatariNo ratings yet
- AL MARAI HADCO STP - Process Description and Seq. of OperationDocument29 pagesAL MARAI HADCO STP - Process Description and Seq. of OperationHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Week - 5 - Assignment and SolutionDocument12 pagesWeek - 5 - Assignment and SolutionAmith SharmaNo ratings yet
- STPDocument16 pagesSTPlaughingwaters100% (1)
- Phi 210896Document14 pagesPhi 210896kstopandmotionNo ratings yet
- Sludge Volume IndexDocument3 pagesSludge Volume IndexNicole Feliciano100% (1)
- Design of Biological Treatment Facility of Waste Disposal Site in Brgy. Felisa, Bacolod CityDocument32 pagesDesign of Biological Treatment Facility of Waste Disposal Site in Brgy. Felisa, Bacolod CityMhelveneNo ratings yet
- VWT Water Recycle and Reuse BrochureDocument8 pagesVWT Water Recycle and Reuse BrochureManjunath GangadharNo ratings yet
- Apjmr-2016 4 4 07 PDFDocument10 pagesApjmr-2016 4 4 07 PDFJason Orolfo Salvadora HLNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering UTHM CQI Test 2Document2 pagesEnvironmental Engineering UTHM CQI Test 2InahMisumiNo ratings yet
- Package Treatment Plant: For Potable WaterDocument4 pagesPackage Treatment Plant: For Potable Watermohammed rafi shaikhNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: 938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon CityDocument5 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: 938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon Cityrisky robertsNo ratings yet
- City Sanitation Plan AllahabadDocument108 pagesCity Sanitation Plan AllahabadAnusha KantNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering I C: Lecture FourDocument30 pagesHighway Engineering I C: Lecture FourHenok YalewNo ratings yet
- Practical No.4 PDFDocument9 pagesPractical No.4 PDFSwarupa ChanchalwadNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Engineering - Treatment and Resource Recovery-Metcalf and Eddy 5th Ed (2014) Sección 8-11Document8 pagesWastewater Engineering - Treatment and Resource Recovery-Metcalf and Eddy 5th Ed (2014) Sección 8-11Ricardo Javier PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- NWMP Data 2018Document56 pagesNWMP Data 2018Copper xNo ratings yet
- Am I A Climate Hero or A Climate Culprit 2Document1 pageAm I A Climate Hero or A Climate Culprit 2leonedith lozano100% (1)
- Appendix F - 250 MLD Chennai Metro Life Cycle CostDocument10 pagesAppendix F - 250 MLD Chennai Metro Life Cycle Costsmbhat25No ratings yet
- Report On Water and Waste Water EngineeringDocument48 pagesReport On Water and Waste Water EngineeringOmaya Tariq100% (2)
- Gambar Rekomendasi WWTP Pet SnackDocument7 pagesGambar Rekomendasi WWTP Pet SnackIvan Sitorus ZvNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and The Built Environment Department of Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering and The Built Environment Department of Civil EngineeringTshidi MuneriNo ratings yet
- Composting - Nature's Way To RecycleDocument6 pagesComposting - Nature's Way To RecycleBobNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper-Humss BDocument19 pagesConcept Paper-Humss Banon_256867255100% (1)
- DNIT Vol 2 Part 1Document196 pagesDNIT Vol 2 Part 1JitendraHatwarNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance Calculation (Ratio)Document1 pageMass Balance Calculation (Ratio)maizanazaNo ratings yet
- ACO Maripur Waste Water Treatment Plant PDFDocument6 pagesACO Maripur Waste Water Treatment Plant PDFValiNo ratings yet