Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agayan Tate Niversity - Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Agayan Tate Niversity - Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Uploaded by
JayLord Mico PacisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Agayan Tate Niversity - Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Agayan Tate Niversity - Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Uploaded by
JayLord Mico PacisCopyright:
Available Formats
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Learning Objectives:
1). To evaluate the hydrostatic pressure loading acting on a body that is
immersed in a liquid.
2). To determine the resultant of a given line, pressure, or body load on a
submerged body and to evaluate the reaction acting on the body that
carries such a load.
3). To do an engineering estimate of the equivalent loading using the
hydrostatic equation both on plane and curved surfaces.
4) To analyze problems involving hydrostatic force on plane and curved
surfaces.
Introduction
On any surface or body that is submerged in water or any other liquid, there is a force
acting because of the hydrostatic pressure. Learn how to determine the magnitude of this
force. Study of hydrostatic forces on submerged or static surfaces is very important for the
design and engineering processes. Construction of dams, installation of underwater
hydraulic systems, and forces exerted on ships are some of the important and crucial
processes that require study of hydrostatic forces.
Please watch video on:
https://youtu.be/VlCrI5YvGfA
Key Points:
Pressure is a scalar quantity defined as force per unit area. Pressure only
concerns the force component perpendicular to the surface upon which
it acts, thus if the force acts at an angle, the force component along the
direction perpendicular to the surface must be used to calculate pressure.
The pressure exerted on a surface by an object increases as the weight of
the object increases or the surface area of contact decreases.
Alternatively, the pressure exerted decreases as the weight of the object
decreases or the surface area of contact increases.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Pressure exerted by ideal gases in confined containers is due to the
average number of collisions of gas molecules with the container walls per
unit time. As such, pressure depends on the amount of gas (in number of
molecules), its temperature, and the volume of the container.
Pressure of a Fluid:
When a fluid is contained in a vessel, it exerts force at all points on the sides &
bottoms of the container. The force exerted per unit area is called pressure.
Pressure head of a liquid:
A liquid is subjected to pressure due to pressure due to its own weight, this
pressure increases as the depth of the liquid increases. Let a bottomless cylinder
stand in the liquid
Let: w = specific weight of the liquid
H = height of the liquid in the cylinder
A = Area of the cylinder
Thus, the intensity of pressure at any point in a liquid is proportional to its
depth.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
ABSOLUTE, GAGUE, ATOMOSPHERIC, AND VACCUME PRESSURES:
Atmospheric Pressure:
The atmospheric air exerts a normal pressure upon all surfaces with which It is in contact
& known as atmospheric pressure.
Absolute pressure:
It is defined as the pressure which is measured with reference to absolute vacuum pressure
or absolute zero pressure.
Gauge pressure:
It is defined as the pressure which is measured with the help of a pressure measuring
instrument in which the atmospheric pressure is taken as datum. The atmospheric pressure
on the scale is marked as zero.
Vacuum pressure:
It is defined as the pressure below the atmospheric pressure.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Pressure Measuring Instruments:
The pressure of a fluid is measured by the following devices
1. Manometers
2. Mechanical Gauges.
Manometers:
Manometers are defined as the device used for measuring the pressure at a point in a
fluid by balancing the column of fluid by the same another column of the fluid. They are
classified as:
(a) Simple manometers.
(b) Differential Manometers.
Mechanical Gauges:
Mechanical gauges are defined as the device used for measuring the
pressure by balancing the fluid column by the spring or dead weight.
Commonly used mechanical pressure gauges are:
Diaphragm pressure gauge
Bourdon tube pressure gauge
Dead –weight pressure gauge
Bellow pressure gauge
Simple Manometers:
A simple manometer of a glass tube having one of its ends connected
to a point where pressure is to be measured and other end remains open to
atmosphere. Common types of simple manometers are:
Piezometer
U- tube Manometer
Single Column Manometer
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Piezometer:
It is the simple form of manometer used for measuring gauge
pressures. One end of this manometer is connected to the point where
pressure is to be measured and other end is open to the atmosphere as
shown in Figure. The rise of liquid gives the pressure head at that point A.
Then pressure at A
U – tube Manometer:
It consist of glass tube bent in U- shape, one end of which is connected to a point
at which pressure is to be measured and other end remains open to the
atmosphere as shown in figure. The tube generally contains mercury.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
(a) For Gauge Pressure:
Let be is the point which is to be measured, whose value is p. The
datum line is A-A.
Pressure is same in a horizontal surface. Hence pressure above the
horizontal datum surface line A-A in the left column and in the right
column of U-tube manometer should be same pressure above A-A in the
left column
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
(b) For Vacuum Pressure:
For measuring vacuum pressure, the level of the heavy liquid
in the manometer will be as shown in figure. Then Pressure above AA in the left
column
Single Column Manometer:
Single column Manometer is modified form of a U- tube manometer in which
a reservoir, having a large cross- sectional area (about 100 times as compared to
the area of the tube) is connected to one of the limbs (say left limb)of the
manometer as shown in figure. Due to large cross- sectional area of the reservoir,
for any variation in pressure, the change in the liquid level in the reservoir will be
very small which may be neglected and hence the pressure is given by the height
of liquid in the other limb. The other limb may be vertical or inclined. Thus there
are two types of single column manometer as:
1. Vertical Single Column Manometer:
Let X-X be the datum line in the reservoir and in the right limb of
the manometer when it is not connected to the pipe. When the
manometer is connected to the pipe, due to high pressure at A, the
heavy liquid in the reservoir will be pushed downward and will rise in the
right limb.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Fall of heavy liquid in the reservoir will cause a rise of heavy liquid
level in the right limb.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Now consider the datum line Y-Y as shown in Fig 2.15.Then
pressure in the right limb above Y-Y.
Pressure in left limb above Y-Y
Equating the pressure, we have
But from equation (i),
As the area A is very large as compared to a, hence ratio becomes very small and
can be neglected. Then
2. Inclined Single Column Manometer:
The given figure shows the inclined single column manometer which is more
sensitive. Due to inclination the distance moved by the heavy liquid in the right
limb will be more.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
From the above equation for the pressure in the single column manometer the pressure
A is
Substituting the value of h2, we get:
Sample Problems: (Manometers)(as presented in www.learnthermo.com)
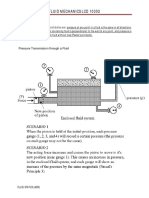
Pressure Measurement Using a Multi-Fluid Manometer
A pressurized vessel contains water with some air above it, as shown below. A multi-fluid
manometer system is used to determine the pressure at the air-water interface, point F. Determine
the gage pressure at point F in kPa gage.
Page
Source: www.learnthermo.com
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Solution:
Read: Use the barometer equation to work your way through the different fluids from point 1 to point 2.
Remember that gage pressure is the difference between the absolute pressure and atmospheric
pressure.
Given: h1 0.24 m rw 1000 kg/m3
h2 0.35 m roil 790 kg/m3
h3 0.52 m rHg 13600 kg/m3
P2 101.325kPa
Find: P1,gauge ??? kPa gauge
Assumptions: 1- The fluids in the system are completely static.
2- The densities of the liquids are uniform and constant.
3- The acceleration of gravity is: g 9.8066 m/s2
kg-m/N-
gC 1 s2
Equations / Data / Solve:
Gage pressure is defined by :
Eqn 1
If we assume that P2 is atmospheric
pressure, then Eqn 1 becomes :
Eqn 2
The key equation is the Barometer
Eqn 3
Equation :
Now, apply Eqn 1 repeatedly
to work our way from point 1 to
point 2.
Eqn 4
Some key observations are: Eqn 5
These are true because the points are connected by open tubing, the fluid is not flowing in this system
and no change in the composition of the fluid occurs between A & B or C & D or D & E.
PA > P2, therefore : Eqn 6
PE > P1, therefore : Eqn 7
PB > PC, therefore : Eqn 8
Combine Eqns 2, 5 & 6 to get : Eqn 9
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Use Eqns 3 & 5 to eliminate PC from Eqn 7 :
Eqn 10
Now, solve for P1 -
Eqn 11
P2 :
Combining Eqns 10
& 2 yields :
Eqn 12
Plugging values into Eqn
12 yields : P1,gage 64287 Pa gage
kPa
P1,gage 64.29 gage
Answers
: P1,gage 64.3 kPa gage
If you are curious : P1 165.61kPa PA = PB 170.68kPa
PC =
P2 101.325kPa PD = PE 167.97kPa
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Practice Problems:
PP No. 1. A U-tube manometer is connected to a closed tank containing air and
water as shown in Figure 2 below. At the closed end of the manometer the
absolute air pressure is 140 kPa. Determine the reading on the pressure gage for
a differential reading of 1.5-m on the manometer. Express your answer in gage
pressure value. Assume standard atmospheric pressure and neglect the weight
of the air columns in the manometer.
PP No. 2. A closed cylindrical tank filled with water has a hemispherical dome
and is connected to an inverted piping system as shown in Figure. The liquid in
the top part of the piping system has a specific gravity of 0.8, and the remaining
parts of the system are filled with water. If the pressure gage reading at A is 60
kPa, determine: a) the pressure in pipe B, and the b) pressure head, in millimeters
of mercury, at the top of the dome (point C).
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
PP No. 3. For the inclined-tube manometer of Figure below, the pressure in pipe
A is 8 kPa. The fluid in both pipes A and B is water, and the gage fluid in the
manometer has a specific gravity of 2.6. What is the pressure in pipe B
corresponding to the differential reading shown?
PP NO. 4. The inverted U-tube manometer of Figure as shown, contains oil (SG =
0.9) and water as shown. The pressure differential between pipes A and B, pA –
pB, is -5 kPa. Determine the differential reading, h.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
FORCES ON PLANE AREA
The total force on any plane area submerged in a liquid by multiplying the
specific weight of the liquid by the product of the area and the depth of its
centroid.
The value of F is independent of the angle of inclination of the plane if the depth
of its centroid is unchanged. Since γhc is pressure at the centroid, the total
pressure force on any plane area submerged in a liquid is the product of the area
and the pressure at the centroid.
Forces on Submerged surfaces:
The force on the surface of hydraulic structure such as gates, vessels, dams,
or other submerged bodies is caused by the weight of the fluid. This force exerted
by the fluid on submerged bodies is called Hydrostatic force. It is important to
compute this force and its location for the design of these hydraulic structures.
We use three different method to compute the hydrostatic force: formula
method, geometrical method, integration method, and project method (used
for curved surfaces).
Source: Torlapati, 2019
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
The resultant force on a hydrostatic surface is given by
The force has a direction that is perpendicular to the plate, since the entire
pressure distribution acts in this direction. The location of the resultant force is
called center of pressure (P). The location of this is determined by the balance of
moments that requires the moment of the resultant force about the x-axis and
about the y-axis.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Consider an inclined plane submerged in a static fluid as shown in the figure. The resultant
force FR is acting perpendicular to the plane since no shear force is present when the
fluid is at rest. FR has a line of action that passes through the point (xcp, ycp), which is called
the center of pressure. Note that the pressure acting perpendicular to the plane surface
is also referred to as the normal stress.
Now take a small differential element dA at a depth of h. The differential force dF
acting on dA is given by
dF= ρghdA
The magnitude of the resultant force can be obtained by integrating the differential force over
the whole area
The integral represents the first moment of the area about the x axis, which is equal to
where yc is the y coordinate of the centroid of the plane surface. From trigonometry,
hc = yc sinθ where hc is the vertical distance from the fluid surface to the centroid of the plane
surface. The resultant force is simplified to FR = ρghcA.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
The center of pressure, xcp and ycp can be obtained by summing moments about the y and x
axis, respectively. First, by equating the sum of moments of all pressure forces about the x axis to
the moment of the resultant force:
where is the second moment of the area or the area moment of inertia
(Ix) about the x axis. According to the parallel axis theorem, the moment of
inertia can also be written as
Ix = Ix' + Ayc2
where Ix' is the second moment of the area with respect to the centroidal axis,
which is parallel to the x axis.
Hence, the center of pressure coordinate ycp is given by
Parallel Axis Theorem
Similarly, xcp can be obtained by equating the sum of moments of all pressure
forces about the y axis to the moment of the resultant force
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
where is the product of inertia (Ixy) of the area about the x and y axes.
Once again according to the parallel axis theorem, it can also be written as
Ixy = Ixy' + Axcyc
where Ixy' is the product of inertia of the area with respect to the centroidal
axes.
Hence, the coordinate xcp is given by
The values for the second moment of inertia and product of inertia with respect
to the centroidal axes for various common geometries are already given during
your Mechanics of Deformable Bodies, kindly review them. From the formulations
of xcp and ycp, it is noted that the center of pressure is always lower in the liquid
than the centroid of the plane area.
Pressure Prism
An alternate approach of determining the hydrostatic force is by means of a
pressure prism. Consider a vertical plane submerged in a static fluid, as shown in
the figure. The pressure increases linearly with the depth. One can then easily
construct a corresponding three-dimensional diagram of the pressure distribution,
and such a volume is called a pressure prism. The resultant force is the total
volume of the pressure prism, that is
FR = Volume = 1/2 (ρgh) (bh)
The resultant force passes through the centroid of the pressure prism. For this
particular example, the centroid of a triangular element is located at a distance
of h/3 from its base and lies in the vertical symmetry axis.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
As illustrated, this method is particularly convenient when the shape of the
pressure prism is a common geometry, in which the volume and centroid can be
readily obtained.
Hydrostatic Pressure Force Exerted
on a Vertical Plane Surface
Source: ecourses.ou.edu
Pressure Prism
Source: ecourses.ou.edu
Total Hydrostatic Force on Curved Surfaces
In the case of curved surface submerged in liquid at rest, it is more convenient
to deal with the horizontal and vertical components of the total force acting on
the surface. Note: the discussion here is also applicable to plane surfaces.
FH=pcgA
Horizontal Component
The horizontal component of the total hydrostatic force on any surface is equal
to the pressure on the vertical projection of that surface.
Page
FV=γV
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Total Hydrostatic Force
𝑭= 𝑭𝟐𝑯 + 𝑭𝒗𝟐
Direction of F
𝐹𝑣
𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝜃 =
𝐹
Case 1: Liquid is above the curve surface
The vertical component of the hydrostatic force is downward and equal to the
volume of the real liquid above the submerged surface.
Source: mathalino.com
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Source: RK Bansal, 2010
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Case 2: Liquid is below the curve surface.
The vertical component of the hydrostatic force is going upward and equal to
the volume of the imaginary liquid above the surface.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Source: mathalino.com
Sample Problems:
SP No.1. (Source: /ecourses.ou.edu/)
A gravity dam can resist a maximum lateral force of Fm = 78, 000 lb. (a) What is
the maximum height of the dam if there is no downstream (right side of dam)?
(b) What if the water depth downstream is 10 ft? (c) Would it be a good idea to
design the dam for the condition of part (b)?
Solution:
(a) The resultant force (FR) due to water pressure is perpendicular to the dam
surface. Here, only concerned with lateral (horizontal) component, so you can
use the projected vertical dimension of the dam.
The lateral force (FH) due to fluid pressure (hydrostatic conditions) acting on the
projected area Ap can be determined for a unit width as
Fh = γ hc Ap = γ (h/2) Ap
where h is the total water depth.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
To find the maximum h, set Fh to the allowable force, Fm, to give
Fh = Fm
(62.4 lb/ft3) (h/2) [h (1 ft)] = 78,000 lb
h = [78,000 / 31.2]0.5 = 50 ft
(b) If the water depth downstream is 10 ft, then a resultant force will act on that
side of the dam, and will counteract the upstream force.
Fh1 - Fh2 = Fm
γ hc1 Ap1- γ hc2 Ap2 = 78,000 lb
62.4 (h/2) [(h)(1)] - 62.4 (5) [(10)(1)] = 78,000
31.2 h2 = 81,120
h = 51.0 ft
(c) Since the 10 ft of water downstream may not exist in times of draught, the
dam should be limited to 50 ft of water.
Sample Problem No. 2.
Given dam shown, compute for the hydrostatic force acting on the dam
surface.
Source: ecourse.ou.edu
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
The magnitude of the resultant force is given by
FR = ρghcA
The vertical distance to the centroid of the dam surface is given by
hc = 700 / 2 = 350 ft
The total length L of the dam surface is calculated to be
L = (6002 + 7002)0.5 = 922 ft
The magnitude of the resultant force is thus given by
FR = (1.94)(32.2)(350)(922) = 20.2 (106) lb
The coordinates for the center of pressure are given by
From the concepts of moment of inertia, for a rectangle,
Ix' = (922)3(1) / 12
Ixy' = 0
Hence, it is found that
xcp = xc
which is at the centerline of the dam surface. The y coordinate for the center of pressure is
ycp = (922)3(1) / (12)(461)(922) + 461 = 614.7 ft
The pressure prism approach can be used to verify the results obtained. Based on the pressure prism
shown in the figure, the magnitude of the resultant force is represented by the total volume of the
pressure prism.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
FR = Volume = 1/2 (43,730)(1)(922) = 20.2 (106) lb
This resultant force passes through the centroid of the pressure prism, which is located at a distance of
922/3 = 307.3 ft from its base and lies in the vertical symmetry axis.
Sample Problem No. 2. As presented by RK Bansal, 2010
A rectangular plane surface is 2m wide and 3m deep. It lies in vertical plane in water. Determine the
total pressure and position of the center of pressure on the plane surface when its upper edges is
horizontal and a) coincides with the water surface, b) 2.5m below the free water surface.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 3. As presented by RK Bansal, 2010
Determine the total pressure on a circular plate of diameter 1.5 m which is placed vertically in water in
such a way that the center of the plate is 3m below the free surface of water. Find the position of the
center of pressure.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 3. As presented by RK Bansal, 2010
A rectangular plane surface 2m wide and 3m deep lies in water in such a way that its plane makes an
angle of 30 degrees with the free surface of water. Determine the total pressure and position of center of
pressure when the upper edge is 1.5 m below the free surface.
Sample Problem No. 4 as presented by Mott & Untener, 2015
A dam, 30.5 m long that retains 8 m of fresh water and is inclined at an angle of
60 degrees. Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force on the dam and the
location of the center pressure.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 5 (as presented by Crowe, et.al., 2009)
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
BUOYANCY AND FLOATATION
Key Points:
When a body is immersed wholly or partially in a fluid, it is subjected to an upward
force which tends to lift (buoy) it up. The tendency of immersed body to be lifted
up in the fluid due to an upward force opposite to action of gravity is known as
buoyancy.
The force tending to lift up the body under such conditions is known as buoyant
force or force of buoyancy or up-thrust. The magnitude of the buoyant force can
be determined by Archimedes’ principle which states:
Consider a body immersed in water as shown:
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Force of buoyancy can also be determined as difference of
weight of a body in air and in liquid.
Sample Problems: (as presented by RK Bansal, 2010)
Sample Problem No. 1. Find the volume of the water
displaced and position of center of buoyancy for a wooden
block of width 2.5m and of depth 1.5m, when it floats
horizontally in water. The density of wooden block is 650
kg/m3 and its length 6.0m.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 2. A wooden log of 0.6m diameter and
5m length is floating in river water. Find the depth of the
wooden log in water when the sp. Gravity of the log is 0.7.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 3. Find the density of metallic body
which floats at the interface of mercury of sp.gr. 13.6 and
water such that 40% of its volume is sub-merged in mercury
and 60% in water.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 4: (as presented by Crowe, et.al, 2009)
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
CENTER OF BUOYANCY:
The point of application of the force of buoyancy on
the body is known as the center of buoyancy. It is always
the center of gravity of the volume of fluid displaced.
Page
Source: RK Bansal, 2010
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problems: (as presented by RK Bansal, 2010)
Sample Problem No. 1. A rectangular pontoon is 5m long, 3m wide and 1.20 m
high. The depth of immersion of the pontoon is 0.80 m in sea water. If the center
of gravity is 0.6m above the bottom of the pontoon, determine the meta-centric
height. The density for sea water = 1025 kg/m3
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
Cagayan State University – Carig Campus BS Civil Engineering Department
Lecture notes in HYDrAuLics (2nD semester sY 2020-2021)
Sample Problem No. 2.
A uniform body of size 3m long x 2m wide x 1m deep floats in water. What is the
weight of the body if depth of immersion is 0.8m? Determine the meta-centric
height also.
Page
CSU VISION: Transforming lives by Educating for the BEST.
Mission : CSU is committed to transform the lives of people and communities through high
quality instruction and innovative production and extension.
You might also like
- LAB Hydrostatic PressureDocument7 pagesLAB Hydrostatic PressureomshakalocaNo ratings yet
- Maths For PilotsDocument3 pagesMaths For PilotsKubilayNo ratings yet
- Ge 4 - Examination Answer SheetDocument1 pageGe 4 - Examination Answer SheetNicole Joy FidelesNo ratings yet
- Fmcpra2 Lab Report PDFDocument20 pagesFmcpra2 Lab Report PDFNzeza Carine100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Gas-Liquid-Solid FluidizationDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Gas-Liquid-Solid Fluidizationfaisal58650100% (1)
- Lessons 3 - 6 Fluid Flow Equations & Flow RatesDocument24 pagesLessons 3 - 6 Fluid Flow Equations & Flow RatesJosephine EugenioNo ratings yet
- File (4) BuoyancyDocument20 pagesFile (4) BuoyancyJosephine EugenioNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Fluid Statics (Pressure Measurement)Document26 pagesUnit 2 Fluid Statics (Pressure Measurement)adilnewaz75No ratings yet
- Calculation of Surface Tension: Theory and ScopeDocument28 pagesCalculation of Surface Tension: Theory and Scopelohit pNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic PressureDocument16 pagesHydrostatic PressureEddie BowokuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: HYDROSTASTIC: Mapua Institute of Technology at Laguna Academic Year 2021 - 2022Document5 pagesExperiment 1: HYDROSTASTIC: Mapua Institute of Technology at Laguna Academic Year 2021 - 2022Dyas FerNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument9 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & Technology17044 AZMAIN IKTIDER AKASHNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 2Document57 pagesHYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 2Rey Angelo Carbilledo Jr.100% (2)
- Gambella University: College of Engineering & Technology Water Resource Engineering DepartmentDocument88 pagesGambella University: College of Engineering & Technology Water Resource Engineering DepartmentGetahun TadesseNo ratings yet
- Tension and Moment Coefficients For HydrDocument8 pagesTension and Moment Coefficients For HydrZeenat ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 Total Hydrostatic Forces and PressuresDocument19 pagesLesson 3.1 Total Hydrostatic Forces and PressuresJohn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Module No. 3Document4 pagesStudy Guide For Module No. 3JanineEsmaoNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument10 pagesHydraulicsMunna ThakurNo ratings yet
- CH 2 HydrostaticsDocument19 pagesCH 2 Hydrostaticsrabiic deeqNo ratings yet
- Activity 4. Lab ReportDocument8 pagesActivity 4. Lab ReportMIGUEL ANGEL MORALES ESTRADANo ratings yet
- BB MCEN1000 Fluids 1bDocument28 pagesBB MCEN1000 Fluids 1bthemarvelbeastNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Fluid Statics (Hydrostatics Forces)Document20 pagesUnit 2 Fluid Statics (Hydrostatics Forces)adilnewaz75No ratings yet
- EXP3Document2 pagesEXP3MavNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidDocument21 pagesProperties of Fluidmeeth504No ratings yet
- Msbte: Electrical Engineering Under I Scheme Submitted by - Roll NoDocument17 pagesMsbte: Electrical Engineering Under I Scheme Submitted by - Roll Nohrishikesh barveNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument228 pagesFluid MechanicsAman gargNo ratings yet
- EXPT. No. 1 Pressure Measuring DevicesDocument12 pagesEXPT. No. 1 Pressure Measuring DevicesLowEnd GamerNo ratings yet
- 10 DT0397Document6 pages10 DT0397Jose Luis Urquidi BareaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics LCD 10302Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics LCD 10302Haryiot MiniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Concepts of Stresses Part 2Document24 pagesUnit 1 Concepts of Stresses Part 2Kiel Francis BanataoNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument37 pagesFluid MechanicsabhiNo ratings yet
- Module-3-HYDROSTATICS FORCES ON SURFACES PDFDocument24 pagesModule-3-HYDROSTATICS FORCES ON SURFACES PDFJulia LabordoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics NotesDocument0 pagesFluid Mechanics Notesamsk24_24No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics-1: Pressure Distribution in A FluidDocument63 pagesFluid Mechanics-1: Pressure Distribution in A FluidNoman ButtNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: (Objective Type)Document16 pagesCivil Engineering: (Objective Type)raainNo ratings yet
- Intze Tank - Seismic Behaviour - SAP2000 PDFDocument7 pagesIntze Tank - Seismic Behaviour - SAP2000 PDFAnonymous fQLEF2tQpqNo ratings yet
- L04 ME 321 Wikiversity Fluid StaticsDocument9 pagesL04 ME 321 Wikiversity Fluid Staticsdnzed35No ratings yet
- Tension and Moment Coefficients For Hydrodynamic Pressure Design of Intze TankDocument9 pagesTension and Moment Coefficients For Hydrodynamic Pressure Design of Intze Tankk08ivanNo ratings yet
- ME326L Research No.1 Pressure Measuring InstrumentDocument11 pagesME326L Research No.1 Pressure Measuring Instrumentemielyn lafortezaNo ratings yet
- Partido State University: I. Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesPartido State University: I. Learning ObjectivesJimmy SadsadNo ratings yet
- FM Unit-I PDFDocument13 pagesFM Unit-I PDFRaagul SanthanamNo ratings yet
- FF Exp 5Document5 pagesFF Exp 52020ch58No ratings yet
- FF Exp 5Document5 pagesFF Exp 52020ch58No ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure Project Linked-Class Problem-Based Learning in EngineeringDocument8 pagesHydrostatic Pressure Project Linked-Class Problem-Based Learning in EngineeringMat TjsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Fluid Statics 1Document39 pagesUnit 1 Fluid Statics 1AniketNo ratings yet
- Sushmita Digar 12Document12 pagesSushmita Digar 12Sushmita DigarNo ratings yet
- 02 - Fluid Statics PDFDocument33 pages02 - Fluid Statics PDFJoan LaksmitaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - 3 - Fluids - StaticDocument54 pagesWeek 2 - 3 - Fluids - StaticHan CokNo ratings yet
- ChE 220 Mod 2 Fluid Mechanics 2020-2021Document25 pagesChE 220 Mod 2 Fluid Mechanics 2020-2021Claire G. MagluyanNo ratings yet
- Civil-Vi-hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design-Drawin (10cv65) - NotesDocument77 pagesCivil-Vi-hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design-Drawin (10cv65) - Notesrishabh67% (3)
- Teacher:: Realized byDocument6 pagesTeacher:: Realized byفتحيNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida: Pressure and Fluid StaticsDocument63 pagesMekanika Fluida: Pressure and Fluid StaticsMarfizalNo ratings yet
- Cien 30064 HydraulicsDocument83 pagesCien 30064 Hydraulicscalebjohnf0512No ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology and Measurements N.V. Raghavendra L. KrishnamurthyDocument54 pagesEngineering Metrology and Measurements N.V. Raghavendra L. KrishnamurthyRandøm TalkìêsNo ratings yet
- Fluid StaticsDocument30 pagesFluid StaticsKalani WakehamNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Sloshing Phenomena in Cubi PDFDocument22 pagesNumerical Simulation of Sloshing Phenomena in Cubi PDFkaviraj TukhooNo ratings yet
- Me2204 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery 3 1 0 4Document33 pagesMe2204 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery 3 1 0 4rammogan_mNo ratings yet
- Principles of Hydrostatics Unit Pressure or Pressure, P: CE 326 HydraulicsDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Hydrostatics Unit Pressure or Pressure, P: CE 326 HydraulicsLydia CariagaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure CenterDocument19 pagesHydrostatic Pressure CenterTinotendaNo ratings yet
- Sea-Level Change in the Pacific Islands Region: A Review of Evidence to Inform Asian Development Bank Guidance on Selecting Sea-Level Projections for Climate Risk and Adaptation AssessmentsFrom EverandSea-Level Change in the Pacific Islands Region: A Review of Evidence to Inform Asian Development Bank Guidance on Selecting Sea-Level Projections for Climate Risk and Adaptation AssessmentsNo ratings yet
- Transforming Urban–Rural Water Linkages into High-Quality InvestmentsFrom EverandTransforming Urban–Rural Water Linkages into High-Quality InvestmentsNo ratings yet
- Burj Khalifa PresentationDocument12 pagesBurj Khalifa PresentationJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Gwapo FloorplanDocument1 pageGwapo FloorplanJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Pacis, Jaylord Mico B.RCDocument1 pagePacis, Jaylord Mico B.RCJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Purok 1, Songsong, Gamu, Isabela: ArchitectDocument1 pagePurok 1, Songsong, Gamu, Isabela: ArchitectJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Try 2Document1 pageTry 2JayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Second Floor Second Floor Second FloorDocument1 pageSecond Floor Second Floor Second FloorJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Maynard 1Document1 pageMaynard 1JayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Transient ModelDocument1 pageTransient ModelJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: A B C D E F G HDocument1 pageDepartment of Civil Engineering: A B C D E F G HJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: Celeste, Maynard Engr. Jowell Talosig FloorplanDocument1 pageDepartment of Civil Engineering: Celeste, Maynard Engr. Jowell Talosig FloorplanJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Pacis, Jaylord Mico B.RCDocument1 pagePacis, Jaylord Mico B.RCJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Design of An Integrated Waste Management Facility in The Republic of IrelandDocument67 pagesDesign of An Integrated Waste Management Facility in The Republic of IrelandJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- BidDocs PSAO-Laguna Phase1 Ro4aDocument101 pagesBidDocs PSAO-Laguna Phase1 Ro4aJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Sed 322 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSed 322 Syllabusapi-251146794No ratings yet
- DID101RDocument5 pagesDID101RWency BuiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 May-June 2016 Memo Afr & EngDocument21 pagesMathematics P2 May-June 2016 Memo Afr & Engaleck mthethwaNo ratings yet
- Finite Difference WikipediaDocument6 pagesFinite Difference Wikipedialetter_ashish4444No ratings yet
- Subtraction Tables 12 001Document1 pageSubtraction Tables 12 001tozion01No ratings yet
- 1.2 Multiplication DrillDocument20 pages1.2 Multiplication DrillYahya MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Exercise SolutionsDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Exercise SolutionsMaham Butt100% (1)
- VT K TextbookDocument529 pagesVT K TextbookPAVAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Radioss Theory Manual: 10.0 Version - January 2009 Large Displacement Finite Element AnalysisDocument179 pagesRadioss Theory Manual: 10.0 Version - January 2009 Large Displacement Finite Element AnalysisAbdel DaaNo ratings yet
- Whittaker Dynamics 17Document442 pagesWhittaker Dynamics 17Mahmoud Ahmed 202201238No ratings yet
- Determining The Intervening Effects of Exploratory Data Analysis and Feature Engineering in Telecoms Customer Churn ModellingDocument7 pagesDetermining The Intervening Effects of Exploratory Data Analysis and Feature Engineering in Telecoms Customer Churn ModellingbanstalaNo ratings yet
- Regular Expressions & FsasDocument6 pagesRegular Expressions & FsasMandeep Kaur KambojNo ratings yet
- Session # 1 Introduction To Operations Research: Course Material GMP21Document20 pagesSession # 1 Introduction To Operations Research: Course Material GMP21Bhargav D.S.No ratings yet
- RCC 7m C.F Re WallDocument30 pagesRCC 7m C.F Re WallArun RawatNo ratings yet
- Rigidity and Mass Center 1480317129Document9 pagesRigidity and Mass Center 1480317129Alban Hysomemaj100% (1)
- C ProgrammimgDocument43 pagesC Programmimgr nivedha0% (1)
- Using Assembler Language in DelphiDocument44 pagesUsing Assembler Language in Delphiamla11100% (2)
- ISB 1 For Students PDFDocument54 pagesISB 1 For Students PDFRitik AggarwalNo ratings yet
- FORTRAN 77 Lesson 7: 1 Numerical IntegrationDocument7 pagesFORTRAN 77 Lesson 7: 1 Numerical IntegrationManjita BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Military College Murree: Entrance Exam Class Viii Syllabus and Test Description Part-1 EnglishDocument4 pagesMilitary College Murree: Entrance Exam Class Viii Syllabus and Test Description Part-1 Englishkiran shaheenNo ratings yet
- Ball LevitationDocument7 pagesBall LevitationsumlusemloNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 MTAP Elimination - 2008Document4 pagesGrade 4 MTAP Elimination - 2008Sheryl Balualua Mape-Salvatierra80% (5)
- Jose Geraldo Pereira, Ruben Aldrovandi - An Introduction To Geometrical Physics-World Scientific (2017)Document812 pagesJose Geraldo Pereira, Ruben Aldrovandi - An Introduction To Geometrical Physics-World Scientific (2017)Zaratustra Nietzche100% (1)
- Gateway To AIIMS2019-Solutions Physics PDFDocument183 pagesGateway To AIIMS2019-Solutions Physics PDFAyush Pandey100% (1)
- Learning DisabilityDocument25 pagesLearning DisabilitySharmishtha100% (1)
- Leonardo Da VinciDocument18 pagesLeonardo Da VinciEmma ClayNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Hydraulic Scissor LiftDocument47 pagesDesign and Analysis of Hydraulic Scissor LiftAnkit MandalNo ratings yet