Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview of Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Uploaded by
Mary Anne Briones0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageOriginal Title
Overview of Endothermic & Exothermic reactions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageOverview of Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Uploaded by
Mary Anne BrionesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
BRIONES,MARY ANNE G.
ENDOTHERMIC AND
EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS
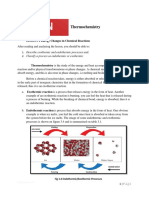
Endothermic reactions are These reactions lower the
chemical reactions in which the temperature of their surrounding
reactants absorb heat energy area, thereby creating a cooling
from the surroundings to form effect. Physical processes can be
products. endothermic as well – Ice cubes
absorb heat energy from their
surroundings and melt to form
liquid water (no chemical bonds
are broken or formed).
ENDOTHERMIC REACTION EXAMPLES
When ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is dissolved in water, an
endothermic reaction takes place. The salt dissociates into
ammonium (NH4+) and chloride (Cl–) ions. The chemical equation can
be written as follows: NH4Cl (s) + H2O (l) ⟶ NH4Cl (aq) – Heat
Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3), an important component in instant
cold packs, dissociates into the ammonium cation (NH4+) and the
nitrate anion (NO3–) when dissolved in water. These ions go on to
form ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) and nitric acid (HNO3)
respectively (by reacting with the OH– and H+ ions in water). This
reaction is endothermic in nature since it cools the surroundings by
absorbing heat from it.
The formation of nitric oxide from the reaction between nitrogen and
oxygen is endothermic since it involves the absorption of
approximately 180.5 kilojoules of heat for every mole of N2 and O2.
Therefore, it can be understood
that the net amount of energy
required to initiate an exothermic
reaction is less than the net
amount of energy released by
the reaction. When a calorimeter,
a device used to measure the
heat released by a chemical
An exothermic reaction is a reaction in which
reaction, the net amount of heat
energy is released in the form of light or heat. energy that flows through the
Thus in an exothermic reaction, energy is device is equal to the negative of
transferred into the surroundings rather than the total energy change of the
taking energy from the surroundings as in an system.
endothermic reaction. In an exothermic reaction,
change in enthalpy ( ΔH) will be negative.
EXAMPLES OF EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS
COMBUSTION DETONATION OF NITROGLYCERIN
Commonly referred to as burning, Nitroglycerin has strong explosive
combustion is an exothermic reaction in powers which can be used via its
which a fuel undergoes reduction when detonation
exposed to an oxidizing agent (which is In the process of detonating nitroglycerin,
usually the oxygen present in the the gases generated, at room
atmosphere) and forms an oxidized product. temperature and pressure would occupy
These reactions give out good amounts of
over 1,200 times the original volume.
energy in the form of heat, but also form
some byproducts such as smoke.
NEUTRALIZATION REACTIONS
NUCLEAR FISSION OF URANIUM-235 The standard enthalpy change (ΔH) for the
The nuclear fission of one atom of reaction between a proton (H+ ion) and a
uranium-235 releases more than 2.5 hydroxide ion (OH– ion) is -57.30 kJ/mol.
million times the energy that is Therefore, neutralization reactions are
produced from the combustion of coal. considered to be exothermic reactions.
You might also like
- EnergeticsDocument10 pagesEnergeticsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument18 pagesExothermic and Endothermic ReactionsAngelika Bernal100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Thermochemistry-Exothermic and EndothermicDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Thermochemistry-Exothermic and EndothermicNadine TariganNo ratings yet
- Exo N Endo ReactionDocument2 pagesExo N Endo ReactionTalha Jamil MalikNo ratings yet
- Exothermic Process: Not To Be Confused WithDocument5 pagesExothermic Process: Not To Be Confused WithFrederic WustNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedDocument68 pagesChm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedNurfarhanah AsyknNo ratings yet
- Section 4 Physical Chemistry: Energy ChangesDocument76 pagesSection 4 Physical Chemistry: Energy ChangesLalitha KurumanghatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 热化学: Endothermic reactions and exothermic reactionsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Thermochemistry 热化学: Endothermic reactions and exothermic reactionsJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Energetics E YDocument12 pagesEnergetics E YEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- BHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy EnergeticsDocument59 pagesBHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy Energeticsabigail allenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CHM476 (Part 1)Document28 pagesChapter 1 CHM476 (Part 1)PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument40 pagesThermo Chemistrypipay vlogsNo ratings yet
- C19 Energy From Chemicals PC SlidesDocument51 pagesC19 Energy From Chemicals PC SlidesBasil ChinNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2.1Document79 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2.1Voon Chen WeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document13 pagesChapter 7Shafiqah AiradzNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument2 pagesEnergeticsAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
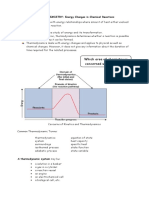
- Which Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pagesWhich Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsSahada KanapiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4thermochemistry 150201074346 Conversion Gate02Document38 pagesChapter4thermochemistry 150201074346 Conversion Gate02eric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument37 pagesEnergeticsrheanna0076No ratings yet
- Energy Changes:: Change in Energy During Chemical ReactionDocument4 pagesEnergy Changes:: Change in Energy During Chemical ReactionadnanNo ratings yet
- C13 Enthalpy ChangeDocument19 pagesC13 Enthalpy ChangeKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Document79 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Phillip TranNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and ExothermicDocument37 pagesEndothermic and Exothermicactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Energetics and Hess's LawDocument76 pagesEnergetics and Hess's LawDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: LESSON 1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesThermochemistry: LESSON 1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsAlexandra minNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in ReactionsDocument2 pagesEnergy Changes in ReactionsShahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Lesson 6 Period 1Document59 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Lesson 6 Period 1Mohammed AnwerNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument11 pagesEnergeticsMuhammadJahangirAlamNo ratings yet
- Ans For ReviewDocument3 pagesAns For Reviewsachi.laurelNo ratings yet
- CIE - AS - and - A-Level - Chemistry - Coursebook - 2nd-Edition (1) - 99-114Document16 pagesCIE - AS - and - A-Level - Chemistry - Coursebook - 2nd-Edition (1) - 99-114An Trương Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- 18cho101t Unit 4 Energy Calculations and Other Chemical Energy Transfer ProcessesDocument46 pages18cho101t Unit 4 Energy Calculations and Other Chemical Energy Transfer ProcessesHruday CoolkidNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions: Chemistry ProjectDocument8 pagesExothermic and Endothermic Reactions: Chemistry ProjectSai prasadNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Y11Document23 pagesThermochemistry Y11ZlureNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2 Chemistry As Book EditedDocument20 pagesUnit 1.2 Chemistry As Book EditedJamsheed KakarNo ratings yet
- Energetics Lesson 1Document13 pagesEnergetics Lesson 1Ghadeer AlkhayatNo ratings yet
- Endothermic & Exothermic ReactionsDocument7 pagesEndothermic & Exothermic ReactionsMR: First humanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - F3Document22 pagesChapter 5 - F3胡欣苓No ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry Notes (Except Unit 1)Document104 pagesIgcse Chemistry Notes (Except Unit 1)michaela menzelNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument48 pagesThermochemistryNurfarhanah KNo ratings yet
- ENERGY CHANGES AND RATES OF REACTIONS FimalDocument11 pagesENERGY CHANGES AND RATES OF REACTIONS FimalIsaacNo ratings yet
- Week 007 Module ThermochemistryDocument12 pagesWeek 007 Module ThermochemistryFigh terNo ratings yet
- Prepared: Ms Alma C. Tesoro.,Rcim., MSCJDocument14 pagesPrepared: Ms Alma C. Tesoro.,Rcim., MSCJbalaoromichael10No ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument70 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic Reactionactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRYadikmuk100% (1)
- 5.1 EnergeticsDocument8 pages5.1 EnergeticsEldin EnggNo ratings yet
- Endothermic ReactionDocument1 pageEndothermic ReactionJose RizalNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument11 pagesChemical EnergeticsSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument5 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionMuhammad Umar SalmanNo ratings yet
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesFirst Law of ThermodynamicsLESTER DEL RIONo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument52 pagesThermochemistryBiddut DasNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardDocument5 pages9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardmotivonovaNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument57 pagesEnergeticsEfraim KasinoNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument11 pagesChemical EnergeticsMerab FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Week 7Document5 pagesChemistry Week 7EDUARDO lll NADATENo ratings yet
- Chemistry ConceptsDocument60 pagesChemistry ConceptsElla Jean LanoteNo ratings yet
- Examples of Exothermic Reactions : NotesDocument6 pagesExamples of Exothermic Reactions : NotesAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Group InvestigationDocument4 pagesGroup InvestigationNohelia GradizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Energetics & ThermochemistryDocument180 pagesChapter 05 Energetics & ThermochemistryJishen ZhuNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes PDFDocument4 pagesEnergy Changes PDFMahmudul Hassan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Science Atomic SpectraDocument1 pageScience Atomic SpectraMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- 10 Types of EnergyDocument13 pages10 Types of EnergyMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure and Boiling PointDocument4 pagesVapor Pressure and Boiling PointMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- Computing Cost of Goods SsoldDocument1 pageComputing Cost of Goods SsoldMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- Computing Cost of Goods SsoldDocument1 pageComputing Cost of Goods SsoldMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- Speed of Sound Study MaterialDocument2 pagesSpeed of Sound Study MaterialMary Anne BrionesNo ratings yet
- CATALOGO Imco Cigarette LightersDocument5 pagesCATALOGO Imco Cigarette LightersManielNo ratings yet
- CERGAS Deteccion de Gases ExplosivosDocument4 pagesCERGAS Deteccion de Gases ExplosivosdanilokaralejicNo ratings yet
- 11 Marine Fuel Properties.Document7 pages11 Marine Fuel Properties.Kevin LeysonNo ratings yet
- The Fire DepartmentDocument27 pagesThe Fire DepartmentSHAHNo ratings yet
- Hyoscyamine Sulphate ReportDocument5 pagesHyoscyamine Sulphate ReportAnonymous EkNpAdl7No ratings yet
- CO2 Energy Vector in The Concept of CircularDocument9 pagesCO2 Energy Vector in The Concept of CircularMr PolashNo ratings yet
- Session 1.2 - Willson - 0 - Methane SlipDocument10 pagesSession 1.2 - Willson - 0 - Methane SlipFauzan PhoneNo ratings yet
- Oil Ignitor Babcock and WilcoxDocument2 pagesOil Ignitor Babcock and WilcoxPriagung Wibowo100% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips - h2 Gas Samator Msds ProduknyaDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips - h2 Gas Samator Msds ProduknyachindyNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine ReportDocument13 pagesGas Turbine Reportwaleed100% (1)
- Atmos Boiler DC18 25 30 40 50GD Instruction Manual Cerbos PDFDocument40 pagesAtmos Boiler DC18 25 30 40 50GD Instruction Manual Cerbos PDFAthanasios AntonopoulosNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Diesel Fuel Blends A Review PDFDocument9 pagesEthanol Diesel Fuel Blends A Review PDFMantap BroNo ratings yet
- (Consumer) Boilers and Heaters - Improving Energy EfficiencyDocument26 pages(Consumer) Boilers and Heaters - Improving Energy Efficiencybiosbg100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: 1 Identification of The Substance and of The CompanyDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1 Identification of The Substance and of The CompanyGianpieroNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine - Combustion, Emissions and Condition Monitoring PDFDocument275 pagesDiesel Engine - Combustion, Emissions and Condition Monitoring PDFSamir Alshaar100% (1)
- Mem (Paper - Me 601) (I.c. Engines)Document4 pagesMem (Paper - Me 601) (I.c. Engines)Rahul BhattNo ratings yet
- Ansys Fluent 12.0 Text Command List: February 2009Document79 pagesAnsys Fluent 12.0 Text Command List: February 2009Frank Azola ArayaNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Analysis of Low Pressure Gas Networks With Decentralized Fuel InjectionDocument5 pagesSimulation and Analysis of Low Pressure Gas Networks With Decentralized Fuel Injectionalorenzo66No ratings yet
- 8LV OpsDocument88 pages8LV OpsAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Rotary Evaporator Manual PDFDocument95 pagesRotary Evaporator Manual PDFomarNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid Rain - Know Its Causes, Effects, Solutions (Full Notes) - UPSC ExamsDocument8 pagesWhat Is Acid Rain - Know Its Causes, Effects, Solutions (Full Notes) - UPSC ExamsJitesh ShrivasNo ratings yet
- ANNEXURE-5 Material Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesANNEXURE-5 Material Safety Data SheetSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Kol R KingDocument2 pagesKol R KingJavier DominguezNo ratings yet
- Centrala Termica Pe Lemn Si Carbune Rima Lmax Manual Tehnic LB EnglezaDocument26 pagesCentrala Termica Pe Lemn Si Carbune Rima Lmax Manual Tehnic LB EnglezaOarga CalinNo ratings yet
- August 11, 2017 Strathmore TimesDocument28 pagesAugust 11, 2017 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen - Natural Gas Blends PDFDocument8 pagesHydrogen - Natural Gas Blends PDFLTE002No ratings yet
- ViessmanDocument100 pagesViessmanIvan LunjakNo ratings yet
- Dissertation 1newDocument37 pagesDissertation 1newShailesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 4 ScienceDocument9 pagesDLL Week 4 ScienceGladish AnsubanNo ratings yet
- Sulfonation and Sulfation ProcessesDocument37 pagesSulfonation and Sulfation Processesanandram100% (1)