Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Bank Smta1101
Uploaded by
Ahmad RazaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank Smta1101
Uploaded by
Ahmad RazaCopyright:
Available Formats
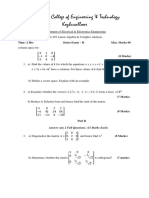
SATHYABAMA
INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
B.E. – ALL BRANCHES EXCEPT BIO-GROUPS
UNIT – 1
PART – A
4 1
1. Given that A =
[ ]
3 2 , find the eigen values of AT.
1 2
2. Show that the square matrix
[ ]
4 3 satisfies its own characteristics equation
.
2 0 1
3. Find the sum and product of the eigen values of the matrix
( 0
1
2
0
0
2 )
2 −1 3
4.
−1 4 −2
Write down the quadratic form whose corresponding matrix is 3 −2 6
[ ] .
5. State Cayley Hamilton theorem.
6. State any two properties of eigen values of a matrix.
A= 7 3
7. Use Cayley-Hamilton theorem to find the inverse of the matrix 2 6 [ ]
2 2 1
8.
[ ]
1 3 1
Two Eigen values of the matrix A = 1 2 2 are equal to 1 each. Find the third Eigen
value.
9. State any one property of Eigen value of a matrix and verify it on the matrix
[31 12 ] .
10. Find the matrix of the Quadratic form x12+3x22+6x32-2x1x2+6x1x3+5x2x3
PART – B
11 −4 −7
1. Find the eigen values and eigen vectors of the matrix A =
[ 7 −2 −8
10 −4 −6 ]
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS – I QUESTION BANK
SATHYABAMA
INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
B.E. – ALL BRANCHES EXCEPT BIO-GROUPS
2 −1 2
2. Verify Cayley-Hamilton theorem for the matrix
[
A= −1
1
2 −1
−1 2 ] .
Hence compute A-1.
2 0 4
3. Reduce the matrix
[ ]
A= 0
4
6
0
0
2 to diagonal form by orthogonal transformation.
4. Reduce the quadratic form
2x 21 + x22 +x32 +2 x1 x 2 −2x 1 x 3 −4 x 3 x 2 to canonical form by an
orthogonal transformation.
1 3 7
5. Verify Cayley-Hamilton Theorem for the matrix
A= 4 2 3
1 2 1 ( )
6. Verify Cayley-Hamilton theorem and hence find the inverse of
1 2 −1
( 3 −3 1
2 1 −2 ) 2 2 2
7. Reduce the quadratic form
6 x 1 +3 x 2 +3 x3 −4 x 1 x 2−2 x 2 x3 +4 x 1 x 3
to canonical form by an orthogonal transformation.
1 1 1
9. Find the inverse of the matrix
A= 1 2 −3
2 −1 3 [ ] by using Cayley-Hamilton theorem.
8. Reduce the Quadratic form 2x2 + 5y2 + 3z2 + 4xy to canonical form by an orthogonal
reduction.
10. Reduce the quadratic form
8 x 21 +7 x 22 +3 x 23−12 x 1 x2 +4 x 1 x 3 −8 x 2 x 3 in to its canonical
form by using orthogonal reduction.
UNIT-II
PART – A
1. Define evolutes and envelope of a curve
2. Write down the formula for radius of curvature in Cartesian coordinates.
x
+ yt=2 c .
3. Find the envelope of t
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS – I QUESTION BANK
SATHYABAMA
INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
B.E. – ALL BRANCHES EXCEPT BIO-GROUPS
4. Find the radius of curvature of the curve given by y = ex at x = 0.
a
y=mx + ,
5. Find the envelope of the family of lines m m being the parameter
6. Find the curvature of the circle x2 + y2 = 25
7. Write the formula to find the center of the circle of curvature and equation to the circle of
curvature.
8. Find the radius of curvature for the curve x = at2, y = 2at.
9. Find the envelope of y = mx + √ a2 m2 +b 2 , where m is the parameter.
10. Define curvature of a curve.
PART – B
1, Find the radius of curvature at the point
( 32a , 32a ) on the curve x3+y3=3axy.
x2 y2
+ =1
2. Find the envelope of the ellipse a2 b2 where a2 + b2 = c2.
3. (a) Find the radius of curvature of the cycloid x = a( + sin); y = a(1 - cos).
(b) Find the envelope of the curve x cos + y sin = a, being the parameter.
4. Find the evolute of the rectangular hyperbola xy = c2.
5. Find the evolute of the parabola y2 = 4ax.
x2 y2
2
+ 2 =1
6. Find the evolute of the ellipse a b
a a
7. Find the equation of the circle of curvature of the curve
(4 4)
√ x+ √ y= √a at , .
8. Find the evolute of y2 = 4ax treating it as the envelope of its normal.
( log x )
y= at x=1
9. (a) Find the radius of curvature for x
(b) Find the envelope (x - )2 + y2 = k where is the parameter.
10. (a) Find the evolute of the parabola x2 = 4ay
x y
+ =1
(b) Find the envelop of a b where a and b are connected by the relation a2 + b2 = c2.
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS – I QUESTION BANK
You might also like
- MA3151-Matrices and Calculus Question BankDocument9 pagesMA3151-Matrices and Calculus Question Bankpraveenin2005No ratings yet
- Ma3151 Matrices and Calculus 1876243520 Que Bank (Ma3151) Mat&CalDocument19 pagesMa3151 Matrices and Calculus 1876243520 Que Bank (Ma3151) Mat&Caldvmohan1979No ratings yet
- 231BS11 Question BankDocument8 pages231BS11 Question BankTechView TeamTamilNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Assignment-1Document2 pagesUnit 1 (Assignment-1ntsiddharthchaturvedi1778136No ratings yet
- Question Bank (Matrix Dinesh Kapoor)Document10 pagesQuestion Bank (Matrix Dinesh Kapoor)Karanpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- VISVODAYA TECHNICAL ACADEMY, KAVALI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS I B.Tech QUESTION BANKDocument2 pagesVISVODAYA TECHNICAL ACADEMY, KAVALI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS I B.Tech QUESTION BANKTharun kondaNo ratings yet
- MA3151 QB IQ - by WWW - Easyengineering.net IQ QB 1Document9 pagesMA3151 QB IQ - by WWW - Easyengineering.net IQ QB 1VarsaNo ratings yet
- MA3151 QB IQ - by WWW - Easyengineering.net IQ QB 1Document9 pagesMA3151 QB IQ - by WWW - Easyengineering.net IQ QB 1VarsaNo ratings yet
- Module-I AM-IDocument3 pagesModule-I AM-IWAQAR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Tut - 1Document2 pagesTut - 1varatharajuNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics 1 - Tut SheetsDocument3 pagesApplied Mathematics 1 - Tut SheetsRajiv MishraNo ratings yet
- QP CODE: 21101240: Where A + B 1Document3 pagesQP CODE: 21101240: Where A + B 1aui207auiNo ratings yet
- Matrix algebra and series problemsDocument1 pageMatrix algebra and series problemsTushar KumarNo ratings yet
- JAFARI COLLEDGE MATHS PRACTICAL EXAMDocument1 pageJAFARI COLLEDGE MATHS PRACTICAL EXAMKamiyabhussainNo ratings yet
- Eng Math II - Tutorial 2Document3 pagesEng Math II - Tutorial 2Tuhafeni HailekaNo ratings yet
- Jntuh Questions PaperDocument2 pagesJntuh Questions PaperDilip YadavNo ratings yet
- Maths QB 2Document5 pagesMaths QB 2rishipandian2006No ratings yet
- I B.Tech I Semester Regular Exams July 2021 Chemistry QuestionsDocument7 pagesI B.Tech I Semester Regular Exams July 2021 Chemistry Questionsmaruthi631No ratings yet
- B.E. Internal Examination 2019 Common Second Semester Assessment Test I Mathematics IIDocument1 pageB.E. Internal Examination 2019 Common Second Semester Assessment Test I Mathematics IISaba Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Mair12 Int 1Document1 pageMair12 Int 1Bharathi VedhanandamNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument2 pagesLinear AlgebraVinay MenakNo ratings yet
- 268 - MA8251 Engineering Mathematics II - 2 Marks Important Questions PDFDocument8 pages268 - MA8251 Engineering Mathematics II - 2 Marks Important Questions PDFGuna 046133No ratings yet
- Ma8251 - Engineering Mathematics - Ii - QBDocument10 pagesMa8251 - Engineering Mathematics - Ii - QBMUTHURAMAN mathsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Sem IV 2023-24 FinalDocument1 pageTutorial 1 Sem IV 2023-24 FinalDibyas Sanjay DubeyNo ratings yet
- Tut Sheet 3 (Matrices)Document2 pagesTut Sheet 3 (Matrices)RishitaNo ratings yet
- Maths Assignment-I PDFDocument3 pagesMaths Assignment-I PDFpadam bhandariNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentVishwansh KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Nithiya MaharajanNo ratings yet
- Assignment I Mathematics I 2018Document2 pagesAssignment I Mathematics I 2018Narayan SinghNo ratings yet
- MA3151 Matrices and Calculus Question Bank 2Document5 pagesMA3151 Matrices and Calculus Question Bank 2VIGNESH VASUNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument2 pagesMatricesvignanarajNo ratings yet
- Tutorial sheet-3-MA1003E-2Document2 pagesTutorial sheet-3-MA1003E-2sara johnNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 (Tma 101)Document1 pageAssignment 01 (Tma 101)Aashish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 3 FDB 5Document3 pages3 FDB 5KOMAL AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Linear - Algebra QuestDocument3 pagesLinear - Algebra QuestShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Refit-Value University Mathematics for Management Group AssignmentDocument2 pagesRefit-Value University Mathematics for Management Group AssignmentTedla GuyeNo ratings yet
- Mathe 111Document3 pagesMathe 111rit dharNo ratings yet
- MM PrefinalDocument4 pagesMM PrefinalMohan RaoNo ratings yet
- Minimum ProblemsDocument3 pagesMinimum ProblemsWittin PrinceNo ratings yet
- SATHYABAMA UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I EXAMDocument4 pagesSATHYABAMA UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I EXAMmashaNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: X, y N X N X yDocument2 pagesGeneral Instructions:: X, y N X N X yAkash VNo ratings yet
- Prev Year Maths Autonomous QPDocument9 pagesPrev Year Maths Autonomous QPsivabavatharniiNo ratings yet
- Transposing MatricesDocument3 pagesTransposing MatricesAgung JatiariskaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test BMDocument2 pagesPractice Test BMjyoti guptaNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering: Department of Science and HumanitiesDocument12 pagesDhanalakshmi Srinivasan College of Engineering: Department of Science and HumanitiesLëøNo ratings yet
- MA 201 Linear Algebra & Complex Analysis Series Exam – IIDocument2 pagesMA 201 Linear Algebra & Complex Analysis Series Exam – IIsyulmnmdNo ratings yet
- MA6151 Part-B 16 Marks PDFDocument7 pagesMA6151 Part-B 16 Marks PDFJoselin DanielNo ratings yet
- Ma3151 Important Questions PadeepzDocument10 pagesMa3151 Important Questions Padeepzvlmohammedadnan9No ratings yet
- M1 May June 2018Document4 pagesM1 May June 2018धर्मराज करंडेNo ratings yet
- I Assignment Question Papers (Set 1 - Set 9)Document9 pagesI Assignment Question Papers (Set 1 - Set 9)Dr. Kamalam MNo ratings yet
- F 3xy I y J When It Moves A ParticleDocument3 pagesF 3xy I y J When It Moves A ParticleAgarvin SuthendranNo ratings yet
- Practice Probems EM-IV IT-NewDocument39 pagesPractice Probems EM-IV IT-NewSanikaNo ratings yet
- Class XII Mathematics Ch-3 Matrices Worksheet: cosα −sin α sin α cosα 1 2 3 4 3 1 2 5 7 11Document4 pagesClass XII Mathematics Ch-3 Matrices Worksheet: cosα −sin α sin α cosα 1 2 3 4 3 1 2 5 7 11haryanv JangidNo ratings yet
- MA5158 Matrices Problem Set-1Document3 pagesMA5158 Matrices Problem Set-1MonishNo ratings yet
- ACSIAM1Document3 pagesACSIAM1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Math1020 Sgta Week6 QnsDocument3 pagesMath1020 Sgta Week6 QnsbangtanmochimanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-I - MATH 1002 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial-I - MATH 1002 PDFBidit MangalNo ratings yet
- IIST MA211 - Linear Algebra Tutorial-I SolutionsDocument3 pagesIIST MA211 - Linear Algebra Tutorial-I SolutionsShiva YadavNo ratings yet
- LINEAR ALGEBRA TEST 1 (SET B) SOLUTIONSDocument2 pagesLINEAR ALGEBRA TEST 1 (SET B) SOLUTIONSpradnya RamgudeNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Usp 1Document14 pagesUsp 1Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- S262Document3 pagesS262yamini seshakala0% (1)
- Landing A Job in A Product Based CompanyDocument8 pagesLanding A Job in A Product Based CompanySmart BoyzNo ratings yet
- S262Document3 pagesS262yamini seshakala0% (1)
- Assignment 4Document6 pagesAssignment 4Fulsoundar ParthNo ratings yet
- ENGR 233 Lecture 24 FinalDocument22 pagesENGR 233 Lecture 24 FinalZiad JreijNo ratings yet
- G 9 Physics1. Module 2Document10 pagesG 9 Physics1. Module 2Marvi TejeroNo ratings yet
- The Hyperbolic Theory of Special RelativityDocument109 pagesThe Hyperbolic Theory of Special RelativityscribblemanNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Elimination With Partial PivotingDocument4 pagesGaussian Elimination With Partial PivotingNi SienNo ratings yet
- Matrix Inversion: Determinants, Inverses, and RankDocument19 pagesMatrix Inversion: Determinants, Inverses, and RankMas GundNo ratings yet
- Homework 4: SOLUTIONS: Drexel University, College of Engineering 2017-2018 Academic YearDocument15 pagesHomework 4: SOLUTIONS: Drexel University, College of Engineering 2017-2018 Academic YearNadim AminNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2 PDFDocument4 pagesMathematics 2 PDFAbsolute ZeroNo ratings yet
- ModulesDocument6 pagesModuleskishalay sarkarNo ratings yet
- 2023 Practice Matrices Modelling TaskDocument16 pages2023 Practice Matrices Modelling TaskEdris ZamaryalNo ratings yet
- JEE Maths DPPDocument14 pagesJEE Maths DPPNikhil MittalNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - Paul DawkinsDocument342 pagesLinear Algebra - Paul Dawkinssumeet141792% (13)
- CHAPTER 02 - Linear CodesDocument31 pagesCHAPTER 02 - Linear CodesSundui BatbayarNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksDocument3 pagesA Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksAnton Van WykNo ratings yet
- Ankur Bansal Engineering Maths Lectures CollectionDocument1 pageAnkur Bansal Engineering Maths Lectures CollectionMayank ShelarNo ratings yet
- 2 Assessment2Document10 pages2 Assessment2مبنيةنميب نتمبيةنNo ratings yet
- Vector and scalar quantitiesDocument5 pagesVector and scalar quantitiesMikee RizonNo ratings yet
- Robot Kinematics Chapter SummaryDocument35 pagesRobot Kinematics Chapter SummaryArunkumar MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of The Critical Time Step For Peridynamic ModelsDocument25 pagesEstimation of The Critical Time Step For Peridynamic Modelsje.nickpNo ratings yet
- CBSE Delhi Govt. Schools PTS-23 Math ExamDocument6 pagesCBSE Delhi Govt. Schools PTS-23 Math ExamShweta ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- LADE13 Inner Product SpacesDocument19 pagesLADE13 Inner Product SpacesRoumen GuhaNo ratings yet
- McaDocument248 pagesMcakunzmilan8383No ratings yet
- A. Cylindrical Coordinates: Ao AzDocument33 pagesA. Cylindrical Coordinates: Ao AzekaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Application of Markov Chains To Analyze and Predict The Time SeriesDocument5 pages2010 Application of Markov Chains To Analyze and Predict The Time SeriesMacLeodNo ratings yet
- Sol 04Document3 pagesSol 04kirk putmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tools and Vector DPP 4Document3 pagesMathematical Tools and Vector DPP 4tan jigNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Bases and Dimensions: ? Linear IndependenceDocument9 pages2.3 Bases and Dimensions: ? Linear IndependenceALMUSTAPHA UMARNo ratings yet
- Vector-04 (Worksheet)Document1 pageVector-04 (Worksheet)Krishna Khanna 11 S6No ratings yet
- Module 1d More On The Augmented MatricesDocument9 pagesModule 1d More On The Augmented MatricesESTEBAN , BETHEL A.No ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1Document6 pagesExercise 3.1harsh dugharNo ratings yet