Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Present Simple: Verb To Be
Uploaded by
Nahia Aznar GonzalezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Present Simple: Verb To Be
Uploaded by
Nahia Aznar GonzalezCopyright:
Available Formats
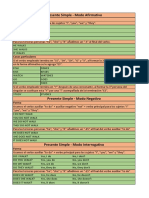
PRESENT SIMPLE
VERB TO BE
(+) (-) (?)
I am (I’m) I am not (I’m not) Am I …?
You are (You’re) You are not (aren’t) Are you …?
He/she/it is (He’s/ She’s/ It’s) He/she/itis not (isn’t) Ishe/she/it …?
We/you/they are We/you/theyaren’t Are we/you/they…?
HAVE GOT (‘VE GOT)
(+) (-) (?) (answer)
I have got I haven’t got Have I got…? Yes, I have/ No, I haven’t
You have got You haven’t got Have you got…? (have you got a pencil/pen/paper ?)
He/she/it has got He/she/it hasn’t got Has he/she/it got…?
We/you/they have got We/you/they haven’t got Have we/you/they got…? (have we got break/time?)
I have 42 years old – MAL
I am 42 (years old). – BIEN ( yo soy 42 años de viejo)
CAN (poder)
(+) (-) (?)
I can I can’t Can I…?
you can You can’t Can you…?
He/she/it can(no lleva “s”!!) He/she/it can’t Can he/she/it …?
We/you/they can We/you/they can can we/you/they …?
THE REST OF THE VERBS
(+)
La forma del "present simple" coincide con la del infinitivo sin la partícula "to", salvo en la 3ª persona del singular en la que se
le añade una "s".
Infinitivo I / you / we / they He / she / it
To eat (comer) eat eats
To run (correr) run runs
Si el verbo termina en "ss", "sh", "ch", "x", "o", al formar la 3ª persona del singular se le añade "-es".
Infinitivo I / you / we / they He / she / it
To kiss (besar) I Kiss He kisses
To watch (observar) I watch He watches
Si el verbo termina en "y" tras consonante, al formar la 3ª persona del singular se sustituye esta "y" por una "i", seguida de la
terminación "es".
Infinitivo I / you / we / they He / she / it
To carry (llevar) I carry He carries
To envy (envidiar) I envy He envies
To cry (llorar) I cry He cries
Si el verbo termina en "y" tras vocal, no se sustituye la “y” y se le añade “s”.
Infinitivo I / you / we / they He / she / it
To play (jugar) I play He Plays
To stay (quedarse) I stay He stays
(-)
Las oraciones negativas se forman con el auxiliar "to do", habitualmente en sus formas contraídas: "don´t" (= do not) para las
personas "I, you, we, they", y "doesn´t" (= does not) para las personas "he, she, it".
I don't play tennis. Yo no juego al tenis
She doesn´t go to the cinema. Ella no va al cine
We don´t know the answer. Nosotros no sabemos la respuesta
(?)
La forma interrogativa se forma también con el auxiliar "to do" al comienzo de la oración ("do" con las personas "I, you, we,
they"; "does" con "he, she, it").
Do you play tennis? ¿Juegas al tenis? Do you like teaching english? / Do you want to go/to come?
Does she go to the cinema? ¿Va ella al cine? does she(you mum) eat japanese?
Do we know the answer? ¿Conocemos la respuesta?
SUBJECT PRONOUNS & POSSESSIVE ADJECTIVES
(Yo mi… / Tú tu… / Ella /él su…)
ARTICULOS INDEFINIDOS: singular (un/una)
Plural: no lleva artículo
I have (some) girlfriends
I have (some) cars
I rode (some) elephants
SOME= algunos (indefinido)
NOUNS: SINGULAR & PLURAL
monkey
You might also like
- Subject / Sujeto Object / Objeto Possessive Adjective / Adjetivo Posesivo ( )Document7 pagesSubject / Sujeto Object / Objeto Possessive Adjective / Adjetivo Posesivo ( )PilarNo ratings yet
- Tabel Conjugari Verb EnglezaDocument2 pagesTabel Conjugari Verb EnglezaMaiden DiNo ratings yet
- Ask DR Gramadeg: Ateb Cwestiynau / Answering QuestionsDocument5 pagesAsk DR Gramadeg: Ateb Cwestiynau / Answering QuestionsVictorCrettónNo ratings yet
- Grammaire AnglaiseDocument48 pagesGrammaire AnglaiseMbemba Doumbouya100% (2)
- English GrammarDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammarfranc_estorsNo ratings yet
- The Verb To HaveDocument4 pagesThe Verb To HaveSol VieraNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument2 pagesSimple PresentTú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Blanca 2Document10 pagesBlanca 2chundy11No ratings yet
- Present Simple - Prosto Sadašnje Vreme: Jednina (Singular) Množina (Plural)Document3 pagesPresent Simple - Prosto Sadašnje Vreme: Jednina (Singular) Množina (Plural)Vladan ColakovicNo ratings yet
- Verb Charts: Be, Have Got, Present Simple and Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesVerb Charts: Be, Have Got, Present Simple and Present ContinuousPau100% (1)
- CLC - LEC - Past Simple - RulesDocument7 pagesCLC - LEC - Past Simple - RulesJosynando XavierNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Verb To BeDocument40 pagesGrammar: Verb To BececiliaguiseNo ratings yet
- Cuadro Gramatical Presente SimpleDocument2 pagesCuadro Gramatical Presente SimpleEduardo Cajas CamposNo ratings yet
- Running, Sit-Sitting, Put-Putting, Stop-Stopping, Swim-Swimming. Begin-BeginningDocument1 pageRunning, Sit-Sitting, Put-Putting, Stop-Stopping, Swim-Swimming. Begin-BeginningGaraNo ratings yet
- English Grammar-B1Document19 pagesEnglish Grammar-B1claudia r.No ratings yet
- Past Perfect Simple or Past SimpleDocument2 pagesPast Perfect Simple or Past SimplelucaNo ratings yet
- El VerboDocument9 pagesEl VerboAri RamirezNo ratings yet
- Gramática y Writing Modificado para B1Document66 pagesGramática y Writing Modificado para B1beticabestNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be: QuestionsDocument5 pagesVerb To Be: QuestionsAgustina CandelariaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica BasicaDocument3 pagesGramatica Basicamoly083No ratings yet
- Gramatica Verbe: Am Am Am Are Are Are Is Is Is Are Are AreDocument5 pagesGramatica Verbe: Am Am Am Are Are Are Is Is Is Are Are AreCiprian FarcasNo ratings yet
- Los Verbos en InglésDocument9 pagesLos Verbos en InglésLolyNo ratings yet
- Being Organized!: Date: June 02 - 2021 Unit 2. Week #2Document4 pagesBeing Organized!: Date: June 02 - 2021 Unit 2. Week #2Eduardo OspinaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present Tense DO Does Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Question (?)Document4 pagesThe Simple Present Tense DO Does Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Question (?)RECEP CANBOLATNo ratings yet
- English Manual: Licenciada Filología Inglesa Colegiada #2811Document36 pagesEnglish Manual: Licenciada Filología Inglesa Colegiada #2811Gema Caro MolinaNo ratings yet
- Vowel Change VerbsDocument8 pagesVowel Change VerbsHilmija FejzovicNo ratings yet
- Conteúdo 1ºs Anos 1º SemestreDocument39 pagesConteúdo 1ºs Anos 1º SemestreSandra Patrícia Miranda da SilvaNo ratings yet
- A3 CartelesDocument5 pagesA3 CartelesAbrilNo ratings yet
- Futuro Going ToDocument7 pagesFuturo Going ToAntioquia EnglishNo ratings yet
- Conjugación Verbal. Adjetivo. Genitivo Sajón: InglésDocument24 pagesConjugación Verbal. Adjetivo. Genitivo Sajón: InglésMichel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple (I Work) Present Simple: FormDocument5 pagesPresent Simple (I Work) Present Simple: FormirmathesweetNo ratings yet
- Being Organized!: Date: May 26-2021 Unit 2. Week #1Document5 pagesBeing Organized!: Date: May 26-2021 Unit 2. Week #1Eduardo OspinaNo ratings yet
- Tenses ChartDocument2 pagesTenses ChartantonsuwantoNo ratings yet
- Ensino Fundamental Módulo 5Document12 pagesEnsino Fundamental Módulo 5Levy Ben YisraelNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Inglesa 3esoDocument6 pagesGramatica Inglesa 3esoOvidio SalomonNo ratings yet
- Grammar ReferenceDocument21 pagesGrammar ReferenceMaría FZNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Verb To Be : Affirmative NEGATIVE (+ Not) Interrogative (Reverse) PresentDocument2 pagesAuxiliary Verb To Be : Affirmative NEGATIVE (+ Not) Interrogative (Reverse) PresentChristina Selby100% (1)
- The English Tenses: S ED Will ShallDocument9 pagesThe English Tenses: S ED Will ShallAnonymous wIlqpnk7BwNo ratings yet
- Grammar For 1º-2º EsoDocument10 pagesGrammar For 1º-2º Esogaby38No ratings yet
- Apuntes GramáticaDocument2 pagesApuntes GramáticaCoral Rodríguez LlamasNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesCheat SheetEmiliano PradaNo ratings yet
- Grammar B1Document12 pagesGrammar B1Alejandro SMNo ratings yet
- SUPAnglDocument30 pagesSUPAngllebete100% (1)
- Conteúdo 1ºs Anos 2º SemestreDocument37 pagesConteúdo 1ºs Anos 2º SemestreSandra Patrícia Miranda da Silva100% (1)
- Basic Language Structures StructuresDocument158 pagesBasic Language Structures StructuresMd Rabby BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- VERBS TO BE AND HAVE GOT - ChartsDocument1 pageVERBS TO BE AND HAVE GOT - ChartsPauNo ratings yet
- English Grammar 20090914Document4 pagesEnglish Grammar 200909143720412No ratings yet
- A 1.octubre - Introducción Al Inglés - Verb To Be and Have GotDocument7 pagesA 1.octubre - Introducción Al Inglés - Verb To Be and Have GotLucia Fernandez CastroNo ratings yet
- 01 BeDocument14 pages01 BedilledebruijnNo ratings yet
- Grammar TheoryDocument28 pagesGrammar TheorybenedettoNo ratings yet
- Learn Spanish With MR CloudDocument132 pagesLearn Spanish With MR Cloudmmmm11No ratings yet
- Penyusunan Kalimat Berdasarkan Waktu TerjadinyaDocument8 pagesPenyusunan Kalimat Berdasarkan Waktu TerjadinyairfanNo ratings yet
- Primele 3 Cele Mai Folosite Verbe in Limba Engleza SuntDocument4 pagesPrimele 3 Cele Mai Folosite Verbe in Limba Engleza SuntMadalina2012100% (1)
- Simple Present Tense - Present Continuous TenseDocument12 pagesSimple Present Tense - Present Continuous TenseIrfan HasifNo ratings yet
- Verbul To Be, Have, DoDocument3 pagesVerbul To Be, Have, DoRotariu Mihaela-LucianaNo ratings yet
- Ammar OdtDocument5 pagesAmmar OdtSamuel Lopez CaseroNo ratings yet
- English Tenses ConjugationsDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses ConjugationsJesus PiñaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica InglesDocument33 pagesGramatica InglesAntonia LorenteNo ratings yet
- Verb Form ExercisesDocument6 pagesVerb Form ExercisesNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- b1-b2 Reading Examples 1Document12 pagesb1-b2 Reading Examples 1Mariana Kanarek100% (1)
- Verb Tense PDFDocument2 pagesVerb Tense PDFTrang LuongNo ratings yet
- There Is, Are - A, An, SomeDocument2 pagesThere Is, Are - A, An, SomeNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense 1Document1 pagePresent Simple Tense 1PIli Mahhon83% (6)
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Present, Past, Present PerfectDocument2 pagesPresent, Past, Present PerfectAmanda CanloNo ratings yet
- Future Will Going To Present Continuos PDFDocument2 pagesFuture Will Going To Present Continuos PDFSylvia Ivonne Ch100% (3)
- Lista de Verbos Irregulares en InglésDocument3 pagesLista de Verbos Irregulares en InglésWilliam Humberto GutierrezNo ratings yet
- t13 PDFDocument2 pagest13 PDFLilo Keiki Nani Hernández100% (1)
- Past Simple - Present Perfect - For, SinceDocument1 pagePast Simple - Present Perfect - For, SinceNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Person - 'S' UseDocument1 page3rd Person - 'S' UseNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Tenses IvanDocument1 pageTenses IvanBiljana NestorovskaNo ratings yet
- I. Complete The Sentences: Had Walked Had Read Hadn't Switched Had Left Had PassedDocument1 pageI. Complete The Sentences: Had Walked Had Read Hadn't Switched Had Left Had PassedNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Business English Grammar ExercisesDocument22 pagesBusiness English Grammar ExercisesbiffinNo ratings yet
- 7271221501523Document1 page7271221501523hhhNo ratings yet
- Numbers, Days, Months, Time and DatesDocument2 pagesNumbers, Days, Months, Time and DatesNahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- EXERCISES-adj. or Adv.Document1 pageEXERCISES-adj. or Adv.Nahia Aznar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Date: Class # Topic:: Colegio Gimnasio Infantil ValleduparDocument3 pagesDate: Class # Topic:: Colegio Gimnasio Infantil ValleduparLaury Vanessa Rocha PalominoNo ratings yet
- Future Tense - Ipa 2019 PDFDocument12 pagesFuture Tense - Ipa 2019 PDFRini Dwi YulianiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Passive VoiceAreli CollaoNo ratings yet
- Research About Adjectives and UsingDocument5 pagesResearch About Adjectives and UsingJEANINA CAROLINA LASCANO FILIANNo ratings yet
- 01 SmartTime gr11 Unit 1Document12 pages01 SmartTime gr11 Unit 1m0% (2)
- Free Printable Parts of Speech ChartDocument1 pageFree Printable Parts of Speech ChartDang CabaticNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Second ConditionalDocument2 pagesLesson Plan-Second Conditionalapi-25706929250% (4)
- КТП 3 класс Smiles-3Document11 pagesКТП 3 класс Smiles-3Данил ГагаринNo ratings yet
- Used To, Didn't Use To - Past Habits and States: What Music To Like When You Were A Child?Document2 pagesUsed To, Didn't Use To - Past Habits and States: What Music To Like When You Were A Child?Erinson CriolloNo ratings yet
- FCE Reading and Use of English Practice Test 4 PrintableDocument7 pagesFCE Reading and Use of English Practice Test 4 PrintableVicky Julianne YoveraNo ratings yet
- Mixed Tense Tenth Grade February 10-21Document3 pagesMixed Tense Tenth Grade February 10-21Santiago Jimenez0% (1)
- Writing A ReviewDocument2 pagesWriting A ReviewNazifah KamarudinNo ratings yet
- MacKenzie, D. N., (1956), Bāǰalānī, Pp. 418-435. Bulletin of The School of Oriental and African StudiesDocument19 pagesMacKenzie, D. N., (1956), Bāǰalānī, Pp. 418-435. Bulletin of The School of Oriental and African StudiesKurdish textsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. SentenceDocument4 pagesLesson 2. SentencemarilouNo ratings yet
- Comparative and SuperlativesDocument16 pagesComparative and SuperlativesSergio Carcamo CastroNo ratings yet
- ST3 English5 Q2Document2 pagesST3 English5 Q2Karen HernandezkhjgNo ratings yet
- Learning Spanish - 6cDocument29 pagesLearning Spanish - 6cChima C. Ugwuegbu80% (5)
- First Quarter Summative Test in English 7Document2 pagesFirst Quarter Summative Test in English 7Sena AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Bitesize Gcse French Write C q1Document6 pagesBitesize Gcse French Write C q1SaddamHCNo ratings yet
- Hindi Word Formation ProcessDocument10 pagesHindi Word Formation ProcessKavita Rastogi100% (1)
- Verb To Be PracticeDocument1 pageVerb To Be PracticeAh Kim Ri SongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For G7 English - 1 QUARTER DateDocument2 pagesLesson Plan For G7 English - 1 QUARTER DateJefferson Mcking FlorNo ratings yet
- WRITTEN TEST UNIT 3 Go Getter 3Document2 pagesWRITTEN TEST UNIT 3 Go Getter 3Ziomara Gustín100% (2)
- GCSE Key Words Booklet EnglishDocument7 pagesGCSE Key Words Booklet EnglishPriyanka Lale100% (1)
- Syntactic AmbiguityDocument5 pagesSyntactic AmbiguityJustineAncenoHinnoNo ratings yet
- Eald Bilingual Dictionary SwahiliDocument96 pagesEald Bilingual Dictionary SwahiliRabby KapelaNo ratings yet
- 11th English 1 Marks Question Paper English Medium PDF DownloadDocument8 pages11th English 1 Marks Question Paper English Medium PDF DownloadJegasri SabariNo ratings yet
- Frayer Model For Reviewing Spanish Preterite TenseDocument1 pageFrayer Model For Reviewing Spanish Preterite TenseCharlotte Bryant MadisonNo ratings yet
- Voice - Active and PassiveDocument7 pagesVoice - Active and Passiveapi-19776105100% (1)
- The Grammar Tree Second Edition TG 7 PDFDocument144 pagesThe Grammar Tree Second Edition TG 7 PDFSyed Hamid50% (6)