Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essential Equations
Uploaded by
Laksh Ramesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThis document summarizes various chemical reactions involving group 2 metals, group 7 elements, halides, halogenoalkanes, and alcohols. It describes how group 2 metals react with water and oxygen, and how their oxides react with water and acids. It also outlines the thermal stability and solubility of group 1 and 2 carbonates and sulfates. Reactions of group 7 elements like chlorine with water and sodium hydroxide are provided. Displacement and tests for halide ions are summarized. The document concludes with reactions of halogenoalkanes and alcohols, including their preparation, oxidation, dehydration, and reaction with sodium.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes various chemical reactions involving group 2 metals, group 7 elements, halides, halogenoalkanes, and alcohols. It describes how group 2 metals react with water and oxygen, and how their oxides react with water and acids. It also outlines the thermal stability and solubility of group 1 and 2 carbonates and sulfates. Reactions of group 7 elements like chlorine with water and sodium hydroxide are provided. Displacement and tests for halide ions are summarized. The document concludes with reactions of halogenoalkanes and alcohols, including their preparation, oxidation, dehydration, and reaction with sodium.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesEssential Equations
Uploaded by
Laksh RameshThis document summarizes various chemical reactions involving group 2 metals, group 7 elements, halides, halogenoalkanes, and alcohols. It describes how group 2 metals react with water and oxygen, and how their oxides react with water and acids. It also outlines the thermal stability and solubility of group 1 and 2 carbonates and sulfates. Reactions of group 7 elements like chlorine with water and sodium hydroxide are provided. Displacement and tests for halide ions are summarized. The document concludes with reactions of halogenoalkanes and alcohols, including their preparation, oxidation, dehydration, and reaction with sodium.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
AS EQUATIONS - Unit 2
Group 2 metals – with H2O
Mg Mg + H2O MgO + H2 (steam only)
Ca,Sr,Ba Ca + 2H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2
Group 2 metals – with O2 2Mg + O2 2MgO
Group 2 metals – with Cl2 Mg + Cl2 MgCl2
Group 2 Oxides – with H2O MgO + H2O Mg(OH)2
Group 2 Oxides – with acids MgO + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2O
Thermal stability
Group 1 Carbonates All stable to heat except for Li2CO3
Group 2 Carbonates MgCO3 MgO + CO2
Group 1 Nitrates Li: 2LiNO3 Li2O + 2NO2 + ½O2
Na, K, Rb, Cs NaNO3 NaNO2 + ½O2
Group 2 – Nitrates Mg(NO3)2 MgO + 2NO2 + ½O2
Solubility
Group 1 and 2 Sulphates Decreases down the group - BaSO4 is insolubl
Group 1 and 2 Hydroxides Increases down the group - Mg(OH)2 is insoluble
Group 7 elements – with H2O Cl2 + H2O HCl + HOCl
Group 7 elements – with NaOH
In Cold Dilute Alkali: Cl2 + 2OH- Cl- + ClO- + H2O
Reaction type - Disproportionation
In Hot Conc. Alkali: 3Cl2 + 6OH- ClO3- + 5Cl- + 3H2O
Reaction type - Disproportionation
Group 7 – Displacement reactions Cl2(g) + 2Br-(aq) → Br2(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)
Observations Green gas orange solution
Halide ions – with conc H2SO4
NaCl(s) + H2SO4 NaHSO4(s) + HCl(g)
Observations Steamy white fumes
NaBr(s) + H2SO4 NaHSO4(s) + HBr(g)
2HBr(g) + H2SO4 Br2(g) + SO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
Observations Steamy white fumes and orange fumes
NaI(s) + H2SO4 Products HI(g), I2(g) + H2S(g) +
Observations Steamy white fumes and purple fumes
Test for halide ions Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl(s)
Observations White ppt – soluble in dilute ammonia
Halogenoalkanes - with aqueous OH- CH3CH2Br + OH- CH3CH2OH + Br-
Mechanism = Nucleophilic substitution (Sn1 or Sn2)
with ethanolic OH- CH3CH2Br + OH- H2C=CH2 + Br- + H2O
Mechanism = Elimination
Halogenoalkanes - with CN- CH3CH2Br + CN- CH3CH2CN + Br-
Mechanism = Nucleophilic substitution
Halogenoalkanes - with aqueous silver nitrate
CH3CH2Br + H2O + Ag+ CH3CH2OH + AgBr
Fastest halogenoalkane = Iodo
Explanation = C-I bond is weaker than C-Br and C-Cl
Halogenoalkanes - with NH3 CH3CH2Br + NH3 CH3CH2NH2 + HBr
Conditions Conc NH3 / heat / closed vessel
Preparation of halogenoalkanes
Chloroalkanes from alcohols CH3CH2OH + Cl- CH3CH2Cl + OH-
Conditions H2SO4 / NaCl / heat
Bromoalkanes from alcohols CH3CH2OH + Br- CH3CH2Br + OH-
Conditions NaBr / H3PO4 / Heat
Not H2SO4 / NaBr / heat as Br2 will form
Iodoalkanes from alcohols CH3CH2OH + I- CH3CH2I + OH-
Conditions PI3 or P / I2
Not H2SO4 / NaI / heat as I2 will form
Alcohols – 1o Partial Oxidation CH3CH2OH + [O] CH3CHO + H2O
Conditions Distil product as it is formed
Alcohols – 1o Complete Oxidation CH3CH2OH + 2[O] CH3CO2H + H2O
Conditions HUR
Alcohols – 2o Oxidation CH3CHOHCH3 + [O] CH3COCH3 + H2O
Alcohols – Dehydration CH3CH2OH H2C=CH2 + H2O
Conditions HUR / NaOH – Aqueous
Alcohols – Reaction with sodium CH3CH2OH + Na CH3CH2O-Na+ + ½ H2
Observation Colourless effervescence
You might also like
- EquationsDocument3 pagesEquationsalbertolabarquillaNo ratings yet
- As Equations: Lithium Monoxide (Contains O) Sodium Peroxide (Contains O) Potassium Superoxide (Contains O)Document4 pagesAs Equations: Lithium Monoxide (Contains O) Sodium Peroxide (Contains O) Potassium Superoxide (Contains O)arcmikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Wise Important Chemical Reactions For Class 10Document9 pagesChapter-Wise Important Chemical Reactions For Class 10Manish SainNo ratings yet
- FN 2Document3 pagesFN 2idon'tgiveachogiwaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLDocument13 pagesPreparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLDocument13 pagesPreparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Class XDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions Class Xaprajita royNo ratings yet
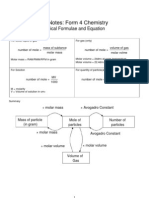
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationJasmeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
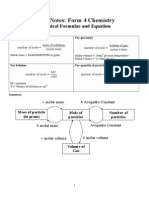
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument14 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationanisnazihahNo ratings yet
- P-Block Elements: Boron Family (Group 13 Elements)Document19 pagesP-Block Elements: Boron Family (Group 13 Elements)Indonesia HarshNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Organic An Inorganic ReactionsDocument14 pagesAS Chemistry Organic An Inorganic Reactionsdenithmayon1No ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On PDocument20 pagesRevision Notes On PBharadwaj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument18 pagesAcid BasechaitanyaNo ratings yet
- P Block EquationsDocument10 pagesP Block EquationsFarha Sh67% (9)
- P Block EquationsDocument10 pagesP Block EquationsDivyansh WaghmareNo ratings yet
- P Block Equations PDFDocument10 pagesP Block Equations PDFDivyansh WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Boron FamilyDocument12 pagesBoron FamilypushpNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSC FormulasDocument6 pagesChemistry HSC Formulashpgc101100% (1)
- Chemical Equations: Preparation For College Chemistry Columbia University Department of ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equations: Preparation For College Chemistry Columbia University Department of ChemistryLakshmi SinghNo ratings yet
- 4th Form Qualitative Analysis Sheet Summary SheetDocument2 pages4th Form Qualitative Analysis Sheet Summary SheetFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDocument12 pagesSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Revision PDFDocument2 pagesData Sheet Revision PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equation (2019)Document1 pageChemical Equation (2019)Ismalinda AbdullahNo ratings yet
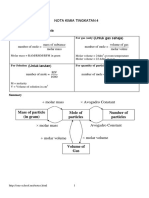
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationTharmendran MaganteranNo ratings yet
- Handout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)Document9 pagesHandout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)twelvefeetNo ratings yet
- Analitycal Chemistry - Lecture 06Document38 pagesAnalitycal Chemistry - Lecture 06Irene BoyaNo ratings yet
- All Chemical ReactionsDocument29 pagesAll Chemical ReactionsManeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Handout For Qualitative AnalysisDocument9 pagesHandout For Qualitative AnalysisJarvin TanNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document12 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4api-292313678No ratings yet
- P Block Elements in PPT FormDocument138 pagesP Block Elements in PPT FormharshadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 Simplifed NotesDocument15 pagesChemistry 10 Simplifed NotesFaina VeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeDocument12 pagesChemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeSooryaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AlkalisDocument3 pagesPhysical Properties of AlkalisTravel Unlimited0% (1)
- Experimental1 ManualDocument6 pagesExperimental1 ManualVasu JayanthiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 6Document2 pagesLab Report 6bjddjkNo ratings yet
- For JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsDocument56 pagesFor JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsLakshmi AnandNo ratings yet
- One Shot JA Block Chem Part 1 12 March FINAL Pankaj Sir FINAL MergedDocument181 pagesOne Shot JA Block Chem Part 1 12 March FINAL Pankaj Sir FINAL Mergedsuvendu shekhar MahakudNo ratings yet
- Sodium HydroxideDocument3 pagesSodium HydroxideISLAM I. Fekry100% (2)
- General EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneral EquationsPyae Sone KyawNo ratings yet
- GRP 15, 16 New P BlockDocument76 pagesGRP 15, 16 New P BlockVedantNo ratings yet
- Oxyg en Fa Mily: OxygenDocument26 pagesOxyg en Fa Mily: Oxygendevli falduNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument37 pagesChemical ReactionsGlydel GealonNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument90 pagesQualitative AnalysisMahesh100% (1)
- AnionsDocument90 pagesAnionsAnish RaoNo ratings yet
- Cramming NotesDocument7 pagesCramming NotesMuhammad ali WasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Periodicity Revision (Document5 pagesChapter 9 Periodicity Revision (Ting NicholasNo ratings yet
- C4 - StoichiometryDocument36 pagesC4 - StoichiometryAbhay BhingradiaNo ratings yet
- IOC All ReactionsDocument56 pagesIOC All ReactionsKeerthana MNo ratings yet
- PCL - Ionic Off White Solid at RTP, Sublimes at 163 C ToDocument1 pagePCL - Ionic Off White Solid at RTP, Sublimes at 163 C ToangelkavsNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Part 2 Acid and BasesDocument11 pages6.1 Part 2 Acid and BasesMarc LoNo ratings yet
- Edexecel IAL Lesson 1Document20 pagesEdexecel IAL Lesson 1Pevin De silvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6, 7 Halohydrocarbon, Alcohol, PhenolDocument89 pagesChapter 6, 7 Halohydrocarbon, Alcohol, PhenolGan Suk Ling100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Ial Oct Nov 2021 Registration FormDocument2 pagesEdexcel Ial Oct Nov 2021 Registration FormLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Ial Price List - Oct Nov 2021Document4 pagesEdexcel Ial Price List - Oct Nov 2021Laksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Class VII Maths Revision WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass VII Maths Revision WorksheetLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Class VII English SA2 2015 16Document6 pagesClass VII English SA2 2015 16Laksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Nelson Mandela: Laksh Ramesh Class-Vi C IsmDocument2 pagesNelson Mandela: Laksh Ramesh Class-Vi C IsmLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Department: Sieve Analysis of SoilDocument6 pagesCivil Engineering Department: Sieve Analysis of SoilLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Department Geotechnology-2 CIVIL-0009: Fall 2015Document16 pagesCivil Engineering Department Geotechnology-2 CIVIL-0009: Fall 2015Laksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Brochure Digital FinalDocument41 pagesBrochure Digital FinalLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- 2 Bedroom OfferDocument17 pages2 Bedroom OfferLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Overview of The ProjectDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Overview of The ProjectLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Add To ContactsDocument4 pagesAdd To ContactsLaksh RameshNo ratings yet
- Aspen HYSYS Simulation For Biodiesel Production FRDocument7 pagesAspen HYSYS Simulation For Biodiesel Production FRعزالدين حسنNo ratings yet
- Low Res CompleteCareLabellingDocument12 pagesLow Res CompleteCareLabellingrummanbsc8923No ratings yet
- Preparation and Investigation of Some Properties of Acrylic Resin Reinforced With Siwak Fiber Used For Denture Base ApplicationsDocument6 pagesPreparation and Investigation of Some Properties of Acrylic Resin Reinforced With Siwak Fiber Used For Denture Base ApplicationsJawad K. OleiwiNo ratings yet
- High Speed Centrifuges: Instruction ManualDocument16 pagesHigh Speed Centrifuges: Instruction ManualNitisha RathoreNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Zematra Mini-Lab: Order Code 1001075Document16 pagesInstruction Manual For Zematra Mini-Lab: Order Code 1001075Dka BayuNo ratings yet
- Concept of Ayurvedic Shodhana Process - Not Mere PurificationDocument3 pagesConcept of Ayurvedic Shodhana Process - Not Mere PurificationCuriosityShopNo ratings yet
- UNIFAC - Properties of Gases and LiquidsDocument37 pagesUNIFAC - Properties of Gases and LiquidsAngelicCamarisPereaNo ratings yet
- AQUAPONICSDocument9 pagesAQUAPONICSExequiel ZoletaNo ratings yet
- BOMBASDocument4 pagesBOMBASjcrrautocadNo ratings yet
- Mew R 7 2010 PDFDocument19 pagesMew R 7 2010 PDFraghuvarmaNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument111 pagesCombustionTesfahun TegegneNo ratings yet
- Priyanka Sen Final Practice School Internship ReportDocument35 pagesPriyanka Sen Final Practice School Internship ReportThakur Aditya PratapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PathologyDocument16 pagesIntroduction To PathologySANI YAKUBUNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Professor, NME 513 1-MEDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Professor, NME 513 1-MEAriel GamboaNo ratings yet
- General Installation Practices: Section EDocument26 pagesGeneral Installation Practices: Section EMohsen ArabifardNo ratings yet
- ##Optics by Ajoy GhatakDocument6 pages##Optics by Ajoy Ghataksvo svoNo ratings yet
- Food ScienceDocument526 pagesFood SciencePuja BarmanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design Excel SheetDocument12 pagesConcrete Mix Design Excel SheetDhanush SNo ratings yet
- P05 020A Determination of Potassium in Inorganic FertilizersDocument2 pagesP05 020A Determination of Potassium in Inorganic FertilizersvhtitinNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction in Hydrometallurgy The Role of Organophosphorus ExtractantsDocument13 pagesSolvent Extraction in Hydrometallurgy The Role of Organophosphorus ExtractantsAbrahan BVNo ratings yet
- Agr 657 Written ReportDocument9 pagesAgr 657 Written ReportjeonsNo ratings yet
- Lumor J Tds 20080918Document2 pagesLumor J Tds 20080918PP043No ratings yet
- Article WJPR 1467435569Document19 pagesArticle WJPR 1467435569PatriciaNo ratings yet
- SikaGrout 215M.MSDSDocument5 pagesSikaGrout 215M.MSDSMuhammad Akbar AriantoNo ratings yet
- CV - Chemical EngineeringDocument2 pagesCV - Chemical EngineeringsohanNo ratings yet
- Alkali-Metals 2Document38 pagesAlkali-Metals 2Japhet Charles Japhet MunnahNo ratings yet
- BOQ Suryadev ChennaiDocument2 pagesBOQ Suryadev Chennaimkpasha55mpNo ratings yet
- SH 5107 Ventilation in Confined Spaces 2022 (Trainees)Document180 pagesSH 5107 Ventilation in Confined Spaces 2022 (Trainees)Shuyuan LuNo ratings yet
- (##) Three in One Air Conditioner-NewDocument67 pages(##) Three in One Air Conditioner-NewMichael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 20 LettersDocument2 pages20 LettersRenz Anthony Espino100% (1)