Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 4
Uploaded by
Cata0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 4
Uploaded by
CataCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Taiwan Semiconductor
MOSFET datasheet parameters introduction
Introduction
When choosing a MOSFET, parameters that are focused on by most engineers intuitively are VDS,
RDS(on), ID. However, in power systems, it is significant to pick up a suitable MOSFET based on
different applications. In this application note, Taiwan Semiconductor (TSC) introduces the definition
of every single parameter of a MOSFET, and from chapter 3, TSC also explains how each parameter is
realized, hoping this would help designers on the power projects.
1. Absolute Maximum Ratings
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER SYMBOL LIMIT UNIT Notes
Drain-Source Voltage VDS 30 V 1.1
Gate-Source Voltage VGS ±20 V 1.2
(Note 1) TC = 25°C 39
Continuous Drain Current ID A 1.3
TA = 25°C 11
Pulsed Drain Current IDM 156 A 1.4
(Note 2)
Single Pulse Avalanche Current IAS 15.6 A 1.5
(Note 2)
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy EAS 36.5 mJ 1.6
TC = 25°C 33
Total Power Dissipation PD W
TC = 125°C 6.6
1.7
TA = 25°C 2.6
Total Power Dissipation PD W
TA = 125°C 0.5
Operating Junction and Storage Temperature range TJ, TSTG - 55 to +150 °C 1.8
1.1 Drain-Source Voltage (VDS )
VDS represents MOSFET absolute maximum voltage between Drain and Source. In operations,
voltage stress of Drain-Source should not exceed maximum rated value.
1.2 Gate-Source Voltage ( VGS )
VGS represents operating driver voltage between Gate and Source. In operations, voltage stress of
Gate-Source should not exceed maximum rated value.
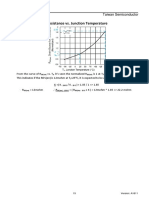
1.3 Continuous Drain Current ( ID )
ID represents MOSFET’s continuous conduction current and could be calculated by below equation.
TJ TC
ID
TJ = Junction Temperature RJC RDS (ON ) K
TC = Case Temperature
RDS(ON) = Drain-Source On-State Resistance
RθJC = Junction to Case Thermal Resistance
K = On-Resistance vs. Junction Temperature
3 Version: A1611
You might also like
- Aon 6926Document10 pagesAon 6926Hermilio ValdizanNo ratings yet
- General Description Product Summary: 30V Dual Asymmetric N-Channel MOSFETDocument10 pagesGeneral Description Product Summary: 30V Dual Asymmetric N-Channel MOSFETBrbrHuehue SzzNo ratings yet
- TSM060NB06CZ: Taiwan SemiconductorDocument6 pagesTSM060NB06CZ: Taiwan Semiconductorn tanevarNo ratings yet
- AON6908A: General Description Product SummaryDocument11 pagesAON6908A: General Description Product SummaryLuis SantosNo ratings yet
- Aon6978 PDFDocument10 pagesAon6978 PDFKakang NggaNo ratings yet
- PK616BA: N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETDocument5 pagesPK616BA: N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETGaraShop TecnologiaNo ratings yet
- AON6906A: General Description Product SummaryDocument10 pagesAON6906A: General Description Product SummaryDjalma MotaNo ratings yet
- EMB12N03VDocument5 pagesEMB12N03VChiapin LeeNo ratings yet
- Srfet: General Description Product SummaryDocument7 pagesSrfet: General Description Product SummaryRafael SantosNo ratings yet
- TK8P65W Datasheet en 20140917Document10 pagesTK8P65W Datasheet en 20140917Leudin Russo PedrozaNo ratings yet
- General Description Product Summary: 30V P-Channel MOSFETDocument6 pagesGeneral Description Product Summary: 30V P-Channel MOSFETluis alberto perez monteroNo ratings yet
- Aon 7702 ADocument6 pagesAon 7702 AXlabs MedanNo ratings yet
- AON6710 - N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorDocument5 pagesAON6710 - N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorLangllyNo ratings yet
- TOSHIBA Field Effect Transistor Silicon N Channel MOS Type (π-MOSV)Document6 pagesTOSHIBA Field Effect Transistor Silicon N Channel MOS Type (π-MOSV)uueyNo ratings yet
- AON7548Document6 pagesAON7548Ahmad AmerNo ratings yet
- TSM900N06: 60V N-Channel Power MOSFETDocument8 pagesTSM900N06: 60V N-Channel Power MOSFETshounakroyNo ratings yet
- General Description Product Summary: 150V N-Channel MOSFETDocument6 pagesGeneral Description Product Summary: 150V N-Channel MOSFETJose Luiz da SilvaNo ratings yet
- AON6414AL: General Description Product SummaryDocument6 pagesAON6414AL: General Description Product SummaryholinsunNo ratings yet
- AOD256Document6 pagesAOD256André De Castro MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- AONY36354 AlphaOmegaSemiconductorsDocument10 pagesAONY36354 AlphaOmegaSemiconductorsCHAMOUXNo ratings yet
- AONR32320CDocument6 pagesAONR32320CJalu JajangkarNo ratings yet
- General Description Product Summary: 30V N-Channel MOSFET SdmosDocument7 pagesGeneral Description Product Summary: 30V N-Channel MOSFET SdmosCleiton SilvaNo ratings yet
- Dual N-Channel Enhancement Mode FET Features Excellent RDS(ON) and Low Gate ChargeDocument8 pagesDual N-Channel Enhancement Mode FET Features Excellent RDS(ON) and Low Gate ChargeTimuçin İLTERNo ratings yet
- Donnees Mosfet NTMYS014N06CL - D-2319325Document8 pagesDonnees Mosfet NTMYS014N06CL - D-2319325Philippe GuillemetNo ratings yet
- Aon 7702Document6 pagesAon 7702Agung HaryantoNo ratings yet
- D Product Summary: BV 30V R 20mΩ I 12A: DSS Dson (Max.) DDocument5 pagesD Product Summary: BV 30V R 20mΩ I 12A: DSS Dson (Max.) Dlalukurniawan100% (1)
- NTD4810N, NVD4810N Power MOSFET: 30 V, 54 A, Single N Channel, DPAK/IPAKDocument8 pagesNTD4810N, NVD4810N Power MOSFET: 30 V, 54 A, Single N Channel, DPAK/IPAKBelkis Amion AlbonigaNo ratings yet
- Sonylcdchasisinformation10!21!20119 883 805 ADocument7 pagesSonylcdchasisinformation10!21!20119 883 805 AHamza Abbasi AbbasiNo ratings yet
- TQM250NB06CR: Taiwan SemiconductorDocument7 pagesTQM250NB06CR: Taiwan Semiconductorn tanevarNo ratings yet
- AON6414A: General Description Product SummaryDocument6 pagesAON6414A: General Description Product SummaryDany Vidal UrdeNo ratings yet
- FET B4 N03RDocument9 pagesFET B4 N03RMaslikan AdemNo ratings yet
- Srfet: AOL1712 N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorDocument6 pagesSrfet: AOL1712 N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorkenyunkNo ratings yet
- AOD4184A: General Description Product SummaryDocument6 pagesAOD4184A: General Description Product SummaryAriel dajaoNo ratings yet
- Me 9926Document5 pagesMe 9926Aurelian ZaharescuNo ratings yet
- AONY36352: 30V Dual Asymmetric N-Channel MOSFETDocument10 pagesAONY36352: 30V Dual Asymmetric N-Channel MOSFETrobertjavi1983No ratings yet
- 3055VL DDocument8 pages3055VL DAnonymous t2LU6MiNo ratings yet
- 30V N-Channel AlphaMOS Power MOSFETDocument6 pages30V N-Channel AlphaMOS Power MOSFETFernando TessadriNo ratings yet
- TK6A65D: Switching Regulator ApplicationsDocument6 pagesTK6A65D: Switching Regulator ApplicationsHumberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- General Description: 30V N-Channel MOSFETDocument6 pagesGeneral Description: 30V N-Channel MOSFETFabian OrtuzarNo ratings yet
- TK22E10N1 Datasheet en 20140630-1140092Document10 pagesTK22E10N1 Datasheet en 20140630-1140092Павлин ПейковNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesDatasheet PDFPriyanka ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- AO6402 AlphaOmegaSemiconductorsDocument4 pagesAO6402 AlphaOmegaSemiconductorsMafia BetawiNo ratings yet
- Switching Regulator, DC/DC Converter and Motor Drive ApplicationsDocument6 pagesSwitching Regulator, DC/DC Converter and Motor Drive ApplicationsMaj HusNo ratings yet
- AO4912 Asymmetric Dual N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorDocument8 pagesAO4912 Asymmetric Dual N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect TransistorAntonioPeriniNo ratings yet
- AON7408Document6 pagesAON7408aldo_suviNo ratings yet
- MDD4N20YDocument6 pagesMDD4N20YAmc Forklift ElektrikNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 200V, 3aDocument6 pagesMosfet 200V, 3aguarounetNo ratings yet
- DtaSheet Aol 1448Document6 pagesDtaSheet Aol 1448Emerson VieiraNo ratings yet
- N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET: Product SummaryDocument5 pagesN-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET: Product SummaryImãos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ntmfs4937n DDocument8 pagesNtmfs4937n DSutirtha MaitiNo ratings yet
- 650V 1.5Ω N-Channel MOSFETDocument5 pages650V 1.5Ω N-Channel MOSFETCesar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TPC8065-H TPC8065-H TPC8065-H TPC8065-HDocument9 pagesTPC8065-H TPC8065-H TPC8065-H TPC8065-HRamiro Q ChNo ratings yet
- Switching Regulator and DC DC Converter and Motor ApplicationsDocument6 pagesSwitching Regulator and DC DC Converter and Motor ApplicationsBruno alencarNo ratings yet
- NTD4813N Power MOSFET: 30 V, 40 A, Single N - Channel, DPAK/IPAKDocument8 pagesNTD4813N Power MOSFET: 30 V, 40 A, Single N - Channel, DPAK/IPAKAnonymous t9tLb3WgNo ratings yet
- TK07H90A: Switching Regulator ApplicationsDocument6 pagesTK07H90A: Switching Regulator Applicationsibere cristiano SilvaNo ratings yet
- TK10A60D: Switching Regulator ApplicationsDocument7 pagesTK10A60D: Switching Regulator ApplicationsAlexNo ratings yet
- Silicon N-Channel MOSFET Features and CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesSilicon N-Channel MOSFET Features and CharacteristicsPabloNo ratings yet
- AONR21357 ReemplazoDocument6 pagesAONR21357 ReemplazoDavid Enrique Rivero CahuichNo ratings yet
- D Product Summary: BV 30V R 9mΩ I 50A: DSS Dson (Max.) DDocument6 pagesD Product Summary: BV 30V R 9mΩ I 50A: DSS Dson (Max.) DThoni Tsaqif BRNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16CataNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET basics-IXYS 2Document1 pagePower MOSFET basics-IXYS 2CataNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET basics-IXYS 3Document1 pagePower MOSFET basics-IXYS 3CataNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET basics-IXYS 1Document1 pagePower MOSFET basics-IXYS 1CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18CataNo ratings yet
- Hukum Termodinamika IIDocument21 pagesHukum Termodinamika IIdiky dharmawanNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 17Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 17CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 16CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20CataNo ratings yet
- Hukum Termodinamika IIDocument21 pagesHukum Termodinamika IIdiky dharmawanNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21CataNo ratings yet
- Package Inductance-Infineon 6Document1 pagePackage Inductance-Infineon 6CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 15CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 20CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 18CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 19CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 21CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 13Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 13CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 14CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 12Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET Datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 12CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 11Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 11CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 10Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 10CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 6Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 6CataNo ratings yet
- Understand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 2Document1 pageUnderstand MOSFET datasheet-TaiwanSemicon 2CataNo ratings yet
- Davall Stock Gears Worm Wheel Gear Sets 17pages PDFDocument17 pagesDavall Stock Gears Worm Wheel Gear Sets 17pages PDFharish ahireNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument8 pagesCasesLinh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- HW1Document1 pageHW1mohsenanNo ratings yet
- Project Feasibility Study For The Establishment of Footwear and Other AccessoriesDocument12 pagesProject Feasibility Study For The Establishment of Footwear and Other Accessoriesregata4No ratings yet
- Friends or Lovers (A Novel by Rory Ridley-Duff) - View in Full Screen ModeDocument336 pagesFriends or Lovers (A Novel by Rory Ridley-Duff) - View in Full Screen ModeRory Ridley Duff92% (24)
- ExcelDocument1 pageExcelJosh KempNo ratings yet
- Tourism and Development Planning: Slide 9.1Document19 pagesTourism and Development Planning: Slide 9.1English TimeNo ratings yet
- Ari Globe Valve SupraDocument26 pagesAri Globe Valve SupraAi-samaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Earth WorkDocument39 pagesChapter 4 Earth WorkYitbarek BayieseNo ratings yet
- One SheetDocument1 pageOne Sheetadeel ghouseNo ratings yet
- Epc50-50e Om 2-20Document46 pagesEpc50-50e Om 2-20Sidhi SadanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Design RulesDocument19 pagesModule 3 - Design RulesSamNo ratings yet
- F404-15 Standard Consumer Safety Specification For High ChairsDocument19 pagesF404-15 Standard Consumer Safety Specification For High ChairsAhmed AlzubaidiNo ratings yet
- United States v. Bueno-Hernandez, 10th Cir. (2012)Document3 pagesUnited States v. Bueno-Hernandez, 10th Cir. (2012)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Feasibility ReportDocument10 pagesFeasibility ReportAdityaNo ratings yet
- RCT Methodology ChecklistDocument6 pagesRCT Methodology ChecklistSyahidatul Kautsar NajibNo ratings yet
- CRAPAC Monthly JanDocument4 pagesCRAPAC Monthly JanJasonMortonNo ratings yet
- How To Recover An XP Encrypted FileDocument2 pagesHow To Recover An XP Encrypted FileratnajitorgNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Nutrition: Things You Need To Know AboutDocument2 pagesPost-Operative Nutrition: Things You Need To Know AboutJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior and Marketing Plan ComponentsDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing Consumer Behavior and Marketing Plan ComponentsK59 Ng� V? Minh Th?No ratings yet
- Ict OhsDocument26 pagesIct Ohscloyd mark cabusogNo ratings yet
- MObile InvoiceDocument1 pageMObile Invoicechandra kiran KodavatiNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire For ThesisDocument5 pagesQuestionnaire For ThesisRamiz HassanNo ratings yet
- Psychrometrics Drying Problems SEODocument5 pagesPsychrometrics Drying Problems SEOStephanie Torrecampo Delima100% (2)
- IVECO NEF SeriesDocument36 pagesIVECO NEF SeriesOlivier ORMANNo ratings yet
- Social and cultural geographies of Southeast Asia exploredDocument18 pagesSocial and cultural geographies of Southeast Asia exploredJohn Lemuel MagnayeNo ratings yet
- PACiS GTW EN O C80Document170 pagesPACiS GTW EN O C80paradiseparasNo ratings yet
- MR Khurram Chakwal 6kw Hybrid - 024627Document6 pagesMR Khurram Chakwal 6kw Hybrid - 024627Shahid HussainNo ratings yet
- Toshiba X-Ray Tube Product InfoDocument10 pagesToshiba X-Ray Tube Product InfoJairo ManzanedaNo ratings yet