Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Vitamin K
Uploaded by
Florence Nightingale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesPhytonadione (Vitamin K) is used as an antidote for overdoses of oral anticoagulants like coumarin and indandione. It works by promoting the liver's synthesis of clotting factors through an unknown mechanism. It is indicated to reverse hypoprothrombinemia caused by oral antibiotics, quinidine, and other drugs. Adverse effects include hypersensitivity reactions, headache, and gastrointestinal upset. Nurses monitor patients for changes in clotting times and bleeding risks after administration.
Original Description:
Original Title
DRUG-STUDY-VITAMIN-K
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhytonadione (Vitamin K) is used as an antidote for overdoses of oral anticoagulants like coumarin and indandione. It works by promoting the liver's synthesis of clotting factors through an unknown mechanism. It is indicated to reverse hypoprothrombinemia caused by oral antibiotics, quinidine, and other drugs. Adverse effects include hypersensitivity reactions, headache, and gastrointestinal upset. Nurses monitor patients for changes in clotting times and bleeding risks after administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesDrug Study Vitamin K
Uploaded by
Florence NightingalePhytonadione (Vitamin K) is used as an antidote for overdoses of oral anticoagulants like coumarin and indandione. It works by promoting the liver's synthesis of clotting factors through an unknown mechanism. It is indicated to reverse hypoprothrombinemia caused by oral antibiotics, quinidine, and other drugs. Adverse effects include hypersensitivity reactions, headache, and gastrointestinal upset. Nurses monitor patients for changes in clotting times and bleeding risks after administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
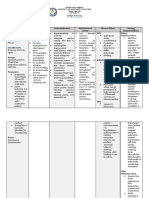
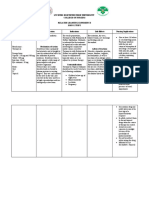
Drug Data Classificatio Mechanism of Indication Contraindi Adverse Effects Nursing
n Action cation responsibilities
Generic Therapeutic Drug of choice as Promotes - Body as a Before:
Name: class: antidote for overdosage liver Hypersensi Whole: - assess vital signs for
Phytonadione Vitamin of coumarin and synthesis of tivity to Hypersensitivity baseline data.
(Vitamin K) indandione oral clotting Phytonadio or anaphylaxis- - asses drug to
Pharmacolog anticoagulants. Also factors by ne like reaction: allergy.
ic class: reverses unknown (Vitamin facial flushing, - prepare the drug
Brand name: Hormones hypoprothrombinemia mechanism. K); cramp-like pains, properly.
Konakion, Mep And secondary to Does not convulsive - explain use and
hyton, Phylloqu Synthetic administration of oral reverse -Severe movements, administration of
inone Substitutes, antibiotics, quinidine, anticoagulan liver chills, fever, drug to patient and
Antidote quinine, salicylates, t action of disease. diaphoresis, family.
sulfonamides, excessive heparin. weakness,
vitamin A, and Reportedly dizziness, shock, During:
secondary to inadequate demonstrate cardiac arrest.. - Monitor patient
absorption and synthesis s wide constantly. Severe
of vitamin K (as in margin of CNS: Headache reactions, including
obstructive jaundice, safety when (after oral dose), fatalities, have
biliary fistula, ulcerative used in brain damage, occurred during and
colitis, intestinal newborns. death immediately after IV
resection, prolonged injection
hyperalimentation). GI: Gastric
Also prophylaxis of and upset. -Monitor therapeutic
therapy for neonatal effectiveness which is
hemorrhagic disease.. Metabolic: indicated by
Hyperbilirubine shortened PT, INR,
mia, kernicterus. bleeding, and clotting
times, as well as
Hematologic: decreased
Paradoxic hemorrhagic
hypoprothrombi tendencies.
nemia (patients -Be aware that
with severe liver patients on large
disease), severe doses may develop
hemolytic temporary resistance
anemia. to coumarin-type
anticoagulants. If oral
Respiratory: anticoagulant is
Bronchospasm, reinstituted, larger
dyspnea, than former doses
sensation of may be needed. Some
chest patients may require
constriction, change to heparin.
respiratory
arrest.
After:
Skin: Pain at - documentation of
injection site, drug administration.
hematoma, and - instruct patient to
nodule promptly report
formation, adverse reactions
erythematous (cramp-like pains,
skin eruptions convulsive
(with repeated movements, chills,
injections) fever, diaphoresis,
weakness, dizziness,
Special Senses: pain at injection site,
Peculiar taste hematoma).
sensation.
-Maintain consistency
in diet and avoid
significant increases
in daily intake of
vitamin K–rich foods
when drug regimen is
stabilized. Know
sources rich in
vitamin K:
Asparagus, broccoli,
cabbage, lettuce,
turnip greens, pork or
beef liver, green tea,
spinach, watercress,
and tomatoes.
References:
Nursing2020 Drug Handbook eBook: Lippincott ... (n.d.).
Nursing2020 Drug Handbook eBook: Lippincott ... (n.d.).
2011 Nurse's Drug Handbook, 10th Edition - Medical Ebooks Download. (2019, September 20).
Beecham GB, Bansal P, Nessel TA, et al. Lidocaine. (2020).
In: Statpearls (internet). Treasure Island FL: Statpearls Publishing
You might also like
- DRUG STUDY Vitamin KDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Vitamin KChristian Daayata50% (2)
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug Studyelle100% (3)
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- Vit K Drug Study PDFDocument2 pagesVit K Drug Study PDFA sisonNo ratings yet
- VITAMIN K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVITAMIN K Drug StudyMarl DumiligNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument6 pagesDrug Study NurseryPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument2 pagesErythromycinEurielle MioleNo ratings yet
- Hep B Vaccine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHep B Vaccine Drug StudyFrian MariñasNo ratings yet
- 2B Diana - BCG Drug StudyDocument3 pages2B Diana - BCG Drug Studymerry100% (1)
- Drug-Study CefepimeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Final Drug Study - PediaDocument2 pagesFinal Drug Study - PediaMae Estillore100% (1)
- Drug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineJustin AncogNo ratings yet
- Ob Case Study - BCG Drug StudyDocument1 pageOb Case Study - BCG Drug StudyAngelica Rose Villegas0% (1)
- Phytonadione DRUG STUDYDocument1 pagePhytonadione DRUG STUDYjoellaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Dexamethasoneamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyYaniiee DeFiestaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Indications: CnsDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Indications: CnsSeno HyeonNo ratings yet
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Eryhtromycin OphthDocument1 pageEryhtromycin OphthLegendX100% (1)
- Patient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGDocument4 pagesPatient 6 Drug Study Day 1 BCGJackieMae100% (1)
- Name of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionJulia Shane Barrios100% (1)
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug Study LosartanIris BalinoNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument1 pageOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (1)
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ErythromycinDocument4 pagesDrug Study ErythromycinSawada TsunayoshiNo ratings yet
- Hyosine N ButylbromideDocument1 pageHyosine N ButylbromideJenny Vi CodenieraNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- Drug-Study Hepa BDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Hepa BPauline Doronila100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Hep BDocument4 pagesDrug Study Hep BSawada TsunayoshiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)NE TdrNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For VaccinesDocument6 pagesDrug Study For VaccinesMarion RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RanitidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study RanitidineTipey SegismundoNo ratings yet
- Terramycin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTerramycin - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNo ratings yet
- Nursery Drug StudyDocument9 pagesNursery Drug StudyNiña Dianne Rubin RustiaNo ratings yet
- Carboprost Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCarboprost Drug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocument3 pagesDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DelanDocument3 pagesDrug Study - DelanJuliana Sophia DelanNo ratings yet
- PhytomenadioneDocument3 pagesPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- Cephalexin Drug StudyDocument1 pageCephalexin Drug StudyAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac and NalbuphineDocument4 pagesKetorolac and NalbuphineMaureen Campos-PineraNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing Considerationsitsmeaya100% (3)
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- BACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Related Learning Experience: Lorma Colleges Con TemplateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Related Learning Experience: Lorma Colleges Con TemplateKrizzia Mae ColladoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefuroxime Drug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- BCG Vaccine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBCG Vaccine Drug StudyJustin Ancog100% (1)
- Drug Study AsDocument3 pagesDrug Study Askev mondaNo ratings yet
- ErythromycinDocument2 pagesErythromycinKathleen PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRenmen Rosito Hortelano100% (3)
- Ertapenem Drug StudyDocument3 pagesErtapenem Drug StudyBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-MethyldopaDocument4 pagesDrug Study-MethyldopaJinnijinniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRae Marie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.Document9 pagesDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNo ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument7 pagesEpinephrineFlorence NightingaleNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateFlorence NightingaleNo ratings yet
- Manifest and Chronic Cardiac Insufficiency - Arrhythmia Absoluta Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument4 pagesManifest and Chronic Cardiac Insufficiency - Arrhythmia Absoluta Supraventricular TachycardiaFlorence NightingaleNo ratings yet
- O'Toole Self-Directed LearningDocument203 pagesO'Toole Self-Directed LearningFlorence NightingaleNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVEDocument5 pagesPURPOSIVERee-Jane Bautista Macaraeg100% (1)
- Notes PDFDocument102 pagesNotes PDFdarkspyder4No ratings yet
- Total Total Total Tota L Total Total Total Total Total T-Score T - Score T - Scor e T - Score T - Score T - Score T - Score T - ScoreDocument2 pagesTotal Total Total Tota L Total Total Total Total Total T-Score T - Score T - Scor e T - Score T - Score T - Score T - Score T - Scorethelegend 2022No ratings yet
- October 2015 Question Paper 1Document16 pagesOctober 2015 Question Paper 1Abdulhaseeb HussainNo ratings yet
- Mirza Ghalib - Poems - 2Document5 pagesMirza Ghalib - Poems - 2Navdeep GillNo ratings yet
- K E-HistoryDocument3 pagesK E-HistoryLovely ReyesNo ratings yet
- Planning Technical ActivitiesDocument29 pagesPlanning Technical ActivitiesMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaNo ratings yet
- HRD Multiple Choice QuestionDocument29 pagesHRD Multiple Choice QuestionHayat TarrarNo ratings yet
- Lauren Gantz On - The Palm Wine Drinkard - E3W Review of BooksDocument2 pagesLauren Gantz On - The Palm Wine Drinkard - E3W Review of BooksjayasriniNo ratings yet
- Davao Sawmill v. CastilloDocument1 pageDavao Sawmill v. CastilloJulie AnnNo ratings yet
- 0004.22-Erma Modes of OperationDocument4 pages0004.22-Erma Modes of OperationDrug Luka PopovicNo ratings yet
- Essay 7232 Writing Correction Task 2Document5 pagesEssay 7232 Writing Correction Task 2yousef shabanNo ratings yet
- Pocket Newtab Intl enDocument12 pagesPocket Newtab Intl enAnonymous ktNyZTNo ratings yet
- Zimbra OS Admin GuideDocument188 pagesZimbra OS Admin GuideCarlitos CustodioNo ratings yet
- Attunity Acx ReferenceDocument830 pagesAttunity Acx Referencewlodar2No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Test: FalseDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Test: FalseXeniaNo ratings yet
- Stapleofnews00jonsuoft PDFDocument348 pagesStapleofnews00jonsuoft PDFCatarina Arnaud BoletoNo ratings yet
- CICS TutorialDocument57 pagesCICS TutorialSarath ChNo ratings yet
- One Past But Many Histories Controversies and Conflicting Views in Philippine HistoryDocument28 pagesOne Past But Many Histories Controversies and Conflicting Views in Philippine HistoryShiela Marie Gadayos100% (1)
- Basic Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Immunology PDFAnastasia ENo ratings yet
- Morphophonemic Processes - ENG 103 Report-FinalDocument9 pagesMorphophonemic Processes - ENG 103 Report-FinalApril Jane PedriñaNo ratings yet
- Wix Singular and PluralDocument9 pagesWix Singular and PluralbashayerNo ratings yet
- 2016 03 31 Basa Pilipinas Quarter 3 Grade 1 English Teacher's Guide (Second Edition) PDFDocument186 pages2016 03 31 Basa Pilipinas Quarter 3 Grade 1 English Teacher's Guide (Second Edition) PDFIris SamonteNo ratings yet
- Thesis MelsonDocument160 pagesThesis MelsonVincent CucumazzøNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Management Styles: NO: 1. It's Not NecessaryDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Management Styles: NO: 1. It's Not NecessaryjulianaNo ratings yet
- Using Logarithm Laws 3Document3 pagesUsing Logarithm Laws 3yddapNo ratings yet
- External Douches or Perineal Care: DefinitionDocument48 pagesExternal Douches or Perineal Care: DefinitionKenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- Inglés B2 Cto Septiembre 2020 (Final) - CorrectorDocument8 pagesInglés B2 Cto Septiembre 2020 (Final) - CorrectorJaneNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument3 pagesCONDITIONALMaria Perez CrespoNo ratings yet
- Hope in Homeless People: A Phenomenological Study: Mary PartisDocument12 pagesHope in Homeless People: A Phenomenological Study: Mary PartisAyesha Malik100% (1)