Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15
Uploaded by
CataCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15
Uploaded by
CataCopyright:
Available Formats
Taiwan Semiconductor
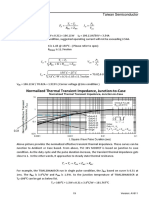
Gate-Source Voltage vs. Gate Charge
Qg
Qgd
Qgs
Gate charge include 3 specified values, Qgs, Qgd ,and Qg. Qgs denotes Gate to Source charge. Qgd
denotes Gate to Drain charge, which is also called the miller effect charge. Qg denotes the total
gate charge.
VGS
VP
VGS(TH)
VDS
ID
T0 T1 T2 T3 T4
Operations of Gate Charge are presented as below from above diagram.
1. T0 ~ T1
When VGS rises and reaches to VGS(TH), CGS is the capacitor to be charged. At the time, both ID
and VDS present unchanged.
2. T1 ~ T2
At this time interval, MOSFET is working in linear region. VGS continues stepping up to the
plateau voltage, VP. CGS is completely charged and ID is raised up to full load current.
3. T2 ~ T3
At this time interval, MOSFET is still working in linear region. And, VDS voltage starts to decrease
and finally drops to zero. So the CGD * (dVDS/dt) becomes big and thus, creates current flowing
through CGD, which blocks VGS keeps rising and maintains constant. During this time, RDS(on)
changes from high impedance to low impedance, entering Ohmic region.
4. T3 ~ T4
In this timing, VGS is raised up to rated value and MOSFET is operated in Ohmic region.
14 Version: A1611
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Power MOSFET basics-IXYS 1Document1 pagePower MOSFET basics-IXYS 1CataNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20CataNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16CataNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Power MOSFET basics-IXYS 2Document1 pagePower MOSFET basics-IXYS 2CataNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET basics-IXYS 3Document1 pagePower MOSFET basics-IXYS 3CataNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21CataNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19CataNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 17Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 17CataNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21CataNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16CataNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hukum Termodinamika IIDocument21 pagesHukum Termodinamika IIdiky dharmawanNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20CataNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20CataNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14CataNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Hukum Termodinamika IIDocument21 pagesHukum Termodinamika IIdiky dharmawanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21CataNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18CataNo ratings yet
- Package Inductance-Infineon 6Document1 pagePackage Inductance-Infineon 6CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 11Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 11CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 13Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 13CataNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 10Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 10CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 12Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 12CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 6Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 6CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14CataNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 2Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 2CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 4Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 4CataNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)