Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1
Uploaded by
Mohsin Iqbal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
ASSIGNMENT 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesAssignment 1
Uploaded by
Mohsin IqbalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Q1:
Explain symmetrical & Unsymmetrical Faults with
Examples.
ANS:
Faults that occurs in transmission lines are broadly
classified as
Symmetrical faults
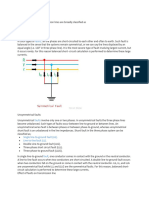
In such types of faults, all the phases are short-circuited
to each other and often to earth. Such fault is balanced in
the sense that the systems remain symmetrical, or we
can say the lines displaced by an equal angle (i.e. 120° in
three phase line). It is the most severe type of fault
involving largest current, but it occurs rarely. For this
reason balanced short- circuit calculation is performed to
determine these large currents.
R у Z Ir lydlzl ly1121 Symmetrical Fault
Unsymmetrical faults:
Unsymmetrical faults involve only one or two phases. In
unsymmetrical faults the three phase lines become
unbalanced. Such types of faults occur between line-to-
ground or between lines. An unsymmetrical series fault is
between phases or between phase-to-ground, whereas
unsymmetrical shunt fault is an unbalanced in the line
impedances. Shunt fault in the three phase system can
be classified as;
1) Single line-to-ground fault (LG).
2) Line-to-line fault (LL).
3) Double Line-to-ground fault (LLG).
4) Three-phase short circuit fault (LLL).
5) Three-phase-to-ground fault (LLLG).
In single line-to-ground fault, one conductor comes in
contact with the ground or the neutral conductor. A line-
to-line fault occurs when two conductors are short
circuited. A double line-to-ground fault occurs when two
conductors fall on the ground or come in contact with
the neutral conductor. LG, LL, and LLG are unsymmetrical
fault while LLL and LLLG are the symmetrical faults. For
this reason, balanced short-circuit calculation is
performed to determine these large currents.
Examples:
Broken conductor and malfunctioning of circuit breaker
in one or more phases.
Internal effects include breakdown of transmission lines
or equipment, aging of insulation, deterioration of
insulation in generator, transformer and other electrical
equipment’s, improper installations and inadequate
design. External effects include overloading of
equipment’s, insulation failure due to lighting surges and
mechanical damage by public.
You might also like
- Understanding Un-Symmetrical FaultDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Un-Symmetrical Faultrakib257aNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Electrical Power Systems and Their EffectsDocument20 pagesTypes of Faults in Electrical Power Systems and Their Effectstebelayhabitamu12No ratings yet
- Types of Fault in Power SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of Fault in Power SystemsSammar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Power SystemDocument6 pagesTypes of Faults in Power Systemcollege safariNo ratings yet
- SGP Ques AnsDocument24 pagesSGP Ques AnsSoumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Protection SectionDocument8 pagesProtection Sectionaam5112002No ratings yet
- Normal Conditions in Power SystemDocument115 pagesNormal Conditions in Power SystemAshish ShahNo ratings yet
- Project On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseDocument106 pagesProject On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwisetitserNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.2 Literature SurveyDocument20 pagesChapter-1: 1.2 Literature SurveyKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument42 pagesPower System Analysismedanite ashebirNo ratings yet
- Lab 11Document4 pagesLab 11Maham AhsanNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Power SystemDocument6 pagesTypes of Faults in Power SystemMalik Tamoor AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Fault Analysis and Automatic ReclosingDocument13 pagesThree Phase Fault Analysis and Automatic Reclosingharsha jumneNo ratings yet
- Current and Kva CalculationsDocument18 pagesCurrent and Kva CalculationsKelvin YipNo ratings yet
- Project On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseDocument34 pagesProject On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseAkashPratap2100% (21)
- Protective Systems for Power NetworksDocument10 pagesProtective Systems for Power NetworksSoumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Faults: Different Types of Faults AreDocument5 pagesFaults: Different Types of Faults AreRohit SarafNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers-lecture-Notes 1Document9 pagesCircuit Breakers-lecture-Notes 1Sidharth PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Power System ProtectionDocument5 pagesPower System ProtectionIndhumathi BabusenanNo ratings yet
- Losses DislisDocument17 pagesLosses Dislisdesi aryantiNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis in Power SystemsDocument3 pagesFault Analysis in Power SystemsdjebienNo ratings yet
- Reactance Diagram:: Per Unit SystemDocument4 pagesReactance Diagram:: Per Unit SystemAbid AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults in Power SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Faults in Power SystemMohamed RafaatNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document13 pagesLec 2Chamod DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults and Their Effects in Electrical Power SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of Faults and Their Effects in Electrical Power SystemsMohammed FaizanNo ratings yet
- Fault (In Electric Power)Document19 pagesFault (In Electric Power)kasehunNo ratings yet
- Negative Phase Sequence ProtectionDocument15 pagesNegative Phase Sequence ProtectionThirumalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System Faults ExplainedDocument16 pagesElectrical Power System Faults ExplainedvinaybabaNo ratings yet
- Fault AnalysisDocument27 pagesFault AnalysisFaiz The EndNo ratings yet
- American International University - Bangladesh (Aiub) : Power System Analysis (Section: B)Document5 pagesAmerican International University - Bangladesh (Aiub) : Power System Analysis (Section: B)M. K. RashedinNo ratings yet
- Realistic Faults: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During AnDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults: Fault Current Means The Electrical Currentthat Flows Through A Circuit During Ansandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Power System Switchgear and Protection (EET-301) : Reference Books AuthorsDocument20 pagesPower System Switchgear and Protection (EET-301) : Reference Books AuthorsAnuja TipareNo ratings yet
- Faults in Power Systems ExplainedDocument32 pagesFaults in Power Systems ExplainedGaylethunder007No ratings yet
- Project Report Transmission Line Fault MonitoringDocument34 pagesProject Report Transmission Line Fault Monitoringkra_amNo ratings yet
- Elements of ProtectionDocument18 pagesElements of ProtectionChetan TawarNo ratings yet
- Power System Switchgear ProtectionDocument21 pagesPower System Switchgear ProtectionGanpat GehlotNo ratings yet
- Course Design: Short Circuit Faults Based On MatlabDocument22 pagesCourse Design: Short Circuit Faults Based On MatlabMd mehadi HasanNo ratings yet
- Realistic Faults in Electrical Systems ExplainedDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults in Electrical Systems Explainedsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- SGP Notes Part 1Document31 pagesSGP Notes Part 1Shristi BhomrajkaNo ratings yet
- Day-30 Notes (EEE)Document1 pageDay-30 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Short Circuit Current Calculations-R1Document46 pagesIntroduction To Short Circuit Current Calculations-R1David WebbNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument36 pagesSymmetrical Fault Analysisdileep kumarNo ratings yet
- Sequence Impedance and Fault AnalysisDocument28 pagesSequence Impedance and Fault AnalysisBelayneh TadesseNo ratings yet
- PSA Notes Unit 3Document45 pagesPSA Notes Unit 3Sandeep AyyagariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Short Circuit Current CalculationsDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Short Circuit Current CalculationsrexNo ratings yet
- Overhead Transmission Line FaultsDocument8 pagesOverhead Transmission Line FaultsQaisar_mastNo ratings yet
- Faults in Electrical Power SystemDocument4 pagesFaults in Electrical Power Systemmaruf048No ratings yet
- Realistic Faults Olted Fault: TransientDocument3 pagesRealistic Faults Olted Fault: Transientsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamentals of Short Circuit Analysis - (DevCourseWeb - Com)Document6 pages1.1 Fundamentals of Short Circuit Analysis - (DevCourseWeb - Com)ElnazeerNo ratings yet
- DeusDocument19 pagesDeusMisango EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis by Symmetrical Components PDFDocument29 pagesFault Analysis by Symmetrical Components PDFAayush PatidarNo ratings yet
- Arcing Fault: Electric ArcDocument3 pagesArcing Fault: Electric Arcsandeep_chauhan3770No ratings yet
- Types of FaultsDocument13 pagesTypes of FaultsRahul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Power System FaultsDocument14 pagesPower System FaultsAnup NaskarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Calculation and MATLAB Programming of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults in Power SystemDocument4 pagesMathematical Calculation and MATLAB Programming of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults in Power SystemLalbahadur MajhiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Neutral, Ground and EarthDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Neutral, Ground and EarthNeeraj RahiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-7 (Welded Connection Design)Document12 pagesLecture-7 (Welded Connection Design)Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 (Welded Connections)Document20 pagesLecture-5 (Welded Connections)Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture-7 (Welded Connection Design)Document12 pagesLecture-7 (Welded Connection Design)Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Apache LicenseDocument5 pagesApache Licenseapi-286574869No ratings yet
- Lecture No. 5Document18 pagesLecture No. 5Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3Document16 pagesLecture No. 3salman ghaffarNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 6Document17 pagesLecture No. 6Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Construction Stakeholders RolesDocument19 pagesConstruction Stakeholders Rolessalman ghaffarNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- 8th Sem Attendance Spring 2021Document4 pages8th Sem Attendance Spring 2021Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 EE208 Activity Outcome 2020mar10!14!32 56Document2 pagesLab 1 EE208 Activity Outcome 2020mar10!14!32 56Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Batch 2 PE CEP Report 2Document10 pagesBatch 2 PE CEP Report 2Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Bill Payment PDF - JSPDocument1 pageBill Payment PDF - JSPMohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- SUIT/SEC/Spring-2021 Appointment as Paper Setter ExaminerDocument1 pageSUIT/SEC/Spring-2021 Appointment as Paper Setter ExaminerMohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- UoapDocument1 pageUoapMohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Bill Payment PDF - JSPDocument1 pageBill Payment PDF - JSPMohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Document2 pagesLab10 - EE208 - Activity Outcome - 2020mar10-14 - 34 - 09Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- CEP Control System Sp2019V2Document3 pagesCEP Control System Sp2019V2Ahmed AkramNo ratings yet
- Introduction - To - Industrial - AutomationDocument13 pagesIntroduction - To - Industrial - AutomationEr Amarsinh RNo ratings yet
- Butter Worth Filter DesignDocument4 pagesButter Worth Filter DesignCan ÇamlıkNo ratings yet
- 1BILL - INVOICES - Rs.510 - 24-06-2021Document1 page1BILL - INVOICES - Rs.510 - 24-06-2021Mohsin IqbalNo ratings yet
- DSP Project ProposalDocument6 pagesDSP Project ProposalMohsin IqbalNo ratings yet