Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accoustics
Uploaded by
Danni Artlife0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
6. ACCOUSTICS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageAccoustics
Uploaded by
Danni ArtlifeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
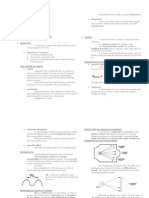
ACCOUSTICS 1.
Cycle - full circuit of particle
SCIENCE & TREATMENT OF SOUND
2. Frequency - number of times a cycle is repeated
ELEMENTS:
1. Source 3. Amplitude - maximum displacement
2. Transmission path
3. Receiver 4. Velocity - speed of sound
POROUS ABSORBENT 5. Wavelength - distance
Best for lower band frequency
6. Pure tone - one energy one frequency
ECHO
The repetition of a sound produced by the reflection of sound waves 7. Musical Tone - many pre tones
from an obstructing surface, loud enough and received late enough
to be perceived as distinct from the source 8. Intensity - rate of flow at sound energy
RESONANCE QUALITY OF SOUND
The intensification and prolongation of sound produced by
sympathetic vibration 1. Reverberation - the prolonging of sound
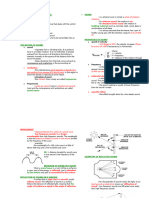
PHON 2. Echo - repetition of sound, with magnitude and delay
Unit of loudness level 3. Flutter - rapid succession of echoes caused by the reflection of sound
waves back and forth between two parallel surfaces
SOUND ABSORPTION
Process of dissipating sound energy by converting it into heat 4. Creep/ Crawl - reflection of sound from a curved surface
SOUND 5. Sound Foci
Fluctuation in pressure, particle displacement in elastic medium
6. Diffusion - sound is everywhere
SABIN
unit of absorption equivalent to 1 sq ft of perfectly absorptive material 7. Refraction - when traveling forward in a straight path, it changes direction as
it passes through different density and causes sound wave to
bend
Frequency - expressed in hertz 8. Diffraction - acoustic phenomenon which causes sound wave to bend
Decibel - unit of sound
Noise - unwanted sound 9. Focusing - sound waves reflected from a concave surface
Decay time - reverberation time
Hertz - the Si unit of frequency
CHARACTER OF SOUND
You might also like
- Basic Principles of Ultrasonic Testing. Theory and Practice.Document42 pagesBasic Principles of Ultrasonic Testing. Theory and Practice.Teckelino89% (9)
- Acoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCDocument14 pagesAcoustics & Sound Insulation: 2 Year B.SCKomal ChopadaNo ratings yet
- Echoes and UltraSoundDocument27 pagesEchoes and UltraSoundjothipriyagNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Dr. CalaquianDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Dr. CalaquianHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Homework #14 (Phy 112) SolutionsDocument25 pagesHomework #14 (Phy 112) SolutionsKvn4N60% (1)
- Blender UvDocument141 pagesBlender UvMarcos LinsNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument39 pagesSound WavesNurlailie Md JamilNo ratings yet
- The Following Are The Various Definitions of "Acoustics" Depending On Its ContextDocument4 pagesThe Following Are The Various Definitions of "Acoustics" Depending On Its ContextPAUL DANIEL CABILLONo ratings yet
- LeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Diana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- GRP 6 Legal Considerations in Urban Design and Design Requirements of Specific Places in Towns and CitiesDocument9 pagesGRP 6 Legal Considerations in Urban Design and Design Requirements of Specific Places in Towns and CitiesDerick Delacruz100% (5)
- Acoustics: Architectural Building ServicesDocument20 pagesAcoustics: Architectural Building ServicesGauri WaikarNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocument14 pages1.6 Sound Wavespanitiafiziksmkb100% (1)
- UAP Docs 200-208Document85 pagesUAP Docs 200-208Julia Esquivias-Virtucio60% (5)
- ReflnDocument20 pagesReflnDaniel Boenfie100% (1)
- BNCA Architectural AcousticsDocument35 pagesBNCA Architectural AcousticsSakshi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Acoustical MaterialDocument31 pagesAcoustical MaterialVISHAL SHARMANo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument8 pagesHistoryPrince Q ChanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sound and AcousticsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Sound and AcousticsWaqar Abid AZNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3 - Acoustics and Lighting SystemsDocument2 pagesBuilding Utilities 3 - Acoustics and Lighting SystemsNICOLE ADRIENNE RIVERANo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Sound in An Enclosed SpaceDocument15 pagesBehaviour of Sound in An Enclosed SpacePrajjwal TakNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Total Internal Reflection 2020 Answer PDFDocument9 pages6.2 Total Internal Reflection 2020 Answer PDFAin NadiaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Architecture ReviewerDocument5 pagesTheory of Architecture ReviewerSharra Lexine100% (5)
- Acoustic Definations and DefectsDocument12 pagesAcoustic Definations and Defectstejaswini C gaur100% (2)
- F2-C10 Sound Waves PDFDocument39 pagesF2-C10 Sound Waves PDFNora SallehNo ratings yet
- Accoustics: Cycle Frequency Amplitude Velocity Wavelength Pure Tone Musical Tone IntensityDocument2 pagesAccoustics: Cycle Frequency Amplitude Velocity Wavelength Pure Tone Musical Tone IntensityRowell Ian Gana-anNo ratings yet
- ACCOUSTICSDocument1 pageACCOUSTICSMACASUSI, GLAIZA MAE A.No ratings yet
- Acoustics: Character of SoundDocument1 pageAcoustics: Character of SoundBaby Grace LegareNo ratings yet
- ACOUSTICS p1 PDFDocument1 pageACOUSTICS p1 PDFNeslie Joy AgotoNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument2 pagesAcousticsIhcee CalveloNo ratings yet
- Accoustic SDocument1 pageAccoustic SMaribeth Sagot AzueloNo ratings yet
- ICA - AREA B (BU, ELECTRICAL Shortcut)Document8 pagesICA - AREA B (BU, ELECTRICAL Shortcut)MARIANE ANGELA PADULLANo ratings yet
- Ica - Area B (Bu, ElectricalDocument8 pagesIca - Area B (Bu, ElectricalMARIANE ANGELA PADULLANo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Module 3Document2 pagesUnit 3 Module 3Eleonor Martinez ManuelNo ratings yet
- Ica - Area B (Bu, ElectricalDocument9 pagesIca - Area B (Bu, ElectricalMARIANE ANGELA PADULLANo ratings yet
- Acoustics and Lighting: FrequenciesDocument15 pagesAcoustics and Lighting: FrequenciesPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesAcoustics and LightingNeslie Joy AgotoNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument15 pagesRRLjerry elizagaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesAcoustics and LightingSam AlvarezNo ratings yet
- C10 Sound WavesDocument3 pagesC10 Sound WavesONG JUN YAO MoeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 8 1st PTDocument6 pagesReviewer in Science 8 1st PTApril AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AcousticsDocument10 pagesReviewer AcousticsCy VinegasNo ratings yet
- Lucifer05 SoundDocument2 pagesLucifer05 SoundTasneem SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Architectural Lighting & Acoustics Pre-LimDocument9 pagesArchitectural Lighting & Acoustics Pre-LimCharles Harvey DaabayNo ratings yet
- Sensation CourseDocument170 pagesSensation CourseAlex BalintNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument8 pagesAcousticsLaila CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acoustical DefectsDocument1 pageAcoustical Defectskookie maeNo ratings yet
- Sound in One Shot - NCERT - Class 09 - SPRINTDocument24 pagesSound in One Shot - NCERT - Class 09 - SPRINTAdityanshu RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sound NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 10 Sound NotesAzaanNo ratings yet
- Acoustic NotesDocument21 pagesAcoustic NoteschriziafreeNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument82 pagesUnit INisarga JNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument460 pagesUnit VNisarga JNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Perception of SoundDocument21 pagesThe Nature and Perception of Soundsheila louiseNo ratings yet
- Acoustics, Sound and Sound Properties: OutlineDocument25 pagesAcoustics, Sound and Sound Properties: OutlineSHREYA LOHAKARENo ratings yet
- Inf 3Document10 pagesInf 3Anabell Tiban100% (1)
- Mario 5Document3 pagesMario 5Mario MartínezNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument9 pagesSoundpuneetNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AcousticsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To AcousticsClarence MamucodNo ratings yet
- Utilities FA1Document2 pagesUtilities FA1FewisNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Module 5: SoundsDocument1 pageUnit 1. Module 5: SoundsMaristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Architectural AcousticsDocument4 pagesEssential Elements of Architectural AcousticsJoanna TamanoNo ratings yet
- Arch 322 ModuleDocument14 pagesArch 322 ModuleGANITANO HEZEL, A.No ratings yet
- Architectural AccousticsDocument25 pagesArchitectural AccousticsJOTHINo ratings yet
- Knowledge Organiser - Year 4 - Sound PDFDocument3 pagesKnowledge Organiser - Year 4 - Sound PDFIrum KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Module 5: Sounds: Longitudinal WaveDocument1 pageUnit 1. Module 5: Sounds: Longitudinal WaveMaristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- F2 Chapter 10 Sound WavesDocument6 pagesF2 Chapter 10 Sound WavesMei Shuen CheamNo ratings yet
- AR315 Topic2 ULOa ALOCELJA, L.Document5 pagesAR315 Topic2 ULOa ALOCELJA, L.Lourainnefaith aloceljaNo ratings yet
- Aurar 501 Architectural Acoustics Unit 1Document53 pagesAurar 501 Architectural Acoustics Unit 1Santhu DasariNo ratings yet
- MCQ From Sound & WaveDocument3 pagesMCQ From Sound & WaveRaktimNo ratings yet
- BT5 - Lesson 1Document38 pagesBT5 - Lesson 1Fritz Dela VegaNo ratings yet
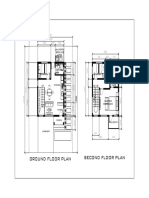
- Second Floor Plan Ground Floor Plan: Laundry/ Service AreaDocument1 pageSecond Floor Plan Ground Floor Plan: Laundry/ Service AreaDanni ArtlifeNo ratings yet
- 004-Geology, Geography & GeomorphologyDocument22 pages004-Geology, Geography & GeomorphologyDanni ArtlifeNo ratings yet
- AllenDocument21 pagesAllenAkshay YadavNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Review - BLM - 10-7 2Document2 pages10.2 Review - BLM - 10-7 29jr9f2rtb7No ratings yet
- Classroom AcousticsDocument21 pagesClassroom AcousticsSham Salonga Pascual100% (1)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument4 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Applied Acoustics: Roy L. Deavenport, Matthew J. Gilchrest, David J. ThomsonDocument9 pagesApplied Acoustics: Roy L. Deavenport, Matthew J. Gilchrest, David J. ThomsonRoy DeavenportNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Phenomena in Chichen ItzaDocument8 pagesAcoustics Phenomena in Chichen Itzajacctito2No ratings yet
- Refresher Fiber OpticsDocument8 pagesRefresher Fiber OpticsspidyanNo ratings yet
- Light and Shadow FormationDocument13 pagesLight and Shadow FormationNikil J.PNo ratings yet
- Surfaces in Precision Engineering, Microengineering and NanotechnologyDocument17 pagesSurfaces in Precision Engineering, Microengineering and NanotechnologyNicola VirgilioNo ratings yet
- Scince 2nd SummDocument2 pagesScince 2nd SummMaria Angelica BermilloNo ratings yet
- 01-Reflection of Light (MCQ) DifficultDocument10 pages01-Reflection of Light (MCQ) DifficultNarendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Photography PresentationDocument92 pagesPhotography PresentationKim QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Optical Computing: The End of Electron-Based ComputingDocument3 pagesOptical Computing: The End of Electron-Based ComputingTRIAD TECHNO SERVICESNo ratings yet
- Bris SextantDocument9 pagesBris Sextantkwayneolson60810% (1)
- 5.0 Properties of Light (Yr4) 2020Document7 pages5.0 Properties of Light (Yr4) 2020Zulkifly Md AlwayiNo ratings yet
- LUMION 6 - Quickstart GuideDocument10 pagesLUMION 6 - Quickstart GuideHải ĐăngNo ratings yet
- A Retrospective of Roland Shack's Global View of DiffractionDocument20 pagesA Retrospective of Roland Shack's Global View of DiffractionBoros Csanád ÖrsNo ratings yet
- 32.4-Light-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qp 2Document10 pages32.4-Light-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qp 2LiliNo ratings yet
- Photo-Realism Fundamentals 0811Document28 pagesPhoto-Realism Fundamentals 0811leonardofullenkampNo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument46 pagesAcousticsbzkizo_sbbNo ratings yet
- L. Sun, H. Hou - Measurement of Sound Absorption by Underwater Acoustic Material Using Pulse-Separation Method (2014)Document5 pagesL. Sun, H. Hou - Measurement of Sound Absorption by Underwater Acoustic Material Using Pulse-Separation Method (2014)Ivan FelisNo ratings yet
- WorksheetsDocument1 pageWorksheetsRuhma YousufNo ratings yet