Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Social Literacy Is A Student
Uploaded by
Divine CardejonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Social Literacy Is A Student
Uploaded by
Divine CardejonCopyright:
Available Formats
Social Literacy is a student’s successful performance and understanding of social Skills, organizational skills,
and communication skills. It is the student’s ability to connect effectively with those around them. Social literacy
spans across interacting with peers, family, coworkers, teachers, and even people we may not have met face
to face.
Social literacy is so crucial in a person’s success. The ability to communicate and voice opinions and thoughts,
as well as listening to opinions and thoughts of others, is essential in learning. Firmly grasping social cues and
norms is extremely beneficial. In literally every single setting of our lives: school, home, work, clubs and
activities, interacting with people (whether face to face or behind technology), we use our social literacy. We
play so many roles every day and we socially need to understand how to play those roles appropriately. For
example: I would speak differently with my friends than I would my mother, or I would chat on Facebook
differently than I would while emailing a professor. Without an understanding of this communication, one
cannot function with success in society.
Social Literacy is "the development of social skills in a social setting, which helps people to communicate in a
respectful manner, as well as becoming involved in a community."
Social literacy emerges at a very young age. Social literacy starts when a child starts to communicate with
others. Children at a very young age start to learn what is acceptable and what is unacceptable. For example,
most children learn at a young age when it is acceptable for them to express what they are thinking. As we
grow older, we learn more on how we should act towards others. As we move into future generations, social
literacy has broadened. It is no longer face-to-face interactions. Children are also learning what is acceptable
to do when relating to technology. Since technology is becoming more prevalent in our lives, children must also
learn how to respectively interact using technology.
Social literacy, from the perspective of the social-cultural theory, is more than the ability to read and write, and
more than mastering literacy skills. Children can learn literacy through social interaction between themselves
and children and/or adults in or outside school. Adults can use books, games, toys, conversations, field trips,
and stories to develop the literacy practices through fun. Collaborative learning between schools, family, and
community can help develop a child's literacy. In addition, given today's technical knowledge, adults can take
into consideration how to use technology in the learning process and to employ it in teaching children how to
read and write in a social context. "Literacy practices and events are always situated in social, cultural,
historical and political relationships and embedded in structures of power. Furthermore, literacy practices
involve social regulation of text, i.e. who has access to it and who can produce it, and such practices are
purposeful and embedded in broader social goals and cultural practices. Moreover, these practices change
and new ones are frequently acquired through processes of informal learning and sense-making" (p. 23). For
that reasons, teachers can design multiple levels of literacy activities and practices to fit different students'
abilities and way of learning and "provide a pedagogical approach which fosters communities of learners, plan
classroom activities that embed meaningful opportunities to engage in the analysis and construction of
multimodal texts, and utilize teaching approaches that move beyond the false tension between abstracting the
codes of language and learning their application for meaningful purposes" (p. 126).
Social skills are the skills we use to communicate and interact with each other, both verbally and non-verbally,
through gestures, body language and our personal appearance. Human beings are sociable creatures and we
have developed many ways to communicate our messages, thoughts and feelings with others.
Human values are the principles, convictions and internal beliefs that people adopt and follow in their daily
activities.
You might also like
- Simple and Silly Social -Cultural Strategies to Fight Isolation in Higher EducationFrom EverandSimple and Silly Social -Cultural Strategies to Fight Isolation in Higher EducationNo ratings yet
- Social LIteracyDocument8 pagesSocial LIteracyJason T. Badillo100% (1)
- BENL Midterms ReviewerDocument11 pagesBENL Midterms ReviewermykeedizonNo ratings yet
- Social LiteracyDocument6 pagesSocial LiteracyElma SintosNo ratings yet
- Social Literacy: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesSocial Literacy: Objectiveslusty brenNo ratings yet
- Module in Education 10 (Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum)Document12 pagesModule in Education 10 (Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum)Ruby YbanezNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument30 pagesHandoutsRudz AlvezNo ratings yet
- Profed08 Chapter 7Document8 pagesProfed08 Chapter 7RobNo ratings yet
- Foundarions of Social StudiesDocument5 pagesFoundarions of Social StudiesJohn Paul RespondeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 3-WPS OfficeCyra AsueloNo ratings yet
- Mtds of Teaching Social StudiesDocument4 pagesMtds of Teaching Social StudiesElias BonkeNo ratings yet
- What Is Social Literacy and Why Is It ImportantDocument2 pagesWhat Is Social Literacy and Why Is It ImportantCarl Lewis83% (6)
- A. Definitions of Traditional LiteraciesDocument6 pagesA. Definitions of Traditional LiteraciesGie Paderes Sande100% (1)
- Social Literacy: II - BSED Values EducationDocument31 pagesSocial Literacy: II - BSED Values EducationJOYCE MAIRENZ LACDAONo ratings yet
- What Are Social Interaction SkillsDocument5 pagesWhat Are Social Interaction SkillsJean BernalNo ratings yet
- Cpe109 Module 3.0Document4 pagesCpe109 Module 3.0Rosalie AbaoNo ratings yet
- Arellano University: Mas 106: Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDocument2 pagesArellano University: Mas 106: Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumCarl LewisNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Literacy Module 2Document6 pagesEnhancing Literacy Module 2Jomari JanolanNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Jclarence P. 5 Pillars of EducationDocument2 pagesNicolas Jclarence P. 5 Pillars of EducationCl ArNo ratings yet
- Essay For Social LiteracyDocument1 pageEssay For Social LiteracyGwen EverNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document1 pageModule 9michelle pornobiNo ratings yet
- Developmental and Social Factors: By: Teresita L. Caballero Educ 1 Sunday 7am-10amDocument16 pagesDevelopmental and Social Factors: By: Teresita L. Caballero Educ 1 Sunday 7am-10amAlexa Kint Obaob100% (1)
- Social Foundation: Jovenal V. Dela Cruz, JRDocument25 pagesSocial Foundation: Jovenal V. Dela Cruz, JRVoj Aled ZurcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Social Skills DevelopmentDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - Social Skills DevelopmentMary Mae EnocNo ratings yet
- Benlac Module 5Document9 pagesBenlac Module 5Pao MejiaNo ratings yet
- Social LiteracyDocument5 pagesSocial LiteracyKareen Mae SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3Angela Catimpohan100% (1)
- REFLECTIONDocument1 pageREFLECTIONJames Cabaldo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Social LiteracyDocument61 pagesSocial LiteracyApril Bagon-Faeldan67% (3)
- Final ExamDocument5 pagesFinal ExamANGIE LYN ROMERONo ratings yet
- Reflection 1Document2 pagesReflection 1api-583811062No ratings yet
- 4 PillarsDocument3 pages4 PillarsRoxan SilorioNo ratings yet
- What Is Democratic EducationDocument4 pagesWhat Is Democratic Educationbillythekid24No ratings yet
- Answer For Chapter 4Document1 pageAnswer For Chapter 4Lovelyn MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Tura Christian College BA. 2 Semester Paper II Foundations of Educations Unit VI - SocialisationDocument4 pagesTura Christian College BA. 2 Semester Paper II Foundations of Educations Unit VI - SocialisationEarlithaNo ratings yet
- Reading LiteracyDocument1 pageReading LiteracyMakuren NexusNo ratings yet
- The School As A Community of Engaged LearnersDocument23 pagesThe School As A Community of Engaged LearnersVũ LanNo ratings yet
- Ed3700 - Farrell Dana - Curriculum AnalysisDocument6 pagesEd3700 - Farrell Dana - Curriculum Analysisapi-330883613No ratings yet
- 21st Century Literacies Activity (Prof Ed 7)Document2 pages21st Century Literacies Activity (Prof Ed 7)Alona GarnerNo ratings yet
- Research Paper SocializationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Socializationebjbytvhf100% (1)
- QUESTION: Discuss The Importance of Sociology of Education To Both Teachers and StudentsDocument8 pagesQUESTION: Discuss The Importance of Sociology of Education To Both Teachers and StudentsHazel Ann SobrepeñaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Sosial EducationDocument3 pagesObjectives of Sosial EducationLing Siew EeNo ratings yet
- Ucu 100 Assignment 1Document4 pagesUcu 100 Assignment 1OGEGA KERUBONo ratings yet
- Social Literacy - Group 3Document17 pagesSocial Literacy - Group 3Melanie PaloNo ratings yet
- HeritageDocument7 pagesHeritageHonest ShokoNo ratings yet
- Rationale For Teaching Social StudiesDocument2 pagesRationale For Teaching Social StudiesMeaghan Ann50% (2)
- San Jose Community CollegeDocument6 pagesSan Jose Community CollegeSimple HeavenNo ratings yet
- English 2Document2 pagesEnglish 2Nhat NamNo ratings yet
- Social StudiesDocument18 pagesSocial StudiesSumathi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Text: "Media To The Filipino Youth" by Alyssa MDocument5 pagesReaction Paper Text: "Media To The Filipino Youth" by Alyssa MMARIFE BUSBUSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document10 pagesLesson 1Rhea amor SabuitoNo ratings yet
- Education As A Social ProcessDocument6 pagesEducation As A Social ProcessEarlitha100% (1)
- Bae Sociology NotesDocument44 pagesBae Sociology NotesSsentongo Nazil0% (1)
- Aas14 Ece13 ReviewerDocument9 pagesAas14 Ece13 ReviewerALMALYN ANDIHNo ratings yet
- RRL For Araling PanlipunanDocument2 pagesRRL For Araling PanlipunanMay-Ann S. Cahilig100% (2)
- Lev Vygostky - Learning TheoriesDocument5 pagesLev Vygostky - Learning TheoriesMaria Jose CarrizoNo ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum 2ndDocument11 pagesBuilding and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum 2ndMaris daveneNo ratings yet
- Eric Drown, Educational PhilosophyDocument2 pagesEric Drown, Educational PhilosophyEric DrownNo ratings yet
- 8606 Assignment AnswerDocument19 pages8606 Assignment Answernaveed shakeelNo ratings yet
- Child and AdolescentDocument12 pagesChild and AdolescentKimberly BoteNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Eng 16Document3 pagesModule 10 Eng 16Divine CardejonNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Eng 16Document4 pagesModule 11 Eng 16Divine Cardejon100% (1)
- Testing Your PeopleDocument4 pagesTesting Your PeopleDivine CardejonNo ratings yet
- JudgeDocument8 pagesJudgeDivine CardejonNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English 8: The Wedding of The Mouse (N.D.) Retrieved November 8, 2021 FromDocument7 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in English 8: The Wedding of The Mouse (N.D.) Retrieved November 8, 2021 FromDivine CardejonNo ratings yet
- Product-Oriented Learning Competencies: (Beginner)Document4 pagesProduct-Oriented Learning Competencies: (Beginner)Kri S ELNo ratings yet
- Student Report: Social Studies Class TestDocument4 pagesStudent Report: Social Studies Class Testila thakurNo ratings yet
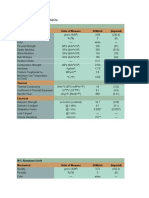
- Engineering Properties (Al O) : 94% Aluminum Oxide Mechanical Units of Measure SI/Metric (Imperial)Document7 pagesEngineering Properties (Al O) : 94% Aluminum Oxide Mechanical Units of Measure SI/Metric (Imperial)Hendy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Critical and Creative ThinkingDocument26 pagesCritical and Creative Thinkingjoaquinricardo20153461No ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument10 pagesExerciseNguyen Mai QuynhNo ratings yet
- Description: Super Thoroseal Is A Blend of PortlandDocument2 pagesDescription: Super Thoroseal Is A Blend of Portlandqwerty_conan100% (1)
- Headworks & Barrage: Chapter # 09 Santosh Kumar GargDocument29 pagesHeadworks & Barrage: Chapter # 09 Santosh Kumar GargUmer WaheedNo ratings yet
- Loading and Hauling Dump Truck: DumperDocument2 pagesLoading and Hauling Dump Truck: DumperRJNo ratings yet
- Stearic Acid MSDSDocument6 pagesStearic Acid MSDSJay LakhaniNo ratings yet
- s145 Series HMM 201902 PDFDocument73 pagess145 Series HMM 201902 PDFEuNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial BehaviourDocument16 pagesEntrepreneurial Behaviournonalyn tomboconNo ratings yet
- Bibliografi 3Document3 pagesBibliografi 3Praba RauNo ratings yet
- Almugea or Proper FaceDocument5 pagesAlmugea or Proper FaceValentin BadeaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Principles of Cooperative ConversationDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Principles of Cooperative Conversationdelilah o balladNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University Lecture NoteDocument65 pagesAddis Ababa University Lecture NoteTADY TUBE OWNER100% (9)
- Module-2: SolidificationDocument16 pagesModule-2: SolidificationSachin AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Preview - ISO+8655 6 2022Document6 pagesPreview - ISO+8655 6 2022s7631040No ratings yet
- Rail Inspection Vehicle Using Ir Sensor and Spot Marking SystemDocument63 pagesRail Inspection Vehicle Using Ir Sensor and Spot Marking SystemNarayananNanuNo ratings yet
- Vernacular in Andhra PradeshDocument1 pageVernacular in Andhra PradeshNandyala Rajarajeswari DeviNo ratings yet
- L5CoachMentorReflectiveLog TemplateDocument9 pagesL5CoachMentorReflectiveLog TemplateHadusssNo ratings yet
- Universal Human Values NotesDocument13 pagesUniversal Human Values NotesS RamNo ratings yet
- Sony DVD Player Power Circuit DiagramDocument40 pagesSony DVD Player Power Circuit DiagramHariyadiNo ratings yet
- Embargoed: Embargoed Until April 24, 2019 at 12:01 A.M. (Eastern Time)Document167 pagesEmbargoed: Embargoed Until April 24, 2019 at 12:01 A.M. (Eastern Time)Las Vegas Review-JournalNo ratings yet
- Makenna Resort: by Drucker ArchitectsDocument12 pagesMakenna Resort: by Drucker ArchitectsArvinth muthuNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Development Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)Document4 pagesHuman Resource Development Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)GuruKPO90% (20)
- AutoCAD 2006 Installing Network License Manager0Document12 pagesAutoCAD 2006 Installing Network License Manager0gurugovindanNo ratings yet
- Low Invasion CoringDocument4 pagesLow Invasion CoringKHALEDFEKAIRNo ratings yet
- Session Outline Template - English - 1 W5ADocument2 pagesSession Outline Template - English - 1 W5ARakhshanda FawadNo ratings yet
- PVTP Complete PDF FreeDocument680 pagesPVTP Complete PDF FreemaxliraNo ratings yet
- Seventh Pay Commission ArrearsDocument11 pagesSeventh Pay Commission Arrearssantosh bharathyNo ratings yet
- English Pronunciation: Pronounce It Perfectly in 4 months Fun & EasyFrom EverandEnglish Pronunciation: Pronounce It Perfectly in 4 months Fun & EasyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (24)
- English. Speaking Master (Proficiency level: Intermediate / Advanced B1-C1 – Listen & Learn)From EverandEnglish. Speaking Master (Proficiency level: Intermediate / Advanced B1-C1 – Listen & Learn)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (47)
- Learn English: Must-Know American English Slang Words & Phrases (Extended Version)From EverandLearn English: Must-Know American English Slang Words & Phrases (Extended Version)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (30)
- How to Improve English Speaking: How to Become a Confident and Fluent English SpeakerFrom EverandHow to Improve English Speaking: How to Become a Confident and Fluent English SpeakerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (56)
- English Vocabulary Master for Intermediate Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B1-B2)From EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master for Intermediate Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B1-B2)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (18)
- English Vocabulary Master: Phrasal Verbs in situations (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)From EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master: Phrasal Verbs in situations (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (43)
- Learn English: Ultimate Guide to Speaking Business English for Beginners (Deluxe Edition)From EverandLearn English: Ultimate Guide to Speaking Business English for Beginners (Deluxe Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (26)
- Teaching Vocabulary, Revised EditionFrom EverandTeaching Vocabulary, Revised EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- English in Situations: Business English – New Edition (16 Topics – Proficiency level: B2 – Listen & Learn)From EverandEnglish in Situations: Business English – New Edition (16 Topics – Proficiency level: B2 – Listen & Learn)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- English Vocabulary Master: 150 Phrasal Verbs (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)From EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master: 150 Phrasal Verbs (Proficiency Level: Intermediate / Advanced B2-C1 – Listen & Learn)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (56)
- Learn English - Level 4: Intermediate English, Volume 1: Lessons 1-25From EverandLearn English - Level 4: Intermediate English, Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- ESL Role Plays: 50 Engaging Role Plays for ESL and EFL ClassesFrom EverandESL Role Plays: 50 Engaging Role Plays for ESL and EFL ClassesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- English Made Easy Volume One: Learning English through PicturesFrom EverandEnglish Made Easy Volume One: Learning English through PicturesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- 7 Shared Skills for Academic IELTS Speaking-WritingFrom Everand7 Shared Skills for Academic IELTS Speaking-WritingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Picture of Dorian Gray (The Original 1890 Uncensored Edition + The Expanded and Revised 1891 Edition)From EverandThe Picture of Dorian Gray (The Original 1890 Uncensored Edition + The Expanded and Revised 1891 Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9054)
- Learn British English - Level 1: Introduction to British English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25From EverandLearn British English - Level 1: Introduction to British English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- English Vocabulary Master for Advanced Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B2-C1)From EverandEnglish Vocabulary Master for Advanced Learners - Listen & Learn (Proficiency Level B2-C1)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Learn English - Level 3: Beginner English, Volume 1: Lessons 1-25From EverandLearn English - Level 3: Beginner English, Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Speak Like An English Professor: A Foolproof Approach to Standard English SpeechFrom EverandSpeak Like An English Professor: A Foolproof Approach to Standard English SpeechNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect: English Conversation, Premium Second EditionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect: English Conversation, Premium Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- 47 ESL Conversation Topics with Questions, Vocabulary & Writing Prompts: For Beginner-Intermediate Teenagers & AdultsFrom Everand47 ESL Conversation Topics with Questions, Vocabulary & Writing Prompts: For Beginner-Intermediate Teenagers & AdultsNo ratings yet
- TOEFL iBT Premium with 8 Online Practice Tests + Online Audio, Eighteenth EditionFrom EverandTOEFL iBT Premium with 8 Online Practice Tests + Online Audio, Eighteenth EditionNo ratings yet
- Learn English - Level 1: Introduction to English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25From EverandLearn English - Level 1: Introduction to English, Volume 1: Volume 1: Lessons 1-25Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Spanish Short Stories For Beginners (Vol 1): Use short stories to learn Spanish the fun way with the bilingual reading natural methodFrom EverandSpanish Short Stories For Beginners (Vol 1): Use short stories to learn Spanish the fun way with the bilingual reading natural methodRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)