Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics 1
Uploaded by
Agyao Yam FaithCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics 1
Uploaded by
Agyao Yam FaithCopyright:
Available Formats
MIDTERM LESSON IN GENETICS 1 CELL CYCLE
ION CHANNEL DEFECTS 2 Types of Cell Cycle:
Channelopathies-are disease caused by Mitosis-is a process of forming
distributed function of ion identical daughter cells by
channel subunits or replicating and dividing the original
the proteins that regulates chromosomes, in effect making a
them. cellular Xerox.
Electrical Signals-are critical for the Meiosis-a process where a single
functions of cell divides twice to produce four
neurons, muscle cells, and cells containing half the original
cardiac amount of genetic information.
myocytes.
Proteins-which regulate electrical signalling 2 Phases of Cell Cycle:
in this a.) Interphase-DNA replication
cells, including voltage gated ion G1-longest period within
channel, several days and maturity of
are logical sites where abnormality the genetic information
might S phase - shorter period
lead to disease. within an hour only.
G2 phase -matured DNA can
Genetic and Biophysical Approaches proceed to mitosis.
Are being used to show that several
disorders result from mutations in 4 Phases of Mitosis:
voltage gated ion channels. 1.) Prophase-the word “pro” in
prophase means before.
FOR EXAMPLE: -the first stage of Mitosis,
1. Migraine, headache and some forms DNA coils tightly.
of epilepsy have been shown to 2.) Metaphase-the first letter of
result from mutations in voltage metaphase which is “M” stands for
gated Ca2+¿ ¿channel genes. middle.
2. QT syndrome is known to result -where chromosomes
from mutations in either K +¿¿ or attach to the spindle at their
Na+¿¿channel genes. centromere and align along
the centre of the cell, which
Where Channelopathies cause by? is called the “equator”.
Genetic 3.) Anaphase-the first letter of
Mutations anaphase which is “A” stands for
Biophysical away.
-the plasma membrane
Myocytes-also known as muscle cell, they indents at the centre, where
are long, tubular cells that develop from the metaphase
myoblasts. chromosomes line up.
Mutations-is a change that occurs in our 4.) Telophase-the final stage of mitosis,
DNA sequence, either due to mistakes the cell looks like a dumbbell with a
when the DNA is copied or as the result of set of chromosomes at each end.
environmental factors. -where the new cells
separate.
Chromosomes-are made up of DNA and in meiosis. Two daughter cells are
protein combined as chromatin. produced after mitosis and
Chromatids-paired duplicated chromosome cytoplasmic division, while four
during joined by a single centromere. daughter cells are produced after
Chromatin-is the coplex combination of meiosis.
DNA and proteins that makes up
chromosomes. CANCER CELLS & APOPTOSIS:
Gametes-are the cells used during sexual
reproduction to produce a new individual Cancer Cells-the substances that causes
organisms or zygote. cancer are called “carcinogen”.
-is the uncontrolled growth of
Note: abnormal cells in the body.
In humans there is 1 set of 23 -caused by accumulated
chromosomes for the female and 1 damage of genes.
set of 23 chromosomes for the
male. Types of Cancer:
If both sex combined we end up a.) Carcinomas-begins in the skin or
with 46 chromosomes. mostly in tissues. One of the
During interphase the cell duplicates common type of cancer
the chromosomes, when you
duplicate 46 chromosomes, you still EXAMPLE:
say there are 46 chromosomes if the Prostate Cancer-for male
newly duplicated portion still attach Breast Cancer-for female
at the centromere region but there Lung Cancer-common for male,
are actually 92 chromatids. smokers.
Colorectal Cancer-focuses on
MITOSIS intestines.
Skin cell
Stomach cell b.) Sarcomas-sarcoma begins in the
Makes body cells tissues that support and connect the
MEIOSIS body.
Sperm cell -a sarcoma can develop in
Egg cell fat,muscles,nerves,tendons,
Makes gametes joints,blood vessels,lymph
vessels,cartilage, or bone.
*Both mitosis and meiosis involved in
making new cells. c.) Leukemia-it is also known as the
*2 daughter cells in mitosis call them cancer of the blood.
“diploid” while 4 daughter cells in meiosis -begins when healthy
call them “haploid”. blood cells change and grow
uncontrollably.
Homologous-means that the chromosomes
are approximately the same size and they 4 Types of Leukemias:
contain the same type of genes at the same 1. Acute lymphocytic leukaemia
location. 2. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
3. Acute myeloid leukaemia
DIFFERENCE OF MITOSIS AND MEOSIS: 4. Chronic myeloid leukaemia
Mitosis involves the division of body
cells, while meiosis involves the Note:
division of sex cells. The division of a Acute-means sudden/biglaan
cell occurs once in mitosis but twice Chronic-accumulation
*If in lymphocytic it involves -Morphe means “form and
lymphocyte and monocyte. logres means “word”.
*If in myeloid it involve meutrophil,
basophil, and eosinophil. 3 Main Types:
a.) Cellular Morphology-is essential in
d.) Lymphomas-begins in lymphatic identifying the shape, structure,
system. form, and size of cells.
-the lymphatic system is b.) Tissue Morphology-typical
a network of vessels and applications involve observing shape
glands that help fight changes of grooves, pores, blebs or
infection. microvilli on the cellular.
c.) Organ Morphology
2 Main Types:
a.) Hodgkin Lymphoma-is a type of Epithelial Cells-are cells that come from
lymphoma in which cancer surfaces of your body, such as your skin,
originates from a specific type of blood vessels, urinary tract, or organs.
white blood cells called
lymphocytes. Squamous
b.) Burkitt Lymphoma-is a form of non- Means wide.
Hodgkin’s lymphoma in which Are thin, flat cells that look like fish
cancer starts in immune cells B-cells. scales, and are found in the tissue
Associated with impaired immunity that forms the surface of the skin.
and is rapidly fatal is left untreated.
Cuboidal
*55% of our blood is RBC while the rest are Means cubed.
divided by WBC, platelets, and Plasma. It is a single layer thick and made of
*WBC and platelets are the lowest. cube-shape cells.
Apoptosis Columnar
Program cell death/ cellular suicide. Means rectangular
Collection by immune cells
Remove cells during development, *Chromosomes-has 2nm-4nm plant.
eliminated potentially cancerous *DNA-has 2nm thick and present inside the
and virus-infected cells, maintains chromosomes.
balance in the body. *1 nucleosome=200 HP
Necrosis *Nucleus-is the smallest molecule inside
Normal cells dies because of injury. the chromatin.
*Tetramer-means four
Splin *Linker DNA-has the same structure.
Found at the back of stomach.
Where the gateway of dead cells. DNA+Protein=Histones
*50% genes from the mother and 50%
Apoptosis vs. Necrosis genes from the father.
They are killed by things that harm
them (such as toxic, chemical, or Special Type of Chromosomes
physical injury), a process called Special because not all the species
necrosis. possess this types of chromosomes.
CHROMOSOMES 1.) Salivary Gland
Also known as polytene.
Morphology-physical appearance.
This chromosomes undergo
complete stomatic pairing to form
units of identical chromosomes
joined their length (in parallel) to
one another.
Polytene-are chromosomes found in the
interphase nuclei and the salivary gland
cells in larvae diptera.
Diptera-another species of bacteria
chromosomes. Also known as
Corynebacterium diptheriae.
2.) Lampbrush Chromosomes-this are
the largest known chromosomes
found in the yolk-rich oocytic nuclei
of certain vertebrates such as fishes,
amphibians, reptiles, and birds.
Female-XX gene
Male-XY gene
Sperm Cell-the one who dictates the baby’s
gender.
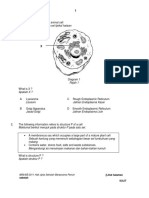
KARYOTYPE IN MAN
Karyotyping
Picture of a person’s chromosomes
The chromosomes are isolated
stained and examined under the
microscope.
WBC-soldiers of the human body.
You might also like
- Genetics TextbookDocument2,553 pagesGenetics Textbookivanna salazar91% (11)
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionLavanya Thevi100% (1)
- Biol Activity 5 Word2003Document16 pagesBiol Activity 5 Word2003Faith Jessica ParanNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science11 - Q1 - MODULE-6 Edited - 08082020Document34 pagesPhysical-Science11 - Q1 - MODULE-6 Edited - 08082020Mary Ann Isanan79% (34)
- Integrating The Theory of Multiple Intelligences in The Teaching of Cell DivisionDocument16 pagesIntegrating The Theory of Multiple Intelligences in The Teaching of Cell DivisionAhmad IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Help Your Kids With ScienceDocument258 pagesHelp Your Kids With ScienceThihaThant423191% (23)
- Genetics 1Document4 pagesGenetics 1Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Session 3: Cell Division: Key ConceptsDocument7 pagesSession 3: Cell Division: Key ConceptsKaylaNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument27 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisNicolette BingtanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle N Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell Cycle N Cell DivisionDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Prometaphase: Somatic Cells Somatic CellsDocument4 pagesPrometaphase: Somatic Cells Somatic CellsMica CapistranoNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Chapter 8Document13 pagesBIO 101 Chapter 8mkmanNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020Document20 pagesTOPIC 3 CELL AND NUCLEAR DIVISION My Notes 2020reeNo ratings yet
- CELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Document7 pagesCELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Alexander LukashenkoNo ratings yet
- Izat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmDocument18 pagesIzat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmSuhailina Mohd IkhwanNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish BetweenDocument2 pagesAneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Betweeneclipse1130No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle LectureDocument3 pagesCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 3.1 Cell Division and Development - OCR (B) Biology A-LevelDocument8 pagesDefinitions - Topic 3.1 Cell Division and Development - OCR (B) Biology A-LevelJawaher KarimNo ratings yet
- BIODocument7 pagesBIOREYES, Kyla Marie M.No ratings yet
- Processes in Nucleus Cell Biology: By: Furi Intan Wahyuni 4401408061Document10 pagesProcesses in Nucleus Cell Biology: By: Furi Intan Wahyuni 4401408061anon_811681548No ratings yet
- Module 2 Meiosis and MitosisDocument88 pagesModule 2 Meiosis and MitosisSevdred CadelinaNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesCell BiologyJen JenNo ratings yet
- Mitosis V MeiosisDocument5 pagesMitosis V MeiosisddaarrsshhiittNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument6 pagesMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - Cell DivisionDocument5 pages2.5 - Cell DivisionAlvin JovanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Document42 pagesChapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Nehjoy GerangueNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNo ratings yet
- MustakDocument3 pagesMustakMh Mari HereNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Note-Genetics Exam GuideDocument6 pagesLecture-Note-Genetics Exam GuideRoCkEnY FlOrEsNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Reproduction ScienceDocument43 pagesCellular-Reproduction ScienceMiel GaboniNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell Division Skeleton NotesDocument15 pages1.6 Cell Division Skeleton Notesadri baigorriNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Document96 pagesMitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- Cell DIVISIONDocument33 pagesCell DIVISIONSharifah NurainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document4 pagesLesson 6Thea MillanesNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell DivisionDocument5 pages1.6 Cell DivisionmariamNo ratings yet
- Batterjee Medical College (BMC) FAST (Preparatory Year) Biology Department 2012-2013Document14 pagesBatterjee Medical College (BMC) FAST (Preparatory Year) Biology Department 2012-2013edain84No ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 4 FinalDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 4 FinalJamille Jam BoholNo ratings yet
- General-Biology-1 - Q1 - Week 4-1-9Document9 pagesGeneral-Biology-1 - Q1 - Week 4-1-9Paul James Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes-Part-4Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-4kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- Honors Biology Ch. 8 NotesDocument9 pagesHonors Biology Ch. 8 NotesChelsey Fowler100% (9)
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- To Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksDocument34 pagesTo Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksPawpaw Chan0% (1)
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleRenzdy MejillaNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology: The CellDocument41 pagesCape Biology: The CellMatt BarhamNo ratings yet
- History of GeneticsDocument13 pagesHistory of GeneticsColeen AvellonesNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 3 2Document9 pagesExercise No. 3 2ramirezllei942No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Structure of Chromosomes XRDocument16 pagesStructure of Chromosomes XRhrishikeshanil123No ratings yet
- What Happens When Food Reaches The StomachDocument9 pagesWhat Happens When Food Reaches The StomachAvegail MantesNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Division BSC StudentsDocument64 pagesReview of Cell Division BSC StudentsKripa SusanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- W9 Mitosis Chapter11Document26 pagesW9 Mitosis Chapter11Ibrahim AlibrahimNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE - MergedDocument26 pagesCELL CYCLE - Mergedsayantanbiswas00768No ratings yet
- Biology Defenition of TermsDocument13 pagesBiology Defenition of TermsJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- 5.cell DivisionDocument54 pages5.cell DivisionRaymond LundaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesActivity 2 Cell DivisionJL Masangcay DayagNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Name: Ibuos, April S. Year and Section: A-1 BSN Subject and # of Module: MODULE 9-10 PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Date Submitted: April 12,2021Document6 pagesName: Ibuos, April S. Year and Section: A-1 BSN Subject and # of Module: MODULE 9-10 PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Date Submitted: April 12,2021Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- 15HWMechanics12 AnswersDocument4 pages15HWMechanics12 AnswersAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chem Quiz 3to6Document2 pagesGen. Chem Quiz 3to6Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- H.A FinalDocument9 pagesH.A FinalAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: James Vincent S. Ibuos - Antonette Franke - Saint Tonis College Inc.Document49 pagesOrganic Chemistry: James Vincent S. Ibuos - Antonette Franke - Saint Tonis College Inc.Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Name:Ibuos, April S. A-1 BSN Purposive Communication Module 7-8 Module #7Document11 pagesName:Ibuos, April S. A-1 BSN Purposive Communication Module 7-8 Module #7Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- H.A FinalDocument9 pagesH.A FinalAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 General Physics 2 ExamDocument1 pageGrade 12 General Physics 2 ExamAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read and Analyze The Following Questions Well and Answer Each Item by Shading The Box Aligned To TheDocument4 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICES: Read and Analyze The Following Questions Well and Answer Each Item by Shading The Box Aligned To TheAgyao Yam Faith0% (1)
- Questions: 1.: R R R IR VDocument5 pagesQuestions: 1.: R R R IR VAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth ScienceAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Department of Teacher Education: Final ExaminationDocument10 pagesDepartment of Teacher Education: Final ExaminationAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry ActivityDocument4 pagesAnalytical Chemistry ActivityAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- College of Teacher Education: Midterm ExaminationDocument11 pagesCollege of Teacher Education: Midterm ExaminationAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 2Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics 2Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- College of Teacher Education: Saint Tonis College, IncDocument3 pagesCollege of Teacher Education: Saint Tonis College, IncAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Summative Math-7Document3 pagesSummative Math-7Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Summative English-7Document3 pagesSummative English-7Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- JhaninaDocument2 pagesJhaninaAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Summative Tle 7Document3 pagesSummative Tle 7Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Summative 7 Answer SheetDocument9 pagesSummative 7 Answer SheetAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- NAME: - SUBJECT: Mathematics in The Modern World COURSE AND YEARDocument4 pagesNAME: - SUBJECT: Mathematics in The Modern World COURSE AND YEARAgyao Yam Faith100% (1)
- Readingd in Philippine History Fabro, Lesly Ann A. DEC. 15, 2020Document3 pagesReadingd in Philippine History Fabro, Lesly Ann A. DEC. 15, 2020Agyao Yam Faith100% (1)
- College of Teacher Education: F = m g = ρ V gDocument5 pagesCollege of Teacher Education: F = m g = ρ V gAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Readingd in Philippine History Fabro, Lesly Ann A. DEC. 15, 2020Document3 pagesReadingd in Philippine History Fabro, Lesly Ann A. DEC. 15, 2020Agyao Yam Faith100% (1)
- Readingd in Philippine History Fabro, Lesly Ann A. DEC. 15, 2020Document3 pagesReadingd in Philippine History Fabro, Lesly Ann A. DEC. 15, 2020Agyao Yam Faith100% (1)
- Class Record: Region Division School Name School Id School YearDocument8 pagesClass Record: Region Division School Name School Id School YearAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Week 3: O B E L U SDocument3 pagesMathematics Week 3: O B E L U SAgyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument9 pagesNotesAllysa Dela Justa TalentoNo ratings yet
- Brevet Biology Session 2 2016 EnglishDocument4 pagesBrevet Biology Session 2 2016 EnglishNick PiresNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AnomaliesDocument30 pagesChromosomal AnomaliesJohn MccartneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Biological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesDocument19 pagesChapter 4 - The Biological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesELOISA N. CASANE100% (1)
- MD AnatomyDocument16 pagesMD AnatomyJaydenNo ratings yet
- Brs Embryology Q&ADocument41 pagesBrs Embryology Q&ASURG BLOCK100% (1)
- Dictionary of Gene 00 K NigDocument197 pagesDictionary of Gene 00 K NigcamsfNo ratings yet
- ch.13 Meiosis Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesch.13 Meiosis Guided ReadingGrace SalaNo ratings yet
- Extra Practise Answers To Practise Questions Not On Test Topic 2 Cells 1 HourDocument7 pagesExtra Practise Answers To Practise Questions Not On Test Topic 2 Cells 1 HouremmaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - 4TH Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesScience 8 - 4TH Quarter ExamJohn Lope BarceNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document12 pagesDay 2Maygel pasaforteNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions of Use For Amoeba Sisters Answer KeysDocument3 pagesTerms and Conditions of Use For Amoeba Sisters Answer KeyscokcreNo ratings yet
- Bonus: Here's Your Perfect By: Jamie MILLERDocument47 pagesBonus: Here's Your Perfect By: Jamie MILLERJack KayatNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument52 pagesBiology Notessree220100% (1)
- Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction: Lesson SummaryDocument14 pagesCell Growth, Division, and Reproduction: Lesson SummaryRylie Degeer50% (2)
- Wk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionDocument34 pagesWk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionShanikMendozaNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Class X - Delhi Code No. 31/1/1: Section - ADocument7 pagesMarking Scheme Class X - Delhi Code No. 31/1/1: Section - AlembdaNo ratings yet
- 2022 AJSO Exam With AnswersDocument24 pages2022 AJSO Exam With AnswersWelly Boss HwiNo ratings yet
- # Form 4 Chapter 6 Biology Cell Division Worksheets Cheryl ScienceDocument12 pages# Form 4 Chapter 6 Biology Cell Division Worksheets Cheryl ScienceVELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 1 Final F4 SBP 2011Document39 pagesQuestion Paper 1 Final F4 SBP 2011Zara LuvoneNo ratings yet
- Gamsat Sample Preview 6Document10 pagesGamsat Sample Preview 6Lily GuoNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceDocument35 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 To 4 Philo To Sexual SelfDocument38 pagesModule 1 To 4 Philo To Sexual SelfMaryjoy MorallosNo ratings yet
- IGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 Opportunities For Practical ActivitiesDocument46 pagesIGCSE BIOLOGY 0610 Opportunities For Practical ActivitiesRyan JenningsNo ratings yet
- Bull Selection PDFDocument50 pagesBull Selection PDFGigiPetreaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument31 pagesCell DivisionShin Thant Ko B10 June SectionNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesCell Biology Questions and Answersapi-19916399No ratings yet