Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Erica P. Manlunas - Tools Used in Community Diagnosis
Erica P. Manlunas - Tools Used in Community Diagnosis
Uploaded by
Erica P. ManlunasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Erica P. Manlunas - Tools Used in Community Diagnosis
Erica P. Manlunas - Tools Used in Community Diagnosis
Uploaded by
Erica P. ManlunasCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Erica P.
Manlunas Date: September 24,2021
BSN 3-A
1. In your opinion, what comprises demography and explain each component.
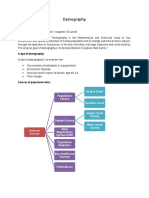
-For me, Demography is the study of the human population size, composition and distribution
in space.
Population size- simply refers to the number of people in a given place or area at a given time.
Describing Population Size Ways in Measuring population size by determining Increase in
population.
Population composition- Characterized in relation to certain variables such as age,
sex, occupation or educational level. Age and sex composition -the age and sex composition
of the population can be described at the same time using a population pyramid. It is a graphical
presentation of the age and sex composition of the population.
Describing spatial distribution- Describes how people are distributed in a specific geographic
location. The distribution of the population and space can be described in terms of urban rural
distribution, population density and crowding index. The measures help the Nurse decide how
meager resources can be justifiably allocated based on concentration of population in a certain
place.
2. Why is it important to know the demography of a certain community?
-Demographics, It's vital to understand who makes up the community. Age, gender, race and
ethnicity, marital status, education, number of people in household, first language these and
other statistics make up the demographic profile of the population. When you put them
together it gives you a clear picture of who community residents are. Demographic data can
help provide a basis for understanding communities as they are now, where they've been and
where they're headed. It can be a powerful tool for tracking change over time and for
uncovering the needs or strengths of a community to guide planning, policy development or
decision making.
3. How is it relevant in the health care delivery system?
-The aging of the population affects the demand for all health care services, including hospitals,
and long-term care. Older persons use more health services than their younger counterparts
because they have more health problems. They are also hospitalized more often and have longer
lengths of stay than younger persons. Changes in population size, age, race and ethnicity affect
the health-care resources needed, the cost of care provided, and even the conditions associated
with each population group. Health-care organizations will have to adapt quickly to meet their
patients’ changing needs all while addressing health-reform requirements.
You might also like
- Age and Sex Structure of Population (2) AssignmentDocument24 pagesAge and Sex Structure of Population (2) Assignmenteman azharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Opthalmic Surgeon On Hong KongDocument6 pagesChapter 20 - Opthalmic Surgeon On Hong KongErica P. Manlunas100% (3)
- Cultural CompetenceDocument19 pagesCultural Competencekmurphy100% (6)
- Public Health C2Document8 pagesPublic Health C2Aprian AcunaNo ratings yet
- Shuby WorkDocument5 pagesShuby WorkJR 180No ratings yet
- Population StudiesDocument5 pagesPopulation StudiesissemoiseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Demography IntroductionDocument13 pagesLecture 1. Demography IntroductionBiruk MengstieNo ratings yet
- 1st Introductory LectureDocument2 pages1st Introductory LectureDr. Zulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- The Study of Demography Encompasses The Following: A. Size and Shape of PopulationDocument1 pageThe Study of Demography Encompasses The Following: A. Size and Shape of PopulationArlene DaroNo ratings yet
- Population Study of SMKCDocument20 pagesPopulation Study of SMKCAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- CHN NCLEX QuestionsDocument58 pagesCHN NCLEX QuestionsKatriona IntingNo ratings yet
- Population and Society VI Sem BA SociologyDocument57 pagesPopulation and Society VI Sem BA SociologybirajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document8 pagesLesson 11jana whiteNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 NUR 1214 Week 4 DemographyDocument17 pagesCHN 2 NUR 1214 Week 4 DemographyLorraine Jazmine AquinoNo ratings yet
- How Cultural Identity Influences Health For Individuals and CommunitiesDocument6 pagesHow Cultural Identity Influences Health For Individuals and Communitiesclive muchokiNo ratings yet
- Population ConceptsDocument11 pagesPopulation ConceptsItisshatakshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1zenakid19No ratings yet
- Community Study OverviewDocument20 pagesCommunity Study OverviewShereen Mohamed Soliman HammoudaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Demography, Health Statistics & EpidemiologyDocument4 pages1.2 Demography, Health Statistics & Epidemiologyライ0% (1)
- Health Care Needs of A Population Cannot Be Measured or Met Without Knowledge of Its Size and CharacteristicsDocument1 pageHealth Care Needs of A Population Cannot Be Measured or Met Without Knowledge of Its Size and CharacteristicssmandangNo ratings yet
- Ipe Asng FaisalDocument14 pagesIpe Asng FaisalMuhammad YounisNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Human Populations."Document6 pagesCharacteristics of Human Populations."Vernika JainNo ratings yet
- Demographic Variables Involved in Formulation of Population PolicyDocument2 pagesDemographic Variables Involved in Formulation of Population PolicyEndugu shanti prasadNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 - Perencanaan Evaluasi KesehatanDocument20 pagesPertemuan 4 - Perencanaan Evaluasi KesehatanSepti19No ratings yet
- Community AssessmentDocument9 pagesCommunity AssessmentKristel AnneNo ratings yet
- People and The EnvironmentDocument2 pagesPeople and The EnvironmentJenmae Dacullo MansiguinNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument22 pagesDemographyTewogbade AdeyinkaNo ratings yet
- Demography Is The Study of Human PopulationsDocument1 pageDemography Is The Study of Human Populationsumali.ebNo ratings yet
- Defining Cultural Competence - A Practical Framework For Addressing RacialEthnic Disparities in Health and Health CareDocument10 pagesDefining Cultural Competence - A Practical Framework For Addressing RacialEthnic Disparities in Health and Health CareMaulidza SiltaNo ratings yet
- Censuse, Vital Events and StatisticsDocument2 pagesCensuse, Vital Events and StatisticsDr. Zulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit - I DemographyDocument17 pagesUnit - I DemographyPhoto GiftNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and CommunityDocument7 pagesNursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and CommunityMae CalicaNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument7 pagesDemographyPaul EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CSR Arianne EsmenaDocument11 pagesChapter 1 CSR Arianne EsmenaTwinie MendozaNo ratings yet
- HC 102 Handouts 1Document6 pagesHC 102 Handouts 1Phantom ScourgeNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Population EducationDocument13 pagesMeaning of Population EducationSteve Mandate100% (2)
- Comm Health NursDocument8 pagesComm Health NursMatt DavidNo ratings yet
- 4 SS 11 PopulationDocument5 pages4 SS 11 PopulationMario BaileyNo ratings yet
- CONTEMPODocument5 pagesCONTEMPOchrisphybatchi28No ratings yet
- Week 8-9 - Population and CommunitiesDocument4 pagesWeek 8-9 - Population and CommunitiesDammy FNo ratings yet
- 02 Scope of Demography Study PoolDocument3 pages02 Scope of Demography Study PoolMuhammad AlamNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Finals ReviewerDocument32 pagesContemporary Finals ReviewerShay GenillaNo ratings yet
- Week 1-3 Lessons Family Planning Terminologies: Plans/Glossary - AspxDocument8 pagesWeek 1-3 Lessons Family Planning Terminologies: Plans/Glossary - AspxMa. Angelica GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Care With Indigenous Populations Considering The Role of Health Care Systems in Health DisparitiesDocument26 pagesIntegrated Care With Indigenous Populations Considering The Role of Health Care Systems in Health DisparitiesCale Holloway100% (1)
- 428441A21 Social DemographyDocument7 pages428441A21 Social DemographyPhuong Nguyen Ngoc BaoNo ratings yet
- SOC 104 2021 - 2022 Lecture Note 1Document4 pagesSOC 104 2021 - 2022 Lecture Note 1Yusuf Zainab100% (1)
- GeographyapproachesDocument3 pagesGeographyapproachesDE hAwKNo ratings yet
- CCHI Special Population Report - FINALDocument21 pagesCCHI Special Population Report - FINALHosam MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Community DiagnosisDocument184 pagesCommunity Diagnosisstephanie valerioNo ratings yet
- Tools Used in Community DiagnosisDocument23 pagesTools Used in Community DiagnosisMaureen A. Bawang33% (3)
- Cultural and Ethnical Diversities and Factors Affectting Nursing Care Towards ElderlyDocument8 pagesCultural and Ethnical Diversities and Factors Affectting Nursing Care Towards ElderlyDannah Jean GranNo ratings yet
- Lonkham Boruah - Geography - UG II Sem (HC) - Age-Sex StructureDocument8 pagesLonkham Boruah - Geography - UG II Sem (HC) - Age-Sex Structure3056 KuldeepNo ratings yet
- New and Emerging Issues in Latinx HealthFrom EverandNew and Emerging Issues in Latinx HealthAirín D. MartínezNo ratings yet
- Demography: Dr. Sheryl M. ReyesDocument18 pagesDemography: Dr. Sheryl M. ReyesNilda ReyesNo ratings yet
- Community Assessment: Prepper by Nariman NOUHDocument25 pagesCommunity Assessment: Prepper by Nariman NOUHN N100% (1)
- Transcu AssignmentDocument9 pagesTranscu AssignmentCharles Gerard B. BeluanNo ratings yet
- Demographics re-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesDemographics re-WPS OfficeJeysha CabreraNo ratings yet
- Tropical Style Book Slideshow For Marketing by SlidesgoDocument85 pagesTropical Style Book Slideshow For Marketing by SlidesgoZhailyn Joy DumlaoNo ratings yet
- CHN PrelimsDocument85 pagesCHN Prelims2100105No ratings yet
- Final Version - EN - Lesson 2 - Size and Structure of PopulationDocument14 pagesFinal Version - EN - Lesson 2 - Size and Structure of PopulationChu NamNo ratings yet
- Culture, Diversity and Health Notes (AutoRecovered)Document116 pagesCulture, Diversity and Health Notes (AutoRecovered)alana.gordon24No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document2 pagesPresentation 1Erica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- New Case TitleDocument2 pagesNew Case TitleErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 Management of Patients With Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument89 pagesWEEK 5 Management of Patients With Fluids and ElectrolytesErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Week 6 ElectrolytesDocument166 pagesWeek 6 ElectrolytesErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDDocument16 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmn FINAL WORDErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Life, Works and Writings SummaryDocument18 pagesJose Rizal Life, Works and Writings SummaryErica P. Manlunas100% (1)
- Jose Rizal Life, Works and Writings SummaryDocument18 pagesJose Rizal Life, Works and Writings SummaryErica P. Manlunas100% (1)
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Atherosclerosis FINALDocument23 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Atherosclerosis FINALErica P. ManlunasNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical MarketingDocument75 pagesPharmaceutical MarketingNagma Aslam ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Grade Seven Geography - Exam Review Booklet 2023Document8 pagesGrade Seven Geography - Exam Review Booklet 2023joshua kessieNo ratings yet
- Gec 3a Reviewer For FinalsDocument9 pagesGec 3a Reviewer For FinalsJulian EntrealgoNo ratings yet
- The Disciplines of Social Sciences: Lesson 1.2Document51 pagesThe Disciplines of Social Sciences: Lesson 1.2Jian Manuyag100% (1)
- The World Population ExplosionDocument9 pagesThe World Population ExplosionKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- 1 - Population iGCSEDocument5 pages1 - Population iGCSEAndy FunnellNo ratings yet
- NCRE - Sample Exam - 2006Document16 pagesNCRE - Sample Exam - 2006MiaDjojowasitoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of External Environment of The OrganizationDocument20 pagesAnalysis of External Environment of The OrganizationKing BascosNo ratings yet
- Part 8 Chapter 2 Population EcologyDocument10 pagesPart 8 Chapter 2 Population EcologyjamesNo ratings yet
- 01 Roche, Sophie - A Sound Family For A Healthy Nation - Motherhood in Tajik National Politics and SocietyDocument19 pages01 Roche, Sophie - A Sound Family For A Healthy Nation - Motherhood in Tajik National Politics and SocietycetinjeNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Population An Introduction To Concepts and Issues 13Th Edition John R Weeks PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Population An Introduction To Concepts and Issues 13Th Edition John R Weeks PDFrichard.tiemann394No ratings yet
- AP HG Academy 2020Document368 pagesAP HG Academy 2020Idan LevyNo ratings yet
- Class XII - Indian Society (Sociology)Document161 pagesClass XII - Indian Society (Sociology)MantraNo ratings yet
- Housman y Dorman (2005) - The Alameda County StudyDocument7 pagesHousman y Dorman (2005) - The Alameda County StudyFrancesscaNo ratings yet
- Global CityDocument26 pagesGlobal CityJewdaly Lagasca Costales100% (1)
- PSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngDocument17 pagesPSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngThanh Thảng Phan ThịNo ratings yet
- Demographic Data SourcesDocument5 pagesDemographic Data SourcesAnanta RoyNo ratings yet
- [Advanced Sciences and Technologies for Security Applications] Anthony J. Masys (Eds.) - Exploring the Security Landscape_ Non-Traditional Security Challenges (2016, Springer International Publishing)Document326 pages[Advanced Sciences and Technologies for Security Applications] Anthony J. Masys (Eds.) - Exploring the Security Landscape_ Non-Traditional Security Challenges (2016, Springer International Publishing)HajiasifAliNo ratings yet
- IMR 3, Vol 1, 1968Document17 pagesIMR 3, Vol 1, 1968pazeabNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Action Around The World - An Empirical Study - Thomas SowellDocument252 pagesAffirmative Action Around The World - An Empirical Study - Thomas SowellPatti Willeford100% (3)
- Foi Reports FinalDocument100 pagesFoi Reports FinalEdgarNo ratings yet
- Aleksandra Vuletic, Censuse in 19th Century in SerbiaDocument25 pagesAleksandra Vuletic, Censuse in 19th Century in SerbiaDejan ZivanovicNo ratings yet
- Approach in IndiaDocument17 pagesApproach in IndiaGerardo VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Pre Fi ModuleDocument12 pagesThe Contemporary World Pre Fi ModuleJunnel VasquezNo ratings yet
- Chapterwise Questions in Anthropology - Paper 01Document7 pagesChapterwise Questions in Anthropology - Paper 01Kaimal HareniNo ratings yet
- Digital Profile of Godawari ReportDocument106 pagesDigital Profile of Godawari ReportYuzvi SolutionsNo ratings yet
- CV 202403Document13 pagesCV 202403api-296683451No ratings yet
- 103 - Marketing ManagementDocument14 pages103 - Marketing ManagementRiyaz BabwaniNo ratings yet
- Educational Expansion and Demographic Change: Pathways of InfluenceDocument10 pagesEducational Expansion and Demographic Change: Pathways of InfluenceMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Cambodia - CSES2014 ReportDocument290 pagesCambodia - CSES2014 Reportalmond2008100% (1)




















































































![[Advanced Sciences and Technologies for Security Applications] Anthony J. Masys (Eds.) - Exploring the Security Landscape_ Non-Traditional Security Challenges (2016, Springer International Publishing)](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/389522933/149x198/a00d56d8f4/1537982889?v=1)











