Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Chem 11-WK 30-2020-2021
Gen Chem 11-WK 30-2020-2021
Uploaded by
Patrick Casquejo AndalesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Chem 11-WK 30-2020-2021
Gen Chem 11-WK 30-2020-2021
Uploaded by
Patrick Casquejo AndalesCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING PACKAGE WEEK NUMBER 30 - March 29-April 3, 2021
What’s More with Cell?
Name: Date Received:
Grade and Section: Date Submitted:
Subject:General Chemistry 2 Teacher’s Name: Mr. Patrick C. Andales Teacher’s Signature:
Standards: The learner…
Content: demonstrates an understanding of spontaneous change, entropy, and free energy;
Performance : prepares a poster on a specific application of one of the following:
a. Acid- base equilibrium
b. Electrochemistry
include in the poster the concepts, principles, and chemical reactions involved, and diagrams of processes and other
relevant materials
Formation : knows and play their role as nation builders
Learning Outcomes/Objectives: The learner…
1. draws the structure of a galvanic cell and label the parts;
2. identifies the reaction occurring in the different parts of the cell; (MELC)
3. reacts on issues concerning the youth
PVMGOV: Produce self-disciplined, responsible, independent, cooperative and Christ-centered individuals.
21st Century Skills: Communication, Critical Thinking-and-Doing, Career and Learning Self-reliance
Introduction :This week let’s learn what galvanic cell is and the reactions happening on it.. Do not forget to pray before and after
doing your learning package.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
Day 1-3
What is Galvanic Cell?
An electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of spontaneous redox reactions into electrical energy is known as a galvanic cell
or a voltaic cell.
Galvanic cell Voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that makes use of chemical reactions to generate electrical energy.
Let us understand how a voltaic or galvanic cell is created.
In oxidation-reduction reactions, electrons are moved from one species to another species. Energy is released if the reaction occurs spontaneously.
Therefore, the released energy is used to do useful work. To tackle this energy, it is required to split the reaction into two separate half-reactions viz.
oxidation and reduction. With the help of two different containers and wire, the reactions are put into them to drive the electrons from one end to the
other end. This creates a voltaic cell.
Principle of Galvanic (Voltaic) Cell
Electric work done by a galvanic cell is mainly due to the Gibbs energy of spontaneous redox reaction in the voltaic cell. It generally consists of two
half cells and a salt bridge. Each half cell further consists of a metallic electrode dipped into an electrolyte. These two half-cells are connected to a
voltmeter and a switch externally with the help of metallic wires. In some cases, when both the electrodes are dipped in the same electrolyte, a salt
bridge is not required.
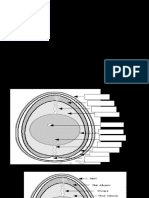
Galvanic Cell (Voltaic Cell) Diagram
Parts of Galvanic Cell
Anode – Oxidation occurs at this electrode.
Cathode – Reduction occurs at this electrode.
Salt bridge – Contains electrolytes which are required to complete the circuit in a galvanic cell.
Half-cells – reduction and oxidation reactions are separated into compartments.
External circuit – Conducts the flow of electrons between electrodes
Load – A part of the circuit utilizes the electron to flow to perform its function.
Working of Galvanic Cell
In a galvanic cell, when an electrode is exposed to the electrolyte at the electrode-electrolyte interface, the atoms of the metal electrode
have a tendency to generate ions in the electrolyte solution leaving behind the electrons at the electrode. Thus, making the metal electrode negatively
charged.
While at the same time metal ions in the electrolyte solution too, have a tendency to deposit on a metal electrode. Thus, making the
electrode positively charged.
Under equilibrium condition, charge separation is observed and depending on the tendencies of two opposing reactions, the electrode can
be positively or negatively charged. Hence, a potential difference is developed between the electrode and electrolyte.
This potential difference is known as electrode potential.
Out of two electrodes, the electrode at which oxidation takes place is called anode while the electrode at which reduction takes place is
called cathode.
The anode has a negative potential with respect to the solution while the cathode has a positive potential with respect to the solution.
Thus, a potential difference develops between two electrodes of the galvanic cell. This potential difference is known as cell potential.
When no current is drawn from the galvanic cell, cell potential is known as the electromotive force of the galvanic cell.
When the switch is set on, due to the potential difference, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode.
Example of Galvanic Cell
Electrochemical or galvanic cells were introduced as a tool for studying the thermodynamic properties of fused salts more than a century ago.
Daniel’s cell is an example of a galvanic cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. In Daniel’s cell, copper ions are reduced at the
cathode while zinc is oxidized at the anode.
Reactions of Daniel cell at cathode and anode are:
At cathode: Cu 2+ + 2e– → Cu
At anode: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e–
To Do:
1. In a short bond paper, draw the structure of a galvanic cell and label the parts;
2. In a 1/2 cross wise sheet of paper, enumerate the reactions occurring in the different part of the cell.
PVMGOV Integration)
Cite and discuss one particular issue about the youth today and as a youth state what could you do in that particular problem.
Summary: (Learning Outcomes/Objectives Check)
Indicate here the activity/ activities that made the competencies realized.__________________________________________
Closure: Don’t be a part of the problem, be a part of the solution.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Day 4 -5 Maundy Thursday and Good Friday
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Resources/Materials: DLP
Teaching Guide for SHS, CHED
General Chemistry 2, Ilao, L., Lontoc, B., Paderna-Gayon,E.
Basic Chemistry, Seese,W., Daub, W.Buthelezi,D., Hainen, and Zike
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change chem.libretexts.org
Galvanic Cells (Voltaic Cell) - Definition, Working Principle & Examples with Videos (byjus.com)
For questions or clarifications please reach me out with this number 09615378578 or through messenger @ Patrick Casquejo
Andales
You might also like
- Defects and Defect Processes in Nonmetallic SolidsFrom EverandDefects and Defect Processes in Nonmetallic SolidsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Arihant CBSE Chemistry Term 2 C - Aditya JangidDocument159 pagesArihant CBSE Chemistry Term 2 C - Aditya JangidSalman100% (1)
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 6Document20 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 6Junelle Ramos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Electrochemistry and Energy PDFDocument57 pagesUnit 3 Electrochemistry and Energy PDFChris-ughn DiazNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up An Electrolytic CellDocument6 pagesHow To Set Up An Electrolytic CellAngel LacabaNo ratings yet
- Nucleation and Growth of Metals: From Thin Films to NanoparticlesFrom EverandNucleation and Growth of Metals: From Thin Films to NanoparticlesNo ratings yet
- MFE Study GuideDocument17 pagesMFE Study Guideahpohy100% (1)
- Toyota New Land Cruiser 70 PDFDocument32 pagesToyota New Land Cruiser 70 PDFIngrid Garcia de Jauregui86% (7)
- Jyotish - Marc Boney - Case Studies - A Night at The Grammy AwardsDocument46 pagesJyotish - Marc Boney - Case Studies - A Night at The Grammy Awardsaha100% (1)
- Chemistry 2: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument60 pagesChemistry 2: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsJenny Mae LopezNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM Q4 Module 6 PDFDocument17 pagesGEN CHEM Q4 Module 6 PDFAnthony CreationNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Document17 pagesModule 6 Gen Chem 2 q4Hazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- CHM 409 - 0Document69 pagesCHM 409 - 0tolaniogunbode52No ratings yet
- Chemistry File XIIDocument34 pagesChemistry File XIITushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mini TeachingDocument5 pagesMini TeachingSomasundariNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 STEM Science Unit 4 Student CompanionDocument55 pagesGrade 10 STEM Science Unit 4 Student CompaniongallantryawardeesNo ratings yet
- Chem AlokDocument19 pagesChem AlokRiya TiwariNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument15 pagesChemistrywww.sandeepmazumder1234567890No ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers Laboratory: CHEM 114Document8 pagesChemistry For Engineers Laboratory: CHEM 114Ivyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- 1Document51 pages1Moh Makhbub AlyNo ratings yet
- Learning Evidence Chemistry Stage 3Document8 pagesLearning Evidence Chemistry Stage 3Fernando CamachoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GRADE 9 MODULE CHemical BondingDocument18 pagesChemistry GRADE 9 MODULE CHemical BondingKelvin MarinasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesModule 1 - ElectrochemistryjeniferNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 1)Document11 pagesModule 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 1)Steven Lee100% (2)
- Class 12th Chemistry ProjectDocument26 pagesClass 12th Chemistry ProjectAarush BansalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment.......Document11 pagesChemistry Assignment.......Masood MughalNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 ElectrochemistryDocument31 pagesMODULE 2 ElectrochemistryChristian Mark De JesusNo ratings yet
- All About Chemical Bonding - IonicDocument7 pagesAll About Chemical Bonding - IonicKev WattsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - THE THERMODYNAMICS OF ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS 2023Document35 pagesModule 4 - THE THERMODYNAMICS OF ELECTROCHEMICAL SYSTEMS 2023andreslloydralfNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Electrochemical CellsDocument39 pages9.2 Electrochemical CellsRose ChanNo ratings yet
- VHSE EET-Cell and Battery - Part1Document15 pagesVHSE EET-Cell and Battery - Part1Syed Shiyaz Mirza100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical Reactionsprincess3canlasNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Lesson PlanDocument19 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Lesson PlanJaya KaushikNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- 11 Cells and BatteriesDocument21 pages11 Cells and BatteriesSok SinNo ratings yet
- EC8252: Electronic DevicesDocument23 pagesEC8252: Electronic DevicesjehovavijayNo ratings yet
- Cell & BatteryDocument5 pagesCell & BatteryShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument24 pagesChemistry ProjectNidhi PorwalNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument14 pagesAcknowledgementRohaan Mohammad100% (2)
- (2nd Month) STM 128 - General Chemistry 2Document36 pages(2nd Month) STM 128 - General Chemistry 2ibnolyn2003No ratings yet
- The Electrochemical CellDocument41 pagesThe Electrochemical CellRaveendra GundlapalliNo ratings yet
- Reduction Potential Oxidation Potential and Cell PotentialDocument19 pagesReduction Potential Oxidation Potential and Cell PotentialKeanne QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Shebu Ejersa Dr. Bekele Hey Memorial School: Choose The Correct Answer From The Given AlternativesDocument2 pagesShebu Ejersa Dr. Bekele Hey Memorial School: Choose The Correct Answer From The Given AlternativesFiraol GeremuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project....Document15 pagesChemistry Project....Ravindra SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Done by JaganDocument19 pagesChemistry Project Done by JaganAthena abrahamNo ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument15 pagesChem ProjectAPARNA GANGWARNo ratings yet
- All About The Electrochemical Cell and Its Different Types: July 2020Document25 pagesAll About The Electrochemical Cell and Its Different Types: July 2020SivaNo ratings yet
- SarveDocument22 pagesSarveAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- College Physics Physics 204Document130 pagesCollege Physics Physics 204Christian OkekeNo ratings yet
- Octet Rule and The Formation of Compounds: For General Chemistry 1/ Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 2Document12 pagesOctet Rule and The Formation of Compounds: For General Chemistry 1/ Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 2ariinnggg onicha100% (1)
- Chemical Effects Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemical Effects Revision WorksheetAbhyuday SwamiNo ratings yet
- ElectroDocument13 pagesElectromamta80819No ratings yet
- G9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pagesG9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsCherrilyn Enverzo33% (3)
- AfzalDocument23 pagesAfzalSTRANGE YTNo ratings yet
- Document 55Document17 pagesDocument 55arequest9777No ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry NotesDocument15 pagesNuclear Chemistry NotesJeevani BattulaNo ratings yet
- 03 GRADE 12 PASAY Physical Science S2 Q3 W2 PDFDocument20 pages03 GRADE 12 PASAY Physical Science S2 Q3 W2 PDFRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Inquiry Into Life 14Th Edition Mader and Windelspecht 0073525529 9780073525525 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Inquiry Into Life 14Th Edition Mader and Windelspecht 0073525529 9780073525525 Full Chapter PDFbarbara.daniels282100% (10)
- Proj - Electrolytic CellDocument19 pagesProj - Electrolytic CellGeetanjali YadavNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod2Document16 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod2Prince U KennardNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Plate Boundaries ObservationDocument26 pagesPlate Boundaries ObservationPatrick Casquejo AndalesNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM 11-Wk28-2020-2021Document2 pagesGEN CHEM 11-Wk28-2020-2021Patrick Casquejo AndalesNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM 11-Wk 32-2020-2021Document1 pageGEN CHEM 11-Wk 32-2020-2021Patrick Casquejo AndalesNo ratings yet
- Genchemtqq4april2020 2021Document2 pagesGenchemtqq4april2020 2021Patrick Casquejo AndalesNo ratings yet
- Level of Difficulty No. of Items Item Number Percentage Easy Average Difficult TotalDocument3 pagesLevel of Difficulty No. of Items Item Number Percentage Easy Average Difficult TotalPatrick Casquejo AndalesNo ratings yet
- Oes Something When Things Observed To Be Disorder: Learning Package WeekDocument2 pagesOes Something When Things Observed To Be Disorder: Learning Package WeekPatrick Casquejo AndalesNo ratings yet
- Pipeline TransportDocument21 pagesPipeline Transportpiping stressNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - PPT Theory of Human NeedsDocument40 pagesGroup 8 - PPT Theory of Human Needs23005767No ratings yet
- Golden Tips Physics Mechanicsburg PaDocument3 pagesGolden Tips Physics Mechanicsburg PaJason25% (4)
- 2nd Quarter CBEA-MAth 7Document2 pages2nd Quarter CBEA-MAth 7Anna Lizette De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Digital Fundamentals: FloydDocument60 pagesDigital Fundamentals: FloydAyesha NazirNo ratings yet
- AUROVILLEDocument25 pagesAUROVILLEallu1100% (1)
- ProQuestDocuments 2020 05 03Document2 pagesProQuestDocuments 2020 05 03đẹp phanNo ratings yet
- Flora & Fauna of Arabian PeninsulaDocument4 pagesFlora & Fauna of Arabian PeninsulaAsma'a OsamaNo ratings yet
- 2012 SLK 350 3.5 V6 (M276 Engine) Spark Plug ReplacementDocument17 pages2012 SLK 350 3.5 V6 (M276 Engine) Spark Plug ReplacementIgor_Predator100% (3)
- Lactase Enzyme LabDocument7 pagesLactase Enzyme Labapi-382372564100% (1)
- MRCP AnswersDocument139 pagesMRCP Answerspal_pal_palNo ratings yet
- Structure of An EggDocument29 pagesStructure of An EggsheilaNo ratings yet
- Durastar DS1910HFDocument2 pagesDurastar DS1910HFEvelyn SigoliNo ratings yet
- 2021 Mastercraft Owners ManualDocument466 pages2021 Mastercraft Owners Manualpedro.menaNo ratings yet
- FR 1 (E6)Document5 pagesFR 1 (E6)JR CastorNo ratings yet
- Belimo - BFL24-T - Datasheet - En-Gb - dAMPER CORTA FOGODocument5 pagesBelimo - BFL24-T - Datasheet - En-Gb - dAMPER CORTA FOGOraphaelNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text DocumentsasgaatwilliamsNo ratings yet
- 2305-01-101 Proposal Attn Ms. Camille PDFDocument11 pages2305-01-101 Proposal Attn Ms. Camille PDFJohn Eduard De LeonNo ratings yet
- Nshba 1401-1605 PDFDocument855 pagesNshba 1401-1605 PDFDiego TorresNo ratings yet
- (Chem 102.2) Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument19 pages(Chem 102.2) Polymerase Chain ReactionRalph John UgalinoNo ratings yet
- Water MetersDocument3 pagesWater MetersRashedNo ratings yet
- Photo Courtesy of Paul Jeffrey.: ON THE WEB: Http://cisr - Jmu.edu/journal/16.2/index - HTMDocument1 pagePhoto Courtesy of Paul Jeffrey.: ON THE WEB: Http://cisr - Jmu.edu/journal/16.2/index - HTMpaulmazziottaNo ratings yet
- 2021 MSF2021 PM MG Precon3dDocument4 pages2021 MSF2021 PM MG Precon3dPavao MarovicNo ratings yet
- BMT300 User Manual 0J PP130409-Revised01MayECDocument41 pagesBMT300 User Manual 0J PP130409-Revised01MayECreza515heiNo ratings yet
- Imec 8 10 12Document152 pagesImec 8 10 12ANDRES FELIPE AYA MEJIA100% (2)
- Pharma Rapid Review FOCUSDocument85 pagesPharma Rapid Review FOCUSKeelNo ratings yet
- El Niño/La Niña-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO, Is A Quasi-Periodic Climate Pattern ThatDocument8 pagesEl Niño/La Niña-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO, Is A Quasi-Periodic Climate Pattern That9995246588No ratings yet