Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Snf2-Bab 11
Uploaded by
NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Snf2-Bab 11
Uploaded by
NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -Copyright:
Available Formats
BAB
B B
11
Bintang dan Galaksi dalam Alam
Semesta
Stars and Galaxies in the Universe
Konsep PENTING
IMPORTANT concepts
i-THINK Peta Pokok
BINTANG DAN GALAKSI DALAM ALAM SEMESTA
STARS AND GALAXIES IN THE UNIVERSE
Jenis galaksi Kitar hidup Ciri-ciri bintang Sistem suria dan
Types of galaxies bintang Characteristics galaksi Bima Sakti
Life cycle of of stars The solar system and
a star Milky Way galaxy
Galaksi elips Kelahiran bintang Suhu Kedudukan
Elliptical galaxies Birth of stars Temperature Location
Galaksi berpilin Kematian bintang Jarak Perbandingan saiz
Spiral galaxies Death of stars Distance relatif
Comparison of the
Galaksi tidak Warna relative size
seragam Colour
Irregular galaxies
Saiz
Size
Kecerahan
Brightness
APAKAH BINTANG, GALAKSI DAN ALAM SEMESTA?
WHAT ARE STARS, GALAXIES AND UNIVERSE?
Bintang ialah sfera bersinar dan banyak bintang boleh dilihat oleh mata kasar kita pada waktu
malam. Matahari ialah satu daripada berbilion bintang dalam galaksi Bima Sakti. Galaksi Bima Sakti
ialah satu daripada berbilion galaksi dalam alam semesta.
A star is a luminous sphere and many stars are visible to the naked eye at night. The Sun is one star among
the billions in the Milky Way galaxy. The Milky Way galaxy is one among the billions of galaxies in the universe.
179
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 179 12/28/17 4:12 PM
NOTA BESTARI
Galaksi Galaxies
1. Terdapat berjuta-juta galaksi dalam alam semesta. 1. There are millions of galaxies in the universe. Each
Setiap galaksi terdiri daripada berjuta-juta bintang. galaxy consists of millions of stars.
2. Galaksi dikelaskan berdasarkan bentuknya, iaitu 2. Galaxies are classified based on their shapes, i.e.
galaksi elips, galaksi berpilin dan galaksi tidak elliptical galaxies, spiral galaxies and irregular
seragam. galaxies.
3. Sistem suria berada dalam galaksi yang disebut 3. The solar system is in a galaxy called the Milky Way
Bima Sakti yang merupakan suatu galaksi berpilin. which is a spiral galaxies.
4. Matahari adalah satu daripada berjuta-juta bintang 4. The Sun is one of the millions of stars in the Milky
dalam Bima Sakti. Way.
Kitar Hidup Bintang (Hipotesis Nebula) Life Cycle of a Star (Nebular Hypothesis)
1. Bintang dilahirkan daripada nebula. 1. A star is formed from a nebula.
2. Nebula ialah awan besar yang terdiri daripada debu 2. A nebula is a large cloud that consists of dust and
dan gas-gas seperti hidrogen dan helium. gases such as hydrogen and helium.
3. Peringkat-peringkat kelahiran bintang: 3. Stages in the birth of a star:
(a) Gas-gas dan zarah-zarah debu dalam nebula (a) Gases and dust particles in the nebula are pulled
ditarik oleh daya tarikan graviti yang kuat dan by the strong gravitational force to form a
membentuk satu gumpalan. globe.
(b) Daya tarikan graviti yang kuat menyebabkan (b) The strong gravitational force causes the globe
gumpalan gas mengecut dan termampat sehingga of gases to shrink and it is compressed until it
sangat padat dan membentuk satu teras. becomes very compact to form a core.
(c) Teras ini semakin kecil dan padat disebabkan (c) This core becomes increasingly smaller
oleh daya tarikan graviti yang semakin kuat. and compact as a result of the increasing
(d) Apabila suhu dan tekanan dalam teras menjadi gravitational force.
terlalu tinggi, tindak balas nuklear berlaku. (d) When the temperature and pressure in the core
(e) Gas hidrogen ditukar kepada helium. Banyak become very high, a nuclear reaction occurs.
tenaga haba dan cahaya terbebas. Teras itu (e) Hydrogen gas is turned into helium. A lot of
menyinar dan satu bintang dilahirkan. heat and light energy are released. The core
4. Peringkat-peringkat kematian bintang yang shines and a star is formed.
sederhana besar seperti Matahari: 4. Stages in the death of a star of moderate size such
(a) Teras bintang kehabisan hidrogen (bahan api), as the Sun:
mengecut dan menjadi lebih panas. (a) The core of the star runs out of hydrogen (fuel),
(b) Haba yang dibebaskan memanaskan lapisan contracts and becomes hotter.
paling luar. Akibatnya, hidrogen dalam lapisan (b) The heat released heats up the outermost layer.
paling luar mula terbakar dan menyebabkan As a result, hydrogen within the outermost layer
bintang itu mengembang. starts to burn, causing the star to expand.
(c Bintang raksasa merah terbentuk. Jika bintang
(c) (c) A red giant star is formed. If the star is too big,
ini terlalu besar, bintang ini akan mengecut it will contract and produce big explosion called
dan menghasilkan letupan besar yang dikenal a supernova. A neutron star or black hole will
sebagai supernova. Bintang neutron atau be formed.
BAB
lohong hitam akan terbentuk. (d) A white dwarf will be formed if the red giant is
(d Bintang kerdil putih akan terbentuk jika bintang
(d) not massive.
11
raksasa merah tidak begitu besar.
Ciri-ciri Bintang
Ciri-ci Characteristics of Stars
1. Bintang
B dikelaskan berdasarkan ciri-ciri seperti suhu, 1. Stars are classified based on characteristics such as
jarak, warna, saiz dan kecerahan.
ja temperature, distance, colour, size and brightness.
2. Bintang yang mempunyai suhu sangat rendah 2. A star with a very low temperature is red while a
berwarna merah manakala bintang yang sangat star that is very hot is blue.
panas berwarna biru.
Nota Grafik
180
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 180 12/28/17 4:12 PM
Standard Kandungan
11.1 Bintang dan galaksi dalam alam semesta Tarikh:
AKTIVITI Ciri-ciri objek angkasa DSKP
11.1 PERBINCANGAN Characteristics of space objects STM
Jawab soalan-soalan tentang galaksi dan alam semesta.
Answer the questions on galaxies and the universe.
1 Berdasarkan gambar foto yang diberikan, nyatakan bentuk-bentuk galaksi.
Based on the photos given, state the shapes of galaxies. TP1 Praktis
Kendiri
Berpilin/Spiral Tidak seragam/Irregular Elips/Elliptical
(a) (b) (c)
Elips Berpilin Tidak seragam
Elliptical Spiral Irregular
aleerrii Info
fo
2 Apakah yang membentuk galaksi?/What forms a galaxy?
Gal
TP1
Berjuta-juta bintang/Millions of stars
Bima Sakti mempunyai diameter
3 (a) Apakah nama galaksi yang terletaknya sistem suria kita? 100 000 tahun cahaya dan
ketebalan 10 000 tahun cahaya.
What is the name of the galaxy where the solar system is located? TP1
The Milky Way has a diameter of
Bima Sakti/The Milky Way 100 000 light years and a
thickness of 10 000 light years.
(b) Apakah bentuk galaksi yang dinyatakan di 3(a)?
What is the shape of the galaxy stated in 3(a)? TP1
Berpilin/Spiral TONTON Keindahan
VIDEO alam semesta
The beauty of
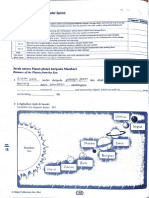
4 (a) Pada rajah angkasa lepas di bawah, lengkapkan petak-petak the universe
dengan perkataan yang berikut. https://www.
youtube.com/
In the diagram of outer space below, fill in the boxes with the following
watch?v=
words. TP1 HsvHpLCZhbg
(a) Galaksi
Galaxy
Galaksi
Galaxy
Sistem suria Bima Sakti
Solar system Milky Way
Alam semesta
Universe
BAB
(b) Alam semesta (c) Bima Sakti
Universe Milky Way
(b) Bandingkan saiz relatif antara objek-objek angkasa lepas dalam peta alir yang diberi.
11
Compare the relative size of the space objects in the given flow map. TP1
Sistem suria Bumi (planet) Alam semesta Galaksi Bima Sakti
akti
Solar system Earth (planet) Universe Milky Way galaxy
Bumi (planet) Sistem suria Galaksi Bima Sakti Alam semesta
Earth (planet) Solar system Milky Way galaxy Universe
Saiz semakin bertambah/Increasing size
181
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 181 12/28/17 4:12 PM
Tarikh:
AKTIVITI Kitar hidup bintang (Hipotesis nebula) DSKP
11.2 PERBINCANGAN The life cycle of a star (Nebular hypothesis) STM
A. Kelahiran bintang/The birth of a star
Lengkapkan petikan di bawah tentang kelahiran bintang.
Complete the passage below on the birth of a star. TP2
Nebula Hidrogen Haba Teras Cahaya Nuklear Muda Helium
Nebula Hydrogen Heat Core Light Nuclear Young Helium
Nebula terdiri daripada debu dan gas-gas seperti hidrogen
dan helium . Debu dan gas-gas dalam nebula ditarik bersama
oleh daya tarikan graviti yang kuat. Teras yang sangat
panas dan padat terbentuk dan menjadi semakin panas sehingga
atom hidrogen berpadu membentuk atom helium .
Tindak balas nuklear berlaku. Banyak tenaga haba
dan tenaga cahaya dibebaskan. Bintang dilahirkan.
Bintang ini disebut bintang muda . Bintang ini akan terus
berkembang menjadi bintang bersaiz sederhana besar seperti Matahari atau menjadi bintang besar.
nebula hydrogen
A is made up of dust and gases such as and
helium . The dust and gases in a nebula are pulled together by strong TONTON Nebula
forces of gravity. A
core that is very hot and dense is formed and it VIDEO Nebula
https://www.
hydrogen helium youtube.com/
becomes hotter until the atoms fuse to form
nuclear heat watch?v=
atoms. A reaction takes place. A lot of energy PBbqotbtT1s
light
and energy are released. A star is born. This star is called a
young star. The star will continue to expand and becomes an average
star like the Sun or becomes a massive star.
B. Kematian bintang sederhana besar seperti Matahari
The death of an average star like the Sun TP2
Terbakar/Burn Hidrogen/Hydrogen Memanaskan/Heats up Raksasa merah/Red giant
Mengembang/Expand Kerdil putih/White dwarf Mengecut/Contracts
Teras bintang kehabisan hidrogen (bahan api), mengecut
dan menjadi lebih panas.
Haba yang dibebaskan memanaskan lapisan bintang yang paling luar. Akibatnya, hidrogen
dalam lapisan bintang yang paling luar ini mula terbakar dan menyebabkan bintang
itu mengembang . Pada peringkat ini, bintang berwarna merah dan disebut raksasa merah .
Bintang kerdil putih akan terbentuk jika bintang raksasa merah tidak begitu besar.
hydrogen contracts
The core of the star runs out of (fuel), and becomes hotter. The heat released
heats up
BAB
the outermost layer. As a result, hydrogen within the outermost layer starts to
burn expand
, causing the star to . At this stage, the star is red and is called a
11 red giant
.A
white dwarf
will be formed if the red giant is not massive.
Galeri Info
fo
Apabila suhu mencapai 15 000°C, tindak balas nuklear berlaku.
When the temperature reaches 15 000°C, the nuclear reaction takes place.
182
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 182 12/28/17 4:12 PM
C. Kematian bintang besar (lebih besar daripada Matahari) dan bintang super besar
The death of a large star (larger than the Sun) and super-large star TP2
Supernova Raksasa merah Super raksasa Graviti
Supernova Red giant Supergiant Gravitational
Lohong hitam Bintang neutron Mengecut Hidrogen
Black hole Neutron star Contracts Hydrogen
Neutron Mengembang Berputar Tumpat
Neutrons Expands Rotates Dense
(a) Teras bintang kehabisan hidrogen , mengecut dan menjadi lebih panas.
hydrogen contracts
The core of the star runs out of , and becomes hotter.
(b) Hidrogen di lapisan paling luar terbakar dan bintang mengembang untuk
membentuk raksasa merah .
expands
Hydrogen within the outermost layer burns and the star to form
red giant
a .
(c) Raksasa merah terus mengembang untuk membentuk bintang
super raksasa .
supergiant
The red giant continues to expand to form a star.
(d) super raksasa
Bintang mengecut dengan cepat dan menghasilkan letupan
besar yang disebut supernova .
supergiant
The star contracts so quickly and produces a big explosion called
supernova .
Jika bintang besar Jika bintang super
If a large star besar
If a super-large star
(f) Lohong hitam
terbentuk.
Objek ini sangat
tumpat
Bintang neutron yang terdiri dan mempunyai
(e) graviti
daya yang sangat
neutron kuat. Objek ini tidak dapat dilihat di
daripada terbentuk.
berputar angkasa lepas.
Bintang ini dan
BAB
A black hole is formed. It is an object
mengeluarkan gelombang radio.
neutron star dense
11
A that consists of that is very and has a very
neutrons gravitational
is formed. This star strong force. It cannot
rotates be seen in outer space.
and gives out radio waves.
TONTON Kitar hidup
VIDEO bintang
Galeri Info
fo Life cycle
of a star
Cahaya di dalam lohong hitam tidak dapat terlepas ke angkasa lepas. Daya https://www.
graviti yang sangat kuat menarik semua bahan di sekelilingnya termasuk cahaya. youtube.com/
Light in a black hole cannot escape to space. The very strong gravitational force watch?v=
u0gEaDqoH58 Praktis
pulls all surrounding materials, including light.
Kendiri
183
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 183 12/28/17 4:12 PM
Tarikh:
AKTIVITI Pengelasan berdasarkan ciri-ciri bintang
11.3 PERBINCANGAN Classification based on the characteristics of stars
1 Pengelasan bintang berdasarkan saiz bintang.
The classification of stars based on the size of stars. TP1
Bintang neutron Bintang super raksasa Bintang raksasa merah Kerdil putih
Neutron star Supergiant star Red giant star White dwarf
Bintang/Stars Penerangan ringkas/Brief explanations
(a) Bintang super raksasa Bintang yang sangat besar iaitu lebih 100 kali lebih besar daripada
Supergiant star Matahari.
A very big star that is more than 100 times bigger than the Sun.
(b) Bintang raksasa merah Bintang yang beberapa puluh kali lebih besar daripada Matahari.
Red giant star A star that is tens of times bigger than the Sun.
(c) Kerdil putih Bintang yang sangat kecil iaitu lebih kecil daripada Matahari.
White dwarf A very small star, smaller than the Sun.
(d) Bintang neutron Bintang yang paling kecil dengan diameter kira-kira 10 km.
Neutron star The smallest star with a diameter of about 10 km.
2 Pengelasan bintang berdasarkan warna dan suhu bintang.
The classification of stars based on the colour and temperature of stars. TP2
(e) Warna bintang bergantung pada
Warna bintang Suhu permukaan (K)
Colours of stars Surface temperature (K) suhunya.
colour
The of a star depends on its
(a) Biru Lebih daripada 25 000 temperature.
Blue More than 25 000 (f) Bintang yang paling panas berwarna
biru .
(b) Biru keputihan
11 000 – 25 000 blue
Bluish-white The hottest stars are in
colour.
(c) Kuning (g) Bintang yang mempunyai suhu yang
5 000 – 6 000
Yellow sangat rendah atau paling sejuk berwarna
merah .
(d) Merah Kurang daripada 3 500
A star with a low temperature or which is the
Red Less than 3 500
red
coolest is in colour.
3 Pengelasan bintang berdasarkan kecerahan bintang dan jarak bintang dari Bumi.
The classification of stars based on the brightness of stars and the distance of the stars from the Earth. TP2
Jarak Jauh Matahari Saiz Malap Suhu
Distance Farther Sun Size Dimmer Temperature
Matahari Pembelajaran
(a) ialah bintang yang paling hampir dengan Bumi dan kelihatan Abad ke-21
BAB
sangat cerah.
Sun
The is the closest star to the Earth and appears to be very bright to us.
11 (b) Kecerahan bintang bergantung pada saiz bintang, jarak bintang dari Bumi
suhu
dan bintang. Sirius dan Rigel ialah contoh-contoh bintang yang cerah di langit.
size distance
The brightness of a star depends on the of the star, the of the star from
temperature
the Earth and the of the star. Sirius and Rigel are examples of the brightest stars in the
sky.
(c) Semakin jauh bintang dari Bumi, semakin malap bintang itu kelihatan
walaupun bintang itu sebenarnya merupakan satu bintang yang sangat cerah.
farther dimmer
The a star is from the Earth, the it will look even though it may actually
be a very bright star.
184
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 184 12/28/17 4:12 PM
REVISI EKSPRES 11
1 Lengkapkan petikan di bawah./Complete the passage below.
Galaksi terdiri daripada berjuta-juta bintang yang dilahirkan daripada nebula .
Terdapat galaksi yang berbentuk elips , berpilin dan
tidak seragam . Sistem suria kita terletak di dalam galaksi yang disebut Bima Sakti
yang berbentuk berpilin. Galaksi-galaksi bertaburan di dalam alam semesta .
A galaxy is made up of millions of stars , which are formed from
nebulae . There are elliptical , spiral and irregular galaxies.
Our solar system is located in a galaxy called the Milky Way which is spiral in shape.
Galaxies are scattered in the universe .
2 Nyatakan bintang di peringkat kematian bintang./State the stars at the stages in the death of stars.
(a) Bintang bersaiz sederhana/Medium-sized star
Bintang bersaiz sederhana
Medium-sized star
Raksasa merah/Red giant Kerdil putih/White dwarf
(b) Bintang besar dan super besar/Large and super-large stars Jika bintang besar
If a large star
Bintang neutron/Neutron star
Jika bintang
super besar
If a super-large
Raksasa merah Super raksasa Supernova star
Red giant Supergiant Supernova
Lohong hitam/Black hole
3 Bintang dikelaskan berdasarkan suhu , saiz , jarak dari
Bumi, warna dan kecerahan ./Stars are classified based on the temperature ,
size , distance from the Earth, colour and brightness .
PT3 PRAKTIS PENGUKUHAN 11
BAB
Arahan: Jawab semua soalan./Instructions: Answer all questions.
1 Tandakan ( ✓ ) bagi pernyataan yang betul dan tandakan ( ✗ ) bagi pernyataan yang salah tentang objek angkasa ngkasa
lepas./ Put a tick ( ✓ ) for a correct statement and a cross ( ✗ ) for an incorrect statement about outer space objects.
s. 11
(a) Suatu bintang malap kelihatan cerah jika bintang itu berdekatan dengan Bumi.
✓
A dim star can appear bright if it is closer to the Earth.
(b) Semua galaksi yang berbentuk elips mempunyai saiz yang sama.
✗
All the elliptical galaxies have the same size.
(c) Bumi terletak di dalam galaksi yang disebut Bima Sakti.
✓
The Earth is located in a galaxy called the Milky Way.
(d) Warna suatu bintang adalah berdasarkan jarak bintang itu daripada Bumi.
✗
The colour of a star is based on the distance of the star from the Earth.
[4 markah/4 marks]
185
11 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB11-Emie2LP.indd 185 12/28/17 4:12 PM
You might also like
- 05 - SPSF2 13 B11Document8 pages05 - SPSF2 13 B11Sarveshrau MagentharauNo ratings yet
- Conquerl. Sains. Dwi Tg2 2023 B11 4th.Document6 pagesConquerl. Sains. Dwi Tg2 2023 B11 4th.Nasihin Bin AzmiNo ratings yet
- SSintang Dan Galaksi Dalam Alam Semesta: I Stars and Galaxies LG The UniverseDocument4 pagesSSintang Dan Galaksi Dalam Alam Semesta: I Stars and Galaxies LG The UniverseIqbal HaikalNo ratings yet
- Geografi Tingkatan 2 Bab 1Document12 pagesGeografi Tingkatan 2 Bab 1anissofea160309No ratings yet
- Bab 9-Sains Form 3Document8 pagesBab 9-Sains Form 3Mohamad Tarmizi0% (1)
- Bintang Dan GalaksiDocument23 pagesBintang Dan GalaksiHafifahNo ratings yet
- Folio Sains Tingkatan 2Document10 pagesFolio Sains Tingkatan 2Kannis KanniahNo ratings yet
- Sains Folio Bab 9 Bintang Dan GalaksiDocument14 pagesSains Folio Bab 9 Bintang Dan GalaksiWei YinNo ratings yet
- Bintang Dan Galaksi Dalam Alam SemestaDocument13 pagesBintang Dan Galaksi Dalam Alam SemestaAMIRAH NADIAH BINTI MOHD NORIZAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2 KSSM Bab 11Document1 pageSains Tingkatan 2 KSSM Bab 11AinNo ratings yet
- RPT 2023 Sains t2 EsembasDocument38 pagesRPT 2023 Sains t2 Esembaskhatijah85No ratings yet
- NOTA SC F2 BAB 11 Zila Khalid )Document26 pagesNOTA SC F2 BAB 11 Zila Khalid )ah221124No ratings yet
- Bab 11 T2 KSSM Bintang Dan Galaksi DalamDocument35 pagesBab 11 T2 KSSM Bintang Dan Galaksi DalamNurl AinaNo ratings yet
- Bab 11 T2 KSSM Bintang Dan Galaksi DalamDocument35 pagesBab 11 T2 KSSM Bintang Dan Galaksi Dalammustamin samadNo ratings yet
- Bab 11 Bintang Dan Galaksi Dalam Alam Semesta Sains T2 2019Document16 pagesBab 11 Bintang Dan Galaksi Dalam Alam Semesta Sains T2 2019lady scorpion100% (1)
- Galaksi SAINS TAHUN 6Document5 pagesGalaksi SAINS TAHUN 6NORNADIRAH A GHANINo ratings yet
- f3 BAB 9 PENEROKAAN ANGKASA LEPASDocument13 pagesf3 BAB 9 PENEROKAAN ANGKASA LEPASAkram HarithNo ratings yet
- Bintang Dan Galaksi Bab 9Document25 pagesBintang Dan Galaksi Bab 9ameermxNo ratings yet
- Bab 11 T2 KSSM Bintang Dan Galaksi DalamDocument35 pagesBab 11 T2 KSSM Bintang Dan Galaksi DalamHanif SallehNo ratings yet
- Bintang-Bintang Dan GalaksiDocument16 pagesBintang-Bintang Dan Galaksijy176473% (15)
- Bintang Dan Galaksi Sains Tingkatan 3Document8 pagesBintang Dan Galaksi Sains Tingkatan 3Hanya DhiaNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Modul 2 Sains T2 PKPPDocument10 pagesJawapan Modul 2 Sains T2 PKPPFatihah My100% (1)
- Kejadian Bintang Dan Teori Big Bang Dalam Hukum Al-Quran Dan Kebuktian SainsDocument36 pagesKejadian Bintang Dan Teori Big Bang Dalam Hukum Al-Quran Dan Kebuktian Sainskakakcun89% (9)
- Sains Bab 9 F3Document19 pagesSains Bab 9 F3Lea NajihahNo ratings yet
- Struktur GalaksiDocument6 pagesStruktur GalaksiRahayu Riandika PutriNo ratings yet
- 9 - Bintang Dan GalaksiDocument14 pages9 - Bintang Dan GalaksiNurul Hidayah YahayaNo ratings yet
- Bab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepasDocument20 pagesBab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepasZaman ZackNo ratings yet
- NOTA SC F3 BAB 9 Zila Khalid )Document29 pagesNOTA SC F3 BAB 9 Zila Khalid )C.No ratings yet
- Tingkatan 3 Bab 9 Bintang Dan Galaksi FolioDocument19 pagesTingkatan 3 Bab 9 Bintang Dan Galaksi FolioMing Lou60% (5)
- Bab 9 Cuaca Angkasa Lepas: Sains Tingkatan 3 KSSM Oleh Cikgu Norazila Khalid SMK Ulu Tiram, JohorDocument29 pagesBab 9 Cuaca Angkasa Lepas: Sains Tingkatan 3 KSSM Oleh Cikgu Norazila Khalid SMK Ulu Tiram, JohorLATHIKKA A/P GANESH MoeNo ratings yet
- SAINS T3 BAB 9 CUACA ANGKASA LEPAS (Struktur Dan Fenomena Di Matahari)Document12 pagesSAINS T3 BAB 9 CUACA ANGKASA LEPAS (Struktur Dan Fenomena Di Matahari)amaniyparkNo ratings yet
- Bab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepasDocument15 pagesBab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepaswanNo ratings yet
- Bab 9 T3 Cuaca Angkasa LepasDocument29 pagesBab 9 T3 Cuaca Angkasa LepasAkari GamingNo ratings yet
- ANGKASADocument22 pagesANGKASAAmir Haziq SemailNo ratings yet
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation 20231022 163533 0000Document7 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation 20231022 163533 0000Nur Hana SyamsulNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sem 10 - HBSC4203 EARTH &SPACEDocument32 pagesAssignment Sem 10 - HBSC4203 EARTH &SPACECrosbie Lim100% (2)
- Presentation 2Document67 pagesPresentation 2Husna DamiaNo ratings yet
- Nota Bumi Dan Alam SemesterDocument105 pagesNota Bumi Dan Alam SemesterSolahudin HanisNo ratings yet
- MatahariDocument5 pagesMatahariRetna KumariNo ratings yet
- Kosmografi Bab 1Document24 pagesKosmografi Bab 1Syarif HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Bab 9Document2 pagesBab 9mdazrilomar08No ratings yet
- Baby Alien Personal Organizer XLDocument17 pagesBaby Alien Personal Organizer XLniniangel36No ratings yet
- Kuliah PDPC 2-Sistem Suria (Konsep & Kandungan)Document13 pagesKuliah PDPC 2-Sistem Suria (Konsep & Kandungan)Nor AdilaNo ratings yet
- Cuaca Luar AngkasaDocument9 pagesCuaca Luar Angkasag-98042058No ratings yet
- Sistem SuriaDocument4 pagesSistem SuriaRahmat HassanuddinNo ratings yet
- New f3 Bab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepasDocument31 pagesNew f3 Bab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepasJaneHLianNo ratings yet
- Angkasa LepasDocument7 pagesAngkasa LepasZarah Tae Yang100% (1)
- Kimia KSSM Tingkatan 4 - Bab 2Document20 pagesKimia KSSM Tingkatan 4 - Bab 2Saidatul SuhadhaNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2 Bab 13 KSSMDocument8 pagesSains Tingkatan 2 Bab 13 KSSMAinNo ratings yet
- Sistem Suria Sg!Grsystem: Jarak Antara Planet-Planet Daripada MatahariDocument4 pagesSistem Suria Sg!Grsystem: Jarak Antara Planet-Planet Daripada MatahariIqbal HaikalNo ratings yet
- Solar and Lunar EclipseDocument16 pagesSolar and Lunar Eclipsezahir azmanNo ratings yet
- Solusi PG (Peserta)Document14 pagesSolusi PG (Peserta)DwiNo ratings yet
- DMTKDocument13 pagesDMTKSiti Fadzilah TaraziNo ratings yet
- Asteroid, Komet Dan MeteorDocument25 pagesAsteroid, Komet Dan Meteorizzuddinkhalid40% (5)
- Makalah Gerhana Matahari Dan BulanDocument21 pagesMakalah Gerhana Matahari Dan BulanUlfa Dira AzhariNo ratings yet
- Sistem SuriaDocument19 pagesSistem SuriaMuhammad ZakuwanNo ratings yet
- Objek SamawiDocument3 pagesObjek SamawiMelodyNo ratings yet
- KOSMOLOGIDocument1 pageKOSMOLOGISiti NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Topik 1.1: Pengenalan Kepada KimiaDocument6 pagesTopik 1.1: Pengenalan Kepada KimiaNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- F5c1-Kadar Tindak BalasDocument10 pagesF5c1-Kadar Tindak BalasNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- SnF1 - Bab 1.3 NEWDocument6 pagesSnF1 - Bab 1.3 NEWNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- F5C4 TermokimiaDocument22 pagesF5C4 TermokimiaNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- SnF1 - Bab 1.1Document7 pagesSnF1 - Bab 1.1NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- F5C2 SebatianDocument19 pagesF5C2 SebatianNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Bab 1.1: Pengenalan Kepada KimiaDocument17 pagesBab 1.1: Pengenalan Kepada KimiaNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- SnF1 - Bab 1.3Document14 pagesSnF1 - Bab 1.3NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- SnF1 - Bab 1.4Document18 pagesSnF1 - Bab 1.4NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- SnF1 - Bab 1.6Document15 pagesSnF1 - Bab 1.6NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Hebat Sains M18Document83 pagesHebat Sains M18NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Sains T1B8 CAHAYA DAN OPTIKDocument47 pagesSains T1B8 CAHAYA DAN OPTIKNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- SnF1 - Bab 2.2Document5 pagesSnF1 - Bab 2.2NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Hebat Sains M18Document83 pagesHebat Sains M18NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Sains T1B5 JIRIMDocument46 pagesSains T1B5 JIRIMNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Sains T1B6 JADUAL BERKALADocument58 pagesSains T1B6 JADUAL BERKALANUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Skema Pemarkahan PPT SN T.2 TBDocument4 pagesSkema Pemarkahan PPT SN T.2 TBEncikMohdNNo ratings yet
- SNF2 Bab 13Document24 pagesSNF2 Bab 13NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Snf2-Bab 6Document12 pagesSnf2-Bab 6NUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Sains T1B3 KOORDINASIDocument21 pagesSains T1B3 KOORDINASINUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Sains T1B2 SELDocument70 pagesSains T1B2 SELNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF2 09 B7Document28 pages05 - SPSF2 09 B7Mohd Aidil Ubaidillah100% (1)
- BukuDocument174 pagesBukuivytan2191No ratings yet