Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics Review
Uploaded by
Marcial Jr. Militante100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
343 views10 pagesPRESENTATION
Original Title
REVIEW_ON_THERMODYNAMICS_PLATE_2_NO_ANS.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPRESENTATION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
343 views10 pagesThermodynamics Review
Uploaded by
Marcial Jr. MilitantePRESENTATION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
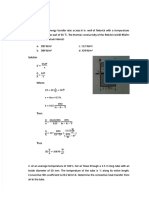
REVIEW ON can be taken out unitl the gage
THERMODYNAMICS reads 138 kPa.
a. 31.20 liters b. 65.32 liters
c. 16.87 liters d. 29.50 liters
PLATE NO. 2
6. A gas initially 103.4 kPa and 0.0566
Instruction: Choose the best answer. m3 undergoes a process to 620.36
kPa and 0.017 m3 during which the
1. The compression ratio of an ideal
enthalpy increases by 16.35 kJ, c v =
Otto cycle is 6:1. Initial conditions
10.217 kJ/kg.K. Determine the cp of
are 101.3 kPa and 20oC. Find the
gas.
pressure and temperature at the
a. 14.33 kJ/kg-K
end of adiabatic compression.
b. 2.34 Btu/lb-R
a. 1244.5 kPa, 599.96 K
c. 13.23 kJ/kg-K
b. 1244.5 kPag, 60oC
d. 10.76 Btu/lb-K
c. 1244.5 kPa, 60oC
d. 1244.5 kPa, 599.96oC 7. While the pressure remains constant
at 689.5 kPa the volume of a
2. Determine the average cp value in
system of air changes from 0.567
kJ/kg-K of a gas of 522 kJ/kg of
m3 to 0.283 m3. Find the change of
heat is necessary to raise the
internal energy.
temperature from 300 K to 800 K
a. 389.68 kJ b. 493.63 kJ
making the pressure constant:
c. 678.68 kJ d. 245.68 kJ
a. 1.440 b. 1.044
c. 1.038 d. 1.026 8. What horsepower is required to
isothermally compress 800 ft3 of air
3. If 10 lbs of water are evaporated at
per minute from 14.7 psia to 120
atmospheric pressure until a volume
psia?
of 288.5 ft3 is computed, how much
a. 13900 Hp b. 28 Hp
work is done?
c. 256 Hp d. 108 Hp
a. 1,680 Btu
b. No work 9. A Carnot engine requires 35 kJ/sec
c. 610,000 ft-lb from the hot source. The engine
d. 550,000 ft-lb produces 15 kW of power and the
temperature of the sink 26oC. What
4. In a diesel cycle, the air compressed
is the temperature of the hot
to one-tenth of its original volume. If
source?
the initial temperature of the air is
a. 245.57 b. 210.10
27oC, what is the final temperature?
c. 250.18 d. 260.68
a. 420oC b. 440oC
c. 460oC d. 480oC 10. The maximum thermal efficiency
possible for a power cycle operating
5. A 4 m3/hr pump delivers water to a
between 1200oF and 225oF is:
pressure tank. At the start, the gage
a. 58% b. 58.73%
reads 138 kPa until in reads 276
c. 57.54% d. 57.40%
kPa and then the pump was shut
off. The volume of the tank is 150 11. An Otto cycle has clearance
liters. At 276 kPa the water volume of 7%. It produces 300 kW
occupied 2/3 of the tank volume. power. What is the amount of heat
Determine the volume of water that rejected in kW?
a. 170 b. 160 c. 73.5% d. 60.02%
c. 152 d. 145
18. Find the enthalpy of 100 psi and
12. An air standard engine has a 97% quality, hf = 298.55 Btu/lb; hfg =
compression ratio of 20 and cut-off 889.119 Btu/lb.
ratio of 5. If the intake air pressure a. 1,170 Btu/lb b. 1,161 Btu/lb
and temperature are 100 kPa and c. 1,734 Btu/lb d. 1,803 Btu/lb
27oC, find the work in kJ per kg.
19. Five kilograms of saturated liquid at
a. 2,976 b. 2,166
kPa is heated until its moisture
c. 2,437 d. 2,751
content is 5%. Find the work done
13. In an air standard Otto cycle, the for this process.
clearance volume is 18% of the a. 813.59 kJ/kg
displacement volume. Find the b. 643.23 kJ/kg
compression ratio and or thermal c. 542.34 kJ/kg
efficiency. d. 753.12 kJ/kg
a. 0.52 b. 0.53
20. Steam at 2 MPa and 250oC in a
c. 0.55 d. 0.60
rigid cylinder is cooled until the
14. For an ideal cycle with overall quality is 50%. Find the heat
value of k = 1.33, compression ratio rejected from the cylinder.
is 15 and cut-off ratio of 2.1, At 2 MPa and 250oC
determine the cycle efficiency. v = 0.11144 m3/kg
a. 50.62% b. 52.90% u = 2,679.6 kJ/kg
c. 46% d. 49% At 2 MPa, (saturated)
vf = 0.0011767 m3/kg
15. An ideal Otto cycle, operating in hot
vg = 0.09963 m3/kg
air with k = 1.34 has compression
uf = 906.44 kJ/kg
ratio of 5. Determine the efficiency
ug = 1,693.8 kJ/kg
of the cycle.
a. -432.23 kJ/kg
a. 42.14% b. 62.27%
b. -926.26 kJ/kg
c. 64.27% d. 36.46%
c. -834.55 kJ/kg
16. In an air standard diesel cycle, d. 1,082.34 kJ/kg
compression start at 100 kPa and
21. At 1.3 MPa, mixture steam and
300 K. The compression ratio is 16
water had an entropy of 4 kJ/kg-K.
to 1. The maximum cycle
Find the enthalpy of the mixture.
temperature is 2,031 K. Determine
At 1.3 MPa:
the cycle efficiency.
sf = 2.2515; sg = 6.4953
a. 60.34% b. 56.23%
hf = 514.93; hfg = 1972.7
c. 65.98% d. 45.45%
a. 1627.71 kJ/kg
17. Determine the air-standard b. 1533.33 kJ/kg
efficiency of an engine operating on c. 1234.45 kJ/kg
the diesel cycle with clearance of d. 1734.45 kJ/kg
8% when the suction pressure is
22. A tank contains exactly one
99.97 kPa and the fuel is injected
kilogram of water consisting of liquid
for 6% of the stroke. Assume k =
and vapor in equilibrium at 1 MPa. If
1.4.
the liquid and vapor each occupy
a. 63.5% b. 51.2%
one-half the volume of the tank,
what is the enthalpy of the content pressure of 413 kPa and 38oC. If
of the tank? 2,900 kJ if heat is added to the
a. 644.40 kJ/kg ammonia until its final pressure and
b. 774.40 kJ/kg temperature are 413 kPa and
c. 833.40 kJ/kg 100oC, respectively, what is the
d. 435.29 kJ/kg amount of work done by the fluid in
kJ?
23. Water substance at 70 bars and
a. 667 b. 304
65oC enters a boiler tube of
c. 420 d. 502
constant inside diameter of 25 mm.
The water leaves the boiler tube at 2. A tank contains 80 ft 3 of air at a
50 bars and 700oK at velocity of 100 pressure of 350 psi; if the air is
m/s. Calculate the inlet velocity cooled until its pressure and
(m/s). temperature decreases to 200 psi
a. 1.56 b. 2.12 and 70oF respectively, what is the
c. 1.672 d. 3.230 decrease in internal energy?
a. +4,575 b. -5,544
24. One lb (0.455 kg) of a mixture of
c. 5,552 d. 0
steam and water at 160 psia (1103.2
kPa) is in rigid vessel. Heat is added 3. A large mining company was
to the vessel until the content are at provided with a 3 m3 of compressed
560 psia (3861.2 kPa) and 600oF air tank. Air pressure in the tank
(315.55oC). Determine the quantity drops from 700 kPa to 180 kPa
of heat in kJ added to the water and while the temperature remains
steam in the tank. constant at 28oC. What percentage
a. 1423.70 b. 1392.34 has the mass of air in the tank been
c. 1562.34 d. 1294.45 reduced?
a. 74 b. 72
25. Steam leaves and industrial boiler
c. 76 d. 78
at 827.4 kPa and 171.6oC. A portion
of the steam is passed through a 4. Determine the vacuum efficiency of
throttling calorimeter and is a surface condenser which operates
exhausted to the atmosphere when at a vacuum of 635 mm Hg and
the calorimeter pressure is 101.4 exhaust steam enters the
o
kPa. How much moisture does the condenser at 45.81 C. The
steam leaving the boiler contain if barometric is 760 mm Hg.
the temperature is 115.6oC? a. 80.4% b. 85.2%
a. 3.78% b. 3.08% c. 92.2% d. 98.3%
c. 4.56% d. 2.34%
5. How much work is necessary to
compress air in an insulated
cylinder from 0.20 m3 to 0.01 m3?
PRACTICE PROBLEM NO. 2 Use T = 20oC and P1 = 100 kPa.
a. 113.4 kJ b. 121.4 kJ
Instruction: Choose the best answer. c. 110.1 kJ d. 115.6 kJ
6. A perfect gas has a value of R =
1. Ammonia weighing 22 kg is 5,808 ft-lb/lb-oR and k = 1.26. If 20
confirmed inside a cylinder Btu are added to 5 lb of this gas at
equipped with a piston has an initial constant volume when initial
temperature is 90oF, find the final heat supplied per 1200 watt-hr of
temperature. work developed in kJ.
a. 100.76oC b. 167.76oC a. 12,343 b. 10,216
c. 103.76oC d. 145.76oC c. 14,218 d. 11,108
7. If initial volume of an ideal gas is 13. The clearance of a diesel cycle is
compressed to one half its original 1.0%. If initial temperature is 27 oC,
volume and to twice its original determine the final temperature.
temperature, the pressure: a. 510oC b. 610oC
a. Doubles c. 540oC d. 1000oC
b. Quadruples
14. An ideal Otto cycle with 15%
c. Remains constant
clearance operates on 0.227 kg/s of
d. Halves
air with k = 1.32. Determine the
8. An ideal gas at 45 psig and 80oF is efficiency of the cycle.
heated in a closed container to a. 50.65% b. 43.84%
130oF. What is the final pressure? c. 41.32% d. 47.89%
a. 62.53 psig b. 49.23 psig
15. An engine operates on the air
c. 60.23 psig d. 50.53 psig
standard Otto cycle. The cycle work
9. A Carnot engine receives 130 Btu of is 900 kJ/kg, the maximum cycle
heat from a hot reservoir at 700 oF temperature at the end of isentropic
and rejects 49 Btu of heat. compression is 600oC. Determine
Calculate the temperature of the the engines compression ratio.
cold reservoir. a. 6.388 b. 10.45
a. -21.9oF b. -24.2oF c. 8.67 d. 7.87
c. -20.8oF d. -22.7oF
16. A diesel engine is operating on a 4-
10. A heat engine is operated between stroke cycle, has a heat rate of
temperature limits of 1370oC and 11315.6 kJ/kW-hr brake. The
260oC. Engine supplies with 14,142 compression ratio is 13. The cut-off
kJ per kW.hr. Find the Carnot cycle ratio is 2. Using k = 1.32, what is the
efficiency in percent. brake engine efficiency.
a. 70.10 b. 65.05 a. 63.5% b. 51.2%
c. 67.56 d. 69.32 c. 73.5% d. 45.3%
11. A closed vessel contains air at a 17. A heat engine (Carnot cycle) has its
pressure of 160 kN/m2 gauge and intake and exhaust temperature if
temperature of 30oC. The air is 157oC and 100oC, respectively.
heated at constant volume of 60 oC What is its efficiency?
with the atmospheric pressure as a. 12.65% b. 14.75%
759 mm Hg. What is the final gauge c. 15.35% d. 13.25%
pressure?
18. 180 grams of saturated water of
a. 174 b. 169
temperature 95oC undergoes
c. 185.8 d. 172
evaporation process until all vapor
12. The thermal efficiency of a completely vaporized. Determine
particular engine operating on an the changed in volume. At 95oC, vf =
ideal cycle is 35%. Calculate the 0.0010397 m3/kg.
a. 0.1656 m3 b. 0.4235 m3
c. 0.2565 m3 d. 0.3656 m3 24. Steam at the rate of 600 kg/hr is
19. Twenty kilograms of water at 40 oC produced by a steady flow system
is confined in a rigid vessel. The boiler from feedwater entering at
heat is supplied until all the water is 40oC. Find the rate at which heat is
completely vaporized. Find the heat transformed in kCal per hour if
added in kJ. enthalpy of steam is 660 kCal/kg
a. 45,422 kJ b. 43,122 kJ and of the feedwater at 40 kCal/kg.
c. 45,252 kJ d. 65,233 kJ a. 372,000 b. 387,000
c. 345,200 d. 312,444
20. The entropy in kJ/kg-K at 90%
moisture of a 1 MPa steam-water 25. Steam enters a throttling
mixture is: calorimeter at a pressure of 1.03
At 1 MPa: sg = 6.5865; sfg = 4.4478 MPa. The calorimeter downstream
a. 4.87 b. 6.14 pressure and temperature are
c. 2.583 d. 4.36 respectively 0.100 MPa and 125oC.
What is the percentage moisture if
21. Mixture with 80% quality at 500
the supply steam?
kPa is heated isothermally until its
Properties of steam:
pressure is 300 kPa. Find the heat
p, MPa hfg hg
added during the process.
1.03 2010.7 2779.25
At 500 kPa:
Note: @ 0.1 MPa and 125oC:
sf = 1.8607; sfg = 4.9606
h = 2726.6 kJ/kg.
At 300 kPa and 151.86oC:
a. 2.62 b. 5.21
s = 7.0888 kJ/kg
c. 3.15 d. 1.98
a. 652.34 kJ/kg
b. 535.16 kJ/kg 26. A vessel of 0.058 m3 capacity is
c. 983.44 kJ/kg well insulated and is divided equally
d. 765.34 kJ/kg by a rigid conducting diaphragm.
Initially both halves contain air at
22. A vessel with a volume of 1 m 3
pressure of 137.8 kPa and 413.4
contains liquid water and water
kPa and temperature 27oC and
vapor in equilibrium at 600 kPa. The
177oC respectively. What is the
liquid water has a mass of 1 kg.
increase of entropy of the system in
Using steam tables, calculate the
kJ/oC?
mass of water vapor.
a. 1.002 b. 0.5080
a. 3.16 kg b. 0.99 kg
c. 0.00173 d. 0.1080
c. 1.57 kg d. 1.89 kg
27. Using steam table. Find the
23. Water substance at 70 bars and
enthalpy of steam at kPa if its
65oC enters a boiler tube of
specific volume is 0.3598 m3/kg.
constant inside diameter of 25 mm.
a. 1625.86 kJ/kg
The water leaves the boiler tube at
b. 1785.34 kJ/kg
50 bars and 700oK at velocity of 100
c. 1543.45 kJ/kg
m/s. Calculate the inlet volume of
d. 1687.55 kJ/kg
100 m/s. Calculate the inlet volume
flow (li/s). 28. A throttling calorimeter is
a. 0.821 b. 1.561 connected to the superheated
c. 0.344 d. 2.133 steam line supplying steam to the
auxiliary feed pump on a ship. The
line pressure measures 2.5 MPa. Find the boiling temperature when
The calorimeter pressure of 137.8 the pressure is increased by 45 psia.
kPa and 413.4 kPa and temperature a. 342.34oF b. 526.34oF
of 27oC and 177oC respectively. c. 479.13oF d. 263.45oF
What is the increase of entropy of
35. What is the temperature in oC of 2
the system in kJ/K?
liters of water at 30oC after 500
a. 6.8 b. 7.2
calories of heat have been added
c. 6.6 d. 7.5
to?
29. Steam enters an isothermal a. 35.70 b. 30.25
compressor at 400oC and 100 kPa. c. 38.00 d. 39.75
The exit pressure is 10 MPa,
36. A mass of 0.36 kg metal having a
determine the change of enthalpy.
temperature of 100oC is plunged
a. 198 kJ/kg b. 178 kJ/kg
into 0.04 kg if water at 20 oC. The
c. 187 kJ/kg d. 182 kJ/kg
temperature of the water and metal
30. Steam enters an adiabatic at 300oC becomes 48oC. The latent heat of
and 400 kPa. It exits as a saturated ice at 0oC is 335 kJ/kg-K, assuming
vapor at 30 kPa. Determine the no heat loss to the surroundings,
work done. determine the specific heat capacity
a. 476.34 kJ/kg of the metal in kJ/kg-K.
b. 441.50 kJ/kg a. 0.234 b. 0.564
c. 436.33 kJ/kg c. 0.754 d. 0.451
d. 524.34 kJ/kg
37. What is the total energy required
3
31. A 0.5 m tank contains saturated heating in raising the temperature of
steam at 300 kPa. Heat is a given amount of water when the
transferred until pressure reaches energy applied is 1000 kW.hr with
100 kPa. Find the final temperature. heat losses of 25%?
a. 94.45oC b. 83.23oC a. 1,000 b. 1,500
c. 99.63oC d. 103.2oC c. 1,333 d. 1,250
32. A 500 li contains a saturated 38. A 30 kg iron was put in a container
mixture of steam and water at with 14.33 kg water. The water is at
300oC. Determine the mass of vapor 10oC and the iron has an initial
if their volumes are equal. temperature of 439 K until the iron
a. 11.54 kg b. 10.34 kg was in thermal equilibrium with
c. 13.45 kg d. 16.34 kg water. Find the change in entropy.
(cp = 0.4 kJ/kg.K).
33. A 1 kg steam-water mixture at 1.0
a. -12.56 kJ/K b. -43.58 kJ/K
MPa is contained in an inflexible
c. -25.78 kJ/K d. -6.6 kJ/K
tank. Heat is added until the
pressure rises to 3.5 MPa and 39. An instrument that measures
400oC. Determine the heat added. density
a. 1378.64 kJ b. 1532.56 kJ a. Manometer b. Barometer
c. 1456.78 kJ d. 1635.45 kJ c. Hydrometer d. Hydraulic meter
34. Atmospheric pressure boils at 40. This law states that pressure
212oF. At the vacuum pressure at 24 applied at a point in a confined
in-Hg, the temperature is 142oF.
liquid is transmitted equally to all 48. An underground formation that
other points. contains sufficient saturated
a. Boyle’s Law permeable material to yield
b. Len’s Law significant quantities of water.
c. Charle’s Law a. aquifer b. wet pit
d. Pascal’s Law c. cavitation d. NPSH
41. At 1 atmosphere, the boiling point 49. The rate of flow of liquid measure
of water is 100oC. If the pressure is per unit time is called:
decreased, the boiling temperature a. capacity b. pump work
will: c. velocity d. pump head
a. increase
50. The reading of a pressure gage at
b. decrease
the discharge of the pump plus the
c. remains the same
velocity head at the point of gage
d. greater than
attachment.
42. What is the pressure above zero? a. total head
a. gage pressure b. NPSH
b. vacuum pressure c. total discharge head
c. absolute pressure d. suction head
d. atmospheric pressure
51. A type of valve installed between
43. Thermodynamic process following the suction of pump and water
the law pVn = constant. mains to prevent any return of
a. polytropic b. isentropic water to mains when pump is
c. isothermal d. isobaric stopped.
a. globe valve b. suction valve
44. Thermodynamic process following
c. check valve d. discharge valve
the law pVn = constant if n is equal
to 1, what is the process? 52. A gauge in the form of a glass one
a. polytropic b. isentropic tube leg of which is open to the
c. isothermal d. isobaric atmosphere, or a straight tube one
end of which is open to the
45. Thermodynamic process following
atmosphere.
the law pVn = constant if n is equal
a. manometer b. differential
to 0, what is the process?
c. piezometer d. compound
a. polytropic b. isentropic
c. isothermal d. isobaric 53. The following are classifications of
pumps except:
46. Thermodynamic process following a. centrifugal b. reciprocating
the law pVn = constant if n is equal c. radial flow d. rotary
to 1.4, what is the process?
a. polytropic b. isentropic 54. The following are types of
c. isothermal d. isobaric reciprocating pumps, except:
a. piston b. peripheral
47. The vertical difference between c. plunger d. diaphragm
the pumping water level and static
water level. 55. The following are types of rotary
a. total head b. static head pumps, except:
c. pump level d. draw-down a. vane b. screw
c. gear d. duplex
66. Piping color for high pressure water
56. The following are types of
and hot water:
centrifugal pumps, except:
a. silver b. red
a. hydraulic b. axial
c. yellow d. green
c. mixed d. radial
67. Piping color for LPG, high vacuum
57. Valve design to open automatically
and producer gas:
to relieve excess pressure.
a. safety red b. orange
a. check valve b. relief valve
c. red d. no color
c. gate valve d. medium valve
68. The sum of the internal energy and
58. _______ is a hollow product of
the product of pressure and specific
round or any other cross section
volume is known as the:
having a continuous periphery.
a. enthalpy b. entropy
a. pipe b. tube
c. flow work d. total work
c. valve d. coupling
69. If the pressure exerted on a liquid is
59. A large pipe or drum into which
higher than the saturation pressure
each of a group of boilers is
corresponding to its temperature,
connected.
the liquid is at the _____ region.
a. muffler b. header
a. saturated liquid
c. manifold d. expansion loop
b. superheated liquid
60. Medium pressure, when applied to c. subcooled liquid
valves and fittings, implies they are d. highly superheated liquid
suitable for a working pressure of
70. The mass and temperature of a gas
from _____ kPa.
are inversely proportional at a
a. 862 to 1207 b. 1207 to 1506
constant pressure process. This is
c. 955 to 1345 d. 1345 to 1750
known as:
61. All piping shall be run ___ to a. Dalton’s Law
building walls. b. Law of Buoyancy
a. opposite b. parallel c. Charles’ Law
c. inclined d. slope d. Newton’s Second Law
62. Piping supports shall be placed 71. In a certain hydro power plant, the
____ mm intervals or less. total head is h and the head loss
a. 3000 b. 4000 due to friction is hf, then what is the
c. 4500 d. 6000 available head of the process?
a. hf – h b. h
63. Piping color for boiled feed water:
c. h – hf d. hf
a. green b. red
c. black d. yellow 72. If air is compressed without heat,
then what do you call this kind of
64. Piping color for acids:
compression?
a. violet b. blue
a. isobaric b. isochoric
c. orange d. red
c. adiabatic d. isothermal
65. Piping color for oil:
73. Difference in pressure measure
a. green b. black
above or below atmospheric
c. white d. brown
pressure:
a. draft b. stack
c. chimney d. breeching 81. Thermodynamic properties that are
dependent of the mass.
74. Servomotor controls
a. extensive properties
a. moving guide vanes
b. intensive properties
b. moving vanes
c. specific properties
c. guide vanes
c. pressure
d. none of these
82. Open system is also known as:
75. Name the process that is no heat
a. controlled mass system
loss or gain and no friction.
b. controlled volume system
a. isentropic process
c. transient system
b. isothermal process
d. isolated system
c. adiabatic
d. non-reversible 83. The vapor that has temperature
equal to the saturation temperature
76. A dimensionless ratio of a fluids
corresponding to an existing
density to some standard reference
pressure.
density.
a. wet vapor
a. specific weight
b. saturated vapor
b. constant
c. superheated vapor
c. factor
d. all of the above
d. specific gravity
84. The one’s defining the physical
77. Attractive force between molecules
condition of the fluid are called:
of different substances.
a. thermodynamic properties
a. cohesion b. adhesion
b. state properties
c. saturation d. evaporation
c. cycle properties
78. When the air is saturated, all three d. substance properties
temperatures are:
85. A drop in internal energy, is seen as
a. equal
a drop in
b. unequal
a. pressure b. volume
c. one is greater
c. enthalpy d. energy
d. one is lesser
86. The velocity always changes from
79. Water lost in small droplets and
supersonic to subsonic across a
carried away by the air flow.
shock wave and there is no loss of
a. water vapor
heat energy, therefore a shock
b. vapor loss
wave is:
c. windage loss
a. an adiabatic process
d. friction loss
b. polytropic process
80. An upward force that acts on all c. isentropic process
objects that are partially or d. hydraulic process
completely submerged in a fluid.
87. A high gas velocity is often
a. weight in air
achieved at the expense of what
b. weight in water
type of energy.
c. object’s mass
a. kinetic energy
d. buoyant force
b. internal energy
c. potential energy
d. gravitational energy
88. If the gas flow is adiabatic and
frictionless (that is, reversible), the
entropy change is zero and the flow
is known as:
a. isentropic flow
b. polytropic flow
c. isovolumic flow
d. isenthalpic flow
89. Heavy water is:
a. B2O
b. W2O
c. H2O
d. D2O
90. A device for measuring the velocity
of wind:
a. aneroid barometer
b. anemoscope
c. anemometer
d. anemograph
You might also like
- Assignment2 Answer-KeyDocument11 pagesAssignment2 Answer-KeyRed Crazy0% (1)
- Thermodynamics IDocument7 pagesThermodynamics IJustinnNo ratings yet
- Power and Industrial Plant EngineeringDocument15 pagesPower and Industrial Plant EngineeringJohn Robert GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pipe Preboard 1Document10 pagesPipe Preboard 1Chyno Kang100% (1)
- PPE Problem Set on Thermodynamics, Rankine Cycle, Diesel EnginesDocument3 pagesPPE Problem Set on Thermodynamics, Rankine Cycle, Diesel EnginesElisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- Helium Gas Compression Problem SolvedDocument37 pagesHelium Gas Compression Problem SolvedYato QtNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument6 pagesThermoE.G Boy GudaNo ratings yet
- Pipe 4Document19 pagesPipe 4Mark AllenNo ratings yet
- Solving Week 8Document14 pagesSolving Week 8Christopher Lennon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Gas Compressor ProblemsDocument2 pagesGas Compressor Problemskim dianon0% (1)
- (x4) Problem 5 - 9 Multi Stage CompressionDocument15 pages(x4) Problem 5 - 9 Multi Stage CompressionLester Alfred M. OlasimanNo ratings yet
- Pipe 02: by TRC - Tiger's Review CenterDocument119 pagesPipe 02: by TRC - Tiger's Review Centerkristan7No ratings yet
- Astig M.E.Document21 pagesAstig M.E.Aj Buniag100% (1)
- Problem Set on Steam TablesDocument1 pageProblem Set on Steam TablesFriend ANo ratings yet
- Questions CombustionDocument3 pagesQuestions CombustionKristian TarucNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document5 pagesChapter 04stephen jamesNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTsolved6 9Document13 pagesASSIGNMENTsolved6 9Samyabrata ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- How humidity is measured in air conditioningDocument122 pagesHow humidity is measured in air conditioningJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Calculate heat transfer across a firebrick wallDocument92 pagesCalculate heat transfer across a firebrick wallClint Baring ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- Mikee EncodedDocument2 pagesMikee EncodedjaysonNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Heat Rejection and Refrigeration Cycle CalculationsDocument8 pagesGas Turbine Heat Rejection and Refrigeration Cycle CalculationsRENE JOSHUA PECASONo ratings yet
- Fluid Compressors Machinery Types Models CyclesDocument12 pagesFluid Compressors Machinery Types Models CyclesRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Problems: Calculating Rates of Heat Flow Through Various MaterialsDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer Problems: Calculating Rates of Heat Flow Through Various Materialskim dianonNo ratings yet
- IPE Practice QuestionsDocument49 pagesIPE Practice QuestionsLeslie CatindigNo ratings yet
- Chap 08 Soln PDFDocument26 pagesChap 08 Soln PDFsoma sundaramNo ratings yet
- Me Final Preboard Pipe PRC Format Set A No AnsDocument9 pagesMe Final Preboard Pipe PRC Format Set A No AnsGerald EspanillaNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Thermo MekfluDocument31 pagesPrinsip Thermo MekfluGhany RadifanNo ratings yet
- ICE - Lecture From MapuaDocument48 pagesICE - Lecture From MapuaMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document8 pagesChapter 03stephen jamesNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Document11 pagesRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNo ratings yet
- FERQUIZDocument5 pagesFERQUIZJerome Olgado100% (1)
- MathematicsDocument8 pagesMathematicsGeorge Isaac McQuilesNo ratings yet
- SteamDocument3 pagesSteamVon A. DamirezNo ratings yet
- Brayton Cycle Gas Turbine ChapterDocument14 pagesBrayton Cycle Gas Turbine ChapterReinzo GallegoNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant Problem Solving Examination NAME: Vincent Rey Olario Y. Bsme - 5 Show Complete Solutions. Solve The Following: Problem 1Document5 pagesDiesel Power Plant Problem Solving Examination NAME: Vincent Rey Olario Y. Bsme - 5 Show Complete Solutions. Solve The Following: Problem 1BensoyNo ratings yet
- PPE Reviewer LooksfamDocument28 pagesPPE Reviewer LooksfamRichelle Valerie BastroNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Activity No. 2 Spur Gear ProblemDocument4 pagesModule 2 Activity No. 2 Spur Gear ProblemLeyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 in PpeDocument3 pagesAssignment No. 1 in PpeJenny Mae PomedaNo ratings yet
- Bautista, Joanna Marie Z. Ganelo, Jethro B. Gaulit, Carlo J. Bsme 3B APRIL 19,2021 Combustion EngineeringDocument8 pagesBautista, Joanna Marie Z. Ganelo, Jethro B. Gaulit, Carlo J. Bsme 3B APRIL 19,2021 Combustion Engineeringjethro ganeloNo ratings yet
- Machine Design, Engineering Materials and Machine Shop Problem Solving Examination No. 4 / Second Semester, A.Y. 2008-2009Document9 pagesMachine Design, Engineering Materials and Machine Shop Problem Solving Examination No. 4 / Second Semester, A.Y. 2008-2009maria katherine pantojaNo ratings yet
- B EngDocument557 pagesB EngHuniBegeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machine ProblemsDocument2 pagesFluid Machine ProblemsFuji0% (1)
- Lesson 1b Ice Refrigeration and Refrigerating CapacityDocument18 pagesLesson 1b Ice Refrigeration and Refrigerating CapacityBenz Dy0% (1)
- Dual CycleDocument2 pagesDual CycleRajesh PandaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Exercises Problem No. 3Document2 pagesModule 6 Exercises Problem No. 3Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- SLSU College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Multi-pressure Refrigeration AssignmentDocument9 pagesSLSU College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Multi-pressure Refrigeration AssignmentNicole MikesellNo ratings yet
- P4-10 ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageP4-10 ThermodynamicsjimrNo ratings yet
- Steam CycleDocument11 pagesSteam CycleRowin Mark SabornidoNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning (EDITED)Document6 pagesAir Conditioning (EDITED)Justin MercadoNo ratings yet
- Plate 1, 2 3 No AnsDocument4 pagesPlate 1, 2 3 No AnsRika MaeNo ratings yet
- Questions and solutions for engineering problemsDocument82 pagesQuestions and solutions for engineering problemsRyan Llona FernandezNo ratings yet
- Problems and SolutionsDocument39 pagesProblems and SolutionsRoberto LuaNo ratings yet
- 4 1Document10 pages4 1Miguel Dominic BernardoNo ratings yet
- Section 16Document97 pagesSection 16Carolina FerrerNo ratings yet
- Worded Problems in Thermodynamics 1 2Document12 pagesWorded Problems in Thermodynamics 1 2Jonel Santos60% (10)
- PDF Worded Problems in Thermodynamics 1 2docx DDDocument6 pagesPDF Worded Problems in Thermodynamics 1 2docx DDErning TutpickNo ratings yet
- Assignment-No 4Document2 pagesAssignment-No 4Adame Obinam100% (1)
- Problem Set PPE Day 4 PDFDocument3 pagesProblem Set PPE Day 4 PDFJuan T AmadNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Problems and SolutionsDocument17 pagesThermodynamics Problems and SolutionsDon Aries Eidos100% (1)
- Brayton Cycle: Avellana, OcceñaDocument54 pagesBrayton Cycle: Avellana, OcceñaMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- An Ideal Brayton Cycle - Problems With SolutionsDocument6 pagesAn Ideal Brayton Cycle - Problems With SolutionsMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- ICE ProblemsDocument3 pagesICE ProblemsVincent SalasNo ratings yet
- ICE - Lecture From MapuaDocument48 pagesICE - Lecture From MapuaMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Sheet 8 SolutionDocument36 pagesSheet 8 SolutionRafa Martínez100% (1)
- Cycle EngineDocument2 pagesCycle Enginecobalt boronNo ratings yet
- PPE Elements (120 Items)Document6 pagesPPE Elements (120 Items)Jerick HernandezNo ratings yet
- PLUMBINGDocument10 pagesPLUMBINGZach LavineNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Solutions ch12Document156 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics Solutions ch12Cierré No'Middlename Jones100% (8)
- Engineering Economy BP2 Set B With SolutionsDocument8 pagesEngineering Economy BP2 Set B With SolutionsZach LavineNo ratings yet
- Elements On Industrial Plants 1Document14 pagesElements On Industrial Plants 1Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- General Engineering Practice Problems 1Document3 pagesGeneral Engineering Practice Problems 1Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- JCSF Engineering Review Center: Examination Answer SheetDocument1 pageJCSF Engineering Review Center: Examination Answer SheetMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Elements of Energy Systems 2Document21 pagesElements of Energy Systems 2Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Elements ReviewDocument9 pagesMechanical Engineering Elements ReviewMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- JCSF Engineering DefinitionsDocument19 pagesJCSF Engineering DefinitionsMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering 2Document5 pagesBasic Engineering 2Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Elements of Energy Systems 2Document21 pagesElements of Energy Systems 2Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Shearing Machine Force Calculation ProblemsDocument4 pagesShearing Machine Force Calculation ProblemsMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Shaft Diameter and Torsional Deflection CalculationDocument4 pagesShaft Diameter and Torsional Deflection CalculationMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- DefrostDocument3 pagesDefrostMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet BRD ExamDocument1 pageAnswer Sheet BRD ExamMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Refrigeration Reviewer Chapter 1Document65 pagesMechanical Engineering Refrigeration Reviewer Chapter 1Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Philippine Mechanical Engineer exam results released in one dayDocument24 pagesPhilippine Mechanical Engineer exam results released in one daymargarett0% (3)
- Ansheet Sheet 2Document2 pagesAnsheet Sheet 2Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Ansheet SheetDocument1 pageAnsheet SheetMarcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Multi-Pressure Refrigeration Systems ReviewDocument20 pagesMulti-Pressure Refrigeration Systems ReviewMarcial Jr. Militante100% (2)
- Ansheet Sheet 2Document2 pagesAnsheet Sheet 2Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- AlgebraI Part2Document42 pagesAlgebraI Part2Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Dynamics WorksheetDocument5 pagesDynamics WorksheetJeremy BowersNo ratings yet
- Ss Iso 91 1 en PDFDocument6 pagesSs Iso 91 1 en PDFChetan LikhiteNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry CalculationsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry CalculationsJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- 11kv HT Cable Hi Pot MrsDocument9 pages11kv HT Cable Hi Pot Mrsjskrish56550% (2)
- AITS 2324 FT III JEEM TD SolDocument15 pagesAITS 2324 FT III JEEM TD Soladoranto737No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Forces & Pressure Teachers GuideDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Forces & Pressure Teachers GuideAhmad Zaidi100% (3)
- ELeventh Physics Textbook SCERtDocument320 pagesELeventh Physics Textbook SCERtRoobala ChelladuraiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Assignment ZeroDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - Assignment ZeroRushikesh Kale100% (1)
- PHYSCIS PROJECT ON Moving Coil GalvanomeDocument18 pagesPHYSCIS PROJECT ON Moving Coil GalvanomeRudra ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1Kristina PonceNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Chapter SummaryDocument11 pagesGravitation Chapter SummaryJaseela NaufalNo ratings yet
- HL 80 AhDocument1 pageHL 80 Ahأبو زينب المهندسNo ratings yet
- Feel Your Chair ExperimentDocument17 pagesFeel Your Chair ExperimentchrisNo ratings yet
- Plano Analitico Ingles 7a Classe 2024Document6 pagesPlano Analitico Ingles 7a Classe 2024Julius Joao NherereNo ratings yet
- Lightning Performance of 275 KV Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesLightning Performance of 275 KV Transmission LinesBernardo NGNo ratings yet
- Solucionario de Circuitos de Corriente ContinuaDocument36 pagesSolucionario de Circuitos de Corriente Continuaalbuhoquenoseve5774No ratings yet
- Physics Work Sheet-SS JCT - AIATS-02 - SolDocument3 pagesPhysics Work Sheet-SS JCT - AIATS-02 - Solhari kroviNo ratings yet
- B9 - High Power Contactors (Ref) enDocument44 pagesB9 - High Power Contactors (Ref) enPablo Andres Jara GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia FormulaDocument10 pagesMoment of Inertia Formulasubbu2051No ratings yet
- 12th Phy ch#16 Test (SEA) PDFDocument4 pages12th Phy ch#16 Test (SEA) PDFasifali jutt100% (1)
- Chemical Formulae and Equations GuideDocument3 pagesChemical Formulae and Equations GuideEinstein PillaiNo ratings yet
- Gas Pipeline Hydraulics B. Tech. Ape (Upstream)Document128 pagesGas Pipeline Hydraulics B. Tech. Ape (Upstream)Palash Ravi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- IB Kinematics ProblemsDocument7 pagesIB Kinematics ProblemsAbhinaya PolakaNo ratings yet
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- Pw2 - Ac RC Series Circuit - v1Document6 pagesPw2 - Ac RC Series Circuit - v1Hairul Anuar MasrolNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation AgitationDocument18 pagesDesign and Calculation AgitationDavid Lambert67% (3)
- Undamped Free Vibration - RahulDocument47 pagesUndamped Free Vibration - Rahulrs100788No ratings yet
- DC XXMX 43F CCDocument2 pagesDC XXMX 43F CCZeroNo ratings yet
- Sizing of Plate and Fin HXDocument6 pagesSizing of Plate and Fin HXNithishNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Work and EnergyDocument11 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies: Work and EnergyJancis TugadeNo ratings yet
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Waves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastFrom EverandWaves and Beaches: The Powerful Dynamics of Sea and CoastRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionFrom EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Marine and Offshore Pumping and Piping SystemsFrom EverandMarine and Offshore Pumping and Piping SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Green Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsFrom EverandGreen Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Quantum Mechanics 3: Wavefunctions, Superposition, & Virtual ParticlesFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics 3: Wavefunctions, Superposition, & Virtual ParticlesNo ratings yet
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Zinn & the Art of Mountain Bike Maintenance: The World's Best-Selling Guide to Mountain Bike RepairFrom EverandZinn & the Art of Mountain Bike Maintenance: The World's Best-Selling Guide to Mountain Bike RepairNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide to API 653 Certified Storage Tank Inspector Syllabus: Example Questions and Worked AnswersFrom EverandA Quick Guide to API 653 Certified Storage Tank Inspector Syllabus: Example Questions and Worked AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (19)
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CFrom EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Explicit Finite Element Method for Nonlinear Transient DynamicsFrom EverandIntroduction to the Explicit Finite Element Method for Nonlinear Transient DynamicsNo ratings yet