Professional Documents
Culture Documents
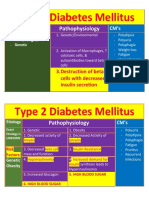
Aminoacidopathies: Metabolic Defect Consequence Manifestation Treatment
Uploaded by
Jean Belciña0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThis document summarizes several aminoacidopathies, which are metabolic disorders caused by defects in the metabolism of amino acids. It lists the metabolic defect, consequences, manifestations, and treatment for several conditions including phenylketonuria (PKU), tyrosinemia types I-III, alkaptonuria, maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), isovaleric acidemia, and homocystinuria. PKU results from a lack of the enzyme PAH and causes high phenylalanine levels if untreated, leading to intellectual disability. Treatment involves a low-phenylalanine diet. Tyrosinemia type I is caused by a lack of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase and manifests as liver
Original Description:
Original Title
AMINOACIDOPATHIES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes several aminoacidopathies, which are metabolic disorders caused by defects in the metabolism of amino acids. It lists the metabolic defect, consequences, manifestations, and treatment for several conditions including phenylketonuria (PKU), tyrosinemia types I-III, alkaptonuria, maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), isovaleric acidemia, and homocystinuria. PKU results from a lack of the enzyme PAH and causes high phenylalanine levels if untreated, leading to intellectual disability. Treatment involves a low-phenylalanine diet. Tyrosinemia type I is caused by a lack of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase and manifests as liver
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesAminoacidopathies: Metabolic Defect Consequence Manifestation Treatment
Uploaded by
Jean BelciñaThis document summarizes several aminoacidopathies, which are metabolic disorders caused by defects in the metabolism of amino acids. It lists the metabolic defect, consequences, manifestations, and treatment for several conditions including phenylketonuria (PKU), tyrosinemia types I-III, alkaptonuria, maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), isovaleric acidemia, and homocystinuria. PKU results from a lack of the enzyme PAH and causes high phenylalanine levels if untreated, leading to intellectual disability. Treatment involves a low-phenylalanine diet. Tyrosinemia type I is caused by a lack of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase and manifests as liver
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
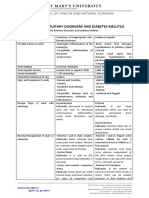
AMINOACIDOPATHIES
METABOLIC DEFECT CONSEQUENCE MANIFESTATION TREATMENT
Phenylketonuria Inherited as an ART Absence of enzyme PAH — PHE levels: > 1200 mmol/L — Brain problems — Fetal effects of maternal PKU
— Upper limit for PHE level in — Musty odor of urine is prevented if the mother is
newborns: 120 mmol/L (2 mg/dL) — Retarded mental development maintained on PHE-restricted
— Untreated PKU: > 2.4 mM/L and microcephaly in infants diet
Enzyme Deficiency Deficiency in the enzymes — Elevated levels of PHE — Goal of the treatment:
needed for the regeneration — Deficient production of maintain PHE blood levels
and synthesis of neurotransmitters from TYR and between 2-10 mg/dL (120-600
tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) TRP mol/L)
— Avoid foods that are rich in
protein
Tyrosinemia Type I Low levels of enzyme — Tyrosine and tyrosine catabolites — Failure to thrive — Low-protein diet
fumarylacetoacetate in urine — Diarrhea
hydrolase — Vomiting
— Jaundice
— Cabbage-like odor
— Distended abdomen
— Swelling of legs
— Increased predisposition for
bleeding
Type II Deficiency of enzyme tyrosine — Mental retardation (50%)
aminotransferase — Excessive tearing
— Photophobia
— Eye pain and redness
— Painful skin lesions on the palms
and soles of the feet
Type III Deficiency of the enzyme 4- — Mental retardation
hydroxyphenylpyruvate — Seizures
dioxygenase — Periodic loss of balance and
coordination
Alkaptonuria Inherited as an Lack of the enzyme — Defect in the metabolism of — Urine turns brownish-black — High-dose Vit C
ARG, (HGD gene) homogentisate oxidase tyrosine and phenylalanine when mixed with air (due to
HGA)
— Ochronosis (pigments in tissues)
— Arthritis-like degeneration
— Dark spots on the sclera
— Pigments in the cartilage of the
ears, nose, and tendons, and
extremities
Maple Syrup Absence or reduced activity — Defect in the metabolism of LEU, — Maple syrup or burnt sugar — Protein-restrictive diet to
Urine Disease of enzyme branched-chain- ILE, and VAL resulting in odor of the urine, breath, and lower the levels of
(MSUD) ketoacid decarboxylase accumulation in blood, urine, and skin accumulating isovaleric acid,
CSF — Infants: lethargy, vomiting, lack which is toxic to the CNS
of appetite, and failure to thrive
— CNS symptoms: muscle rigidity,
stupor, and respiratory
irregularities
— Severe mental retardation,
seizures, acidosis, and
hypoglycemia
— Death is left untreated
Isovaleric Anemia Deficiency of the enzyme — Defect in the metabolism of the — Sweaty feet odor — Protein-restrictive diet to
isovaleryl-CoA branched-chain amino acid LEU — In severe cases, it could cause lower the levels of
dehydrogenase damage to the brain and accumulating isovaleric acid,
nervous system which is toxic to the CNS
— In infants: failure to thrive,
vomiting, lethargy that can
progress to seizures, coma, and
death
Homocystinuria Lack of the enzyme — Elevated plasma and urine levels — Infants: relatively healthy — Dietary restriction of
cystathionine- synthetase of MET and of the precursor — Late childhood: osteoporosis, methionine (low protein) as
homocysteine dislocated lenses in the eye, and well as high doses of vitamin
mental retardation B6
— Multisystemic disorders of the
CT, muscles, CNS, thinning and
weakening of bones, and
thrombosis if left untreated
Citrullinemia Type I- GD Urea cycle disorder — — — High-calorie, protein-
Type II- GD — — restrictive diet
— Arginine supplementation
— Administration of sodium
benzoate and sodium
phenylacetate
Argininosuccinic Genetic Disease Lack of the enzyme — Elevated levels of argininosuccinic — In newborn: lethargy and — High-calorie, protein-
Aciduria argininosuccinic acid lyase also cause buildup of the amino unwillingness to eat restrictive diet
acid citrulline in the blood — Arginine supplementation
— Urea cycle cannot proceed — Administration of sodium
normally and nitrogen benzoate and sodium
accumulates in the blood in the phenylacetate
form of ammonia. Ammonia is
neurotoxic & hepatotoxic.
Cystinuria Defect in the amino acid — Inadequate reabsorption of — Hematuria, pain in the side due — Increasing the volume of urine
transport system rather than cystine during the filtering to kidney pain, and UTI to reduce the concentration
a metabolic enzyme process in the kidneys, resulting of cystine in the urine and
deficiency in an excessive concentration of reduce its precipitating from
this amino acid the urine and forming stone
— Cystine precipitates out of the
urine and forms stones in the
kidneys, ureters, or bladder
You might also like
- SUMMARY: Care of Patients With Endocrine Disorders: Disease Condition and Main Problem Signs and Symptoms ManagementDocument7 pagesSUMMARY: Care of Patients With Endocrine Disorders: Disease Condition and Main Problem Signs and Symptoms ManagementKev Llanera0% (1)
- SGD Aa PDFDocument11 pagesSGD Aa PDFyasiraNo ratings yet
- 0304 ConsultantoncallDocument4 pages0304 Consultantoncallnessimmounir1173No ratings yet
- Laboratory Values: ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesLaboratory Values: ElectrolytesLauren Agatha ManipolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioDocument5 pagesEndocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Opioids & MSK TreatmentDocument6 pagesOpioids & MSK TreatmentNashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Hypo and Hyper ParathyrodismDocument31 pagesHypo and Hyper ParathyrodismJazh AyochokNo ratings yet
- Badassery For Patho Exam 3Document19 pagesBadassery For Patho Exam 3HannaNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument9 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersXyleene Jency Bien IINo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism DisordersDocument61 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism DisordersNikitha RafeekNo ratings yet
- 3 - PorphyriasDocument14 pages3 - PorphyriasHamzehNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument28 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- 2.02 - Nutritional Status AssessmentDocument3 pages2.02 - Nutritional Status AssessmentPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Hypophosphat Emia: Presented By: Ramirez, Nichole Robles, Hannah Saquilayan, Kristine Siazon, ColeenDocument37 pagesHypophosphat Emia: Presented By: Ramirez, Nichole Robles, Hannah Saquilayan, Kristine Siazon, ColeenKyle De Sagun OtedaNo ratings yet
- Modifiable Non-Modifiable: Increased Activity of The Brain Due To Dopamine Over LoadDocument4 pagesModifiable Non-Modifiable: Increased Activity of The Brain Due To Dopamine Over LoadGj PaguidianNo ratings yet
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Portfolio-Checkpoint3Document7 pagesE-Learning Portfolio-Checkpoint3api-539733789No ratings yet
- Chapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney DisordersDocument40 pagesChapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study01Document6 pagesDrug Study01JrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument3 pagesPharmaConcepcion NazaredoNo ratings yet
- Limos Drug-StudyDocument2 pagesLimos Drug-StudyClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- DRUGS DURING PREGNANCY (Feso4, Folic Acid)Document2 pagesDRUGS DURING PREGNANCY (Feso4, Folic Acid)Angelyn Bucaso50% (2)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Ammonia Manganese: AstrocytesDocument2 pagesAmmonia Manganese: AstrocytesJULIUS ART VINCENT A. PADINITNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Vitamin-Related Diseases - ArangoDocument7 pagesWorksheet For Vitamin-Related Diseases - ArangoDaniel Angelo Arango100% (1)
- PorphyriaDocument21 pagesPorphyriasdasdasNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Synonyms Chemistry Coenzyme Form RDA Sources Properties Physiologic Role DeficiencyDocument9 pagesVitamins Synonyms Chemistry Coenzyme Form RDA Sources Properties Physiologic Role Deficiencykristian markus delos santosNo ratings yet
- Anemia CaseDocument6 pagesAnemia CaseMark Tristan AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- All Diuretics - Sheet1Document1 pageAll Diuretics - Sheet1Anisha GillNo ratings yet
- Drug Order - YhonDocument12 pagesDrug Order - YhonMarcelius EchavezNo ratings yet
- 8.metabolism of HemeDocument27 pages8.metabolism of HemeAbdulRahman MuthannaNo ratings yet
- Phenylalanine Theonine Histidine Valine Isoleucine Arginine (Semi-Essential in Kids Only) Tryptophan Methionine LysineDocument7 pagesPhenylalanine Theonine Histidine Valine Isoleucine Arginine (Semi-Essential in Kids Only) Tryptophan Methionine LysineApril BasilioNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsDocument7 pagesPharmacologic: Onset: Peak: CnsCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument4 pagesDrug Study FormRhea LaplanaNo ratings yet
- Aminoacid MetabolismDocument25 pagesAminoacid MetabolismMischief ManagerNo ratings yet
- Iron Supplement - During Pregnancy, Requirements For Iron IncreaseDocument1 pageIron Supplement - During Pregnancy, Requirements For Iron Increasegeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledDaniel Angelo ArangoNo ratings yet
- Activity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesActivity On Pituitary Disorders and Diabetes MellitusSherlyn Miranda GarcesNo ratings yet
- Metabolic-Disorders NotesDocument8 pagesMetabolic-Disorders NotesKeannu HavanaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolyteDocument4 pagesElectrolyteRon Vien'sNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyBella Cy LopezNo ratings yet
- Taking The Long View of Canine Hypoadrenocorticism OutlineDocument4 pagesTaking The Long View of Canine Hypoadrenocorticism OutlineJuniClaudia13No ratings yet
- Protein Metab 2 Dra. SantosDocument7 pagesProtein Metab 2 Dra. SantosMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Medication Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Drug Reaction GenericDocument1 pageMedication Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Drug Reaction GenericTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Legend: - Precipitating Factors - Flow - Medical Diagnosis - Nursing Diagnosis - Lab Results - MedicationsDocument1 pageLegend: - Precipitating Factors - Flow - Medical Diagnosis - Nursing Diagnosis - Lab Results - MedicationsEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod4Document2 pagesNCM 112-Mod4Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- LMR Pharmacology - CnsDocument6 pagesLMR Pharmacology - CnsYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry Lab 3 PDFDocument7 pagesClinical Biochemistry Lab 3 PDFNael NomanNo ratings yet
- Porphyrias: 9 Types of Porphyria DefectDocument8 pagesPorphyrias: 9 Types of Porphyria DefectMohmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- PIGMENTS Mbbs - Dr. SuchitaDocument53 pagesPIGMENTS Mbbs - Dr. SuchitaRushi VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TransDocument8 pagesUnit 6 TransGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- Exogenous and Endogenous Pigment.....Document30 pagesExogenous and Endogenous Pigment.....Mohan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug Study PDFDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug Study PDFLiza Marie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Normal Daily Urine Output: 600-2000mL (With Night Urine 400mL) Average Urine Output: 1200-1500mL (1% of The Filtered Plasma Volume)Document8 pagesNormal Daily Urine Output: 600-2000mL (With Night Urine 400mL) Average Urine Output: 1200-1500mL (1% of The Filtered Plasma Volume)Chrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Marinov - Urinary System 2016 (Eng)Document25 pagesMarinov - Urinary System 2016 (Eng)Самат Джусупбекович ДжусупбековNo ratings yet
- Point of Care Testing: Microhematocrit Centrifuge Conductometric MethodDocument4 pagesPoint of Care Testing: Microhematocrit Centrifuge Conductometric MethodJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- (Trans) Aubf: Safety and Quality Assessment: Jean BelciñaDocument5 pages(Trans) Aubf: Safety and Quality Assessment: Jean BelciñaJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Training and Procedures: Bacteriological TechniquesDocument8 pagesLaboratory Training and Procedures: Bacteriological TechniquesJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- (Trans) Aubf: Urinalysis Iii: Jean BelciñaDocument2 pages(Trans) Aubf: Urinalysis Iii: Jean BelciñaJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Environment Laboratory Utilities Personal Hygiene First Aid KitDocument3 pagesLaboratory Environment Laboratory Utilities Personal Hygiene First Aid KitJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- (Trans) Aubf: Urinalysis Iii: Jean BelciñaDocument2 pages(Trans) Aubf: Urinalysis Iii: Jean BelciñaJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument2 pagesLaboratory ApparatusJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- (Hematology) Chapter 7: Hematopoiesis: BloodDocument5 pages(Hematology) Chapter 7: Hematopoiesis: BloodJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Good Literature Review Poor Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesGood Literature Review Poor Literature ReviewJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- (Bacteriology) Chapter 8: Use of Colonial Morphology For The Presumptive Identification of MicroorganismsDocument6 pages(Bacteriology) Chapter 8: Use of Colonial Morphology For The Presumptive Identification of MicroorganismsJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument24 pagesPerpetuation of LifeDuane AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah BHL (Moluska - Jurnal - 3) - 2021 DaringDocument20 pagesMateri Kuliah BHL (Moluska - Jurnal - 3) - 2021 DaringAlifia Nabilla PutriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Apryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics 36 15 4350Document3 pagesBioinformatics 36 15 4350mgcu2019csit3019No ratings yet
- Biology IIDocument9 pagesBiology IIabdulrab amjadNo ratings yet
- 2019 EAZA BPG Husbandry and Management Guidelines For Demonstration Birds Parrot SupplementDocument7 pages2019 EAZA BPG Husbandry and Management Guidelines For Demonstration Birds Parrot SupplementCamila Carvalho De SouzaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionDocument12 pagesGen Bio 2 Genetics To EvolutionLeonard CubeloNo ratings yet
- PV92 PCR Kit ManualDocument100 pagesPV92 PCR Kit ManualdnajenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Chapter 5 - Principles of Inheritance VariationDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Chapter 5 - Principles of Inheritance VariationNameNo ratings yet
- Olympic 10 2018Document13 pagesOlympic 10 2018Bảo TrâmNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Biology Prelim SA2 Raffles InstitutionDocument77 pages2017 H2 Biology Prelim SA2 Raffles InstitutionSalman ShethNo ratings yet
- Specialized - STEM - General Biology1 1 1Document48 pagesSpecialized - STEM - General Biology1 1 1zedrickjoseNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Patent and Patent LawsDocument53 pagesModule 5 Patent and Patent LawsRachana CHNo ratings yet
- Coprophilous Fungi Antibiotic DiscoveryDocument17 pagesCoprophilous Fungi Antibiotic DiscoveryNathan Ulises Reyes JimenezNo ratings yet
- 5905 Et 21-Biosystematics-EtDocument10 pages5905 Et 21-Biosystematics-EtAnjali Singh100% (1)
- Solutions To Practice Problems For Molecular Biology, Session 3: Transcription, TranslationDocument2 pagesSolutions To Practice Problems For Molecular Biology, Session 3: Transcription, TranslationJen AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Purpose of The AuthorDocument16 pagesPurpose of The AuthorJ Francis Alain OraaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Endang Sukara, PHD Prof. Dr. Dedi Darnedi Prof. Dr. Jatna Supriatna Dr. Fachruddin Mangunjaya, MsiDocument11 pagesProf. Endang Sukara, PHD Prof. Dr. Dedi Darnedi Prof. Dr. Jatna Supriatna Dr. Fachruddin Mangunjaya, MsiAbee Rizki AlnyongkiyinNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelMena YasserNo ratings yet
- (Eysenck, 1990) Genetic and Environmental Contributions To Individual Differences. The Three Major Dimensions of PersonalityDocument18 pages(Eysenck, 1990) Genetic and Environmental Contributions To Individual Differences. The Three Major Dimensions of PersonalityangieNo ratings yet
- Xenobiotics MetabolismDocument47 pagesXenobiotics Metabolismademabdella38No ratings yet
- Rufus Giwa Polytechnic, Owo, Ondo State: AN Assignment Prepared BY Onokhua Happy OsedebamenDocument3 pagesRufus Giwa Polytechnic, Owo, Ondo State: AN Assignment Prepared BY Onokhua Happy OsedebamenEkoh EnduranceNo ratings yet
- HomoDocument3 pagesHomoPlanet CscNo ratings yet
- Classrecord MELCDocument13 pagesClassrecord MELCJade MillanteNo ratings yet
- Exercise in Enzymes - Lorenz NAVALDocument1 pageExercise in Enzymes - Lorenz NAVALLorenz NAVALNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Williams Hematology Malignant Lymphoid Diseases PDFDocument26 pagesFull Download Book Williams Hematology Malignant Lymphoid Diseases PDFronald.jewell170100% (15)
- Test Bank For Goulds Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 5th Edition by VanmeterDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Goulds Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 5th Edition by Vanmeterjosephestradakmbaizgpyj100% (25)
- Bio102 General Biology II SummaryDocument47 pagesBio102 General Biology II SummaryIkenna Okpala100% (1)
- WBI11 - 01 - Que - 20200305 With AnswerDocument28 pagesWBI11 - 01 - Que - 20200305 With AnswerDEEBAN75% (8)
- Etulay Online Tutorial: Physical ScienceDocument39 pagesEtulay Online Tutorial: Physical ScienceTara SantosNo ratings yet