Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Software Data: Hardware
Uploaded by
Mohammad ShahnurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Software Data: Hardware
Uploaded by
Mohammad ShahnurCopyright:
Available Formats
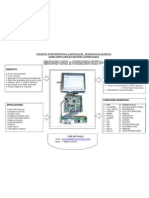
A Geographic Information System (GIS) links locational (spatial) and database (tabular) information and enables
a person to visualize patterns, relationships, and trends. This process gives an entirely new perspective to data
analysis that cannot be seen in a table or list format. The five components of a GIS are listed below.
SOFTWARE
01S software provides the functions and fools
1.:sers need to store, analyze, and display
HARDWARE seographlcal Information. The key sollware
components are
• GIS Software
D ATA
The hardware is the computer and • Database Software One of the most important component of GIS
peripherals on which the GIS operates. Today, • OS Software is the data, II is absolutely essential 111at data be
this could be a centralized oomputer server running • Network Software accura1e. The following are different da1a types:
the UNIX or Windows NT operating systems,
a desktop PC, or an Apple Macintosh. The • Vector Data
computer may operate In Isolation or In a • Raster Data
-----�I
networked configuration. • Image Data
GIS
· Computers • Attribute Data
• Networks
· Peripheral Devices •
• Printers
• Plotters
• Digitizers
PEOPLE METHODS
GIS technology is clearly of limited value without Methods are well designed plans and application•
�pie 10 manage the sySlem and to develop plans specific business rules describing how technology
for applying it. Users of GIS range from highly qualified is applied. This includes the following:
technical specialists to planners, foresters, and market • GuldellnM
•• ..
analysts who use GIS to telp with their everyday work. • Specifications
•'
• Admlnls1rators • Standard•
• Managers • Procedures
• GIS Technicians
• Application Experts
1•
V ,1 ·! "
• End Users
• Consumers ,. • • I . . � \
1 \
You might also like
- Sap BPC Business Blueprint DocumentDocument12 pagesSap BPC Business Blueprint DocumentgeneNo ratings yet
- Components and ObjectivesDocument13 pagesComponents and ObjectivesKorada NaveenNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5 Tutorials: Mechanism Design & AnimationDocument36 pagesCATIA V5 Tutorials: Mechanism Design & AnimationValentinNo ratings yet
- CAD Systems in Mechanical and Production EngineeringFrom EverandCAD Systems in Mechanical and Production EngineeringRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Aquaculture and Fish Farming (PDFDrive)Document234 pagesAquaculture and Fish Farming (PDFDrive)Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Definition and Process of GISDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Definition and Process of GISNOR NAFIESHA FAZIANA AHMAD FAISALNo ratings yet
- Spring Boot PDF Durasoft Spring Boot Notes CompressDocument118 pagesSpring Boot PDF Durasoft Spring Boot Notes Compresssuraj satav100% (3)
- Types of SoftwareDocument39 pagesTypes of SoftwareDann Sarte100% (4)
- Big Data, Predictive Analytics, and Data Analytics in Construction IndustryDocument2 pagesBig Data, Predictive Analytics, and Data Analytics in Construction IndustryPrateek VyasNo ratings yet
- Software Data: Geographic Information SystemsDocument1 pageSoftware Data: Geographic Information SystemsMaxim GhereaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Introduction To Geographic Information SystemDocument35 pagesChap 1 - Introduction To Geographic Information SystemAthirah HattaNo ratings yet
- GGE 4203-Introduction To GIS and Remote Sensing: Lecture TwoDocument26 pagesGGE 4203-Introduction To GIS and Remote Sensing: Lecture TwoKiprono VincentNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument6 pagesREVIEWERJay AnnNo ratings yet
- Geographic Information Systems I: Livingstone AsemDocument40 pagesGeographic Information Systems I: Livingstone Asemedward tamekloeNo ratings yet
- WasssDocument83 pagesWasssፍቅር እስከ መቃብርNo ratings yet
- Basic GISDocument61 pagesBasic GISsaven jayamannaNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument1 pageBrochureGaurav RajputNo ratings yet
- Ggis FinalDocument25 pagesGgis Finalmennamohamed200yNo ratings yet
- Leica Infinity Help v4.1.0 enDocument385 pagesLeica Infinity Help v4.1.0 enWilliams TaipicuriNo ratings yet
- GISA - Components of A GIS - Lecture 2 - Edited14092023Document30 pagesGISA - Components of A GIS - Lecture 2 - Edited14092023Jecinta wNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument1 pageBrochureGaurav RajputNo ratings yet
- DDCA Ch1Document19 pagesDDCA Ch1heloCNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 PDFDocument23 pagesTopic 1 PDFAzry HafizeNo ratings yet
- Wind Catcher DatasheetDocument2 pagesWind Catcher DatasheetSher Amir NasirNo ratings yet
- Intro To GIS and GIS Vector and Raster Data ModelsDocument44 pagesIntro To GIS and GIS Vector and Raster Data ModelsSaumya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Leica Captivate DS 0621en LRDocument2 pagesLeica Captivate DS 0621en LRmichael18071972No ratings yet
- What S New in Mentum Planet 6.0 ExternalDocument63 pagesWhat S New in Mentum Planet 6.0 ExternalhazzanollyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document6 pagesLecture 2JudyNo ratings yet
- Digital Application in Architecture: Geographical Information System (GIS)Document19 pagesDigital Application in Architecture: Geographical Information System (GIS)Tariq UmarNo ratings yet
- Material Fellowship Class 2022 Publishing and Mobile ApplicationDocument28 pagesMaterial Fellowship Class 2022 Publishing and Mobile ApplicationKordas PgtlNo ratings yet
- Etc GIS IntroDocument51 pagesEtc GIS IntroShril K BhardwajNo ratings yet
- GisDocument96 pagesGiscybertechnocomputer861No ratings yet
- Lidar 360 BrochureDocument9 pagesLidar 360 BrochureputrantowardhanaNo ratings yet
- Data Processing SystemsDocument48 pagesData Processing SystemsWage YadoNo ratings yet
- GIS Svy 2 LabDocument219 pagesGIS Svy 2 LabHassan BhattiNo ratings yet
- Ds Gigasmart RsDocument6 pagesDs Gigasmart RsErnesto MorenoNo ratings yet
- DSP ArchitechtureDocument6 pagesDSP Architechtureankur22021980No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GisintroductionDocument14 pagesChapter 1 GisintroductionelNo ratings yet
- Competencies: Basic Application SoftwareDocument7 pagesCompetencies: Basic Application Softwareapi-19794302No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - (Add. Notes)Document20 pagesChapter 1 - (Add. Notes)Mohamad Airil Imran Bin MazalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-7 Kroenke, David, Mcgraw-Hill, 1992: Management Information Systems, 2 Ed., NDDocument16 pagesChapter 5-7 Kroenke, David, Mcgraw-Hill, 1992: Management Information Systems, 2 Ed., NDIrfan ALiNo ratings yet
- Unit I I (C) Components and Functional Elements of GIS TBMDocument22 pagesUnit I I (C) Components and Functional Elements of GIS TBMNo StanzinNo ratings yet
- Gis App and Plannin of Gis DatabaseDocument21 pagesGis App and Plannin of Gis DatabaseAnkit R ShahNo ratings yet
- GIS1Document97 pagesGIS1YONAS TADELENo ratings yet
- Ec 1403 Satellite Communication: Eographical Nformation Ystem (Gis)Document23 pagesEc 1403 Satellite Communication: Eographical Nformation Ystem (Gis)sharonfranklinNo ratings yet
- Inpho Software: LpmasterDocument2 pagesInpho Software: LpmasterDelasdriana WiharjaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Data Management and Processing SystemDocument43 pagesUnit 2 Data Management and Processing SystemShasan SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Arc GIS - Dr. Ahmed AbdallahDocument76 pagesLecture 2 - Arc GIS - Dr. Ahmed Abdallahshayma190852No ratings yet
- Unit2 GisSpatialDataModels Updated KRBDocument65 pagesUnit2 GisSpatialDataModels Updated KRBBhosadi WalaNo ratings yet
- Pamfleat - Multibeam Survey and Processing-Charting - Product LeafletDocument2 pagesPamfleat - Multibeam Survey and Processing-Charting - Product LeafletMuhammad Rizky ArifiantoNo ratings yet
- Practical Work in Geography Ch-6 Gis NewDocument44 pagesPractical Work in Geography Ch-6 Gis NewSooraj ChoukseyNo ratings yet
- Components of GISDocument10 pagesComponents of GISNagendra DuhanNo ratings yet
- Basic of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)Document111 pagesBasic of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)Patrick MasaluNo ratings yet
- Cpena 120 Topic 1Document11 pagesCpena 120 Topic 1lykarossele.nuestroNo ratings yet
- Deswik - CAD Module SummaryDocument2 pagesDeswik - CAD Module Summarymatias79No ratings yet
- Joint Research Centre: © European Union, 2013Document2 pagesJoint Research Centre: © European Union, 2013Makhlouf RejebNo ratings yet
- CompGraph QizhongDocument13 pagesCompGraph Qizhongnicholas040903No ratings yet
- Introduction To GeoInformaticsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To GeoInformaticssaviouraliyuNo ratings yet
- 8085 Architecture Instruction SetDocument92 pages8085 Architecture Instruction SetMadhusmita BarikNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: A Practitioners Approach, The Unified Modeling Language User GuideDocument2 pagesSoftware Engineering: A Practitioners Approach, The Unified Modeling Language User GuideSeher Cemre TuranNo ratings yet
- Cpen 125 Reviewer1Document29 pagesCpen 125 Reviewer1lykarossele.nuestroNo ratings yet
- ARM10Document1 pageARM10sudhakar472No ratings yet
- LSL 88 LampsDocument2 pagesLSL 88 LampsCarlos GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- The Design and Implementation of Geographic Information SystemsFrom EverandThe Design and Implementation of Geographic Information SystemsNo ratings yet
- Factors Influence Expatriates Compensation in MNC 2023Document11 pagesFactors Influence Expatriates Compensation in MNC 2023Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Processes in Coastal and Marine Ecosystems: Executive SummaryDocument30 pagesNitrogen Processes in Coastal and Marine Ecosystems: Executive SummaryMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Lesson I. Satellite Oceanography OverviewDocument19 pagesLesson I. Satellite Oceanography OverviewMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Final Report Mud Crab Bangladesh March 2013Document22 pagesFinal Report Mud Crab Bangladesh March 2013Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of Spatial Data and The Design of Data Model: Tiejun CUIDocument6 pagesCharacteristic of Spatial Data and The Design of Data Model: Tiejun CUIMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- MUCK Corer Ekman Dredge: or Contact Us at Laccore@umn - EduDocument2 pagesMUCK Corer Ekman Dredge: or Contact Us at Laccore@umn - EduMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Generation and Migration.: October 2006Document23 pagesHydrocarbon Generation and Migration.: October 2006Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document35 pagesChapter 11Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Emff Feapposition FinalDocument6 pagesEmff Feapposition FinalMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- DRAFT Future Trends Report 3rd EditionDocument68 pagesDRAFT Future Trends Report 3rd EditionMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Operational OceanographyDocument27 pagesAn Overview of Operational OceanographyMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Vector Data Analysis: Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer WidthDocument21 pagesChapter 11 Vector Data Analysis: Box 11.1 Riparian Buffer WidthMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Eden Help Gis FormatDocument6 pagesEden Help Gis FormatMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Attribute Data Input and ManagementDocument13 pagesChapter 8. Attribute Data Input and ManagementMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Catching Plankton ResourcesDocument5 pagesCatching Plankton ResourcesMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Raster Data Model: Box 4.1 Rules in Determining A Categorical Cell ValueDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Raster Data Model: Box 4.1 Rules in Determining A Categorical Cell ValueMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Basic Definition of GISDocument45 pagesBasic Definition of GISMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- CastanosM1998 Farming Techniques For SeaweedsDocument8 pagesCastanosM1998 Farming Techniques For SeaweedsMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Agronomy 11 01415Document27 pagesAgronomy 11 01415Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Application Note 35Document5 pagesApplication Note 35Mohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept in GISDocument32 pagesBasic Concept in GISMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Organic Phosphorus in Marine Sediments: Chemical Structure, Diagenetic Alteration, and Mechanisms of PreservationDocument285 pagesOrganic Phosphorus in Marine Sediments: Chemical Structure, Diagenetic Alteration, and Mechanisms of PreservationMohammad ShahnurNo ratings yet
- Emc Networker Module For Microsoft For SQL Vdi: User GuideDocument180 pagesEmc Networker Module For Microsoft For SQL Vdi: User Guidepuneetgoyal100No ratings yet
- A Star Is Born Eldin's BlogDocument3 pagesA Star Is Born Eldin's BlogEldin ZaimovićNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC Networking N1100 Series Spec SheetDocument3 pagesDell EMC Networking N1100 Series Spec SheetAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- HCIqDocument78 pagesHCIqOanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Web 3 MetDocument16 pagesWeb 3 MetpedrovesgamypNo ratings yet
- STC Anuual Report 2019-EnDocument174 pagesSTC Anuual Report 2019-EnAlexis johnNo ratings yet
- Science: Bhadrak Autonomous CollegeDocument16 pagesScience: Bhadrak Autonomous CollegeSwarupa SwainNo ratings yet
- CSE 231L Lab Report 1Document23 pagesCSE 231L Lab Report 1Rayhan Amin 2212830042No ratings yet
- Node - Js Interview Questions: PremiseDocument19 pagesNode - Js Interview Questions: PremiseSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Hi-4Tc Performance: Motorcycle IgnitionDocument4 pagesHi-4Tc Performance: Motorcycle IgnitionoldtrukluvrNo ratings yet
- Banking Resume TemplateDocument8 pagesBanking Resume Templateafiwhyqrv100% (2)
- User Manual: REM - Land / BLDG - Lease in ContractsDocument78 pagesUser Manual: REM - Land / BLDG - Lease in ContractsEE civil DimapurNo ratings yet
- ZTEWelink+MG2639 V3+Datasheet V1.3Document2 pagesZTEWelink+MG2639 V3+Datasheet V1.3राघवतोतलाNo ratings yet
- Business Rule TemplateDocument1 pageBusiness Rule TemplateThomz AsadinawanNo ratings yet
- WatchPower User ManualDocument47 pagesWatchPower User Manualtongai100% (1)
- Minimizing Active Power LossesDocument8 pagesMinimizing Active Power LossesChelsea wijayasanthaNo ratings yet
- Konfiguracija RelejaDocument7 pagesKonfiguracija RelejaAldijana ZildžićNo ratings yet
- The Basic of SAPDocument23 pagesThe Basic of SAPKasim KhanNo ratings yet
- Unique Identification Number - RahulDocument31 pagesUnique Identification Number - RahulNitika Kataria0% (1)
- Moxa Tech Note - EtherNet IP Scanner Configuration For MGate 5105-MB-EIPDocument9 pagesMoxa Tech Note - EtherNet IP Scanner Configuration For MGate 5105-MB-EIPSergio RiveraNo ratings yet
- Numerical Ability Worksheet 27Document3 pagesNumerical Ability Worksheet 27Areum YuNo ratings yet
- Itpm Chapter 2Document21 pagesItpm Chapter 2Misale FelemaNo ratings yet
- Comm Net Exam 2016Document22 pagesComm Net Exam 2016nazligul keskeNo ratings yet
- Important Reminders: Step 1Document4 pagesImportant Reminders: Step 1Magdaleno GalaponNo ratings yet
- SAXSIM 2019 Schramm UweDocument18 pagesSAXSIM 2019 Schramm UweADVOKASI PPI MALAYSIANo ratings yet
- NDA M5 SystemsDocument2 pagesNDA M5 Systemslagib78166No ratings yet
- Over Current ProctectionDocument25 pagesOver Current ProctectionSarah FrazierNo ratings yet